Java IO流
Java、IO流
一、IO流
1.流概念
文件流:从一端流动到另一端,即从java内存流动到存储介质中。存储介质包括:硬盘文件、数据库与网络等节点 (数据源)。记住:一切以java内存为中心。
2.数据源
data source. 提供原始数据的原始媒介。常见的:数据库、文件、其他程序、内存、网络连接、IO设备。数据源就像水箱,流就像水管中流着的水流,程序就是我们最终的用户。 流是一个抽象、动态的概念,是一连串连续动态的数据集合。
3.IO流分类
1) 、数据分类
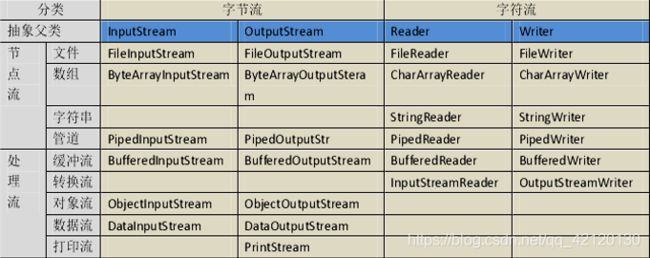
按处理数据单位分为:字节流和字符流。处理数据是音频、视频、doc、文本等一切为字节流,仅能处理文本的为字符流。 字节流和字符流的用法几乎完全一致,区别在于它们所操作的数据单元不同,字节流(8 位)、字符流(16 位)、字节流主要由 InputStream 和OutputStream作为基类,字符流主要由Reader 和 Writer作为基类。
2) 、流向分类
输入流和输出流。从节点到java 内存叫输入流,从java 内存到节点叫输出流。Java的输入流主要由InputStream和Reader作为基类,输出流主要由OutputStream和Writer作为基类。
3) 、功能分类
节点流和处理流。从/向一个特定的I/0设备(磁盘、网络等)读写数据的流称为节点流,也常被称为低级流。 处理流则对于一个已存在的节点流进行连接或封装,常被称为高级流(装饰器设计模式)。处理流为增强、提升性能的,本身不具备直接操作节点的能力。如扩音器,就是放大声音的。 节点流处于io操作的第一线,所有操作必须通过他们进行;处理流可以对其他流 进行处理(提高效率或操作灵活性)
处理流的功能主要体现在:
a、性能的提高:主要以增加缓冲的方式来提高输入/输出的效率 ;
b、操作的便捷:提供了系列便捷的方法来一次输入/输出大批量内容
4、操作 IO流的步骤
核心步骤如下
1)、建立联系
2)、选择流
3)、操作:写出 读取
4)、释放资源(程序中打开的文件 IO 资源不属于内存中的资源,垃圾回收无法回收,需要显示关闭。)
二、输入流
字节流和字符流的操作方式几乎完全一样,只是操作的数据单元不同而已 。字节流可
以操作所有文件,字符流仅操作纯文本。
1、抽象类:InputStream 和 Reader
InputStream和Reader是所有输入流的基类,它们是两个抽象类,是所有输入流的模版,其中定义的方法在所有输入流中都可以使用。
在InputStream里包含如下三个方法

在Reader中包含如下三个方法
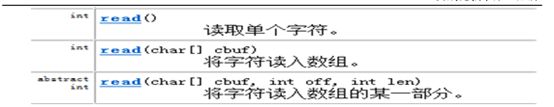
对比InputStream和Reader 所提供的方法,可以看出这两个基类的功能基本相似。返回结果为-1 时表明到了输入流的结束点。
InputStream 和 Reade 都是抽象的,不能直接创建它们的实例,可以使用它们的子类。
2、文件节点类: FileInputStream 和 FileReader
FileInputStream 和 FileReader,它们都是节点流,直接和指定文件关联。 操作方式基本一致。
1) 、单个字节读取
【实例】FileInputStream
public class SingleFileRead {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 1、建立联系 File对象
File file = new File("f:/IO/test.txt");
// 2、选择流
InputStream in = null;// 提升作用域
try {
in = new FileInputStream(file);
// 3、操作 单个字节读取
long fileLength = file.length(); // 接收实际读取的字节数
// 计数器
System.out.println(fileLength);
long num = 0;
// 循环读取
while (num < fileLength) {
char ch = (char) in.read();
System.out.println(ch);
num++;
}
} catch (FileNotFoundException e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
System.out.println("文件不存在,不能进行下一步操作");
} catch (IOException e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
System.out.println("读取文件失败");
} finally {
try {
// 4、释放资料
if (in != null) {
in.close();
}
} catch (IOException e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
System.out.println("关闭文件输入流失败");
}
}
}
}
2) 、批量读取 ( 字节 | 字符重点 )
public class ReadFile {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//1、字节读取:建立联系 File对象
File file=new File("f:/IO/test.txt");
//2、选择流
InputStream in=null;//提升作用域
try {
in=new FileInputStream(file);
//3、操作 不断读取 缓冲数组
byte[]car=new byte[1024];
int len=0; //接收实际读取的大小
//循环读取
while(-1!=(len=in.read(car))){
//输出,字节数组转成字符串
String info=new String(car,0,len);
System.out.println(info);
}
} catch (FileNotFoundException e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
System.out.println("文件不存在");
} catch (IOException e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
System.out.println("读取文件失败");
}finally{
try {
//4、释放资料
if(in!=null){
in.close();
}
} catch (IOException e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
System.out.println("关闭文件输入流失败");
}
}
}
}
//字符读取1、创建源
File src=new File("f:/char.txt");
//2、选择流
Reader reader=new FileReader(src);
//3、读取操作
char[] flush=new char[1024];
int len=0;
while(-1!=(len=reader.read(flush))){
//字符数组转换为字符串
String str=new String(flush,0,len);
System.out.println(str);
}
//4、释放资源
reader.close();
3、缓冲处理类:BufferedInputStream和 BufferedReader(重点)
