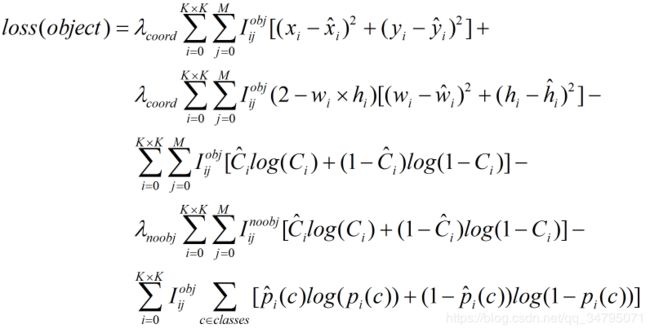yoloV3代码详解(注释)
原文链接:https://www.cnblogs.com/hujinzhou/p/guobao_2020_3_13.html
0.摘要
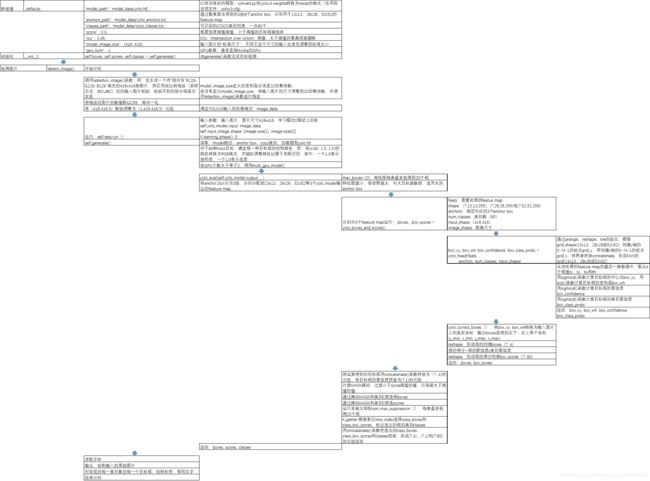
最近一段时间在学习yolo3,看了很多博客,理解了一些理论知识,但是学起来还是有些吃力,之后看了源码,才有了更进一步的理解。在这里,我不在赘述网络方面的代码,网络方面的代码比较容易理解,下面将给出整个yolo3代码的详解解析,整个源码中函数的作用以及调用关系见下图:
参考:https://blog.csdn.net/weixin_41943311/article/details/95672137?depth_1-utm_source=distribute.pc_relevant.none-task&utm_source=distribute.pc_relevant.none-task
1.model.py
1.1 yolo_head()
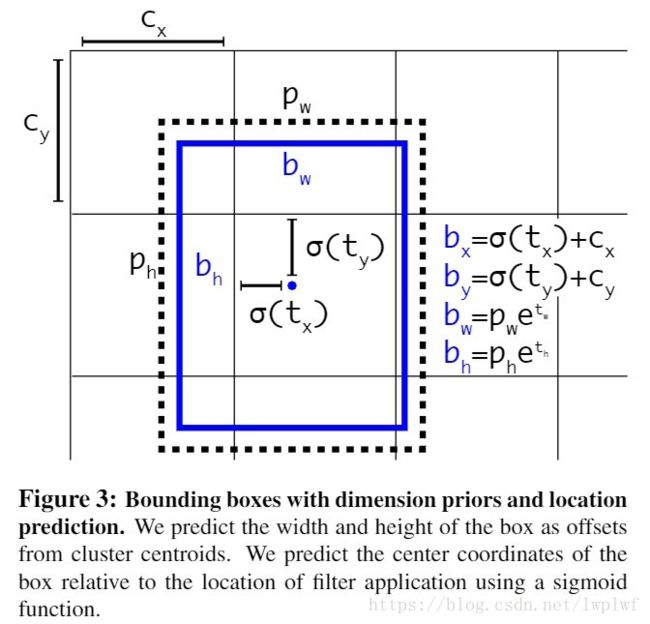
yolo_head()函数的输入是Darknet53的最后输出的三个特征图feats,anchors,num_class,input_shpe,此函数的功能是将特征图的进行解码,这一步极为重要,如其中一个特征图的shape是(13,13,255),其实质就是对应着(13,13,3,85),分别对应着13*13个网格,每个网格3个anchors,85=(x,y,w,h,confident),此时box的xy是相对于网格的偏移量,所以还需要经过一些列的处理,处理方式见下图:
def yolo_head(feats, anchors, num_classes, input_shape, calc_loss=False):
"""Convert final layer features to bounding box parameters."""
num_anchors = len(anchors)#num_anchors=3
# Reshape to batch, height, width, num_anchors, box_params.
anchors_tensor = K.reshape(K.constant(anchors), [1, 1, 1, num_anchors, 2])
#anchors=anchors[anchors_mask[1]]=anchors[[6,7,8]]= [116,90], [156,198], [373,326]
"""#通过arange、reshape、tile的组合,根据grid_shape(13x13、26x26或52x52)创建y轴的0~N-1的组合grid_y,再创建x轴的0~N-1的组合grid_x,将两者拼接concatenate,形成NxN的grid(13x13、26x26或52x52)"""
grid_shape = K.shape(feats)[1:3] # height, width,#13x13或26x26或52x52
grid_y = K.tile(K.reshape(K.arange(0, stop=grid_shape[0]), [-1, 1, 1, 1]),
[1, grid_shape[1], 1, 1])
grid_x = K.tile(K.reshape(K.arange(0, stop=grid_shape[1]), [1, -1, 1, 1]),
[grid_shape[0], 1, 1, 1])
grid = K.concatenate([grid_x, grid_y])
grid = K.cast(grid, K.dtype(feats))
#cast函数用法:cast(x, dtype, name=None),x:待转换的张量,type:需要转换成什么类型
"""grid形式:(0,0),(0,1),(0,2)......(1,0),(1,1).....(12,12)"""
feats = K.reshape(
feats, [-1, grid_shape[0], grid_shape[1], num_anchors, num_classes + 5])
"""(batch_size,13,13,3,85)"""
"此时的xy为中心坐标,相对于左上角的中心坐标"
