python实现图的深度优先搜索(DFS)和广度优先搜索(BFS)算法及Dijkstra最短路径应用
上篇文章介绍了树的常见遍历方式,这次我们一次来看看图的吧。深度优先搜索(Depth-First-Search)和广度优先搜索(Breadth-First-Search)是图论中比较重要的两种算法,面试题中经常遇到,我们主要看看python的实现代码,然后理论思想大家可以参考:深度优先遍历(DFS)和广度优先遍历(BFS)。
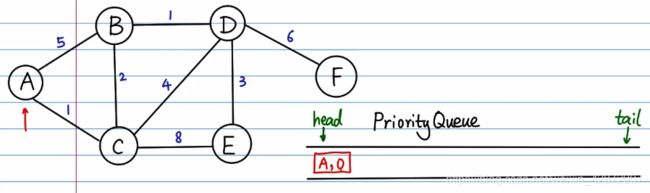
我们以下图为例,分别介绍广度优先搜索和深度优先搜索。
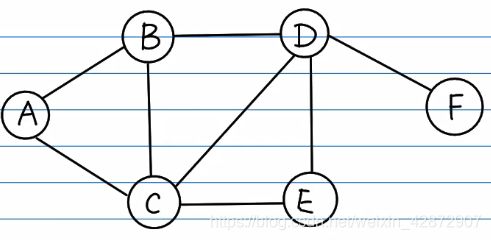
广度优先搜索:
#图节点
graph={
'A':['B','C'],
'B':['A','C','D'],
'C':['A','B','D','E'],
'D':['B','C','E','F'],
'E':['C','D'],
'F':['D']
}
// 广度优先搜索(BFS)
def BFS(graph,s):
queue=[] #建立队列
queue.append(s)
seen=[] #记录已经遍历过的点
seen.append(s)
while queue:
vertex=queue.pop(0) #队列,先进先出
nodes=graph[vertex]
for w in nodes:
if w not in seen:
queue.append(w)
seen.append(w)
print(vertex)
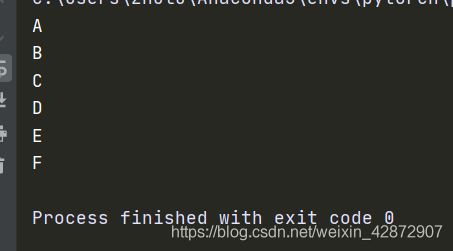
BFS(graph,'A')
// 深度优先搜索(DFS)
def DFS(graph,s):
stack=[]
stack.append(s)
seen=[]
seen.append(s)
while stack:
vertex=stack.pop() #栈,取出最后一个并删掉 先进后出
nodes=graph[vertex]
for w in nodes:
if w not in seen:
stack.append(w)
seen.append(w)
print(vertex)
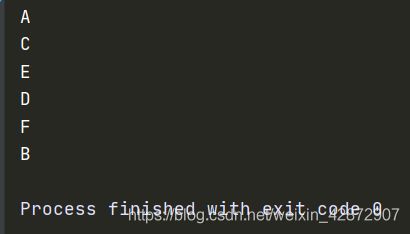
DFS(graph,'A')
广度优先求出路径(多了一步-记录父节点)
// An highlighted block
#广度优先求最短路径
def min_BFS(graph,s):
queue=[]
queue.append(s)
seen=[]
seen.append(s)
parent={s:None}
while queue:
vertex=queue.pop(0) #队列,先进先出
nodes=graph[vertex]
for w in nodes:
if w not in seen:
queue.append(w)
seen.append(w)
parent[w]=vertex
print(vertex)
return parent
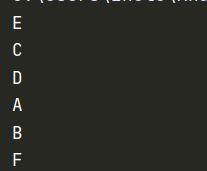
parent=min_BFS(graph,'E')
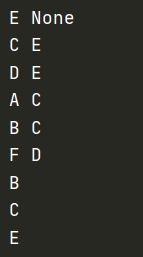
for i in parent:
print(i,parent[i])
# 求得'E'->'B'最短距离
v='B'
while v:
print(v)
v=parent[v]
输出结果
路径:E->C->B
// Dijkstra
import heapq
import math
#定义图及路径
graph={
'A':{'B':5,'C':1},
'B':{'A':5,'C':2 ,'D':1},
'C':{'A':1,'B':2,'D':4,'E':8},
'D':{'B':1,'C':4,'E':3,'F':6},
'E':{'C':8,'D':3},
'F':{'D':6}
}
#初始化距离
def init_distance(graph,s):
distance={s:0}
for vertex in graph:
if vertex != s:
distance[vertex]=math.inf
return distance
#dijkstra算法
def dijkstra(graph,s):
queue=[] #初始化队列
heapq.heappush(queue,(0,s)) #放入第一个元素
seen=[] #已经取出来的
parent={s:None} #父节点
distance=init_distance(graph,s) #初始化距离
while queue:
pair=heapq.heappop(queue) #heapq每次加入后自动排序,heappop每次取把距离小的放前面,取出来的格式为(0,s)
cur_dist=pair[0] #当前的距离
vertex=pair[1] #当前的节点
nodes=graph[vertex].keys() #该节点下的相邻各个节点
seen.append(vertex)
for n in nodes:
if n not in seen:
if cur_dist+graph[vertex][n]<distance[n]:
heapq.heappush(queue,(cur_dist+graph[vertex][n],n))
distance[n]=cur_dist+graph[vertex][n]
parent[n]=vertex
return parent,distance
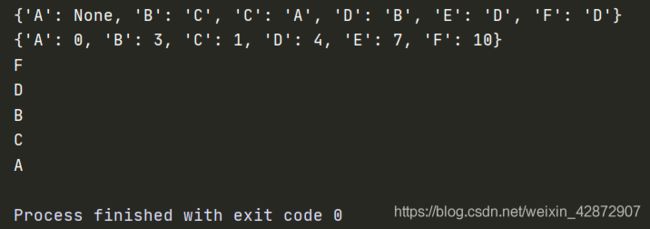
parent,distance=dijkstra(graph,'A')
print(parent)
print(distance)
#根据节点倒推,输出A->F最短路径
v='F'
while v:
print(v)
v=parent[v]
参考视频:https://www.bilibili.com/video/BV1LZ4y1j7JY?p=3