缓冲提高性能: 字节流直接套上即可;字符缓冲流 +新增方法(不能使用多态)
//1、创建源,建立联系
File src =new File("test.txt");
//2、选择缓冲流
InputStream is =new BufferedInputStream(new FileInputStream(src)); //3、操作 : 多个读取
byte[] car =new byte[2];
int len =0;
while(-1!=(len=is.read(car))){
//获取数组的内容 字节数组转字符串 new String(字节数组,0,length)
System.out.println(new String(car,0,len));
}
//4、释放资源
is.close();
//创建源:
File src =new File("test.txt");
//使用字符缓冲流 提高性能读取文件 +新增方法(不能使用多态)
BufferedReader br =new BufferedReader(new FileReader(src));
//操作 行读取
String line=null;
while(null!=(line=br.readLine())){
System.out.println(line);
}
//释放资源
br.close();
三、输出流
1、抽象类:OutputStream 和 Writer
OutputStream和Writer也非常相似。
在OutputStream 里包含如下方法
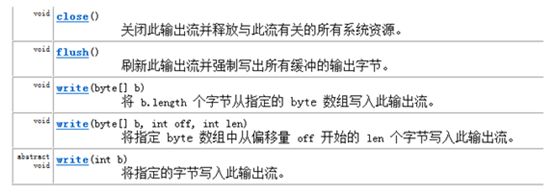
在Writer 中, 因为字符流直接以字符作为操作单位,所以
Writer 可以用字符串来代替字符数组,即以String对象来作为参数。 包含如下方法

2、文件节点类:FileOutputStream 和 FileWriter
FileOutputStream 和FileWriter,它们都是节点流,直接和指定文件关联。
public class WriteFile {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//1、建立联系 File对象 源头 目的地
File dest=new File("c:/IO/print.txt");
//2、选择流 文件输出流 OutputStream FileOutputStream
OutputStream out=null;
//以追加形式写出文件 必须为true 否则会覆盖
try {
out=new FileOutputStream(dest,true);
//3、操作
String str="shsxt is very good \r\n good good good";
//字符串转成字节数组
byte[] data=str.getBytes();
out.write(data,0,data.length);
out.flush();//强制刷新出去
} catch (FileNotFoundException e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
System.out.println("文件未找到");
} catch (IOException e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
System.out.println("文件写出失败");
}finally{
try {
if(out!=null){
out.close();
}
} catch (IOException e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
System.out.println("关闭输出流失败");
}
}
}
}
//1、创建源
File dest=new File("f:/IO/char.txt");
//2、选择流
Writer wr=new FileWriter(dest,true);
//3、写出
String str="锄禾日当午\r\n码农真辛苦\r\n一本小破书\r\n一读一上午";
wr.write(str);
//追加内容
wr.append("我就是追加进去的");
wr.flush();//强制刷出
//4、关闭资源
wr.close();
结合输入输出流,可以实现文件拷贝
public static void copyFile(String srcPath, String destPath) throws FileNotFoundException,IOException{
// 1、建立联系 源(存在且为文件) 目的地(文件可以不存在)
File src = new File(srcPath);
File dest = new File(destPath);
if(!src.isFile()){//不是文件或者为null时抛出异常
System.out.println("只能拷贝文件");
throw new IOException("只能拷贝文件");
}
// 2、选择流
InputStream in = new FileInputStream(src);
OutputStream out = new FileOutputStream(dest);
// 3、操作
byte[] flush = new byte[1024];
int len = 0;
// 读取
while (-1 != (len = in.read(flush))) {
// 写出
out.write(flush, 0, len);
}
out.flush();// 强制刷出
// 关闭流 先打开的后关闭
out.close();
in.close();
}
3、缓冲处理流:BufferedOutputStream 和 BufferedWriter
缓冲流提升性能,BufferedWriter存在新增方法newLine(),不能发生多态
public static void copyFile(String srcPath, String destPath) throws FileNotFoundException,IOException{
// 1、建立联系 源(存在且为文件) 目的地(文件可以不存在)
File src = new File(srcPath);
File dest = new File(destPath);
if(!src.isFile()){//不是文件或者为null时抛出异常
System.out.println("只能拷贝文件");
throw new IOException("只能拷贝文件");
}
// 2、选择流
InputStream in = new BufferedInputStream(new FileInputStream(src));
OutputStream out =new BufferedOutputStream(new FileOutputStream(dest));
// 3、操作
byte[] flush = new byte[1024];
int len = 0;
// 读取
while (-1 != (len = in.read(flush))) {
// 写出
out.write(flush, 0, len);
}
out.flush();// 强制刷出
// 关闭流 先打开的后关闭
out.close();
in.close();
}
}
//1、创建源 仅限于 字符的纯文本
File src=new File("f:/char.txt");
File dest=new File("f:/testIO/char.txt");
//2、选择流
