Resnet网络回归的简单实现
注:参考《动手学深度学习》一书
构建的网络模型是ResNet-18,即4个残差块,每块里面有四层卷积(不包括用以改变通道数的1×1卷积层),以及最开始的卷积层和最后的全连接层,总共18层
数据集类型为简单的array或pd.DataFrame类型的二维表或二维矩阵
1、加载测试数据
1.1、构建训练数据的X-y的Dataset类,用以后续的批处理和shuffle
class AnalysisDataset(Dataset):
def __init__(self, in_data, column_X, column_Y):
self.data = in_data
self.column_X = column_X
self.column_Y = column_Y
def __len__(self):
return len(self.data)
def __getitem__(self, index):
X = self.data[self.column_X]
y = self.data[self.column_Y]
tensor_X = torch.from_numpy(np.array(X.iloc[index])).float()
tensor_y = torch.from_numpy(np.array(y.iloc[index])).float()
return tensor_X.view(1, tensor_X.shape[0], 1), tensor_y1.2、构建预测数据的X的Dataset类
class PredictDataset(Dataset):
def __init__(self, in_data, column_X):
self.data = in_data
self.column_X = column_X
def __len__(self):
return len(self.data)
def __getitem__(self, index):
X = self.data[self.column_X]
tensor_X = torch.from_numpy(np.array(X.iloc[index])).float()
return tensor_X.view(1, tensor_X.shape[0], 1)1.3 导入训练测试数据
def loadData(batch_size, X, y):
if not isinstance(X, pd.DataFrame):
X = pd.DataFrame(X, columns=list(np.linspace(0, X.shape[1] -1, X.shape[1])))
if not isinstance(y, pd.DataFrame):
y = pd.DataFrame(y, columns=list(np.linspace(X.shape[1], X.shape[1] + y.shape[1] - 1, y.shape[1])))
column_X = X.columns
column_y = y.columns
temp_df = X.join(y)
train_set, test_set = train_test_split(temp_df, test_size=0.2, random_state=10, shuffle=True)
torch_trainset = AnalysisDataset(train_set, column_X, column_y)
torch_testset = AnalysisDataset(test_set, column_X, column_y)
# 批量导入
if sys.platform.startswith("win"):
works_num = 1
else:
works_num = 4
train_batch = Data.DataLoader(torch_trainset, batch_size=batch_size, shuffle=True, num_workers=works_num)
# for X, y in train_batch:
# print(X.shape)
# print(y.shape)
test_batch = Data.DataLoader(torch_testset, batch_size=batch_size, shuffle=False, num_workers=works_num)
return train_batch, test_batch2、构建ResNet网络
2.1 相关工具计算类
class GlobalAvgPool2d(torch.nn.Module):
# 全局平均池化层可通过将池化窗口形状设置成输入的高和宽实现
def __init__(self):
super(GlobalAvgPool2d, self).__init__()
def forward(self, x):
return F.avg_pool2d(x, kernel_size=x.size()[2:])
class FlattenLayer(torch.nn.Module):
# 用于全连接层
def __init__(self):
super(FlattenLayer, self).__init__()
def forward(self, x):