# Adjust preditions to each spatial grid point and anchor size.
"""将预测值调整为真实值"""
"将中心点相对于网格的坐标转换成在整张图片中的坐标,相对于13/26/52的相对坐标"
"将wh转换成预测框的wh,并处以416归一化"
box_xy = (K.sigmoid(feats[..., :2]) + grid) / K.cast(grid_shape[::-1], K.dtype(feats))#实际上就是除以13或26或52
#box_xy = (K.sigmoid(feats[:,:,:,:2]) + grid) / K.cast(grid_shape[::-1], K.dtype(feats))
# ...操作符,在Python中,“...”(ellipsis)操作符,表示其他维度不变,只操作最前或最后1维;
box_wh = K.exp(feats[..., 2:4]) * anchors_tensor / K.cast(input_shape[::-1], K.dtype(feats))
box_confidence = K.sigmoid(feats[..., 4:5])
box_class_probs = K.sigmoid(feats[..., 5:])
#切片省略号的用法,省略前面左右的冒号,参考博客:https://blog.csdn.net/z13653662052/article/details/78010654?depth_1-utm_source=distribute.pc_relevant.none-task&utm_source=distribute.pc_relevant.none-task
if calc_loss == True:
return grid, feats, box_xy, box_wh
return box_xy, box_wh, box_confidence, box_class_probs
#预测框相对于整张图片中心点的坐标与预测框的wh
1.2 yolo_correct_box()
此函数的功能是将yolo_head()输出,也即是box相对于整张图片的中心坐标转换成box的左上角右下角的坐标
1 def yolo_correct_boxes(box_xy, box_wh, input_shape, image_shape):
2 '''Get corrected boxes'''
3 '''对上面函数输出的预测的坐标进行修正
4 比如
5 image_shape
6 为[600,800],input_shape
7 为[300, 500],那么
8 new_shape
9 为[300, 400]
10
11 offset
12 为[0, 0.125]
13 scales
14 为[0.5, 0.625]'''
15
16
17 # 将box_xy, box_wh转换为输入图片上的真实坐标,输出boxes是框的左下、右上两个坐标(y_min, x_min, y_max, x_max)
18 # ...操作符,在Python中,“...”(ellipsis)操作符,表示其他维度不变,只操作最前或最后1维;
19 # np.array[i:j:s],当s<0时,i缺省时,默认为-1;j缺省时,默认为-len(a)-1;所以array[::-1]相当于array[-1:-len(a)-1:-1],也就是从最后一个元素到第一个元素复制一遍,即倒序
20 box_yx = box_xy[..., ::-1]#将xy坐标进行交换,反序(y,x)
21 box_hw = box_wh[..., ::-1]
22 input_shape = K.cast(input_shape, K.dtype(box_yx))
23 image_shape = K.cast(image_shape, K.dtype(box_yx))
24 new_shape = K.round(image_shape * K.min(input_shape/image_shape))
25 #.round用于取近似值,保留几位小数,第一个参数是一个浮点数,第二个参数是保留的小数位数,可选,如果不写的话默认保留到整数
26 offset = (input_shape-new_shape)/2./input_shape
27 scale = input_shape/new_shape
28 box_yx = (box_yx - offset) * scale
29 box_hw *= scale
30 """获得预测框的左上角与右下角的坐标"""
31 box_mins = box_yx - (box_hw / 2.)
32 box_maxes = box_yx + (box_hw / 2.)
33 boxes = K.concatenate([
34 box_mins[..., 0:1], # y_min
35 box_mins[..., 1:2], # x_min
36 box_maxes[..., 0:1], # y_max
37 box_maxes[..., 1:2] # x_max
38 ])#...操作符,在Python中,“...”(ellipsis)操作符,表示其他维度不变,只操作最前或最后1维;
39
40 # Scale boxes back to original image shape.
41 boxes *= K.concatenate([image_shape, image_shape])
42 return boxes#得到预测框的左下角坐标与右上角坐标
1.3 yolo_box_and_score
获得box与得分
1 def yolo_boxes_and_scores(feats, anchors, num_classes, input_shape, image_shape):
2 '''Process Conv layer output'''
3 box_xy, box_wh, box_confidence, box_class_probs = yolo_head(feats,
4 anchors, num_classes, input_shape)
5 boxes = yolo_correct_boxes(box_xy, box_wh, input_shape, image_shape)
6 boxes = K.reshape(boxes, [-1, 4])#reshape,将不同网格的值转换为框的列表。即(?,13,13,3,4)->(?,4) ?:框的数目
7 box_scores = box_confidence * box_class_probs
8 box_scores = K.reshape(box_scores, [-1, num_classes])#reshape,将框的得分展平,变为(?,80); ?:框的数目
9 return boxes, box_scores#返回预测框的左下角与右上角的坐标与得分
1.4 yolo_eval()
此函数的作用是删除冗余框,保留最优框,用到非极大值抑制算法
1 def yolo_eval(yolo_outputs,
2 anchors,
3 num_classes,
4 image_shape,
5 max_boxes=20,
6 score_threshold=.6,
7 iou_threshold=.5):
8 """Evaluate YOLO model on given input and return filtered boxes."""
9 """ yolo_outputs #模型输出,格式如下【(?,13,13,255)(?,26,26,255)(?,52,52,255)】 ?:bitch size; 13-26-52:多尺度预测; 255:预测值(3*(80+5))
10 anchors, #[(10,13), (16,30), (33,23), (30,61), (62,45), (59,119), (116,90), (156,198),(373,326)]
11 num_classes, # 类别个数,coco集80类
12 image_shape, #placeholder类型的TF参数,默认(416, 416);
13 max_boxes=20, #每张图每类最多检测到20个框同类别框的IoU阈值,大于阈值的重叠框被删除,重叠物体较多,则调高阈值,重叠物体较少,则调低阈值
14 score_threshold=.6, #框置信度阈值,小于阈值的框被删除,需要的框较多,则调低阈值,需要的框较少,则调高阈值;
15 iou_threshold=.5): #同类别框的IoU阈值,大于阈值的重叠框被删除,重叠物体较多,则调高阈值,重叠物体较少,则调低阈值"""
16 num_layers = len(yolo_outputs)# #yolo的输出层数;num_layers = 3 -> 13-26-52
17 anchor_mask = [[6,7,8], [3,4,5], [0,1,2]] if num_layers==3 else [[3,4,5], [1,2,3]] # default setting
18 # 每层分配3个anchor box.如13*13分配到[6,7,8]即[(116,90)(156,198)(373,326)]
19 input_shape = K.shape(yolo_outputs[0])[1:3] * 32
20 # 输入shape(?,13,13,255);即第一维和第二维分别*32 ->13*32=416; input_shape:(416,416)
21 #yolo_outputs=[(batch_size,13,13,255),(batch_size,26,26,255),(batch_size,52,52,255)]
22 #input_shape=416*416
23 boxes = []
24 box_scores = []
25 for l in range(num_layers):
26 _boxes, _box_scores = yolo_boxes_and_scores(yolo_outputs[l],
27 anchors[anchor_mask[l]], num_classes, input_shape, image_shape)
28 boxes.append(_boxes)
29 box_scores.append(_box_scores)
30 boxes = K.concatenate(boxes, axis=0)
31 box_scores = K.concatenate(box_scores, axis=0) #K.concatenate:将数据展平 ->(?,4)
32
33 #可能会产生很多个预选框,需要经过(1)阈值的删选,(2)非极大值抑制的删选
34 mask = box_scores >= score_threshold#得分大于置信度为True,否则为Flase
35 max_boxes_tensor = K.constant(max_boxes, dtype='int32')
36 boxes_ = []
37 scores_ = []
38 classes_ = []
39 """
40 # ---------------------------------------#
41 # 1、取出每一类得分大于score_threshold
42 # 的框和得分
43 # 2、对得分进行非极大抑制
44 # ---------------------------------------#
45 # 对每一个类进行判断"""
46 for c in range(num_classes):
47 # TODO: use keras backend instead of tf.
