并发-CountDownLatch
文章目录
- 前言
- 问题
- 简介
- CountDownLatch是什么?
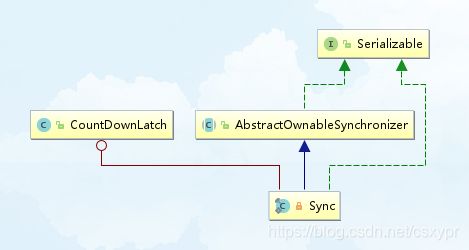
- 类结构:Sync为CountDownLatch的内部类
- 特性
- 构造函数
- void await()方法
- boolean await(long timeout,TimeUnit unit)方法
- void countDown()方法
- 具体实例
- CountDownLatch的初始次数是否可以调整?
- CountDownLatch底层是利用什么实现的?
- 小结
前言
最近小咸儿在看项目代码时发现有用到CountDownLatch,那这个到底是什么回事呢?又用来干什么呢?让小咸儿来一探究竟。
问题
1、CountDownLatch是什么?
2、CountDownLatch有什么特性?
3、CountDownLatch适用于什么场景?
4、CountDownLatch的初始次数是否可以调整?
5、CountDownLatch底层是运行什么实现的?
简介
CountDownLatch是什么?
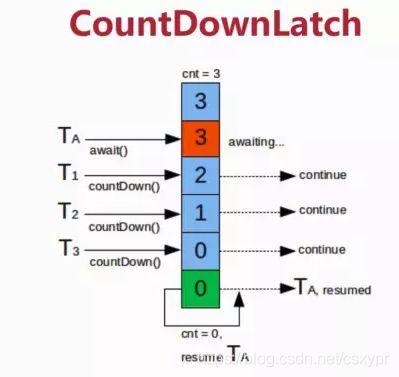
CountDownLatch是一个计数器闭锁,通过它可以完成类似阻塞当前线程的功能,即:一个线程或多个线程一直等待,直到其他线程执行的操作完成。
类结构:Sync为CountDownLatch的内部类
特性
构造函数
/**
* Constructs a {@code CountDownLatch} initialized with the given count.
*
* @param count the number of times {@link #countDown} must be invoked
* before threads can pass through {@link #await}
* @throws IllegalArgumentException if {@code count} is negative
*/
public CountDownLatch(int count) {
if (count < 0) throw new IllegalArgumentException("count < 0");
this.sync = new Sync(count);
}
// Sync内部类方法,传入初始次数
Sync(int count) {
setState(count);
}
通过构造器初始化计数器的值,可实际上是把计数器的值赋值给了AQS的state,也就是用AQS的状态值来表示计数器值。
接下来看一下CountDownLatch中几个重要方法内部是如何调用AQS来实现功能的。
void await()方法
当前线程调用了CountDownLatch对象的await()方法后,当前线程会被阻塞,直到下面情况之一才会返回:
- 当所有的线程都调用了CountDownLatch对象的countDown()方法后,也就是计数器为0的时候。
- 其他线程调用了当前线程的interrupt()方法中断了当前线程,当前线程会抛出InterruptedException
异常后返回。
接下来看一下await()方法内部具体是如何实现的?
// CountDownLatch的await()方法
public void await() throws InterruptedException {
// 调用AQS的acquireSharedInterruptibly()方法
sync.acquireSharedInterruptibly(1);
}
实际上调用的是AQS的acquireSharedInterruptibly()方法
/**
* Acquires in shared mode, aborting if interrupted. Implemented
* by first checking interrupt status, then invoking at least once
* {@link #tryAcquireShared}, returning on success. Otherwise the
* thread is queued, possibly repeatedly blocking and unblocking,
* invoking {@link #tryAcquireShared} until success or the thread
* is interrupted.
* @param arg the acquire argument.
* This value is conveyed to {@link #tryAcquireShared} but is
* otherwise uninterpreted and can represent anything
* you like.
* @throws InterruptedException if the current thread is interrupted
*/
public final void acquireSharedInterruptibly(int arg)
throws InterruptedException {
// 如果线程被中断则抛异常
if (Thread.interrupted())
throw new InterruptedException();
// 尝试看当前是否计数值为0,为0则返回,否则进入AQS的队列等待
if (tryAcquireShared(arg) < 0)
// 继续阻塞线程
doAcquireSharedInterruptibly(arg);
}
Sync类的tryAcquireShared()方法,内部类:Sync
private static final class Sync extends AbstractQueuedSynchronizer {
private static final long serialVersionUID = 4982264981922014374L;
// 传入初始次数
Sync(int count) {
setState(count);
}
// 获取还剩的次数
int getCount() {
return getState();
}
// 尝试获取共享锁
protected int tryAcquireShared(int acquires) {
// 当state为0时,返回1,表明获取成功
// 当state不为0时,返回-1,表明需要排队,即让当前线程阻塞
return (getState() == 0) ? 1 : -1;
}
// 尝试释放锁
protected boolean tryReleaseShared(int releases) {
// Decrement count; signal when transition to zero
for (;;) {
// state得值
int c = getState();
// 等于0了,则无法再释放了
if (c == 0)
return false;
// 将count的值减1
int nextc = c-1;
// CAS原子更新state的值
if (compareAndSetState(c, nextc))
// 减为0的时候返回true,这时会唤醒后面排队的线程
return nextc == 0;
}
}
}
await()方法是等待其他线程完成的方法,它会先尝试获取一下共享锁,如果失败则进入AQS的队列中排队等待被唤醒。
boolean await(long timeout,TimeUnit unit)方法
当线程调用了CountDownLatch对象的该方法后,当前线程会被阻塞,直到下面的情况之一发生才会返回:
- 当所有线程都调用了CountDownLatch对象的countDown方法后,也就是计时器值为0的时候,这时候
返回true。 - 设置的timeout时间到了,因为超时而返回false。
- 其他线程调用了当前线程的interrupt()方法中断了当前线程,当前线程会抛出InterruptedException
异常后返回。
public boolean await(long timeout, TimeUnit unit)
throws InterruptedException {
return sync.tryAcquireSharedNanos(1, unit.toNanos(timeout));
}
调用AQS中的tryAcquireSharedNanos()方法
public final boolean tryAcquireSharedNanos(int arg, long nanosTimeout)
throws InterruptedException {
if (Thread.interrupted())
throw new InterruptedException();
return tryAcquireShared(arg) >= 0 ||
doAcquireSharedNanos(arg, nanosTimeout);
}
此方法与await()类似,只不过等待有限。若到达等待时间state值不为0则直接执行不等待;
void countDown()方法
当前线程调用该方法后,会递减计数器的值,递减后如果计数器为0则会唤醒所有调用await方法而被阻塞的线程,否则什么都不做。
接下来看一下countDown()方法内部具体是如何实现的?