BufferedReader reader=new BufferedReader(new FileReader(src));
BufferedWriter wr=new BufferedWriter(new FileWriter(dest,true));pend(msg2);
//3、新增方法操作
String line=null;
while(null!=(line=reader.readLine())){
wr.write(line);
//wr.append("\r\n");
//换行符号
wr.newLine();
}
wr.flush();//强制刷出
// 4、关闭流 先打开的后关闭
out.close();
in.close();
【实例】复制文件夹
package com.company;
import java.io.*;
public class Main{
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
File file = new File("E:/abc/abc.txt");
File beginFile=new File("E:/abc");
File endFile=new File("E:/cde");
//把文件夹abc.txt的所有文件拷贝到cde文件夹下
CopyFile.copyFile(file, endFile);
//把文件夹abc的所有文件拷贝到cde文件夹下
CopyFolder.copyFolder(beginFile, endFile);
}
}
class CopyFile{
public static void copyFile(String src,String dest){
copyFile(new File(src),new File(dest));
}
//复制文件
public static void copyFile(File scr ,File dest){
String str = dest.getAbsolutePath() + "\\" + scr.getName();
System.out.println(str);
//创建io流对象
InputStream is = null;
OutputStream os = null;
try {
is = new FileInputStream(scr);
os = new FileOutputStream(str);
//定义一个字节数组
byte[] bytes = new byte[1024];
int len = -1;
//以字节的形式读取文件,字节流
while ((len=is.read(bytes))!=-1){
//以字节的形式写入文件
os.write(bytes,0,len);
}
os.flush();
} catch (FileNotFoundException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}finally {
//关闭io流
if(os != null){
try {
os.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
if(is != null){
try {
is.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}
}
class CopyFolder{
public static void testFolder(String src , String dest) throws IOException { testFolder(new File(src), new File(dest)); }
//判断是否允许赋值当前文件夹
public static void testFolder(File src , File dest) throws IOException {
String srcStr = src.getAbsolutePath();
String destStr = dest.getAbsolutePath();
int index=srcStr.lastIndexOf('\\');
String str = srcStr.substring(0, index);
if(str.equals(dest) ||( str+"\\").equals(dest)||tautonym(srcStr,destStr)){
throw new IOException("不能把文件拷贝在当前文件所在路径下");
}
if(destStr.contains(str)&&tautonym(srcStr,destStr)){
throw new IOException("不能把文件拷贝到文件的子文件路径下");
}
}
//判断相同路径时是否出现重名
private static boolean tautonym(String src , String dest){
int index = src.lastIndexOf('\\');
String beginStr=src.substring(0,index);
if(beginStr.equals(dest)) {//判断文件是否拷贝在当前文件所在路径
return true;
}else{
//判断文件是否拷贝在当前文件的子文件路径下
String endStr = src.substring(index + 1);
String endString = dest.substring(index + 1);
int endIndex = endString.indexOf('\\');
if (endIndex != -1)
endString = endString.substring(0, endIndex);
if (endStr.equals(endString))
return true;
else
return false;
}
}
public static void copyFolder(String src , String dest) throws IOException{
copyFolder(new File(src),new File(dest));}
//复制文件夹
public static void copyFolder(File src , File dest) throws IOException {
testFolder(src, dest);
newPath(src, dest);
File[] lf = src.listFiles();
for(File fc:lf) {
if (fc.isDirectory()) { //若是目录,则递归打印该目录下的文件
copyFolder(fc, newPath(src, dest));
}
if (fc.isFile()){// 若是文件,直接打印
CopyFile.copyFile(fc,newPath(src,dest));
}
}
}
//创建文件夹的新路径
private static File newPath(File src,File dest){
//获取文件的绝对地址
String strSrc = src.getAbsolutePath();
String strDest = dest.getAbsolutePath();
int index=strSrc.lastIndexOf('\\');
String str = strSrc.substring(index+1);
//生成新路径的文件
File newRoute=new File(strDest + "\\" + str);
//对新文件在系统中生成目录
newRoute.mkdir();
return newRoute;
}
}