利用Spring-Data-Jpa中的QueryByExample和SpecificationExecutor两个接口实现复杂业务场景的数据库查询
在之前有关Spring-Data-Jpa的文章中,笔者实现了基本的CRUD操作和分页及排序查找功能,还不足以应对工作中出现的复杂业务场景。那么本文就来带领大家利用Spring-Data-Jpa中的
QueryByExampleExecutor和JpaSpecificationExecutor两个接口实现相对复杂的业务场景,相信看完本文,读者对于使用Spring-Data-Jpa实现复杂的数据库查询业务会有不少收获。
本文的demo代码构建在笔者的上一篇有关spring-data-jpa的文章
Spring-Data-Jpa中的常用注解详解及其用法
1 QueryByExampleExecutor的使用
按示例查询(QBE)是一种用户友好的查询技术,具有简单的接 口。它允许动态查询创建,并且不需要编写包含字段名称的查询。从 UML图中,可以看出继承JpaRepository接口后,自动拥有了按“实例”进行查询的诸多方法。可见Spring Data的团队已经认为了QBE是 Spring JPA的基本功能了,继承QueryByExampleExecutor和继承 JpaRepository都会有这些基本方法。
1.1 QueryByExampleExecutor的详细配置
public interface QueryByExampleExecutor<T> {
/**
* 根据样例查找一个符合条件的对象,如果没找到将返回null;如果返回多个对象时将抛出
*org.springframework.dao.IncorrectResultSizeDataAccessException异常
*/
<S extends T> Optional<S> findOne(Example<S> example);
/**
*根据样例查找符合条件的所有对象集合
*/
<S extends T> Iterable<S> findAll(Example<S> example);
/**
*根据样例查找符合条件的所有对象集合,并根据排序条件排好序
*/
<S extends T> Iterable<S> findAll(Example<S> example, Sort sort);
/**
*根据样例查找符合条件的所有对象集合,并根据分页条件分页
*/
<S extends T> Page<S> findAll(Example<S> example, Pageable pageable);
/**
*查询符合样例条件的记录数样
*/
<S extends T> long count(Example<S> example);
/**
*检查数据库表中是否包含符合样例条件的记录,存在返回true,否则返回false
*/
<S extends T> boolean exists(Example<S> example);
}
所以我们看Example基本上就可以掌握的它的用法和API了。
注意: Example接口在org.springframework.data.domain包下
public interface Example<T> {
/**
*创建一个泛型对象的样例,泛型对象必须是与数据库表中一条记录对应的实体类
*/
static <T> Example<T> of(T probe) {
return new TypedExample<>(probe, ExampleMatcher.matching());
}
/**
* 根据实体类和匹配规则创建一个样例
* @return
*/
static <T> Example<T> of(T probe, ExampleMatcher matcher) {
return new TypedExample<>(probe, matcher);
}
/**
*获取样例中的实体类对象
*/
T getProbe();
/**
*获取样例中的匹配器
*/
ExampleMatcher getMatcher();
/**
*获取样例中的实体类类型
*/
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
default Class<T> getProbeType() {
return (Class<T>) ProxyUtils.getUserClass(getProbe().getClass());
}
}
从源码中可以看出Example主要包含三部分内容:
- Probe: 这是具有填充字段的域对象的实际实体类,即查询条 的封装类。必填。
- ExampleMatcher:ExampleMatcher有关于如何匹配特定字段的 匹配规则,它可以重复使用在 多个示例。必填。如果不填,用 默认的。
- Example:Example由探针和ExampleMatcher组成,它用于创建查询。
1.2 QueryByExampleExecutor的使用示例
- 将bootDemo项目下的
UserRepository接口改为继承自JpaRepository
public interface UserRepository extends JpaRepository<UserInfo,Long{
}
- UserService接口下新增两个抽象方法,一个查询单个对象,另一个查询符合条件的集合
public interface UserService >{
UserInfo findOneByExample(UserInfo userInfo);
List findAllByExample(UserInfo userInfo);
//其他抽象方法此处省略......
}
- 完成实现方法
@Service
@Slf4j
public class UserServiceImpl implements UserService{
//其他实现方法此处省略......