# x shape: (batch_size, *, *, ...)
return x.view(x.shape[0], -1)2.2、基本框架
def ResNet():
model = torch.nn.Sequential(
torch.nn.Conv2d(1, 4, kernel_size=2, padding=1, stride=1),
torch.nn.BatchNorm2d(4),
torch.nn.ReLU(),
torch.nn.MaxPool2d(kernel_size=2)
)
# 添加残差层
# ...... #
model.add_module("global_avg_pool", GlobalAvgPool2d())
model.add_module("fc", torch.nn.Sequential(FlattenLayer(), torch.nn.Linear(32, 2)))2.3 残差块
def resnet_block(in_channels, out_channels, num_residuals, first_block=False):
'''
:param in_channels: 输入层通道数
:param out_channels: 输出层通道数
:param num_residuals: 残差层数
:param first_block: 是否是第一个resnet块
:return:
'''
# 第一个模块的通道数同输入通道数一致。
# 由于之前已经使用了步幅为2的最大池化层,所以无须减小高和宽。
# 之后的每个模块在第一个残差块里将上一个模块的通道数翻倍,并将高和宽减半
if first_block:
# 第一个块 输入和输出的通道数需一致
assert in_channels == out_channels
block = []
for i in range(num_residuals):
if i == 0 and not first_block:
block.append(Residual(in_channels, out_channels, use_1x1conv=True, stride=1))
else:
block.append(Residual(out_channels, out_channels))
return torch.nn.Sequential(*block)2.3.1 核心类Residual
class Residual(torch.nn.Module):
def __init__(self, in_channels, out_channels, use_1x1conv=False, stride=1):
'''
:param in_channels: 输入的通道数
:param out_channels: 输出的通道数
:param use_1x1conv: 是否使用1*1卷积层
:param stride: 步长
'''
super(Residual, self).__init__()
# kernel_size=3, padding=1, stride=1保证输入与输出宽高一致
self.conv1 = torch.nn.Conv2d(in_channels, out_channels, kernel_size=3, padding=1, stride=stride)
self.conv2 = torch.nn.Conv2d(out_channels, out_channels, kernel_size=3, padding=1)
if use_1x1conv:
self.conv3 = torch.nn.Conv2d(in_channels, out_channels, kernel_size=1, stride=stride)
else:
self.conv3 = None
# 批量归一化
self.b1 = torch.nn.BatchNorm2d(out_channels)
self.b2 = torch.nn.BatchNorm2d(out_channels)
def forward(self, X):
Y = F.relu(self.b1(self.conv1(X)))
Y = self.b2(self.conv2(Y))
if self.conv3 is not None:
X = self.conv3(X)
# 输出和输入,此时Y = F(X) - X为残差层的输出,所以残差层实际拟合的是F(X)-X
return F.relu(Y + X)3、训练验证模型
3.1 训练模型
def train(model, train_batch, test_batch, batch_size, optimizer, device, num_epochs):
model = model.to(device)
print("run in " , device)
# 损失函数,MSE函数
loss = torch.nn.MSELoss()
for epoch in range(num_epochs):
train_loss_sum, train_rmse_sum, n, batch_count = 0.0, 0.0, 0, 0
start = time.time()
for X, y in train_batch:
# 转置
X = X.to(device)
y = y.to(device)
# 前向计算
y_pre = model(X)
l = loss(y_pre, y)
# 梯度清零
optimizer.zero_grad()
l.backward()
optimizer.step()
train_loss_sum += l.cpu().item()
train_rmse_sum += torch.sqrt(((y_pre-y)**2).sum()).cpu().item()
n += y.shape[0]
batch_count += 1
test_rmse = evaluate_rmse(test_batch, model)
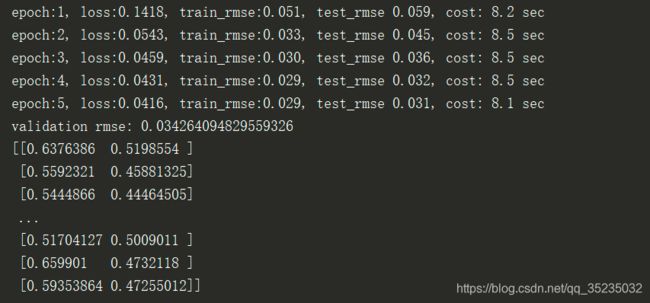
print("epoch:%d, loss:%.4f, train_rmse:%.3f, test_rmse %.3f, cost: %.1f sec" %
(epoch + 1, train_loss_sum / batch_count, train_rmse_sum / n, test_rmse, time.time() - start))
3.1.1 计算rmse的函数
def evaluate_rmse(data_batch, model, device = None):
if device is None and isinstance(model, torch.nn.Module):
