Astar A*算法 最短路径算法
通常情况下,迷宫寻路算法可以使用深度优先或者广度优先算法,但是由于效率的原因,不会直接使用这些算法,在路径搜索算法中最常见的就是A*寻路算法。使用A*算法的魅力之处在于它不仅能找到地图中从A到B的一条路径,还能保证找到的是一条最短路径,它是一种常见的启发式搜索算法,类似于Dijkstra算法一样的最短路径查找算法,很多游戏应用中的路径搜索基本都是采用这种算法或者是A*算法的变种。
下面我们来了解一下A*算法相关的理论知识:
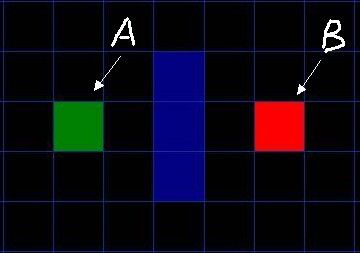
如图,我们需要在迷宫中找到A点到B点的一条最短的可以通过的路径,A和B直接被一面墙堵住了。在上一篇博客中我们说到了,地图是有二维数组组成的,墙表示不能通过的地方,用1表示,A*算法所要做的就是从A找到一条最短的通向B的路径。当然,不能从墙上飞过去,也不能瞬移到B。只能每次移动一个格子,一步一步地移动到B目标位置。问题在于,每次移动一格的时候,有上下左右四个方向,这里我们限制物体斜向移动,如何选择下一个移动方向呢?按照我们的想法,不就是找一条离目标最近的路吗?那我们可以在这四个方向中,找一个最接近目标点的位置,当然,还要考虑障碍因素,基于这个思想,A*算法采用了以下的搜索步骤来实现:
1.首先把起始位置点加入到一个称为“open List”的列表,在寻路的过程中,目前,我们可以认为open List这个列表会存放许多待测试的点,这些点是通往目标点的关键,以后会逐渐往里面添加更多的测试点,同时,为了效率考虑,通常这个列表是个已经排序的列表。
2.如果open List列表不为空,则重复以下工作:
(1)找出open List中通往目标点代价最小的点作为当前点;
(2)把当前点放入一个称为close List的列表;
(3)对当前点周围的4个点每个进行处理(这里是限制了斜向的移动),如果该点是可以通过并且该点不在close List列表中,则处理如下;
(4)如果该点正好是目标点,则把当前点作为该点的父节点,并退出循环,设置已经找到路径标记;
(5)如果该点也不在open List中,则计算该节点到目标节点的代价,把当前点作为该点的父节点,并把该节点添加到open List中;
(6)如果该点已经在open List中了,则比较该点和当前点通往目标点的代价,如果当前点的代价更小,则把当前点作为该点的父节点,同时,重新计算该点通往目标点的代价,并把open List重新排序;
3.完成以上循环后,如果已经找到路径,则从目标点开始,依次查找每个节点的父节点,直到找到开始点,这样就形成了一条路径。
以上,就是A*算法的全部步骤,按照这个步骤,就可以得到一条正确的路径。这里有一个关键的地方,就是如何计算每个点通往目标点的代价,之所以称为A*算法为启发式搜索,就是因为通过评估这个代价值来搜索最近的路径,对于任意一个点的代价值,在A*算法中通常使用下列的公式计算:
代价F=G+H
在这里,F表示通往目标点的代价,G表示从起始点移动到该点的距离,H则表示从该点到目标点的距离,比如图中,可以看到小狗的附近格子的代价值,其中左上角的数字代表F值,左下角的数字代表G值,右下角的数字代表H值。拿小狗上方的格子来举例,G=1,表示从小狗的位置到该点的距离为1个格子,H=6,表示从小狗到骨头的距离是6个格子,则F=G+H=7。在此处,距离的算法是采用曼哈顿距离,它计算从当前格子到目的格子之间水平和垂直的方格的数量总和,例如在平面上,坐标(x1,y1)的点和坐标(x2,y2)的点的曼哈顿距离为:
|x1-x2|+|y1-y2|
当然,距离的算法也可以采用其他的方法,实际在游戏中,这个移动的代价除了要考虑距离因素外,还要考虑当前格子的游戏属性。比如有的格子表示水路、草地、陆地,这些有可能影响人物移动的速度,实际计算的时候还要把这些考虑在内。
另一个需要注意的就是,在计算这个距离的时候是毋须考虑障碍因素的,因为在以上A*算法步骤中会剔除掉障碍。
这样,按照前面所说的A*算法的步骤,第一次循环open List的时候,把A点作为当前点,同时把A周围的四个点放入到open List中。第二次循环的时候把A右边的点作为当前点,该点的父节点就是A,这是处理当前点的时候,只需要把当前点的上下两个点放入open List中,因为左边的A已经在close List中,而右边的是墙,所以直接被忽略。
伪代码:
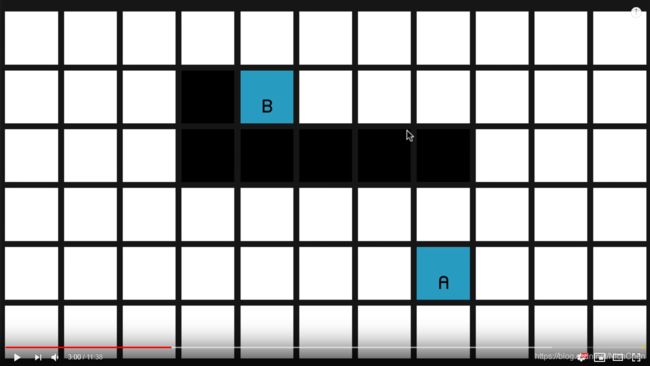
具体例子:
代码:
astar.h
#ifndef ASTAR_H
#define ASTAR_H
#include
#include
#include
namespace AStar
{
struct Vec2i
{
int x, y;
bool operator == (const Vec2i& coordinates_);
};
using uint = unsigned int;
using HeuristicFunction = std::function;
using CoordinateList = std::vector;
struct Node
{
uint G, H;
Vec2i coordinates;
Node *parent;
Node(Vec2i coord_, Node *parent = nullptr);
uint getScore();
};
using NodeSet = std::set;
class Generator
{
// default private
bool detectCollision(Vec2i coordinates_);
Node* findNodeOnList(NodeSet &nodes_, Vec2i coordinates_);
void releaseNodes(NodeSet &nodes_);
public:
Generator();
void setWorldSize(Vec2i worldSize_);
void setDiagonalMovement(bool enable_);
void setHeuristic(HeuristicFunction heuristic_);
CoordinateList findPath(Vec2i source_, Vec2i target_);