@Override
public UserInfo findOneByExample(UserInfo userInfo) {
//构建ExampleMatcher对象,matchingAll表示要匹配所有
ExampleMatcher exampleMatcher = ExampleMatcher.matchingAll();
exampleMatcher.withMatcher("userName", ExampleMatcher.GenericPropertyMatcher.of(ExampleMatcher.StringMatcher.EXACT,true));
//利用Example类的静态构造函数构造Example实例对象
Example<UserInfo> example = Example.of(userInfo,exampleMatcher);
return userRepository.findOne(example).get();
}
@Override
public List<UserInfo> findAllByExample(UserInfo userInfo) {
//匹配任意一个符合条件的字段
ExampleMatcher exampleMatcher = ExampleMatcher.matchingAll();
exampleMatcher.withMatcher("userRole",ExampleMatcher.GenericPropertyMatchers.startsWith());
exampleMatcher.withMatcher("userName",ExampleMatcher.GenericPropertyMatchers.startsWith());
//不区分大小写
exampleMatcher.isIgnoreCaseEnabled();
Example<UserInfo> example = Example.of(userInfo,exampleMatcher);
return userRepository.findAll(example);
}
}
4) UserInfoController类中新增两个路由方法
@RestController
@RequestMapping("/user")
@Slf4j
public class UserInfoController {
@GetMapping("/example/{userName}")
public ServiceResponse<UserInfo> findOneByExampleUserName(@PathVariable("userName") String userName){
ServiceResponse<UserInfo> response = new ServiceResponse<>();
log.info("userName={}",userName);
UserInfo userInfo = new UserInfo();
userInfo.setUserName(userName);
UserInfo data = userInfoService.findOneByExample(userInfo);
response.setData(data);
return response;
}
@GetMapping("/example/list")
public ServiceResponse<List<UserInfo>> findListByExample(@RequestParam("userName") String userName,@RequestParam("userRole") String userRole){
ServiceResponse<List<UserInfo>> response = new ServiceResponse<>();
log.info("userName={},userRole={}",userName,userRole);
UserInfo userInfo = new UserInfo();
userInfo.setUserName(userName);
userInfo.setUserRole(userRole);
List<UserInfo> data = userInfoService.findAllByExample(userInfo);
response.setData(data);
return response;
}
//其他路由方法此处省略......
}
- postman测试
启动项目后可利用postman对开发的http接口进行测试
GET http://localhost:8088/apiBoot/user/example/ZhuGeLiang
//接口响应信息
{
"status": 200,
"message": "ok",
"data": {
"userId": 22,
"userName": "ZhuGeLiang",
"password": "cea79d52d2117875eb9d377bfe68f65e",
"userNameCn": "诸葛亮",
"userSex": "M",
"userRole": "Admin",
"telNum": 15200001309,
"email": "[email protected]",
"regDate": "2019-03-06",
"birthDay": "1972-10-08",
"createdBy": "system",
"createdTime": "2020-04-30 10:00:00",
"lastUpdatedBy": "x_heshengfu",
"lastUpdatedTime": "2020-06-10 10:00:00"
}
}
//根据样例查询符合对象的集合
GET http://localhost:8088/apiBoot/user/example/list?userName=Zhangfei&userRole=Admin
//接口相应信息
{
"status": 200,
"message": "ok",
"data": [
{
"userId": 21,
"userName": "ZhangFei",
"password": "956c5c8200854fb09c24ec10144747d0",
"userNameCn": "张飞",
"userSex": "M",
"userRole": "Admin",
"telNum": 15200001308,
"email": "[email protected]",
"regDate": "2018-03-05",
"birthDay": "1969-08-01",
"createdBy": "system",
"createdTime": "2020-04-30 10:00:00",
"lastUpdatedBy": "x_heshengfu",
"lastUpdatedTime": "2020-06-10 10:00:00"
}
]
}
通过测试和日志信息笔者发现通过样例的ExampleMatcher.GenericPropertyMatchers.startsWith()走的其实还是完全匹配,并不是起始匹配,后台日志中的sql参数化查询信息如下:
select
userinfo0_.user_id as user_id1_1_,
userinfo0_.birth_day as birth_da2_1_,
userinfo0_.created_by as created_3_1_,
userinfo0_.created_time as created_4_1_,
userinfo0_.email as email5_1_,
userinfo0_.last_updated_by as last_upd6_1_,
userinfo0_.last_updated_time as last_upd7_1_,
userinfo0_.password as password8_1_,
userinfo0_.reg_date as reg_date9_1_,
userinfo0_.tel_num as tel_num10_1_,
userinfo0_.user_name as user_na11_1_,
userinfo0_.user_name_cn as user_na12_1_,
userinfo0_.user_role as user_ro13_1_,
userinfo0_.user_sex as user_se14_1_
from
user_info userinfo0_
where
userinfo0_.user_name=?
and userinfo0_.user_role=?