48 class_boxes = tf.boolean_mask(boxes, mask[:, c])#将输入的数组挑出想要的数据输出,将得分大于阈值的坐标挑选出来
49 #将第c类中得分大于阈值的坐标挑选出来
50 class_box_scores = tf.boolean_mask(box_scores[:, c], mask[:, c])
51 # 将第c类中得分大于阈值的框挑选出来
52 """非极大值抑制部分"""
53 # 非极大抑制,去掉box重合程度高的那一些
54 """原理:(1)从最大概率矩形框F开始,分别判断A~E与F的重叠度IOU是否大于某个设定的阈值;
55
56 (2)假设B、D与F的重叠度超过阈值,那么就扔掉B、D;并标记第一个矩形框F,是我们保留下来的。
57
58 (3)从剩下的矩形框A、C、E中,选择概率最大的E,然后判断E与A、C的重叠度,重叠度大于一定的阈值,那么就扔掉;并标记E是我们保留下来的第二个矩形框。
59
60 就这样一直重复,找到所有被保留下来的矩形框。"""
61 nms_index = tf.image.non_max_suppression(
62 class_boxes, class_box_scores, max_boxes_tensor, iou_threshold=iou_threshold)
63 class_boxes = K.gather(class_boxes, nms_index)
64 class_box_scores = K.gather(class_box_scores, nms_index)
65 classes = K.ones_like(class_box_scores, 'int32') * c#将class_box_scores中的数变成1
66 boxes_.append(class_boxes)
67 scores_.append(class_box_scores)
68 classes_.append(classes)
69 boxes_ = K.concatenate(boxes_, axis=0)
70 scores_ = K.concatenate(scores_, axis=0)
71 classes_ = K.concatenate(classes_, axis=0)
72 #return 经过非极大值抑制保留下来的一个框
73
74 return boxes_, scores_, classes_
1.5 preprocess_true_box()
1 def preprocess_true_boxes(true_boxes, input_shape, anchors, num_classes):
2 '''
3 在preprocess_true_boxes中,输入:
4
5 true_boxes:检测框,批次数16,最大框数20,每个框5个值,4个边界点和1个类别序号,如(16, 20, 5);
6 input_shape:图片尺寸,如(416, 416);
7 anchors:anchor box列表;
8 num_classes:类别的数量;
9 Preprocess true boxes to training input format
10
11 Parameters
12 ----------
13 true_boxes: array, shape=(m, T, 5)
14 Absolute x_min, y_min, x_max, y_max, class_id relative to input_shape.
15 input_shape: array-like, hw, multiples of 32
16 anchors: array, shape=(N, 2), wh
17 num_classes: integer
18
19 Returns
20 -------
21 y_true: list of array, shape like yolo_outputs, xywh are reletive value
22
23 '''
24 # 检查有无异常数据 即txt提供的box id 是否存在大于 num_class的情况
25 # true_boxes.shape = (图片张数,每张图片box个数,5)(5是左上右下点坐标加上类别下标)
26 assert (true_boxes[..., 4]'class id must be less than num_classes'
27 num_layers = len(anchors)//3 # default setting
28 anchor_mask = [[6,7,8], [3,4,5], [0,1,2]] if num_layers==3 else [[3,4,5], [1,2,3]]
29
30 true_boxes = np.array(true_boxes, dtype='float32')
31 input_shape = np.array(input_shape, dtype='int32') # [416 416] shape(2,)
32 # 将每个box的左上点和右下点坐标相加除2,即取中点!
33 """计算true_boxes:
34
35 true_boxes:真值框,左上和右下2个坐标值和1个类别,如[184, 299, 191, 310, 0.0],结构是(16, 20, 5),16是批次数,20是框的最大数,5是框的5个值;
36 boxes_xy:xy是box的中心点,结构是(16, 20, 2);
37 boxes_wh:wh是box的宽和高,结构也是(16, 20, 2);
38 input_shape:输入尺寸416x416;
39 true_boxes:第0和1位设置为xy,除以416,归一化,第2和3位设置为wh,除以416,归一化,如[0.449, 0.730, 0.016, 0.026, 0.0]。"""
40 boxes_xy = (true_boxes[..., 0:2] + true_boxes[..., 2:4]) // 2
41 # 得到box宽高
42 boxes_wh = true_boxes[..., 2:4] - true_boxes[..., 0:2]
43 # 中心坐标 和 宽高 都变成 相对于input_shape的比例
44 true_boxes[..., 0:2] = boxes_xy/input_shape[::-1]
45 true_boxes[..., 2:4] = boxes_wh/input_shape[::-1]
46 # 这个m应该是batch的大小 即是输入图片的数量
47 m = true_boxes.shape[0]
48 # grid_shape [13,13 ] [26,26] [52,52]
49 grid_shapes = [input_shape//{0:32, 1:16, 2:8}[l] for l in range(num_layers)]
50 #y_true是全0矩阵(np.zeros)列表,即[(16,13,13,3,6), (16,26,26,3,6), (16,52,52,3,6)]
51 y_true = [np.zeros((m,grid_shapes[l][0],grid_shapes[l][1],len(anchor_mask[l]),5+num_classes),
52 dtype='float32') for l in range(num_layers)]
53 # y_true m*13*13*3*(5+num_clasess)
54 # m*26*26*3*(5+num_classes)
55 # m*52*52*3*(5+num_classes)
56 # Expand dim to apply broadcasting.
57
58 # Expand dim to apply broadcasting.
59 #在原先axis出添加一个维度,由(9,2)转为(1,9,2)
60 anchors = np.expand_dims(anchors, 0)
61 # 网格中心为原点(即网格中心坐标为 (0,0) ), 计算出anchor 右下角坐标
62 anchor_maxes = anchors / 2.
63 #计算出左上标
64 anchor_mins = -anchor_maxes
65 # 去掉异常数据
66 valid_mask = boxes_wh[..., 0]>0
67
68 for b in range(m):
69 # Discard zero rows.
70 wh = boxes_wh[b, valid_mask[b]]
71 if len(wh)==0: continue
72 # Expand dim to apply broadcasting.
73 wh = np.expand_dims(wh, -2)
74 box_maxes = wh / 2.
75 box_mins = -box_maxes
76 # # 假设 bouding box 的中心也位于网格的中心
77
78 """计算标注框box与anchor box的iou值,计算方式很巧妙:
79
80 box_mins的shape是(7,1,2),anchor_mins的shape是(1,9,2),intersect_mins的shape是(7,9,2),即两两组合的值;
81 intersect_area的shape是(7,9);
82 box_area的shape是(7,1);
83 anchor_area的shape是(1,9);
84 iou的shape是(7,9);
85 IoU数据,即anchor box与检测框box,两两匹配的iou值"""
86 intersect_mins = np.maximum(box_mins, anchor_mins)#逐位比较
87 intersect_maxes = np.minimum(box_maxes, anchor_maxes)
88 intersect_wh = np.maximum(intersect_maxes - intersect_mins, 0.)
