Qt对图像的二值化处理
学习一下图像处理的基础算法,写下来总结一下:
1. 灰度图像
二值化图像的第一步是先将彩色图片转变为灰度图像,灰度图像算法如下:
*以上内容来自百度
2. 图像二值化
二值化是先设定一个阈值,然后将灰度图像中每个像素的颜色值与阈值相比较,小于阈值的设置为0(黑色),大于等于的则设为255(白色);这个阈值可以设定为固定值,也可以是像素平均值,我这里使用otsu算法,查找出合适的阈值。
源码如下:
binarization.h
#ifndef CBINARIZATION_H
#define CBINARIZATION_H
#include
#include
using namespace std;
class CBinarization
{
public:
CBinarization(QString imgPath);
QImage* grayScaleImg();
int Otsu(QImage* img);
QImage* process(QImage* img);
int threshold;
private:
QImage* _img;
vector Histogram(QImage* img);
};
#endif // CBINARIZATION_H
binarization.cpp
#include "cbinarization.h"
CBinarization::CBinarization( QString imgPath )
: threshold(0)
{
// 加载图片
_img = new QImage();
if (NULL != _img)
{
_img->load(imgPath);
}
}
// 生成灰度图像
QImage* CBinarization::grayScaleImg()
{
if (NULL == _img)
{
return NULL;
}
int nWidth = _img->width();
int nHeight = _img->height();
// 这里留意,我使用了QImage::Format_Grayscale8格式的图片,这种图片每个像素只用了8bit存储灰度颜色值
QImage* grayImg = new QImage(nWidth, nHeight, QImage::Format_Grayscale8);
QRgb rgbVal = 0;
int grayVal = 0;
for (int x = 0; x < nWidth; ++x)
{
for (int y = 0; y < nHeight; ++y)
{
rgbVal = _img->pixel(x, y);
grayVal = qGray(rgbVal); // 这里调用Qt的函数,使用(R * 11 + G * 16 + B * 5)/32的方法计算
grayImg->setPixel(x, y, QColor(grayVal, grayVal, grayVal).rgb());
}
}
return grayImg;
}
int CBinarization::Otsu(QImage* img)
{
if (NULL == img)
{
return -1;
}
vector histogram = Histogram(img);
int total = 0;
for (int i = 0; i != histogram.size(); ++i)
{
total += histogram[i];
}
double sum = 0.0;
for (unsigned int i = 1; i < histogram.size(); ++i)
sum += i * histogram[i];
double sumB = 0.0;
double wB = 0.0;
double wF = 0.0;
double mB = 0.0;
double mF = 0.0;
double max = 0.0;
double between = 0.0;
double threshold = 0.0;
for (int i = 0; i != 256; ++i)
{
wB += histogram[i];
if (wB == 0)
continue;
wF = total - wB;
if (wF == 0)
break;
sumB += i * histogram[i];
mB = sumB / wB;
mF = (sum - sumB) / wF;
between = wB * wF * (mB - mF) * (mB - mF);
if ( between > max )
{
threshold = i;
max = between;
}
}
return threshold;
}
QImage* CBinarization::process(QImage* img)
{
if (NULL == img)
{
return NULL;
}
int width = img->width();
int height = img->height();
int bytePerLine = img->bytesPerLine(); // 每一行的字节数
unsigned char *data = img->bits();
unsigned char *binarydata = new unsigned char[bytePerLine * height];
unsigned char g = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < height; ++i)