上面的代码示例中是这样创建实例的:Example.of(userInfo,exampleMatcher);我们看到,Example对象,由 userInfo和matcher共同创建,为讲解方便,我们先来明确一些定义:
(1)Probe:实体对象,在持久化框架中与Table对应的域对 象,一个对象代表数据库表中的一条记录,如上例中UserInfo对象。 在构建查询条件时,一个实体对象代表的是查询条件中的字段值部 分。如:要查询姓名为 “ZhangFei”的客户,实体对象只能存储条件值为可忽略大小写的“Zhangfei”。
(2)ExampleMatcher:匹配器,它是匹配“实体对象”的,表 示了如何使用“实体对象”中的“值”进行查询,它代表的是“查询 方式”,解释了如何去查的问题。
(3)Example:实例对象,代表的是完整的查询条件,由实体对象(查询条件值)和匹配器(查询方式)共同创建。
1.3 QueryByExampleExecutor的特点及约束
(1)支持动态查询。即支持查询条件个数不固定的情况,如:用户列表中有多个过滤条件,用户使用时在“用户名”查询框中输入了值,就需要按用户名进行过滤,如果没有输入值,就忽略这个过滤条件。对应的实现是,在构建查询条件UserInfo对象时,将email属性值设置为具体的条件值或设置为null。
(2)不支持过滤条件分组。即不支持过滤条件用or(或)来连 接,所有的过滤查件,都是简单一层的用and(并且)连接。如 firstname = ?0 or (firstname = ?1 and lastname = ?2)。
(3)正是由于这个限 制,有些查询是没办法支持的,例如要查询某个时间段内添加的客 户,对应的属性是addTime,需要传入“开始时间”和“结束时 间”两个条件值,而这种查询方式没有存两个值的位置,所以就没办法完成这样的查询。
1.4 ExampleMatcher详解
1.4.1 源码解读
public interface ExampleMatcher {
/*
* 使用字符串匹配器
*/
ExampleMatcher withStringMatcher(StringMatcher defaultStringMatcher);
/**
*忽略大小写的匹配器
*/
default ExampleMatcher withIgnoreCase() {
return withIgnoreCase(true);
}
/**
*传参决定是否忽略大小写
*/
ExampleMatcher withIgnoreCase(boolean defaultIgnoreCase);
/**
*根据与表字段对应的属性名propertyPath和匹配配置器匹配
*/
default ExampleMatcher withMatcher(String propertyPath, MatcherConfigurer<GenericPropertyMatcher> matcherConfigurer) {
Assert.hasText(propertyPath, "PropertyPath must not be empty!");
Assert.notNull(matcherConfigurer, "MatcherConfigurer must not be empty!");
GenericPropertyMatcher genericPropertyMatcher = new GenericPropertyMatcher();
matcherConfigurer.configureMatcher(genericPropertyMatcher);
return withMatcher(propertyPath, genericPropertyMatcher);
}
/**
*同上,第二个参数为GenericPropertyMatcher类型
*/
ExampleMatcher withMatcher(String propertyPath, GenericPropertyMatcher genericPropertyMatcher);
//其他源码省略
static ExampleMatcher matchingAll() {
return new TypedExampleMatcher().withMode(MatchMode.ALL);
}
}
ExampleMatcher接口的实现类为TypedExampleMatcher类
1.4.2 关键属性分析
(1)nullHandler:Null值处理方式,枚举类型,有2个可选值:
- INCLUDE(包括)
- IGNORE(忽略)
标识作为条件的实体对象中,一个属性值(条件值)为Null时, 表示是否参与过滤。当该选项值是INCLUDE时,表示仍参与过滤,会匹配数据库表中该字段值是Null的记录;若为IGNORE值,表示不参与 过滤。
(2)defaultStringMatcher:默认字符串匹配方式,枚举类 型,有6个可选值:
- DEFAULT(默认,效果同EXACT)
- EXACT(相等)
- STARTING(开始匹配)
- ENDING(结束匹配)
- CONTAINING(包含,模糊匹配)
- REGEX(正则表达式)
本人亲测试过程中发现除了EXACT精确匹配,其他都不生效,所以就不深入研究了