89 intersect_area = intersect_wh[..., 0] * intersect_wh[..., 1]#宽*高
90 box_area = wh[..., 0] * wh[..., 1]
91 anchor_area = anchors[..., 0] * anchors[..., 1]
92 iou = intersect_area / (box_area + anchor_area - intersect_area)
93
94 # Find best anchor for each true box
95 best_anchor = np.argmax(iou, axis=-1)
96
97 """设置y_true的值:
98
99 t是box的序号;n是最优anchor的序号;l是层号;
100 如果最优anchor在层l中,则设置其中的值,否则默认为0;
101 true_boxes是(16, 20, 5),即批次、box数、框值;
102 true_boxes[b, t, 0],其中b是批次序号、t是box序号,第0位是x,第1位是y;
103 grid_shapes是3个检测图的尺寸,将归一化的值,与框长宽相乘,恢复为具体值;
104 k是在anchor box中的序号;
105 c是类别,true_boxes的第4位;
106 将xy和wh放入y_true中,将y_true的第4位框的置信度设为1,将y_true第5~n位的类别设为1;"""
107 for t, n in enumerate(best_anchor):
108 # 遍历anchor 尺寸 3个尺寸
109 # 因为此时box 已经和一个anchor box匹配上,看这个anchor box属于那一层,小,中,大,然后将其box分配到那一层
110 for l in range(num_layers):
111 if n in anchor_mask[l]:
112 #因为grid_shape格式是hw所以是x*grid_shapes[l][1]=x*w,求出对应所在网格的横坐标,这里的x是相对于整张图片的相对坐标,
113 # 是在原先坐标上除以了w,所以现在要乘以w
114 i = np.floor(true_boxes[b,t,0]*grid_shapes[l][1]).astype('int32')
115 #np.around 四舍五入
116 #np.floor向下取整
117 #np.ceil向上取整
118 #np.where条件选取
119 # np.floor 返回不大于输入参数的最大整数。 即对于输入值 x ,将返回最大的整数 i ,使得 i <= x。
120 # true_boxes x,y,w,h, 此时x y w h都是相对于整张图像的
121 # 第b个图像 第 t个 bounding box的 x 乘以 第l个grid shap的x(grid shape 格式是hw,
122 # 因为input_shape格式是hw)
123 # 找到这个bounding box落在哪个cell的中心
124 #i,j是所在网格的位置
125 j = np.floor(true_boxes[b,t,1]*grid_shapes[l][0]).astype('int32')
126 # 找到n 在 anchor_box的索引位置
127 k = anchor_mask[l].index(n)
128 # 得到box的id
129 c = true_boxes[b,t, 4].astype('int32')
130 # 第b个图像 第j行 i列 第k个anchor x,y,w,h,confindence,类别概率
131 y_true[l][b, j, i, k, 0:4] = true_boxes[b,t, 0:4]
132 y_true[l][b, j, i, k, 4] = 1
133 # 置信度是1 因为含有目标
134 y_true[l][b, j, i, k, 5+c] = 1
135 # 类别的one-hot编码
136
137 return y_true
1.6 yolo_loss
此函数定义损失函数,损失函数包括三个部分,坐标损失,置信度损失,类别损失:
1 def yolo_loss(args, anchors, num_classes, ignore_thresh=.5, print_loss=False):
2 """true_boxes : 实际框的位置和类别,我们的输入。三个维度:
3 第一个维度:图片张数
4 第二个维度:一张图片中有几个实际框
5 第三个维度: [x, y, w, h, class],x,y 是实际框的中心点坐标,w,h 是框的宽度和高度。x,y,w,h 均是除以图片分辨率得到的[0,1]范围的值。
6 anchors : 实际anchor boxes 的值,论文中使用了五个。[w,h],都是相对于gird cell 长宽的比值。二个维度:
7 第一个维度:anchor boxes的数量,这里是5
8 第二个维度:[w,h],w,h,都是相对于gird cell 长宽的比值。
9 """
10 '''Return yolo_loss tensor
11
12 Parameters
13 ----------
14 yolo_outputs: list of tensor, the output of yolo_body or tiny_yolo_body
15 y_true: list of array, the output of preprocess_true_boxes
16 anchors: array, shape=(N, 2), wh
17 num_classes: integer
18 ignore_thresh: float, the iou threshold whether to ignore object confidence loss
19
20 Returns
21 -------
22 loss: tensor, shape=(1,)
23
24 '''
25 num_layers = len(anchors)//3 # default setting
26 yolo_outputs = args[:num_layers]
27 y_true = args[num_layers:]
28 anchor_mask = [[6,7,8], [3,4,5], [0,1,2]] if num_layers==3 else [[3,4,5], [1,2,3]]
29 input_shape = K.cast(K.shape(yolo_outputs[0])[1:3] * 32, K.dtype(y_true[0]))
30 grid_shapes = [K.cast(K.shape(yolo_outputs[l])[1:3], K.dtype(y_true[0])) for l in range(num_layers)]
31 loss = 0
32 m = K.shape(yolo_outputs[0])[0] # batch size, tensor
33 mf = K.cast(m, K.dtype(yolo_outputs[0]))
34
35 for l in range(num_layers):
36 object_mask = y_true[l][..., 4:5]#置信度
37 true_class_probs = y_true[l][..., 5:]#类别
38
39 grid, raw_pred, pred_xy, pred_wh = yolo_head(yolo_outputs[l],
40 anchors[anchor_mask[l]], num_classes, input_shape, calc_loss=True)
41 pred_box = K.concatenate([pred_xy, pred_wh])
42
43 # Darknet raw box to calculate loss.
44 # 这是对x,y,w,b转换公式的反变换
45 raw_true_xy = y_true[l][..., :2]*grid_shapes[l][::-1] - grid
46 raw_true_wh = K.log(y_true[l][..., 2:4] / anchors[anchor_mask[l]] * input_shape[::-1])
47 # 这部操作是避免出现log(0) = 负无穷,故当object_mask置信率接近0是返回全0结果
48 # K.switch(条件函数,返回值1,返回值2)其中1,2要等shape
49 raw_true_wh = K.switch(object_mask, raw_true_wh, K.zeros_like(raw_true_wh)) # avoid log(0)=-inf
50 #提升针对小物体的小技巧:针对 YOLOv3来说,regression损失会乘一个(2-w*h)的比例系数,
51 # w 和 h 分别是ground truth 的宽和高。如果不减去 w*h,AP 会有一个明显下降。如果继续往上加,如 (2-w*h)*1.5,总体的 AP 还会涨一个点左右(包括验证集和测试集),大概是因为 COCO 中小物体实在太多的原因。
52
53 box_loss_scale = 2 - y_true[l][...,2:3]*y_true[l][...,3:4]
54
55 # Find ignore mask, iterate over each of batch.
56 ignore_mask = tf.TensorArray(K.dtype(y_true[0]), size=1, dynamic_size=True)
57 object_mask_bool = K.cast(object_mask, 'bool')
58 ##将真实标定的数据置信率转换为T or F的掩膜
59
60 def loop_body(b, ignore_mask):
61 true_box = tf.boolean_mask(y_true[l][b,...,0:4], object_mask_bool[b,...,0])#挑选出置信度大于0的框的相应的坐标,truebox形式为中心坐标xy与hw
62
63 iou = box_iou(pred_box[b], true_box)#计算iou,pre_box是通过yolo_head解码之后的xywh
64 best_iou = K.max(iou, axis=-1)#选取最大iou的
65 ignore_mask = ignore_mask.write(b, K.cast(best_iou<ignore_thresh, K.dtype(true_box)))
66 return b+1, ignore_mask
67 _, ignore_mask = K.control_flow_ops.while_loop(lambda b,*args: b<m, loop_body, [0, ignore_mask])
68 ignore_mask = ignore_mask.stack()#将一个列表中维度数目为R的张量堆积起来形成维度为R+1的新张量
69 ignore_mask = K.expand_dims(ignore_mask, -1)
70
71 # K.binary_crossentropy is helpful to avoid exp overflow.