void addCollision(Vec2i coordinates_);
void removeCollision(Vec2i coordinates_);
void clearCollision();
private:
HeuristicFunction heuristic;
CoordinateList direction, walls;
Vec2i worldSize;
uint directions;
};
class Heuristic
{
private:
static Vec2i getDelta(Vec2i source_, Vec2i target_);
public:
static uint manhattan(Vec2i source_, Vec2i target_);
static uint euclidean(Vec2i source_, Vec2i target_);
static uint octagonal(Vec2i source_, Vec2i target_);
};
}
#endif // ASTAR_H
astar.cpp
#include "astar.h"
#include
using namespace std::placeholders;
bool AStar::Vec2i::operator == (const Vec2i &coordinates_)
{
return (x == coordinates_.x && y == coordinates_.y);
}
AStar::Vec2i operator + (const AStar::Vec2i& left_, const AStar::Vec2i& right_)
{
return { left_.x + right_.x, left_.y + right_.y };
}
AStar::Node::Node(Vec2i coordinates_, Node *parent_)
{
parent = parent_;
coordinates = coordinates_;
G = H = 0;
}
AStar::uint AStar::Node::getScore()
{
return G + H;
}
AStar::Generator::Generator()
{
setDiagonalMovement(false);
setHeuristic(&Heuristic::manhattan);
direction = {
{ 0, 1 }, { 1, 0 }, { 0, -1 }, { -1, 0 },
{ -1, -1 }, { 1, 1 }, { -1, 1 }, { 1, -1 }
};
}
void AStar::Generator::setWorldSize(Vec2i worldSize_)
{
worldSize = worldSize_;
}
void AStar::Generator::setDiagonalMovement(bool enable_)
{
directions = (enable_ ? 8 : 4);
}
void AStar::Generator::setHeuristic(HeuristicFunction heuristic_)
{
heuristic = std::bind(heuristic_, _1, _2);
}
void AStar::Generator::addCollision(Vec2i coordinates_)
{
walls.push_back(coordinates_);
}
void AStar::Generator::removeCollision(Vec2i coordinates_)
{
auto it = std::find(walls.begin(), walls.end(), coordinates_);
if (it != walls.end()) {
walls.erase(it);
}
}
void AStar::Generator::clearCollision()
{
walls.clear();
}
/* key function */
AStar::CoordinateList AStar::Generator::findPath(Vec2i source_, Vec2i target_)
{
Node *current = nullptr;
NodeSet openSet, closedSet;
openSet.insert(new Node(source_));
while (!openSet.empty())
{
current = *openSet.begin();
for (auto node : openSet) {
if (node->getScore() <= current->getScore()) {
current = node;
}
}
if (current->coordinates == target_) {
break;
}
closedSet.insert(current);
openSet.erase(std::find(openSet.begin(), openSet.end(), current));
for (uint i = 0; i < directions; ++i) {
Vec2i newCoordinates(current->coordinates + direction[i]);
if (detectCollision(newCoordinates) ||
findNodeOnList(closedSet, newCoordinates)) {
continue;
}
uint totalCost = current->G + ((i < 4) ? 10 : 14);
Node *successor = findNodeOnList(openSet, newCoordinates);
if (successor == nullptr) {
successor = new Node(newCoordinates, current);
successor->G = totalCost;
successor->H = heuristic(successor->coordinates, target_);