2 JpaSpecificationExecutor的详细使用
JpaSpecificationExecutor是JPA 2.0提供的Criteria API,可 以用于动态生成query。Spring Data JPA支持Criteria查询,可以很 方便地使用,足以应付工作中的所有复杂查询的情况了,可以对JPA实现最大限度的扩展。
2.1 JpaSpecificationExecutor的使用方法
public interface JpaSpecificationExecutor<T> {
//根据Specificatio条件查询单个结果
Optional<T> findOne(@Nullable Specification<T> spec);
//根据Specificatio条件查询List结果集
List<T> findAll(@Nullable Specification<T> spec);
//根据Specificatio条件分页查询
Page<T> findAll(@Nullable Specification<T> spec, Pageable page);
//根据Specificatio条件查询并排序
List<T> findAll(@Nullable Specification<T> spec, Sort sort);
//根据Specificatio条件查询符合条件的数量
long count(@Nullable Specification<T> spec);
}
这个接口基本是围绕着Specification接口来定义的, Specification接口中只定义了如下一个方法:
@Nullable
Predicate toPredicate(Root<T> root, CriteriaQuery<?> query, CriteriaBuilder cb);
所以可看出,JpaSpecificationExecutor是针对Criteria API进 行了predicate标准封装,帮我们封装了通过EntityManager的查询和 使用细节,操作Criteria更加便利了一些
2.1 Criteria概念的简单介绍
(1)Root:代表了可以查询和操作的实体对象的根。如 果将实体对象比喻成表名,那root里面就是这张表里面的字段。这不 过是JPQL的实体字段而已。通过里面的Path来获得我们操作的字段。
(2)CriteriaQueryquery:代表一个specific的顶层查询对 象,它包含着查询的各个部分,比如:select、from、where、group by、order by等。CriteriaQuery对象只对实体类型或嵌入式类型的 Criteria查询起作用,简单理解,它提供了查询ROOT的方法。常用的方法有:
//单个查询
CriteriaQuery<T> select(Selection<? extends T> selection);
//多个查询,等同于联合查询
CriteriaQuery<T> multiselect(Selection... selections);
//where 条件过滤
CriteriaQuery<T> where(Predicate... restrictions);
//分组查询
CriteriaQuery<T> groupBy(Expression... expressions);
//having过滤
CriteriaQuery<T> having(Predicate... restrictions);
(3)CriteriaBuilder cb:用来构建CritiaQuery的构建器对 象,其实就相当于条件或者是条件组合,以谓语即Predicate的形式 返回。构建简单的Predicate示例:
Predicate p1 = cb.like(root.get("name").as(String.class),"%"+param.getName()+"%");
Predicate p2 = cb.equal(root.get("uuid").as(Integer.class),param.getUuid());
Predicate p3 = cb.gt(root.get("age").as(Integer.class),param.getAge());
//构建组合的Predicate示例:
Predicate p = cb.and(p3,cb.or(p1,p2));
(4) 实际经验:到此我们发现其实JpaSpecificationExecutor 帮我们提供了一个高级的入口和结构,通过这个入口,可以使用底层 JPA的Criteria的所有方法,其实就可以满足了所有业务场景。但实 际工作中,需要注意的是,如果一旦我们写的实现逻辑太复杂,一般的程序员看不懂的时候,那一定是有问题的,我们要寻找更简单的, 更易懂的,更优雅的方式。比如:
- 分页和排序我们就没有自己再去实现一遍逻辑,直接用其开放的Pageable和Sort即可。
- 当过多地使用group或者having、sum、count等内置的SQL函数 的时候,我们想想就是我们通过Specification实现了逻辑, 这种效率真的高吗?是不是数据的其他算法更好?
- 当我们过多地操作left join和inner Join链表查询的时候, 我们想想,是不是通过数据库的视图(view)更优雅一点?