72 xy_loss = object_mask * box_loss_scale * K.binary_crossentropy(raw_true_xy, raw_pred[...,0:2], from_logits=True)
73 wh_loss = object_mask * box_loss_scale * 0.5 * K.square(raw_true_wh-raw_pred[...,2:4])
74 confidence_loss = object_mask * K.binary_crossentropy(object_mask, raw_pred[...,4:5], from_logits=True)+ \
75 (1-object_mask) * K.binary_crossentropy(object_mask, raw_pred[...,4:5], from_logits=True) * ignore_mask
76 class_loss = object_mask * K.binary_crossentropy(true_class_probs, raw_pred[...,5:], from_logits=True)
77
78 xy_loss = K.sum(xy_loss) / mf
79 wh_loss = K.sum(wh_loss) / mf
80 confidence_loss = K.sum(confidence_loss) / mf
81 class_loss = K.sum(class_loss) / mf
82 loss += xy_loss + wh_loss + confidence_loss + class_loss
83 if print_loss:
84 loss = tf.Print(loss, [loss, xy_loss, wh_loss, confidence_loss, class_loss, K.sum(ignore_mask)], message='loss: ')
85 return loss
2.train.py
整个训练分为两个阶段,第一个阶段为0~50epoch,训练最后的loss层,前面的层被冻结,第二个阶段为50~100个epoch训练前面的层
1 def _main():
2 annotation_path = '2007_train.txt'
3 log_dir = 'logs/000/'
4 classes_path = 'model_data/voc_classes.txt'
5 anchors_path = 'model_data/yolo_anchors.txt'
6 class_names = get_classes(classes_path)
7 num_classes = len(class_names)
8 anchors = get_anchors(anchors_path)
9
10 input_shape = (416,416) # multiple of 32, hw
11
12 is_tiny_version = len(anchors)==6 # default setting
13 if is_tiny_version:
14 model = create_tiny_model(input_shape, anchors, num_classes,
15 freeze_body=2, weights_path='model_data/tiny_yolo_weights.h5')
16 else:
17 model = create_model(input_shape, anchors, num_classes,
18 freeze_body=2, weights_path='model_data/yolo_weights.h5') # make sure you know what you freeze
19
20 logging = TensorBoard(log_dir=log_dir)
21 checkpoint = ModelCheckpoint(log_dir + 'ep{epoch:03d}-loss{loss:.3f}-val_loss{val_loss:.3f}.h5',
22 monitor='val_loss', save_weights_only=True, save_best_only=True, period=3)
23 reduce_lr = ReduceLROnPlateau(monitor='val_loss', factor=0.1, patience=3, verbose=1)
24 """monitor:被监测的量
25 factor:每次减少学习率的因子,学习率将以lr = lr*factor的形式被减少
26 patience:当patience个epoch过去而模型性能不提升时,学习率减少的动作会被触发
27 mode:‘auto’,‘min’,‘max’之一,在min模式下,如果检测值触发学习率减少。在max模式下,当检测值不再上升则触发学习率减少。
28 epsilon:阈值,用来确定是否进入检测值的“平原区”
29 cooldown:学习率减少后,会经过cooldown个epoch才重新进行正常操作
30 min_lr:学习率的下限"""
31 early_stopping = EarlyStopping(monitor='val_loss', min_delta=0, patience=10, verbose=1)
32 """monitor: 被监测的数据。
33 min_delta: 在被监测的数据中被认为是提升的最小变化, 例如,小于 min_delta 的绝对变化会被认为没有提升。
34 patience: 没有进步的训练轮数,在这之后训练就会被停止。
35 verbose: 详细信息模式。
36 mode: {auto, min, max} 其中之一。 在 min 模式中, 当被监测的数据停止下降,训练就会停止;在 max 模式中,当被监测的数据停止上升,训练就会停止;在 auto 模式中,方向会自动从被监测的数据的名字中判断出来。
37 baseline: 要监控的数量的基准值。 如果模型没有显示基准的改善,训练将停止。
38 restore_best_weights: 是否从具有监测数量的最佳值的时期恢复模型权重。 如果为 False,则使用在训练的最后一步获得的模型权重"""
39
40 val_split = 0.1
41 with open(annotation_path) as f:
42 lines = f.readlines()
43 np.random.seed(10101)
44 np.random.shuffle(lines)
45 np.random.seed(None)
46 num_val = int(len(lines)*val_split)
47 num_train = len(lines) - num_val
48
49 # Train with frozen layers first, to get a stable loss.
50 # Adjust num epochs to your dataset. This step is enough to obtain a not bad model.
51 if True:
52 model.compile(optimizer=Adam(lr=1e-3), loss={
53 # use custom yolo_loss Lambda layer.
54 # # 使用定制的 yolo_loss Lambda层
55 'yolo_loss': lambda y_true, y_pred: y_pred})
56 #解释:模型compile时传递的是自定义的loss,而把loss写成一个层融合到model里面后,
57 # y_pred就是loss。自定义损失函数规定要以y_true, y_pred为参数
58
59 batch_size = 32
60 print('Train on {} samples, val on {} samples, with batch size {}.'.format(num_train, num_val, batch_size))
61 model.fit_generator(data_generator_wrapper(lines[:num_train], batch_size, input_shape, anchors, num_classes),
62 steps_per_epoch=max(1, num_train//batch_size),
63 validation_data=data_generator_wrapper(lines[num_train:], batch_size, input_shape, anchors, num_classes),
64 validation_steps=max(1, num_val//batch_size),
65 epochs=50,
66 initial_epoch=0,
67 callbacks=[logging, checkpoint])
68 model.save_weights(log_dir + 'trained_weights_stage_1.h5')
69
70 # Unfreeze and continue training, to fine-tune.
71 # Train longer if the result is not good.
72 if True:
73 for i in range(len(model.layers)):
74 model.layers[i].trainable = True
75 model.compile(optimizer=Adam(lr=1e-4), loss={'yolo_loss': lambda y_true, y_pred: y_pred}) # recompile to apply the change
76 print('Unfreeze all of the layers.')
77
78 batch_size = 32 # note that more GPU memory is required after unfreezing the body
79 print('Train on {} samples, val on {} samples, with batch size {}.'.format(num_train, num_val, batch_size))
80 model.fit_generator(data_generator_wrapper(lines[:num_train], batch_size, input_shape, anchors, num_classes),
81 steps_per_epoch=max(1, num_train//batch_size),
82 validation_data=data_generator_wrapper(lines[num_train:], batch_size, input_shape, anchors, num_classes),
83 validation_steps=max(1, num_val//batch_size),
84 epochs=100,
85 initial_epoch=50,
86 callbacks=[logging, checkpoint, reduce_lr, early_stopping])
87 model.save_weights(log_dir + 'trained_weights_final.h5')
88
89 # Further training if needed.
90
91
92 def get_classes(classes_path):
93 '''loads the classes'''
94 with open(classes_path) as f:
95 class_names = f.readlines()
96 class_names = [c.strip() for c in class_names]
97 return class_names
98
99 def get_anchors(anchors_path):
100 '''loads the anchors from a file'''
101 with open(anchors_path) as f:
102 anchors = f.readline()
103 anchors = [float(x) for x in anchors.split(',')]
104 return np.array(anchors).reshape(-1, 2)
105
106
107 def create_model(input_shape, anchors, num_classes, load_pretrained=True, freeze_body=2,
108 weights_path='model_data/yolo_weights.h5'):
109 '''create the training model'''
110 K.clear_session() # get a new session
111 image_input = Input(shape=(None, None, 3))
112 h, w = input_shape
113 num_anchors = len(anchors)
114
115 y_true = [Input(shape=(h//{0:32, 1:16, 2:8}[l], w//{0:32, 1:16, 2:8}[l], \
116 num_anchors//3, num_classes+5)) for l in range(3)]
117
118 model_body = yolo_body(image_input, num_anchors//3, num_classes)
119 print('Create YOLOv3 model with {} anchors and {} classes.'.format(num_anchors, num_classes))
120
121 if load_pretrained:
122 model_body.load_weights(weights_path, by_name=True, skip_mismatch=True)
123 print('Load weights {}.'.format(weights_path))
124 """根据预训练权重的地址weights_path,加载权重文件,设置参数为,按名称对应by_name,
125 略过不匹配skip_mismatch;
126
127 选择冻结模式:模式1是冻结185层,模式2是保留最底部3层,其余全部冻结。
128 整个模型共有252层;将所冻结的层,设置为不可训练,trainable=False;"""
129 if freeze_body in [1, 2]:
130 # Freeze darknet53 body or freeze all but 3 output layers.
