深入了解EurekaClient的注册过程
深入了解EurekaClient的注册过程
目录
1.注册方法–register()
2.插曲:意外的收获–服务续租
3.实现Runnable接口重写run()
4.向注册中心更新状态的flag:isDirty
5.初始化定时任务 initScheduledTasks()
6.总结:EurekaClient register 流程
Eureka 的注册机制
jar: eureka-client-1.6.2.jar
package: com.netflix.discovery
class: EurekaClient 该接口继承了LookupService
@ImplementedBy(DiscoveryClient.class)
public interface EurekaClient extends LookupService { ... }通过EurekaClient接口上的注解@ImplementedBy(DiscoveryClient.class)我们知道这个接口的默认实现类是DiscoveryClient,这个类中定义了一些客户端的操作方法,本篇仅是看看客户端注册的流程,所以我们将目标放在register()这个方法:
注册方法- - -register()
/**
* Register with the eureka service by making the appropriate REST call.
*/
boolean register() throws Throwable {
logger.info(PREFIX + appPathIdentifier + ": registering service...");
EurekaHttpResponse httpResponse;
try {
httpResponse = eurekaTransport.registrationClient.register(instanceInfo);
} catch (Exception e) {
logger.warn("{} - registration failed {}", PREFIX + appPathIdentifier, e.getMessage(), e);
throw e;
}
if (logger.isInfoEnabled()) {
logger.info("{} - registration status: {}", PREFIX + appPathIdentifier, httpResponse.getStatusCode());
}
return httpResponse.getStatusCode() == 204;
}
不难看出,这里调用的register方法仅是将客户端的一些信息使用http请求发送到注册中心,顺藤摸瓜,使用ctrl+alt+h 搜索一哈register()的调用方发现有两个地方调用了register(),分别是renew(),run(),其中renew()是Eureka的心跳定时任务中的run()方法调用的,作用是向注册中心发送心跳,表明这个服务还活着,是客户端实现服务续租功能时调用的方法
插曲:意外的收获–服务续租
/**
* Renew with the eureka service by making the appropriate REST call
*/
boolean renew() {
EurekaHttpResponse httpResponse;
try {
httpResponse = eurekaTransport.registrationClient.sendHeartBeat(instanceInfo.getAppName(), instanceInfo.getId(), instanceInfo, null);
logger.debug("{} - Heartbeat status: {}", PREFIX + appPathIdentifier, httpResponse.getStatusCode());
if (httpResponse.getStatusCode() == 404) {
REREGISTER_COUNTER.increment();
logger.info("{} - Re-registering apps/{}", PREFIX + appPathIdentifier, instanceInfo.getAppName());
return register();
}
return httpResponse.getStatusCode() == 200;
} catch (Throwable e) {
logger.error("{} - was unable to send heartbeat!", PREFIX + appPathIdentifier, e);
return false;
}
} 那么这个renew()方法并不是我们找的,将目标锁定run():
实现Runnable接口重写run()
public void run() {
try {
discoveryClient.refreshInstanceInfo();
Long dirtyTimestamp = instanceInfo.isDirtyWithTime();
if (dirtyTimestamp != null) {
discoveryClient.register();
instanceInfo.unsetIsDirty(dirtyTimestamp);
}
} catch (Throwable t) {
logger.warn("There was a problem with the instance info replicator", t);
} finally {
Future next = scheduler.schedule(this, replicationIntervalSeconds, TimeUnit.SECONDS);
scheduledPeriodicRef.set(next);
}
}粗略看run(),一个try-catch-finally块里面套这个if语句,而调用register(),就放在if语句中,那么我们就有必要知道这条语句执行的条件,dirtyTimestamp!=null ,顺藤摸瓜,看看isDirtyWithTime()。
向注册中心更新状态的flag:isDirty
/**
* @return the lastDirtyTimestamp if is dirty, null otherwise.
*/
public synchronized Long isDirtyWithTime() {
if (isInstanceInfoDirty) {
return lastDirtyTimestamp;
} else {
return null;
}
}一个同步方法,简单的if语句,于是将目标变成isInstanceInfoDirty什么时候为true,查找当前类中,发现了一个setIsDirty()方法:
/**
* Sets the dirty flag so that the instance information can be carried to
* the discovery server on the next heartbeat.
