Spring IoC 源码系列(一)BeanDefinition 初始化与注册
一、BeanDefinition
1.1 什么是 BeanDefinition
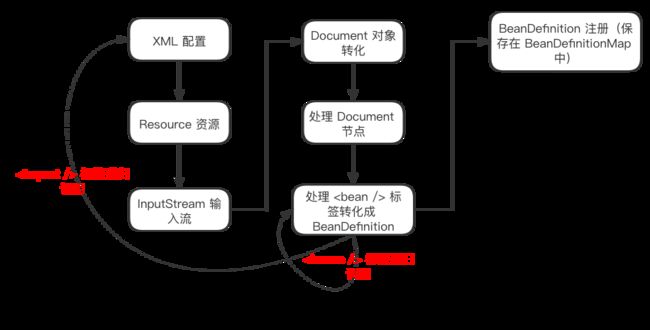
在一般的 Spring 项目中,主要通过 XML 的方式配置 bean,而 BeanDefinition 就是 XML 配置属性的载体,XML 文件首先会被转化成 Document 对象,通过解析 Document,把 XML 中 BeanDefinition 供 IoC 容器创建 bean 时使用。
我们可以来做个测试。
<bean id="typeMismatch" class="org.springframework.tests.sample.beans.TestBean" scope="prototype">
<property name="name"><value>typeMismatchvalue>property>
<property name="age"><value>34xvalue>property>
<property name="spouse"><ref bean="rod"/>property>
bean>
下面是 debug 后抓到的 BeanDefinition 属性。
1.2 BeanDefinition 初始化流程图
二、源码分析
Debug 测试类入口:org.springframework.beans.factory.xml.XmlBeanDefinitionReaderTests#withOpenInputStream。
下面只是把核心流程拿出来作了分析,一些细节知识点,有兴趣的可以自行了解。
测试代码如下
@Test(expected = BeanDefinitionStoreException.class)
public void withOpenInputStream() {
/**
* 注意这里初始化的是 SimpleBeanDefinitionRegistry 不具备 BeanFactory 功能
* 仅仅用来注册 BeanDefinition,不能用来创建 bean
*/
SimpleBeanDefinitionRegistry registry = new SimpleBeanDefinitionRegistry();
Resource resource = new InputStreamResource(getClass().getResourceAsStream("test.xml"));
new XmlBeanDefinitionReader(registry).loadBeanDefinitions(resource);
}
loadBeanDefinitions 源码如下
@Override
public int loadBeanDefinitions(Resource resource) throws BeanDefinitionStoreException {
// 使用 EncodedResource 包装 Resource,EncodedResource 可以指定字符集编码
return loadBeanDefinitions(new EncodedResource(resource));
}
public int loadBeanDefinitions(EncodedResource encodedResource) throws BeanDefinitionStoreException {
Assert.notNull(encodedResource, "EncodedResource must not be null");
if (logger.isTraceEnabled()) {
logger.trace("Loading XML bean definitions from " + encodedResource);
}
// 获取已经加载过的资源集合
Set<EncodedResource> currentResources = this.resourcesCurrentlyBeingLoaded.get();
if (currentResources == null) {
// 初始化 currentResources
currentResources = new HashSet<>(4);
// 设置初始化的 currentResources
this.resourcesCurrentlyBeingLoaded.set(currentResources);
}
if (!currentResources.add(encodedResource)) {
throw new BeanDefinitionStoreException(
"Detected cyclic loading of " + encodedResource + " - check your import definitions!");
}
try {
// 根据 Resource 获取输入流
InputStream inputStream = encodedResource.getResource().getInputStream();
try {
InputSource inputSource = new InputSource(inputStream);
if (encodedResource.getEncoding() != null) {
inputSource.setEncoding(encodedResource.getEncoding());
}
// 核心逻辑,加载 bean 资源
return doLoadBeanDefinitions(inputSource, encodedResource.getResource());
}
finally {
inputStream.close();
}
}
catch (IOException ex) {
throw new BeanDefinitionStoreException(
"IOException parsing XML document from " + encodedResource.getResource(), ex);
}
finally {
currentResources.remove(encodedResource);
if (currentResources.isEmpty()) {
this.resourcesCurrentlyBeingLoaded.remove();
}
}
}
2.1 获取输入流
测试类中定义的是 InputStreamResource,下面 InputStreamResource 中 getInputStream() 的实现。
@Override
public InputStream getInputStream() throws IOException {
InputStream is;
if (this.clazz != null) {
is = this.clazz.getResourceAsStream(this.path);
}