131 num = (185, len(model_body.layers)-3)[freeze_body-1]
132 for i in range(num): model_body.layers[i].trainable = False
133 print('Freeze the first {} layers of total {} layers.'.format(num, len(model_body.layers)))
134 """Lambda是Keras的自定义层,输入为model_body.output和y_true,输出output_shape是(1,),即一个损失值;
135
136 自定义Lambda层的名字name为yolo_loss;
137
138 层的参数是锚框列表anchors、类别数num_classes和IoU阈值ignore_thresh。
139 其中,ignore_thresh用于在物体置信度损失中过滤IoU较小的框;
140
141 yolo_loss是损失函数的核心逻辑。"""
142 model_loss = Lambda(yolo_loss, output_shape=(1,), name='yolo_loss',
143 arguments={'anchors': anchors, 'num_classes': num_classes, 'ignore_thresh': 0.5})(
144 [*model_body.output, *y_true])
145 """把loss写成一个层,作为最后的输出,搭建模型的时候,就只需要将模型的output定义为loss
146 ,而compile的时候,直接将loss设置为y_pred(因为模型的输出就是loss,所以y_pred就是loss),
147 无视y_true,训练的时候,y_true随便扔一个符合形状的数组进去就行了"""
148 #keras.layer.Lambda将任意表达式封装为 Layer 对象
149 #keras.layers.Lambda(function, output_shape=None, mask=None, arguments=None)
150 #function: 需要封装的函数。 将输入张量作为第一个参数。
151 # output_shape: 预期的函数输出尺寸。可以是元组或者函数。 如果是元组,它只指定第一个维度;
152 # arguments: 可选的。传递给函数function的关键字参数。
153
154 model = Model([model_body.input, *y_true], model_loss)
155 #构建了以图片数据和图片标签(y_true)为输入,
156 # 模型损失(model_loss)为输出(y_pred)的模型 model。
157
158 return model
159
160 def create_tiny_model(input_shape, anchors, num_classes, load_pretrained=True, freeze_body=2,
161 weights_path='model_data/tiny_yolo_weights.h5'):
162 '''create the training model, for Tiny YOLOv3'''
163 K.clear_session() # get a new session
164 image_input = Input(shape=(None, None, 3))
165 h, w = input_shape
166 num_anchors = len(anchors)
167
168 y_true = [Input(shape=(h//{0:32, 1:16}[l], w//{0:32, 1:16}[l], \
169 num_anchors//2, num_classes+5)) for l in range(2)]
170
171 model_body = tiny_yolo_body(image_input, num_anchors//2, num_classes)
172 print('Create Tiny YOLOv3 model with {} anchors and {} classes.'.format(num_anchors, num_classes))
173
174 if load_pretrained:
175 model_body.load_weights(weights_path, by_name=True, skip_mismatch=True)
176 print('Load weights {}.'.format(weights_path))
177 if freeze_body in [1, 2]:
178 # Freeze the darknet body or freeze all but 2 output layers.
179 num = (20, len(model_body.layers)-2)[freeze_body-1]
180 for i in range(num): model_body.layers[i].trainable = False
181 print('Freeze the first {} layers of total {} layers.'.format(num, len(model_body.layers)))
182
183 model_loss = Lambda(yolo_loss, output_shape=(1,), name='yolo_loss',
184 arguments={'anchors': anchors, 'num_classes': num_classes, 'ignore_thresh': 0.7})(
185 [*model_body.output, *y_true])
186 model = Model([model_body.input, *y_true], model_loss)
187
188 return model
189
190 def data_generator(annotation_lines, batch_size, input_shape, anchors, num_classes):
191
192 '''data generator for fit_generator
193 annotation_lines:标注数据的行,每行数据包含图片路径,和框的位置信息,种类
194 batch_size:每批图片的大小
195 input_shape: 图片的输入尺寸
196 anchors: 大小
197 num_classes: 类别数
198 '''
199
200 n = len(annotation_lines)
201 i = 0
202 while True:
203 image_data = []
204 box_data = []
205 for b in range(batch_size):
206 if i==0:
207 np.random.shuffle(annotation_lines)
208 image, box = get_random_data(annotation_lines[i], input_shape, random=True)#从标记的样本分离image与box,得到样本图片与样本label
209 image_data.append(image)
210 box_data.append(box)
211 i = (i+1) % n
212 image_data = np.array(image_data)
213 box_data = np.array(box_data)
214 y_true = preprocess_true_boxes(box_data, input_shape, anchors, num_classes)
215 yield [image_data, *y_true], np.zeros(batch_size)
216
217 def data_generator_wrapper(annotation_lines, batch_size, input_shape, anchors, num_classes):
218 n = len(annotation_lines)
219 if n==0 or batch_size<=0: return None
220 return data_generator(annotation_lines, batch_size, input_shape, anchors, num_classes)
221
222 if __name__ == '__main__':
223 _main()
3.utils.py
3.1 letter_image_box(),此函数的作用主要是将输入的图片进行等比例缩小,并在空余地方填成灰色
1 def letterbox_image(image, size):
2 '''resize image with unchanged aspect ratio using padding'''
3 iw, ih = image.size#图像初始的大小,任意值 以(1000,500)为例
4 w, h = size #模型要求的(416,416)
5 scale = min(w/iw, h/ih)#416/1000 0.416<0.832 ,416/500
6 nw = int(iw*scale) #416/1000*1000=416
7 nh = int(ih*scale)#416/1000*400=208
8
9 image = image.resize((nw,nh), Image.BICUBIC)
10 new_image = Image.new('RGB', size, (128,128,128))#new : 这个函数创建一幅给定模式(mode)和尺寸(size)的图片。如果省略 color 参数,则创建的图片被黑色填充满,
11 # 如果 color 参数是 None 值,则图片还没初始化
12 new_image.paste(image, ((w-nw)//2, (h-nh)//2)) #w-nw=0,(h-nh)//2=(416-208)//2=108
13 return new_image
它的作用如下:
3.2 get_random_data()
此函数的功能主要是进行数据增强与输入图像预处理(同letter_image_box)
1 def get_random_data(annotation_line, input_shape, random=True, max_boxes=20, jitter=.3, hue=.1, sat=1.5, val=1.5, proc_img=True):
2 '''random preprocessing for real-time data augmentation
3 annotation_lines:标注数据的行,每行数据包含图片路径,和框的位置信息,种类
4 return:imagedata是经过resize并填充的样本图片,resize成(416,416),并填充灰度
5 boxdata是每张image中做的标记label,shpe,对应着truebox,批次数16,最大框数20,每个框5个值,4个边界点和1个类别序号,如(16, 20, 5)
6 为(,batchsize,maxbox,5),每张图片最多的有maxbox个类,5为左上右下的坐标'''
7 line = annotation_line.split()#删除空格
8 image = Image.open(line[0])
9 iw, ih = image.size
10 h, w = input_shape#(416,416)
11 box = np.array([np.array(list(map(int,box.split(',')))) for box in line[1:]])
12
13 if not random:
14 # resize image
15 #将图片等比例转换为416x416的图片,其余用灰色填充,
16 # 即(128, 128, 128),同时颜色值转换为0~1之间,即每个颜色值除以255;
17
18
19 scale = min(w/iw, h/ih)
20 nw = int(iw*scale)
21 nh = int(ih*scale)
22 dx = (w-nw)//2
23 dy = (h-nh)//2
24 image_data=0
25 if proc_img:
26 image = image.resize((nw,nh), Image.BICUBIC)
27 new_image = Image.new('RGB', (w,h), (128,128,128))
28 new_image.paste(image, (dx, dy))
29 image_data = np.array(new_image)/255.