{
for (int j = 0; j < width; ++j)
{
g = *(data + i * bytePerLine + j);
if(int(g) >= threshold)
{
binarydata[ i * bytePerLine + j] = 0xFF;
}
else
{
binarydata[ i * bytePerLine + j] = 0x00;
}
}
}
QImage *ret = new QImage(binarydata, width, height, bytePerLine, QImage::Format_Grayscale8);
return ret;
}
std::vector CBinarization::Histogram( QImage* img )
{
unsigned char* graydata = img->bits();
vector hist(256); // 256色
for (int i = 0; i != img->width(); ++i)
{
for (int j = 0; j != img->height(); ++j)
{
int index = int(*graydata);
hist[index] += 1;
graydata += 1; // step
}
}
graydata = NULL;
return hist;
}
main.cpp
CBinarization* binImg = new CBinarization("D:/girl.png");
if (NULL == binImg)
{
return; // error
}
QImage* grayImage = binImg->grayScaleImg();
if (NULL == grayImage)
{
return; // error
}
grayImage->save("D:/grayimg.png");
int threshold = binImg->Otsu(grayImage); // 这就是计算出的阈值
if (-1 == threshold)
{
return; // error
}
binImg->threshold = threshold;
QImage* binaryImg = binImg->process(grayImage);
if (NULL == binaryImg)
{
return; // error
}
binaryImg->save("D:/binaryimg.png");这样就生成灰度图和二值化以后的图:
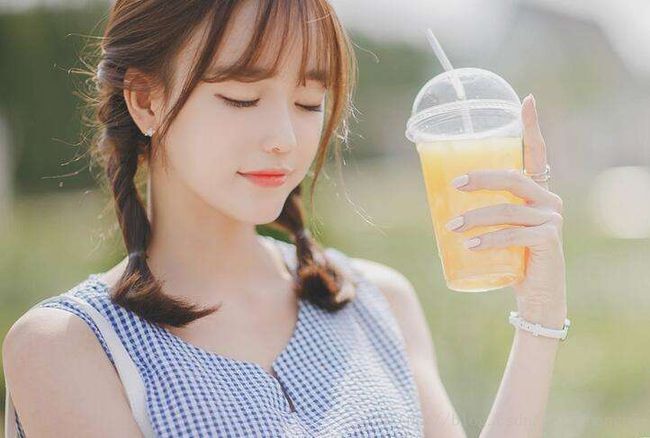
原图(来自百度,如有侵权,必删):
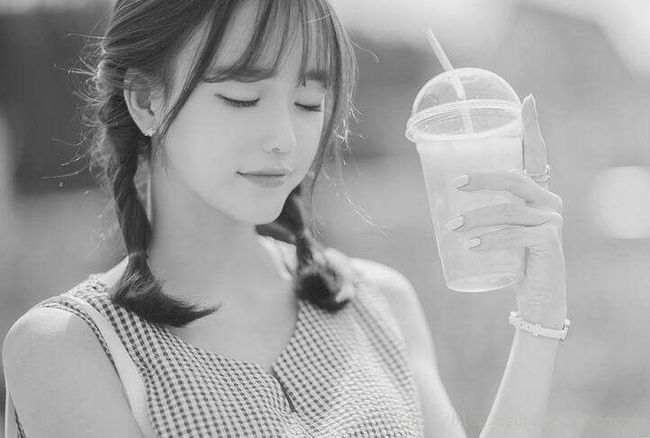
灰度图:
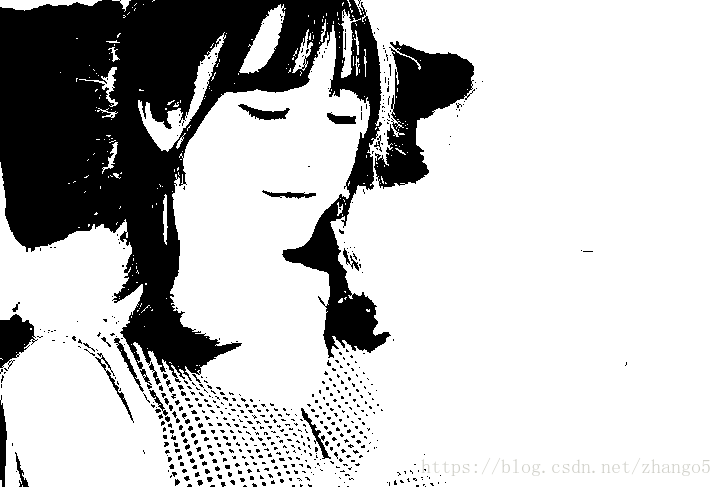
二值化:
能看出来,二值化以后的图虽然奶茶杯子不见了,但是最重要的女孩还是保留的很好的。
注意:
1. 代码中我生成灰度图的时候使用图片格式为 QImage::Format_Grayscale8 ,Qt助手中给出的解释The image is stored using an 8-bit grayscale format可以看出,这种图片中用8-bit存储灰度值,所以每个像素只有1字节;这里我也试过 QImage::Format_RGB888 格式(The image is stored using a 24-bit RGB format (8-8-8)),这时每个像素有3个字节,这里牵扯后面代码中有不同的地方。
2. 在Otsu生成图像直方图时Histogram函数中,因为我用的Grayscale8的格式,所以数据每次只移动1个字节(step注释处,如果是RGB888,则需要移动3个字节);
3. process函数中 img->bytesPerLine() 返回图片每一行的字节数,Grayscale8格式下与宽度相等,RGB888格式下则等于宽度的3倍;RGB888格式时,代码应修改为以下形式:
unsigned char g = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < height; ++i)
{
for (int j = 0; j < width; ++j)
{
g = *(data + i * bytePerLine + j * 3); // 这里j 乘以 3
if(int(g) >= threshold)
{
binarydata[ i * bytePerLine + j * 3] = 0xFF; // 每个色值需要对3个字节赋值
binarydata[ i * bytePerLine + j * 3 + 1] = 0xFF;
binarydata[ i * bytePerLine + j * 3 + 2] = 0xFF;
}
else
{
binarydata[ i * bytePerLine + j * 3] = 0x00;
binarydata[ i * bytePerLine + j * 3 + 1] = 0x00;
binarydata[ i * bytePerLine + j * 3 + 2] = 0x00;
}
}
}每次处理3个字节的数据。
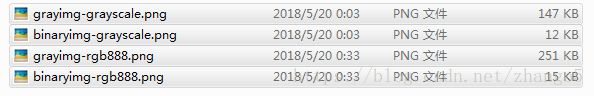
4. 两种格式下生成的图片大小也不同:
但效果看上去是一样的。
非常感谢 keybord_dancer 的 使用Qt实现一个图像处理软件0 ,我是参考他的帖子整理出我的代码。