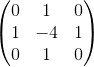边缘检测(opencv_python下)
参考:
OpenCV-Python教程(6、Sobel算子)
OpenCV-Python教程(7、Laplacian算子)
Python下opencv使用笔记(七)(图像梯度与边缘检测)
Sobel算子
原型
Sobel算子依然是一种过滤器,只是其是带有方向的。在OpenCV-Python中,使用Sobel的算子的函数原型如下:
dst = cv2.Sobel(src, ddepth, dx, dy[, dst[, ksize[, scale[, delta[, borderType]]]]])
函数返回其处理结果。
前四个是必须的参数:
- 第一个参数是需要处理的图像;
- 第二个参数是图像的深度,-1表示采用的是与原图像相同的深度。目标图像的深度必须大于等于原图像的深度;
- dx和dy表示的是求导的阶数,0表示这个方向上没有求导,一般为0、1、2。
其后是可选的参数:
- dst不用解释了;
- ksize是Sobel算子的大小,必须为1、3、5、7。
- scale是缩放导数的比例常数,默认情况下没有伸缩系数;
- delta是一个可选的增量,将会加到最终的dst中,同样,默认情况下没有额外的值加到dst中;
- borderType是判断图像边界的模式。这个参数默认值为cv2.BORDER_DEFAULT。
import cv2
import numpy as np
from matplotlib import pyplot as plt
img = cv2.imread("D:\\software_my_programming\
\\relate_to_irisrecog\\CASIA-Iris-Lamp\\001\\L\\S2001L01.jpg",0)
#读取图像,0为灰度图像,1为彩色图像
x = cv2.Sobel(img,cv2.CV_16S,1,0)
y = cv2.Sobel(img,cv2.CV_16S,0,1)
absX = cv2.convertScaleAbs(x)
absY = cv2.convertScaleAbs(y)#转回uint8
dst = cv2.addWeighted(absX,0.5,absY,0.5,0)
plt.subplot(221),plt.imshow(img,'gray')
plt.subplot(222),plt.imshow(absX,'gray')
plt.subplot(223),plt.imshow(absY,'gray')
plt.subplot(224),plt.imshow(dst,'gray')
plt.show()
在Sobel函数的第二个参数这里使用了cv2.CV_16S。因为OpenCV文档中对Sobel算子的介绍中有这么一句:“in the case of 8-bit input images it will result in truncated derivatives”。即Sobel函数求完导数后会有负值,还有会大于255的值。而原图像是uint8,即8位无符号数,所以Sobel建立的图像位数不够,会有截断。因此要使用16位有符号的数据类型,即cv2.CV_16S。
在经过处理后,别忘了用convertScaleAbs()函数将其转回原来的uint8形式。否则将无法显示图像,而只是一副灰色的窗口。convertScaleAbs()的原型为:
dst = cv2.convertScaleAbs(src[, dst[, alpha[, beta]]])
其中可选参数alpha是伸缩系数,beta是加到结果上的一个值。结果返回uint8类型的图片。
由于Sobel算子是在两个方向计算的,最后还需要用cv2.addWeighted(...)函数将其组合起来。其函数原型为:
dst = cv2.addWeighted(src1, alpha, src2, beta, gamma[, dst[, dtype]])
其中alpha是第一幅图片中元素的权重,beta是第二个的权重,gamma是加到最后结果上的一个值。
laplacian算子
其核模板为:
在OpenCV-Python中,Laplace算子的函数原型如下:
dst = cv2.Laplacian(src, ddepth[, dst[, ksize[, scale[, delta[, borderType]]]]])
前两个是必须的参数:
- 第一个参数是需要处理的图像;
- 第二个参数是图像的深度,-1表示采用的是与原图像相同的深度。目标图像的深度必须大于等于原图像的深度;
- 其后是可选的参数:
- dst不用解释了;
- ksize是算子的大小,必须为1、3、5、7。默认为1。
- scale是缩放导数的比例常数,默认情况下没有伸缩系数;
- delta是一个可选的增量,将会加到最终的dst中,同样,默认情况下没有额外的值加到dst中;
- borderType是判断图像边界的模式。这个参数默认值为cv2.BORDER_DEFAULT。
以上三种检测算子的一个代码:
import cv2
import numpy as np
from matplotlib import pyplot as plt
img = cv2.imread("D:\\software_my_programming\
\\relate_to_irisrecog\\CASIA-Iris-Lamp\\001\\L\\S2001L01.jpg",0)
#读取图像,0为灰度图像,1为彩色图像
sobelx = cv2.Sobel(img,cv2.CV_64F,1,0,ksize=3)#默认ksize=3
sobely = cv2.Sobel(img,cv2.CV_64F,0,1)
sobelxy = cv2.Sobel(img,cv2.CV_64F,1,1)
laplacian = cv2.Laplacian(img,cv2.CV_64F)#默认ksize=3
#人工生成一个高斯核,去和函数生成的比较
kernel = np.array([[0,-1,0],[-1,4,-1],[0,-1,0]],np.float32)#
img1 = np.float64(img)#转化为浮点型的
img_filter = cv2.filter2D(img1,-1,kernel)
sobelxy1 = cv2.Sobel(img1,-1,1,1)#目标图像深度不够
plt.figure()
plt.subplot(221),plt.imshow(sobelx,'gray')
plt.subplot(222),plt.imshow(sobely,'gray')
plt.subplot(223),plt.imshow(sobelxy,'gray')
plt.subplot(224),plt.imshow(laplacian,'gray')
plt.figure()
plt.imshow(img_filter,'gray')
plt.show()
关于canny算子:
canny算子
不完善代码:
import cv2
import numpy as np
from matplotlib import pyplot as plt
img = cv2.imread("D:\\software_my_programming\
\\relate_to_irisrecog\\CASIA-Iris-Lamp\\001\\L\\S2001L01.jpg",0)
#读取图像,0为灰度图像,1为彩色图像
edges = cv2.Canny(img,50,90)
plt.subplot(121)
plt.imshow(img,'gray')
plt.subplot(122)
plt.imshow(edges,'gray')
plt.show()
over!