30 # 上面的作用和letter_box一致,加了一个把rgb范围变成0-1
31 # correct boxes max_boxes=20
32
33 # correct boxes
34 # 将边界框box等比例缩小,再加上填充的偏移量dx和dy,因为新的图片部分用灰色填充,影
35 # 响box的坐标系,box最多有max_boxes个,即20个
36 box_data = np.zeros((max_boxes,5))#shap->(20,5)
37 if len(box)>0:
38 np.random.shuffle(box)
39 if len(box)>max_boxes: box = box[:max_boxes]
40 box[:, [0,2]] = box[:, [0,2]]*scale + dx
41 box[:, [1,3]] = box[:, [1,3]]*scale + dy
42 box_data[:len(box)] = box
43
44 return image_data, box_data
45
46 # resize image
47 #通过jitter参数,随机计算new_ar和scale,生成新的nh和nw,
48 # 将原始图像随机转换为nw和nh尺寸的图像,即非等比例变换图像。
49 #也即是数据增强
50 new_ar = w/h * rand(1-jitter,1+jitter)/rand(1-jitter,1+jitter)
51 scale = rand(.25, 2)
52 if new_ar < 1:
53 nh = int(scale*h)
54 nw = int(nh*new_ar)
55 else:
56 nw = int(scale*w)
57 nh = int(nw/new_ar)
58 image = image.resize((nw,nh), Image.BICUBIC)
59
60 # place image
61 dx = int(rand(0, w-nw))
62 dy = int(rand(0, h-nh))
63 new_image = Image.new('RGB', (w,h), (128,128,128))
64 new_image.paste(image, (dx, dy))
65 image = new_image
66
67 # flip image or not
68 #根据随机数flip,随机左右翻转FLIP_LEFT_RIGHT图片
69 flip = rand()<.5
70 if flip: image = image.transpose(Image.FLIP_LEFT_RIGHT)
71
72 # distort image
73 #在HSV坐标域中,改变图片的颜色范围,hue值相加,sat和vat相乘,
74 # 先由RGB转为HSV,再由HSV转为RGB,添加若干错误判断,避免范围过大
75 hue = rand(-hue, hue)
76 sat = rand(1, sat) if rand()<.5 else 1/rand(1, sat)
77 val = rand(1, val) if rand()<.5 else 1/rand(1, val)
78 x = rgb_to_hsv(np.array(image)/255.)
79 x[..., 0] += hue
80 x[..., 0][x[..., 0]>1] -= 1
81 x[..., 0][x[..., 0]<0] += 1
82 x[..., 1] *= sat
83 x[..., 2] *= val
84 x[x>1] = 1
85 x[x<0] = 0
86 image_data = hsv_to_rgb(x) # numpy array, 0 to 1
87
88 # correct boxes
89 #将所有的图片变换,增加至检测框中,并且包含若干异常处理,避免变换之后的值过大或过小,去除异常的box
90 box_data = np.zeros((max_boxes,5))
91 if len(box)>0:
92 np.random.shuffle(box)
93 box[:, [0,2]] = box[:, [0,2]]*nw/iw + dx
94 box[:, [1,3]] = box[:, [1,3]]*nh/ih + dy
95 if flip: box[:, [0,2]] = w - box[:, [2,0]]
96 box[:, 0:2][box[:, 0:2]<0] = 0
97 box[:, 2][box[:, 2]>w] = w
98 box[:, 3][box[:, 3]>h] = h
99 box_w = box[:, 2] - box[:, 0]
100 box_h = box[:, 3] - box[:, 1]
101 box = box[np.logical_and(box_w>1, box_h>1)] # discard invalid box
102 if len(box)>max_boxes: box = box[:max_boxes]
103 box_data[:len(box)] = box
104
105 return image_data, box_data
4.yolo.py()
此函数主要用于检测图片或者视频
1 def generate(self):
2 """①加载权重参数文件,生成检测框,得分,以及对应类别
3
4 ②利用model.py中的yolo_eval函数生成检测框,得分,所属类别
5
6 ③初始化时调用generate函数生成图片的检测框,得分,所属类别(self.boxes, self.scores, self.classes)"""
7 model_path = os.path.expanduser(self.model_path)
8 assert model_path.endswith('.h5'), 'Keras model or weights must be a .h5 file.'
9
10 # Load model, or construct model and load weights.
11 num_anchors = len(self.anchors)
12 num_classes = len(self.class_names)
13 is_tiny_version = num_anchors==6 # default setting
14 try:
15 self.yolo_model = load_model(model_path, compile=False)
16 except:
17 self.yolo_model = tiny_yolo_body(Input(shape=(None,None,3)), num_anchors//2, num_classes) \
18 if is_tiny_version else yolo_body(Input(shape=(None,None,3)), num_anchors//3, num_classes)
19 self.yolo_model.load_weights(self.model_path) # make sure model, anchors and classes match
20 else:
21 ##[-1]:网络最后一层输出。 output_shape[-1]:输出维度的最后一维。 -> (?,13,13,255)
22 # 255 = 9/3*(80+5). 9/3:每层特征图对应3个anchor box 80:80个类别 5:4+1,框的4个值+1个置信度
23
24 assert self.yolo_model.layers[-1].output_shape[-1] == \
25 num_anchors/len(self.yolo_model.output) * (num_classes + 5), \
26 'Mismatch between model and given anchor and class sizes'
27 #Python assert(断言)用于判断一个表达式,在表达式条件为 false 的时候触发异常。
28
29 #断言可以在条件不满足程序运行的情况下直接返回错误,而不必等待程序运行后出现崩溃的情况
30
31 print('{} model, anchors, and classes loaded.'.format(model_path))
32
33 # Generate colors for drawing bounding boxes.
34 # Generate colors for drawing bounding boxes.
35 # 生成绘制边框的颜色。
36 # h(色调):x/len(self.class_names) s(饱和度):1.0 v(明亮):1.0
37
38 # 对于80种coco目标,确定每一种目标框的绘制颜色,即:将(x/80, 1.0, 1.0)的颜色转换为RGB格式,并随机调整颜色以便于肉眼识别,
39 # 其中:一个1.0表示饱和度,一个1.0表示亮度
40
41 hsv_tuples = [(x / len(self.class_names), 1., 1.)
42 for x in range(len(self.class_names))]
43 self.colors = list(map(lambda x: colorsys.hsv_to_rgb(*x), hsv_tuples)) #hsv转换为rgb
44 # hsv取值范围在【0,1】,而RBG取值范围在【0,255】,所以乘上255
45 self.colors = list(
46 map(lambda x: (int(x[0] * 255), int(x[1] * 255), int(x[2] * 255)),
47 self.colors))
48 np.random.seed(10101) # Fixed seed for consistent colors across runs.
49 np.random.shuffle(self.colors) # Shuffle colors to decorrelate adjacent classes.
50 np.random.seed(None) # Reset seed to default.
51
52 # Generate output tensor targets for filtered bounding boxes.
