/** Spark SQL源代码分析系列文章*/
在SQL的世界里,除了官方提供的经常使用的处理函数之外。一般都会提供可扩展的对外自己定义函数接口,这已经成为一种事实的标准。
在前面Spark SQL源代码分析之核心流程一文中,已经介绍了Spark SQL Catalyst Analyzer的作用,其中包括了ResolveFunctions这个解析函数的功能。可是随着Spark1.1版本号的公布。Spark SQL的代码有非常多新完好和新功能了。和我先前基于1.0的源代码分析多少有些不同,比方支持UDF:
spark1.0及曾经的实现:
protected[sql] lazy val catalog: Catalog = new SimpleCatalog
@transient
protected[sql] lazy val analyzer: Analyzer =
new Analyzer(catalog, EmptyFunctionRegistry, caseSensitive = true) //EmptyFunctionRegistry空实现
@transient
protected[sql] val optimizer = OptimizerSpark1.1及以后的实现:
protected[sql] lazy val functionRegistry: FunctionRegistry = new SimpleFunctionRegistry //SimpleFunctionRegistry实现。支持简单的UDF
@transient
protected[sql] lazy val analyzer: Analyzer =
new Analyzer(catalog, functionRegistry, caseSensitive = true)一、引子:
对于SQL语句中的函数,会经过SqlParser的的解析成UnresolvedFunction。UnresolvedFunction最后会被Analyzer解析。
SqlParser:
除了非官方定义的函数外,还能够定义自己定义函数。sql parser会进行解析。
ident ~ "(" ~ repsep(expression, ",") <~ ")" ^^ {
case udfName ~ _ ~ exprs => UnresolvedFunction(udfName, exprs) 仅仅是这个Expression的dataType等一系列属性和eval计算方法均无法訪问。强制訪问会抛出异常,由于它没有被Resolved,仅仅是一个载体。
case class UnresolvedFunction(name: String, children: Seq[Expression]) extends Expression {
override def dataType = throw new UnresolvedException(this, "dataType")
override def foldable = throw new UnresolvedException(this, "foldable")
override def nullable = throw new UnresolvedException(this, "nullable")
override lazy val resolved = false
// Unresolved functions are transient at compile time and don't get evaluated during execution.
override def eval(input: Row = null): EvaluatedType =
throw new TreeNodeException(this, s"No function to evaluate expression. type: ${this.nodeName}")
override def toString = s"'$name(${children.mkString(",")})"
}Analyzer:
Analyzer初始化的时候会须要Catalog,database和table的元数据关系,以及FunctionRegistry来维护UDF名称和UDF实现的元数据,这里使用SimpleFunctionRegistry。
/**
* Replaces [[UnresolvedFunction]]s with concrete [[catalyst.expressions.Expression Expressions]].
*/
object ResolveFunctions extends Rule[LogicalPlan] {
def apply(plan: LogicalPlan): LogicalPlan = plan transform {
case q: LogicalPlan =>
q transformExpressions { //对当前LogicalPlan进行transformExpressions操作
case u @ UnresolvedFunction(name, children) if u.childrenResolved => //假设遍历到了UnresolvedFunction
registry.lookupFunction(name, children) //从UDF元数据表里查找udf函数
}
}
}二、UDF注冊
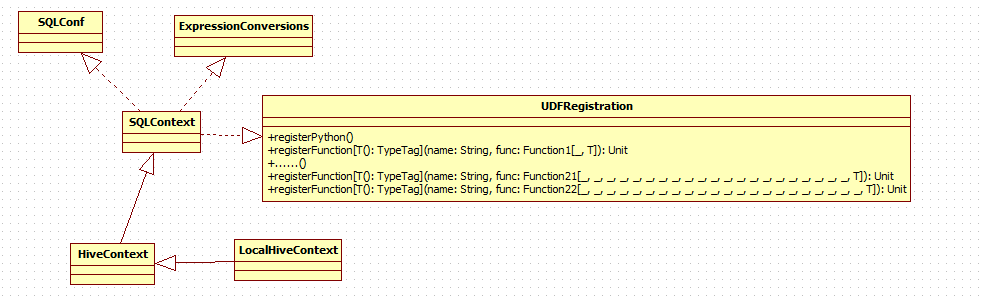
2.1 UDFRegistration
registerFunction("len", (x:String)=>x.length)registerFunction是UDFRegistration下的方法,SQLContext如今实现了UDFRegistration这个trait。仅仅要导入SQLContext,即能够使用udf功能。
UDFRegistration核心方法registerFunction:
registerFunction方法签名def registerFunction[T: TypeTag](name: String, func: Function1[_, T]): Unit
接受一个udfName 和 一个FunctionN。能够是Function1 到Function22。
即这个udf的參数仅仅支持1-22个。
(scala的痛啊)
内部builder通过ScalaUdf来构造一个Expression,这里ScalaUdf继承自Expression(能够简单的理解眼下的SimpleUDF即是一个Catalyst的一个Expression),传入scala的function作为UDF的实现,而且用反射检查字段类型是否是Catalyst同意的,见ScalaReflection.