2.2 JpaSpecificationExecutor使用示例
继续以user_info表为被查询的表作演示
(1) 新建一个用于动态查询的参数类UserParam
@NoArgsConstructor
public class UserParam implements Serializable {
@Setter
@Getter
private String userName;
@Setter
@Getter
private String userNameCn;
@Setter
@Getter
private String userSex;
@Setter
@Getter
private String email;
@Setter
@Getter
private Long telNum;
@Setter
@Getter
private String beginCreateTime;
@Setter
@Getter
private String endCreateTime;
}
(2)在配置类中配置一个JpaSpecificationExecutor接口实现类SimpleJpaRepository的bean
@Configuration
public class BeansConfiguration {
@Autowired
private EntityManager entityManager;
@Bean("userSpecificationRepository")
public SimpleJpaRepository userSpecificationRepository(){
//构造SimpleJpaRepository实例时需要注入EntityManager实例
return new SimpleJpaRepository<UserInfo,Long>(UserInfo.class,entityManager);
}
}
注意:在2.1版本以上的spring-boot-data-jpa中仅通过定义一个继承自JpaSpecificationExecutor的接口是行不通的,那样会导致项目启动时报错,无法创建JpaSpecificationExecutor接口对应的实现类bean
(3)UserService接口中新建一个动态查询的抽象方法
List<UserInfo> findAllByDynamicConditions(UserParam userParam);
(4) UserServiceImpl类中注入simpleJpaRepository,调用findAll(Specification方法完成动态查询逻辑
@Autowired
private SimpleJpaRepository<UserInfo,Long> simpleJpaRepository;
@Override
public List<UserInfo> findAllByDynamicConditions(UserParam userParam) {
return simpleJpaRepository.findAll((root,query,cb)->{
List<Predicate> predicates = new ArrayList<>();
if(!StringUtils.isEmpty(userParam.getUserName())){
predicates.add(cb.like(root.get("userName"),userParam.getUserName()+"%"));
}
if(!StringUtils.isEmpty(userParam.getUserNameCn())){
predicates.add(cb.like(root.get("userNameCn"),userParam.getUserNameCn()+"%"));
}
if(!StringUtils.isEmpty(userParam.getUserSex())){
predicates.add(cb.equal(root.get("userSex"),userParam.getUserSex()));
}
if(userParam.getTelNum()!=null){
predicates.add(cb.equal(root.get("telNum"),userParam.getTelNum()));
}
if(!StringUtils.isEmpty(userParam.getEmail())){
predicates.add(cb.like(root.get("email"),userParam.getEmail()+"%"));
}
//根据时间区间查询
if(userParam.getBeginCreateTime()!=null && userParam.getEndCreateTime()!=null){
predicates.add(cb.between(root.get("createdTime"),userParam.getBeginCreateTime(),userParam.getEndCreateTime()));
}
return query.where(predicates.toArray(new Predicate[predicates.size()])).getRestriction();
});
}
(5) UserInfoController类中完成动态查询路由方法
@PostMapping("/list/conditions")
public ServiceResponse<List<UserInfo>> findUsersByConditions(@RequestBody UserParam userParam){
log.info("userParam={}",JSON.toJSON(userParam));
ServiceResponse<List<UserInfo>> response = new ServiceResponse<>();
List<UserInfo> data = userInfoService.findAllByDynamicConditions(userParam);
response.setData(data);
return response;
}
(6)postman测试接口效果
重启服务器后可利用postman对新开发的http接口进行测试
/**postman软件
*请求类型选择POST
*URL栏填写:http://localhost:8088/apiBoot/user/list/conditions
*入参body选择raw类型,json格式 如上图所示
*/
//接口入参
{
"userName":"Zh",
"beginCreateTime":"2020-03-10 00:00:00",
"endCreateTime": "2020-04-30 10:00:00"
}
//接口相应信息
{
"status": 200,
"message": "ok",
"data": [
{
"userId": 21,
"userName": "ZhangFei",
"password": "956c5c8200854fb09c24ec10144747d0",