53 #为过滤的边界框生成输出张量目标
54 self.input_image_shape = K.placeholder(shape=(2, ))
55 if self.gpu_num>=2:
56 self.yolo_model = multi_gpu_model(self.yolo_model, gpus=self.gpu_num)
57 boxes, scores, classes = yolo_eval(self.yolo_model.output, self.anchors,
58 len(self.class_names), self.input_image_shape,
59 score_threshold=self.score, iou_threshold=self.iou)
60 return boxes, scores, classes
61
62 def detect_image(self, image):
63 """开始计时->①调用letterbox_image函数,即:先生成一个用“绝对灰”R128-G128-B128填充的416×416新图片,然后用按比例缩放(采样方式:BICUBIC)后的输入图片粘贴,粘贴不到的部分保留为灰色。②model_image_size定义的宽和高必须是32的倍数;若没有定义model_image_size,将输入的尺寸调整为32的倍数,并调用letterbox_image函数进行缩放。③将缩放后的图片数值除以255,做归一化。④将(416,416,3)数组调整为(1,416,416,3)元祖,满足网络输入的张量格式:image_data。
64
65 ->①运行self.sess.run()输入参数:输入图片416×416,学习模式0测试/1训练。
66 self.yolo_model.input: image_data,self.input_image_shape: [image.size[1], image.size[0]],
67 K.learning_phase(): 0。②self.generate(),读取:model路径、anchor box、coco类别、加载模型yolo.h5.,对于80中coco目标,确定每一种目标框的绘制颜色,即:将(x/80,1.0,1.0)的颜色转换为RGB格式,并随机调整颜色一遍肉眼识别,其中:一个1.0表示饱和度,一个1.0表示亮度。③若GPU>2调用multi_gpu_model()
68
69 ->①yolo_eval(self.yolo_model.output),max_boxes=20,每张图没类最多检测20个框。
70 ②将anchor_box分为3组,分别分配给三个尺度,yolo_model输出的feature map
71 ③特征图越小,感受野越大,对大目标越敏感,选大的anchor box->
72 分别对三个feature map运行out_boxes, out_scores, out_classes,返回boxes、scores、classes。
73 """
74 start = timer()
75 # # 调用letterbox_image()函数,即:先生成一个用“绝对灰”R128-G128-B128“填充的416x416新图片,
76 # 然后用按比例缩放(采样方法:BICUBIC)后的输入图片粘贴,粘贴不到的部分保留为灰色
77
78 if self.model_image_size != (None, None): #判断图片是否存在
79 assert self.model_image_size[0]%32 == 0, 'Multiples of 32 required'
80 assert self.model_image_size[1]%32 == 0, 'Multiples of 32 required'
81 # assert断言语句的语法格式 model_image_size[0][1]指图像的w和h,且必须是32的整数倍
82 boxed_image = letterbox_image(image, tuple(reversed(self.model_image_size)))
83 # #letterbox_image对图像调整成输入尺寸(w,h)
84 else:
85 new_image_size = (image.width - (image.width % 32),
86 image.height - (image.height % 32))
87 boxed_image = letterbox_image(image, new_image_size)
88 image_data = np.array(boxed_image, dtype='float32')
89
90 print(image_data.shape)#(416,416,3)
91 image_data /= 255.#将缩放后图片的数值除以255,做归一化
92 image_data = np.expand_dims(image_data, 0) # Add batch dimension.
93 # 批量添加一维 -> (1,416,416,3) 为了符合网络的输入格式 -> (bitch, w, h, c)
94
95 out_boxes, out_scores, out_classes = self.sess.run(
96 [self.boxes, self.scores, self.classes],
97 feed_dict={
98 self.yolo_model.input: image_data,#图像数据
99 self.input_image_shape: [image.size[1], image.size[0]],#图像尺寸416x416
100 K.learning_phase(): 0#学习模式 0:测试模型。 1:训练模式
101 })#目的为了求boxes,scores,classes,具体计算方式定义在generate()函数内。在yolo.py第61行
102
103 print('Found {} boxes for {}'.format(len(out_boxes), 'img'))
104 # 绘制边框,自动设置边框宽度,绘制边框和类别文字,使用Pillow绘图库(PIL,头有声明)
105 # 设置字体
106
107
108 font = ImageFont.truetype(font='font/FiraMono-Medium.otf',
109 size=np.floor(3e-2 * image.size[1] + 0.5).astype('int32'))
110 # 设置目标框线条的宽度
111 thickness = (image.size[0] + image.size[1]) // 300#厚度
112 ## 对于c个目标类别中的每个目标框i,调用Pillow画图
113
114 for i, c in reversed(list(enumerate(out_classes))):
115 predicted_class = self.class_names[c] #类别 #目标类别的名字
116 box = out_boxes[i]#框
117 score = out_scores[i]#置信度
118
119 label = '{} {:.2f}'.format(predicted_class, score)
120 draw = ImageDraw.Draw(image)#创建一个可以在给定图像上绘图的对象
121 label_size = draw.textsize(label, font)##标签文字 #返回label的宽和高(多少个pixels)
122 #返回给定字符串的大小,以像素为单位。
123 top, left, bottom, right = box
124 # 目标框的上、左两个坐标小数点后一位四舍五入
125 """防止检测框溢出"""
126 top = max(0, np.floor(top + 0.5).astype('int32'))
127
128 left = max(0, np.floor(left + 0.5).astype('int32'))
129 # 目标框的下、右两个坐标小数点后一位四舍五入,与图片的尺寸相比,取最小值
130 # 防止边框溢出
131 bottom = min(image.size[1], np.floor(bottom + 0.5).astype('int32'))
132 right = min(image.size[0], np.floor(right + 0.5).astype('int32'))
133 print(label, (left, top), (right, bottom))
134 # 确定标签(label)起始点位置:标签的左、下
135 if top - label_size[1] >= 0:
136 text_origin = np.array([left, top - label_size[1]])
137 else:
138 text_origin = np.array([left, top + 1])
139
140 # My kingdom for a good redistributable image drawing library.
141 # 画目标框,线条宽度为thickness
142 for i in range(thickness):#画框
143 draw.rectangle(
144 [left + i, top + i, right - i, bottom - i],
145 outline=self.colors[c])
146 # 画标签框
147 draw.rectangle( #文字背景
148 [tuple(text_origin), tuple(text_origin + label_size)],
149 fill=self.colors[c])
150 # 填写标签内容
151 draw.text(text_origin, label, fill=(0, 0, 0), font=font)#文案
152 del draw
153
154 end = timer()
155 print(end - start)
156 return image
157
158 def close_session(self):
159 self.sess.close()
以上即是主要yolo3的主要部分,下面将会对模型进行测试
5.测试
在理解完原理与上述代码之后,下面进行测试(当然也可以不用理解源码也可以直接测试)
(1) 首先需要下载yolo3.weights,下载地址:
https://pjreddie.com/media/files/yolov3.weights
(2) 在pycharm的终端中输入python convert.py yolov3.cfg yolov3.weights model_data/yolo_weights.h5
作用是将yolo3.weights文件转换成Keras可以处理的.h5权值文件,
(3)随便在网上下载一张图片进行测试,比如笔者用一张飞机的照片
(4)在源码中,不能直接运行yolo.py,因为在此代码中没有if__name__=='__main__':
所以需要自己添加:
1 if __name__ == '__main__':
2 """测试图片"""
3 yolo = YOLO()
4 path = r'F:\chorme_download\keras-yolo3-master\微信图片_20200313132254.jpg'
5 try:
6 image = Image.open(path)
7 except:
8 print('Open Error! Try again!')
9 else:
10 r_image = yolo.detect_image(image)
11 r_image.show()
12
13 yolo.close_session()
14 """测试视频,将detect_video中的path置0即调用自己电脑的摄像头"""
15 yolo=YOLO()
16 detect_video(yolo,0)
6.结果
本文为原创,制作不易,转载请标明出处,谢谢!!!
好文要顶 关注我 收藏该文

 0
0
0
0
« 上一篇: Keras框架下用.flow_from_directoryt自己构建数据集
» 下一篇: .npy文件的保存与加载
posted @
2020-03-13 20:02 控制工程小小白 阅读(
796) 评论(
0) 编辑 收藏
最新 IT 新闻:
· 荣耀 X10 Max 图赏:7.09 英寸大屏幕,还有双扬声器
· 惠普 Spectre Folio 体验:皮革和限量,正试图摆脱同质化的笔记本电脑
· 东航「周末随心飞」变「闹心飞」,套路消费者的坑真不少
· 北极 38 度了,我们可能正在经历有史以来最热的一年
· 阅文新合同一个月:谁在逃离,谁在回归?
» 更多新闻...