def registerFunction[T: TypeTag](name: String, func: Function1[_, T]): Unit = {
def builder(e: Seq[Expression]) = ScalaUdf(func, ScalaReflection.schemaFor(typeTag[T]).dataType, e)//构造Expression
functionRegistry.registerFunction(name, builder)//向SQLContext的functionRegistry(维护了一个hashMap来管理udf映射)注冊
}注意:这里FunctionBuilder是一个type FunctionBuilder = Seq[Expression] => Expression
class SimpleFunctionRegistry extends FunctionRegistry {
val functionBuilders = new mutable.HashMap[String, FunctionBuilder]() //udf映射关系维护[udfName,Expression]
def registerFunction(name: String, builder: FunctionBuilder) = { //put expression进Map
functionBuilders.put(name, builder)
}
override def lookupFunction(name: String, children: Seq[Expression]): Expression = {
functionBuilders(name)(children) //查找udf,返回Expression
}
}三、UDF计算:
UDF既然已经被封装为catalyst树里的一个Expression节点,那么计算的时候也就是计算ScalaUdf的eval方法。
先通过Row和表达式计算function所须要的參数。最后通过反射调用function,来达到计算udf的目的。
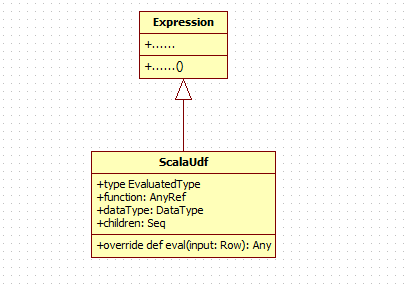
ScalaUdf继承自Expression:
scalaUdf接受一个function, dataType,和一系列表达式。
比較简单。看凝视就可以:
case class ScalaUdf(function: AnyRef, dataType: DataType, children: Seq[Expression])
extends Expression {
type EvaluatedType = Any
def nullable = true
override def toString = s"scalaUDF(${children.mkString(",")})"
override def eval(input: Row): Any = {
val result = children.size match {
case 0 => function.asInstanceOf[() => Any]()
case 1 => function.asInstanceOf[(Any) => Any](children(0).eval(input)) //反射调用function
case 2 =>
function.asInstanceOf[(Any, Any) => Any](
children(0).eval(input), //表达式參数计算
children(1).eval(input))
case 3 =>
function.asInstanceOf[(Any, Any, Any) => Any](
children(0).eval(input),
children(1).eval(input),
children(2).eval(input))
case 4 =>
......
case 22 => //scala function仅仅支持22个參数。这里枚举了。
function.asInstanceOf[(Any, Any, Any, Any, Any, Any, Any, Any, Any, Any, Any, Any, Any, Any, Any, Any, Any, Any, Any, Any, Any, Any) => Any](
children(0).eval(input),
children(1).eval(input),
children(2).eval(input),
children(3).eval(input),
children(4).eval(input),
children(5).eval(input),
children(6).eval(input),
children(7).eval(input),
children(8).eval(input),
children(9).eval(input),
children(10).eval(input),
children(11).eval(input),
children(12).eval(input),
children(13).eval(input),
children(14).eval(input),
children(15).eval(input),
children(16).eval(input),
children(17).eval(input),
children(18).eval(input),
children(19).eval(input),
children(20).eval(input),
children(21).eval(input))
四、总结
Spark眼下的UDF事实上就是scala function。将scala function封装到一个Catalyst Expression其中,在进行sql计算时。使用相同的Eval方法对当前输入Row进行计算。
编写一个spark udf非常easy。仅仅需给UDF起个函数名,而且传递一个scala function就可以。
依靠scala函数编程的表现能力,使得编写scala udf比較简单。且相较hive的udf更easy使人理解。
——EOF——
原创文章。转载请注明:
转载自:OopsOutOfMemory盛利的Blog。作者: OopsOutOfMemory
本文链接地址:http://blog.csdn.net/oopsoom/article/details/39395641
注:本文基于署名-非商业性使用-禁止演绎 2.5 中国大陆(CC BY-NC-ND 2.5 CN)协议,欢迎转载、转发和评论,可是请保留本文作者署名和文章链接。如若须要用于商业目的或者与授权方面的协商。请联系我。