"userNameCn": "张飞",
"userSex": "M",
"userRole": "Admin",
"telNum": 15200001308,
"email": "[email protected]",
"regDate": "2018-03-05",
"birthDay": "1969-08-01",
"createdBy": "system",
"createdTime": "2020-04-30 10:00:00",
"lastUpdatedBy": "x_heshengfu",
"lastUpdatedTime": "2020-06-10 10:00:00"
},
{
"userId": 1,
"userName": "ZhangSan",
"password": "2060a7a94bbf5d5fbec8ca4b1f7337d6",
"userNameCn": "张三",
"userSex": "M",
"userRole": "Developer",
"telNum": 13100001001,
"email": "[email protected]",
"regDate": "2018-10-10",
"birthDay": "1990-05-18",
"createdBy": "system",
"createdTime": "2020-03-13 23:45:35",
"lastUpdatedBy": "admin",
"lastUpdatedTime": "2020-04-26 11:28:29"
},
{
"userId": 25,
"userName": "ZhouYu",
"password": "8b9e0e71284ee5110b98ea9f3ecef61d",
"userNameCn": "周瑜",
"userSex": "M",
"userRole": "Developer",
"telNum": 15200001312,
"email": "[email protected]",
"regDate": "2018-04-05",
"birthDay": "1972-08-10",
"createdBy": "system",
"createdTime": "2020-04-30 10:00:00",
"lastUpdatedBy": "x_heshengfu",
"lastUpdatedTime": "2020-06-10 10:00:00"
},
{
"userId": 22,
"userName": "ZhuGeLiang",
"password": "cea79d52d2117875eb9d377bfe68f65e",
"userNameCn": "诸葛亮",
"userSex": "M",
"userRole": "Admin",
"telNum": 15200001309,
"email": "[email protected]",
"regDate": "2019-03-06",
"birthDay": "1972-10-08",
"createdBy": "system",
"createdTime": "2020-04-30 10:00:00",
"lastUpdatedBy": "x_heshengfu",
"lastUpdatedTime": "2020-06-10 10:00:00"
}
]
}
实际工作中应该大部分都是这种写法, 就算扩展也是百变不离其宗。
接口响应信息说明spring-data-jpa实现的动态查询时可行而简便的,测试过程中后台系统打印出了如下sql 预编译查询日志信息:
select
userinfo0_.user_id as user_id1_1_,
userinfo0_.birth_day as birth_da2_1_,
userinfo0_.created_by as created_3_1_,
userinfo0_.created_time as created_4_1_,
userinfo0_.email as email5_1_,
userinfo0_.last_updated_by as last_upd6_1_,
userinfo0_.last_updated_time as last_upd7_1_,
userinfo0_.password as password8_1_,
userinfo0_.reg_date as reg_date9_1_,
userinfo0_.tel_num as tel_num10_1_,
userinfo0_.user_name as user_na11_1_,
userinfo0_.user_name_cn as user_na12_1_,
userinfo0_.user_role as user_ro13_1_,
userinfo0_.user_sex as user_se14_1_
from
user_info userinfo0_
where
(
userinfo0_.user_name like ?
)
and (
userinfo0_.created_time between ? and ?
)
2.3 Specification工作中的一些扩展
我们在实际工作中会发现,如果按上面的逻辑,简单重复,总感 觉是不是可以抽出一些公用方法呢,此时我们引入一种工厂模式,帮 我们做一些事情。基于JpaSpecificationExecutor的思路,我们创建一个SpecificationFactory.Java,内容如下:
public final class SpecificationFactory {
/**
* 模糊查询,匹配对应字段
* @param attribute
* @param value
* @return
*/
public static Specification containsLike(String attribute,String value){
return (root, query, cb) -> cb.like(root.get(attribute),"%"+value+"%");
}
/**
* 获取某字段等于value的查询条件
* @param attribute
* @param value
* @return
*/
public static Specification equal(String attribute,Object value){
return (root,query,cb)->cb.equal(root.get(attribute),value);
}
/**
* 插叙某字段在一个区间的范围
* @param attribute
* @param min
* @param max
* @return
*/
public static Specification isBetween(String attribute,int min,int max){
return (root,query,cb)->cb.between(root.get(attribute),min,max);
}
public static Specification isBetween(String attribute,double min,double max){