else if (this.classLoader != null) {
is = this.classLoader.getResourceAsStream(this.path);
}
else {
is = ClassLoader.getSystemResourceAsStream(this.path);
}
if (is == null) {
throw new FileNotFoundException(getDescription() + " cannot be opened because it does not exist");
}
return is;
}
2.2 转化 Document 对象
protected int doLoadBeanDefinitions(InputSource inputSource, Resource resource)
throws BeanDefinitionStoreException {
try {
// 获取 XML 对应 document 实例
Document doc = doLoadDocument(inputSource, resource);
// 调用 registerBeanDefinitions 方法注册 BeanDefinitions
int count = registerBeanDefinitions(doc, resource);
if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
logger.debug("Loaded " + count + " bean definitions from " + resource);
}
return count;
}
catch (Throwable ex) {
throw new BeanDefinitionStoreException(resource.getDescription(),
"Unexpected exception parsing XML document from " + resource, ex);
}
}
doLoadBeanDefinitions 方法中调用 doLoadDocument 初始化 Document 对象,内部实现比较简单,下面一起来看一下。
protected Document doLoadDocument(InputSource inputSource, Resource resource) throws Exception {
return this.documentLoader.loadDocument(inputSource, getEntityResolver(), this.errorHandler,
getValidationModeForResource(resource), isNamespaceAware());
}
上面涉及到几个关于 XML 的知识点,下面简单的介绍一下,最后有列出参考文章,有兴趣的可以翻翻。
EntityResolver:XML 文件解析器errorHandler:解析出错处理机制getValidationModeForResource(): 获取 XML 验证格式,XML 一般支持 DTD 与 XSD,也可以自定义,主要用来约束与验证 XML 文档格式isNamespaceAware():判断解析器是否支持解析当前 XML 文件,xmlns就是命名空间
@Override
public Document loadDocument(InputSource inputSource, EntityResolver entityResolver,
ErrorHandler errorHandler, int validationMode, boolean namespaceAware) throws Exception {
// 创建 DocumentBuilderFactory
DocumentBuilderFactory factory = createDocumentBuilderFactory(validationMode, namespaceAware);
if (logger.isTraceEnabled()) {
logger.trace("Using JAXP provider [" + factory.getClass().getName() + "]");
}
// 创建一个 DocumentBuilder
DocumentBuilder builder = createDocumentBuilder(factory, entityResolver, errorHandler);
// 以 SAX 形式解析 XML
return builder.parse(inputSource);
}
上面 DocumentBuilderFactory 与 DocumentBuilder 都是 JDK 中提供的类,根据 XML 输入流获取 Document 的过程没有深入跟踪,这里就不展开分析了。
2.3 处理 Document 节点
public int registerBeanDefinitions(Document doc, Resource resource) throws BeanDefinitionStoreException {
// 通过反射创建一个 BeanDefinitionDocumentReader 对象
BeanDefinitionDocumentReader documentReader = createBeanDefinitionDocumentReader();
// 获取已经注册的 BeanDefinition 的数量,-> beanDefinitionMap 的 size
int countBefore = getRegistry().getBeanDefinitionCount();
// 创建 XmlReaderContext,注册 BeanDefinitions
documentReader.registerBeanDefinitions(doc, createReaderContext(resource));
// 返回最新注册的 bean 的数量
return getRegistry().getBeanDefinitionCount() - countBefore;
}
@Override
public void registerBeanDefinitions(Document doc, XmlReaderContext readerContext) {
this.readerContext = readerContext;
doRegisterBeanDefinitions(doc.getDocumentElement());
}
protected void doRegisterBeanDefinitions(Element root) {
BeanDefinitionParserDelegate parent = this.delegate;
this.delegate = createDelegate(getReaderContext(), root, parent);