*/
public synchronized void setIsDirty() {
isInstanceInfoDirty = true;
lastDirtyTimestamp = System.currentTimeMillis();
}又用到了源码三键 ctrl+alt+h 找到了规律:
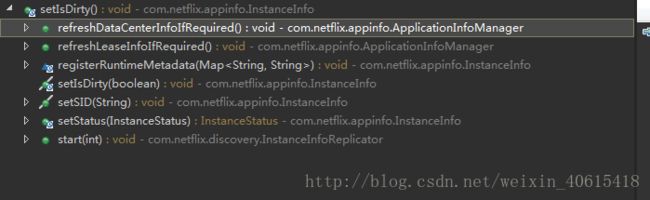
这几个地方要么是初始化的时候设置instanceinfo,要么是刷新instanceinfo的时候,而isDirty的定义就是是否跟原来的instanceinfo一样,就像上面方法中的文档所说,这是一个是否进行重新注册,发送心跳的标志。于是乎这里的逻辑都理通了。
下面回到run(),不难发现try块中第一件事情就是refreshInstanceInfo(),也就是检查之前的配置信息和现在的是否相同,为后面的register()立flag。
顺藤摸瓜 ctrl+alt+h 找到
初始化定时任务 initScheduledTasks()
/**
* Initializes all scheduled tasks.
*/
private void initScheduledTasks() {
if (clientConfig.shouldFetchRegistry()) { ... }
if (clientConfig.shouldRegisterWithEureka()) { ... }
}我们发现了老朋友,这不就是咱们最最最开始设置的两兄弟吗,还记得YAML中的设置吗,当我们将微服务作为EurekaClient时,我们并没有设置这两个值,它们默认为TRUE,看来我们找对了,于是看看这两个if块中都有什么:
if (clientConfig.shouldFetchRegistry()) {
// registry cache refresh timer
int registryFetchIntervalSeconds = clientConfig.getRegistryFetchIntervalSeconds();
int expBackOffBound = clientConfig.getCacheRefreshExecutorExponentialBackOffBound();
scheduler.schedule(
new TimedSupervisorTask(
"cacheRefresh",
scheduler,
cacheRefreshExecutor,
registryFetchIntervalSeconds,
TimeUnit.SECONDS,
expBackOffBound,
new CacheRefreshThread()
),
registryFetchIntervalSeconds, TimeUnit.SECONDS);
}设置了一个定时任务,用来定时刷新注册中心的服务列表
if (clientConfig.shouldRegisterWithEureka()) {
int renewalIntervalInSecs = instanceInfo.getLeaseInfo().getRenewalIntervalInSecs();
int expBackOffBound = clientConfig.getHeartbeatExecutorExponentialBackOffBound();
logger.info("Starting heartbeat executor: " + "renew interval is: " + renewalIntervalInSecs);
// Heartbeat timer
scheduler.schedule(
new TimedSupervisorTask(
"heartbeat",
scheduler,
heartbeatExecutor,
renewalIntervalInSecs,
TimeUnit.SECONDS,
expBackOffBound,
new HeartbeatThread()
),
renewalIntervalInSecs, TimeUnit.SECONDS);
// InstanceInfo replicator
instanceInfoReplicator = new InstanceInfoReplicator(
this,
instanceInfo,
clientConfig.getInstanceInfoReplicationIntervalSeconds(),
2); // burstSize
statusChangeListener = new ApplicationInfoManager.StatusChangeListener() {
@Override
public String getId() {
return "statusChangeListener";
}
@Override
public void notify(StatusChangeEvent statusChangeEvent) {
if (InstanceStatus.DOWN == statusChangeEvent.getStatus() ||
InstanceStatus.DOWN == statusChangeEvent.getPreviousStatus()) {
// log at warn level if DOWN was involved
logger.warn("Saw local status change event {}", statusChangeEvent);
} else {
logger.info("Saw local status change event {}", statusChangeEvent);
}
instanceInfoReplicator.onDemandUpdate();
}
};
if (clientConfig.shouldOnDemandUpdateStatusChange()) {
applicationInfoManager.registerStatusChangeListener(statusChangeListener);
}
instanceInfoReplicator.start(clientConfig.getInitialInstanceInfoReplicationIntervalSeconds());
} else {
logger.info("Not registering with Eureka server per configuration");
}这里做了几件事情:
1.设置发送心跳的定时任务
2.设置状态改变的监听者,当instance状态改变时更新向注册中心更新信息
最后这个初始化的方法是在DiscoveryClient( … ){ .. }的构造方法中调用的,到此EurekaClient的注册就说完了,我们来捋一捋
总结:EurekaClient register 流程
项目启动》构造DiscoveryClient对象》调用initScheduledTasks()》初始化定时任务》执行注册、获取服务列表细心的小伙伴已经发现了,这里并没有直接调用线程的start()方法,而是设置了一个延迟,
instanceInfoReplicator.start(clientConfig.getInitialInstanceInfoReplicationIntervalSeconds());
这个值默认为40秒,所以服务启动的时候并不是直接向服务中心进行注册的,而是延迟40秒才发送请求。