public void countDown() {
// 调用AQS的释放共享锁方法
sync.releaseShared(1);
}
调用AQS中的releaseShared()方法
/**
* Releases in shared mode. Implemented by unblocking one or more
* threads if {@link #tryReleaseShared} returns true.
*
* @param arg the release argument. This value is conveyed to
* {@link #tryReleaseShared} but is otherwise uninterpreted
* and can represent anything you like.
* @return the value returned from {@link #tryReleaseShared}
*/
public final boolean releaseShared(int arg) {
// 尝试释放共享锁,如果成功了就唤醒排队的线程
if (tryReleaseShared(arg)) {
// AQS的释放资源方法
doReleaseShared();
return true;
}
return false;
}
可以看出来CountDownLatch的countDown()方法是委托了sync调用了AQS的releaseShared方法,后者调用了sync实现的AQS的tryReleaseShared()方法,具体代码如下:CountDownLatch类中sync内的方法。
protected boolean tryReleaseShared(int releases) {
// Decrement count; signal when transition to zero
// 循环进行CAS,直到当前线程成功完成CAS使计数值(状态值state)减1并更新到state
for (;;) {
int c = getState();
// 如果当前状态值为0则直接返回
if (c == 0)
return false;
// CAS设置计数值减1
int nextc = c-1;
// 通过原子操作把改变后的state值写入内存中
if (compareAndSetState(c, nextc))
return nextc == 0;
}
}
countDown()方法,会释放一个共享锁,也就是count的次数会减1。首先会获取当前状态值(计数器值),如果当前状态值为0则直接返回false,则countDown()方法直接返回;否则使用CAS设置计数器减1,CAS失败则循环重试,否则如果当前计数器为0则返回true。返回true后,说明当前线程为最后一个调用countDown()方法的线程,那么该线程除了让计数器减1外,还需要唤醒调用CountDownLatch的await()方法而被阻塞的其他线程。
具体实例
CountDownLatch 等待游戏玩家准备完成后,主线程开始游戏
package concurrent;
import java.util.Random;
import java.util.concurrent.CountDownLatch;
public class CountDownLatchExample2 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {
CountDownLatch latch = new CountDownLatch(4);
for (int i = 0; i < latch.getCount(); i ++){
new Thread(new MyThread(latch),"player"+i).start();
}
System.out.println("正在等待所有玩家准备好");
latch.await();
System.out.println("开始游戏");
}
private static class MyThread implements Runnable{
private CountDownLatch latch;
public MyThread(CountDownLatch latch){
this.latch = latch;
}
@Override
public void run() {
try {
Random rand = new Random();
// 产生1000到3000之间的随机整数
int randomNum = rand.nextInt((3000 - 1000) + 1) + 1000;
Thread.sleep(randomNum);
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + "已经准备好了,所是使用的时间为 " + ((double) randomNum / 1000) + "s");
latch.countDown();
} catch (Exception e){
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}
CountDownLatch的初始次数是否可以调整?
不能,它没有提供修改(增加或者减少)次数的方法,除非利用反射作弊。
CountDownLatch底层是利用什么实现的?
AQS和CAS(具体在上述源码解析中有体现)
| 黑色背景 |
小结
- CountDownLatch表示允许一个或多个线程等待其他线程的操作执行完毕后再执行后续的操作。
- CountDownLatch使用AQS的共享锁机制实现。
- CountDownLatch初始化的时候需要传入次数count。
- 每次调用countDown()方法,count的次数减1。
- 每次调用await()方法的时候会尝试获取锁,这里的获取锁其实是检查AQS的state变量的值是否为0。
- 当state(count)的值减为0时会唤醒排队着的线程。
除了CountDownLatch之外,还有CyclicBarrier和Semaphore等待着小咸儿去学习和总结。
参考文章:Java并发编程笔记之CountDownLatch闭锁的源码分析
死磕Java同步系列之CountDownLatch源码解析
感谢您的阅读~~