return (root,query,cb)->cb.between(root.get(attribute),min,max);
}
public static Specification isBetween(String attribute, Date min, Date max){
return (root,query,cb)->cb.between(root.get(attribute),min,max);
}
/**
* 通过属性名和集合实现In查询
* @param attribute
* @param c
* @return
*/
public static Specification in(String attribute, Collection c){
return (root,query,cb)->root.get(attribute).in(c);
}
public static Specification greaterThan(String attribute, BigDecimal value){
return (root,query,cb)->cb.greaterThan(root.get(attribute),value);
}
public static Specification greaterThan(String attribute, Long value){
return (root,query,cb)->cb.greaterThan(root.get(attribute),value);
}
}
可以根据实际工作需要和场景进行不断扩充
调用示例1:
@Override
public List<UserInfo> findAllByContainsLike(String attribute, String value) {
return simpleJpaRepository.findAll(SpecificationFactory.containsLike(attribute,value));
}
配合Specification使用,调用示例2:
@Override
public List<UserInfo> findAllByContainsLikeAndBetween(String attribute, String value, Date min, Date max) {
return simpleJpaRepository.findAll(SpecificationFactory
.containsLike(attribute,value)
.and(SpecificationFactory.isBetween("createdTime",min,max)));
}
Specification是Spring Data JPA对Specification的聚合操作工具类,里面有以下4个方法:
static <T> Specification<T> not(Specification<T> spec) {
return Specifications.negated(spec);
}
static <T> Specification<T> where(Specification<T> spec) {
return Specifications.where(spec);
}
default Specification<T> and(Specification<T> other) {
return Specifications.composed(this, other, CompositionType.AND);
}
default Specification<T> or(Specification<T> other) {
return Specifications.composed(this, other, CompositionType.OR);
}
2.4 JpaSpecificationExecutor实现原理
(1)在IDEA中打开SimpleJpaRepository类右键选择Diagram弹出如下图所示的类继承和实现接口关系图:
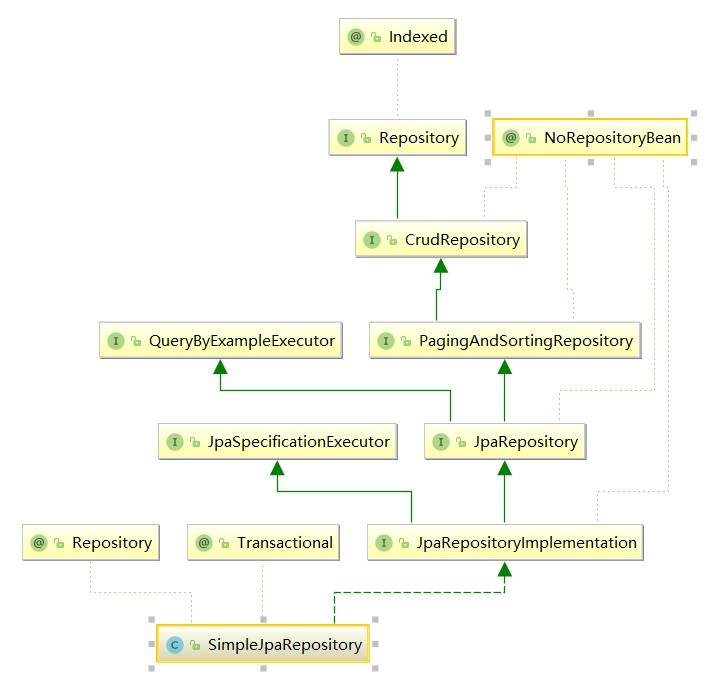
由上图可以看出SimpleJpaRepository类实现了JPA中大部分的Repository接口
(2)SimpleJpaRepository实现类中的关键源码:
/**
*以findOne为例
*/
public Optional<T> findOne(@Nullable Specification<T> spec) {
try {
return Optional.of(this.getQuery(spec, Sort.unsorted()).getSingleResult());
} catch (NoResultException var3) {
return Optional.empty();
}
}
/**
*解析Specification,利用EntityManager直接实现调用逻辑
*/
protected <S extends T> TypedQuery<S> getQuery(@Nullable Specification<S> spec, Class<S> domainClass, Sort sort) {
CriteriaBuilder builder = this.em.getCriteriaBuilder();
CriteriaQuery<S> query = builder.createQuery(domainClass);
Root<S> root = this.applySpecificationToCriteria(spec, domainClass, query);
query.select(root);
if (sort.isSorted()) {
query.orderBy(QueryUtils.toOrders(sort, root, builder));
}
return this.applyRepositoryMethodMetadata(this.em.createQuery(query));
}
3 小结
- 本文主要讲解了使用
spring-data-jpa中QueryByExampleExecutor和JpaSpecificationExecutor两个接口中的方法完成复杂的数据库业务查询; - 同时扩展了
JpaSpecificationExecutor创建了一个更加方便使用的工厂类SpecificationFactory; - 对
JpaSpecificationExecutor接口的实现类SimpleJpaRepository类的关键源码进行了简易分析; - 利用好
JpaSpecificationExecutor接口中的API几乎可以高效实现任意复杂场景需求的数据库查询
4 参考书籍
张振华著《Spring Data Jpa从入门到精通》之第6章:JpaRepository扩展详解
欢迎扫描下方二维码关注本人的微信公众号,定期更新技术干货

注公众号后发送消息【bootDemo项目源码】可获得本项目源码地址
-END-