device = list(model.parameters())[0].device
rmse_sum, n = 0, 0
with torch.no_grad():
for X, y in data_batch:
if isinstance(model, torch.nn.Module):
# 评估模式,关闭dropout
model.eval()
rmse_sum += torch.sqrt(((model(X.to(device)) - y) ** 2).sum()).cpu().item()
# 改回训练模式
model.train()
else:
# 自定义模型
if ('is_training' in model.__code__.co_varnames):
# 如果有is_training这个参数
# 将is_training设置成False
rmse_sum += torch.sqrt(((model(X.to(device), is_training=False) - y) ** 2).sum()).cpu().item()
else:
rmse_sum += torch.sqrt(((model(X.to(device)) - y) ** 2).sum()).cpu().item()
n += y.shape[0]
return rmse_sum / n3.2 验证
def validation(model, test_batch, device=None):
if device is None and isinstance(model, torch.nn.Module):
device = list(model.parameters())[0].device
predX, predy = iter(test_batch).next()
rmse_sum, n = 0, 0
with torch.no_grad():
if isinstance(model, torch.nn.Module):
rmse_sum += torch.sqrt(((model(predX.to(device)) - predy) ** 2).sum()).cpu().item()
else:
if ('is_training' in model.__code__.co_varnames):
# 如果有is_training这个参数
# 将is_training设置成False
rmse_sum += torch.sqrt(((model(predX.to(device), is_training=False) - predy) ** 2).sum()).cpu().item()
else:
rmse_sum += torch.sqrt(((model(predX.to(device)) - predy) ** 2).sum()).cpu().item()
n += predy.shape[0]
# print("pre:", model(predX))
return rmse_sum / n4、预测
def predict(model, df_X, batch_size, device=None):
''' 预测
:param model: 训练好的resnet模型
:param df_X: 待预测的自变量, dataframe类型
:return:
'''
if device is None and isinstance(model, torch.nn.Module):
device = list(model.parameters())[0].device
if not isinstance(df_X, pd.DataFrame):
df_X = pd.DataFrame(df_X, columns=list(np.linspace(0, df_X.shape[1] -1, df_X.shape[1])))
predict_dataset = PredictDataset(df_X, df_X.columns)
if sys.platform.startswith("win"):
works_num = 1
else:
works_num = 4
predict_batch = Data.DataLoader(predict_dataset, batch_size=batch_size, shuffle=False, num_workers=works_num)
estimated_Y = torch.tensor([])
for X in predict_batch:
X = X.to(device)
temp_Y = model(X)
# 合并
estimated_Y = torch.cat([estimated_Y, temp_Y], dim=0)
estimated_Y = estimated_Y.detach().numpy()
return estimated_Y5、程序入口
if __name__ == "__main__":
batch_size = 100
x = np.random.randn(1000, 8)
y = np.asarray(
[
[0.8, 0.4],
[0.4, 0.3],
[0.34, 0.45],
[0.67, 0.32],
[0.88, 0.67],
[0.78, 0.77],
[0.55, 0.66],
[0.55, 0.43],
[0.54, 0.1],
[0.1, 0.5],
] * 100
)
train_batch, test_batch = loadData(batch_size, x, y)
# for X, y in train_batch:
# print("train_X", X.shape)
# print("train_y", y.shape)
# for X, y in test_batch:
# print("test_X", X.shape)
# print("test_y", y.shape)
# 加载模型
lr, num_epochs = 0.001, 5
model = ResNet()
optimizer = torch.optim.Adam(model.parameters(), lr=lr)
# 训练模型
train(model, train_batch, test_batch, batch_size, optimizer, device, num_epochs)
# 验证
valid_rmse = validation(model, test_batch)
print("validation rmse:", valid_rmse)
# 预测
x = np.random.randn(1000, 8) * 1.1
print(predict(model, x, batch_size))