openSet.insert(successor);
}
else if (totalCost < successor->G) {
successor->parent = current;
successor->G = totalCost;
}
}
}
CoordinateList path;
while (current != nullptr) {
path.push_back(current->coordinates);
current = current->parent;
}
releaseNodes(openSet);
releaseNodes(closedSet);
return path;
}
AStar::Node* AStar::Generator::findNodeOnList(NodeSet& nodes_, Vec2i coordinates_)
{
for (auto node : nodes_) {
if (node->coordinates == coordinates_) {
return node;
}
}
return nullptr;
}
void AStar::Generator::releaseNodes(NodeSet& nodes_)
{
for (auto it = nodes_.begin(); it != nodes_.end();) {
delete *it;
it = nodes_.erase(it);
}
}
bool AStar::Generator::detectCollision(Vec2i coordinates_)
{
if (coordinates_.x < 0 || coordinates_.x >= worldSize.x ||
coordinates_.y < 0 || coordinates_.y >= worldSize.y ||
std::find(walls.begin(), walls.end(), coordinates_) != walls.end()) {
return true;
}
return false;
}
AStar::Vec2i AStar::Heuristic::getDelta(Vec2i source_, Vec2i target_)
{
return{ abs(source_.x - target_.x), abs(source_.y - target_.y) };
}
AStar::uint AStar::Heuristic::manhattan(Vec2i source_, Vec2i target_)
{
auto delta = std::move(getDelta(source_, target_));
return static_cast(10 * (delta.x + delta.y));
}
AStar::uint AStar::Heuristic::euclidean(Vec2i source_, Vec2i target_)
{
auto delta = std::move(getDelta(source_, target_));
return static_cast(10 * sqrt(pow(delta.x, 2) + pow(delta.y, 2)));
}
AStar::uint AStar::Heuristic::octagonal(Vec2i source_, Vec2i target_)
{
auto delta = std::move(getDelta(source_, target_));
return 10 * (delta.x + delta.y) + (-6) * std::min(delta.x, delta.y);
}
main.cpp
#include
#include "astar.h"
#include
using namespace std;
int main()
{
AStar::Generator generator;
generator.setWorldSize({11, 6});
generator.setHeuristic(AStar::Heuristic::euclidean);
generator.setDiagonalMovement(true);
std::cout << "Generate path ... \n";
vector> arr = {{3, 1},
{3, 2},
{4, 2},
{5, 2},
{6, 2},
{7, 2}};
AStar::Vec2i colli;
for (size_t i = 0; i < arr.size(); ++i) {
colli.x = arr[i][0];
colli.y = arr[i][1];
generator.addCollision(colli);
}
auto path = generator.findPath({7, 4}, {4, 1});
for(int i = path.size() - 1; i >= 0; --i) {
std::cout << path[i].x << " " << path[i].y << "\n";
}
}
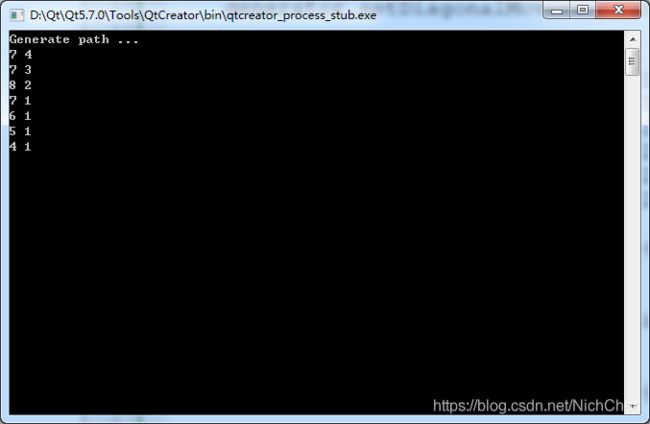
运行结果:
实际结果:(代码求解与实际结果一致)
注:
- A*算法是一种启发式算法,它的启发作用(在扩展路径时让路径点与start和target之间的距离之和最小)使得其性能比BFS和DFS来寻找最短路径更优
- A*算法由于保持了启发作用,相当于有一股外力在让start和target之间的路径趋向于最短化,因此,在这种启发下逐步搜寻处的路径,一定是最短路径(用曼哈顿距离作为启发距离则很容易理解,因为在后面从inList中选择点时,是选择的F值最小的点,若是曼哈顿距离,则在任意路径中,F都是一个非减函数,因此每次选择最小的F值比为最优值,即最短路径)
参考资料:
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=-L-WgKMFuhE
https://github.com/daancode/a-star
http://www.cnblogs.com/msxh/p/5674417.html