// 检查 标签的命名空间是否为空,或者是 http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans
if (this.delegate.isDefaultNamespace(root)) {
// 获取 profile 的值,beans 标签可以设置 profile 属性用于多环境配置管理
String profileSpec = root.getAttribute(PROFILE_ATTRIBUTE);
if (StringUtils.hasText(profileSpec)) {
// 处理 profile 多个值
String[] specifiedProfiles = StringUtils.tokenizeToStringArray(
profileSpec, BeanDefinitionParserDelegate.MULTI_VALUE_ATTRIBUTE_DELIMITERS);
// 判断是否有默认启用的 profile
if (!getReaderContext().getEnvironment().acceptsProfiles(specifiedProfiles)) {
if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
logger.debug("Skipped XML bean definition file due to specified profiles [" + profileSpec +
"] not matching: " + getReaderContext().getResource());
}
return;
}
}
}
// 解析前处理,空实现,可自定义
preProcessXml(root);
// 解析 document 实例
parseBeanDefinitions(root, this.delegate);
// 解析后处理,空实现,可自定义
postProcessXml(root);
this.delegate = parent;
}
protected void parseBeanDefinitions(Element root, BeanDefinitionParserDelegate delegate) {
// 命名空间检查,Spring XML 中不仅可以配置 在获取 Document 对象后,后续流程会遍历所有子节点,根据子标签名分别走不同的处理流程,我们主要是来了解怎么初始化与注册 BeanDefinition 的,其他标签就不详细介绍了。
- 利用反射创建
BeanDefinitionDocumentReader对象 - 获取已经注册的
BeanDefinition的数量,其实就是beanDefinitionMap的 size 大小 - 检查
http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans,如果条件满足,获取profile指定的环境属性值,判断指定的环境是否有处于启用状态的,都不启用直接返回,不会对Document进行解析,关于profile属性的作用,最后会给一些参考文章 - 解析前置处理,空实现,可自定义
- 如果是默认命名空间,获取 下所有子标签,进行遍历,判断子标签是
import、alias、bean还是beans - 解析后置处理,空实现,可自定义
2.3 BeanDefinition 初始化
protected void processBeanDefinition(Element ele, BeanDefinitionParserDelegate delegate) {
// 处理 初始化 BeanDefinition 的过程就是把 BeanDefinition 中,没有什么复杂的逻辑。
2.4 注册 BeanDefinition
public static void registerBeanDefinition(
BeanDefinitionHolder definitionHolder, BeanDefinitionRegistry registry)
throws BeanDefinitionStoreException {
// Register bean definition under primary name.
// 获取 beanName 并根据 beanName 注册 BeanDefinition
String beanName = definitionHolder.getBeanName();
registry.registerBeanDefinition(beanName, definitionHolder.getBeanDefinition());
// Register aliases for bean name, if any.
// 从 BeanDefinition 中获取所有的别名,并根据 beanName 注册别名
String[] aliases = definitionHolder.getAliases();
if (aliases != null) {
for (String alias : aliases) {
// 注册所有的别名,保存到 aliasMap 中
registry.registerAlias(beanName, alias);
}
}
}
@Override
public void registerBeanDefinition(String beanName, BeanDefinition beanDefinition)
throws BeanDefinitionStoreException {
Assert.hasText(beanName, "'beanName' must not be empty");
Assert.notNull(beanDefinition, "BeanDefinition must not be null");
// 保存到 beanDefinitionMap 中
this.beanDefinitionMap.put(beanName, beanDefinition);
}
因为测试类中定义的是 SimpleBeanDefinitionRegistry,因此应该定位到 SimpleBeanDefinitionRegistry 中的 registerBeanDefinition,这里的处理流程很简单,直接把 BeanDefinition 与 beanName 关联保存到 beanDefinitionMap 中。
SimpleBeanDefinitionRegistry 并不是一个工厂,不具备初始化 bean 的能力。后面在创建 bean 的流程中还会接触到 DefaultListableBeanFactory#registerBeanDefinition 注册流程,稍微比这个复杂些,但是其核心逻辑都是保存到 beanDefinitionMap 。
参考阅读
XML中DTD,XSD的区别与应用
xsd,dtd,tld有什么区别和联系?
细说java解析XML文档的常用方法(含实例)
详解Spring中的Profile