Java多线程(九)线程池之ScheduledThreadPoolExecutor概述
简介
在探讨时 ThreadPoolExecutor 只介绍了FixedThreadPool、CachedThreadPool、SingleThreadExecutor,并没有去介绍ScheduledThreadPoolExecutor,因为 ScheduledThreadPoolExecutor 与其他线程池的概念有些区别,它是一个支持任务周期性调度的线程池。
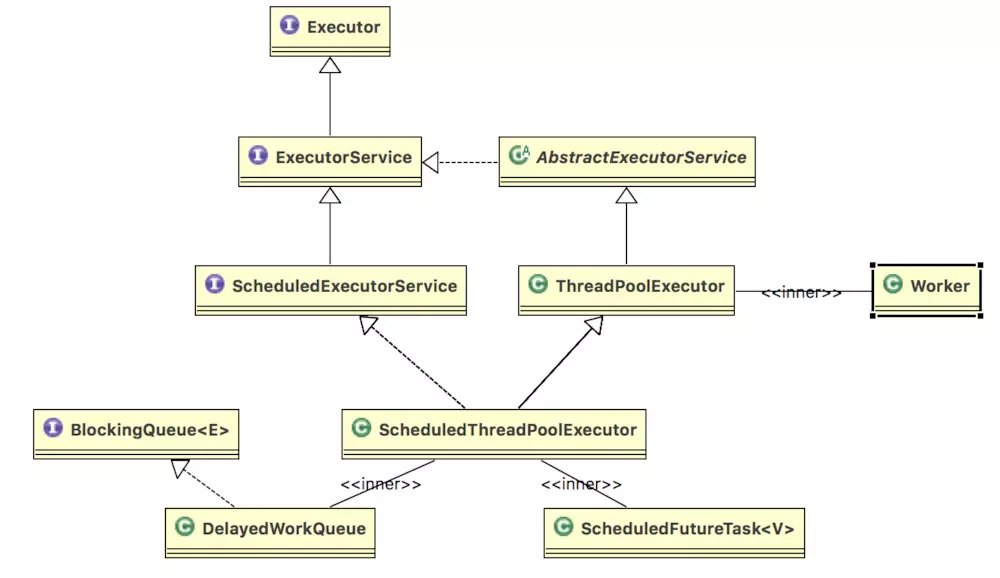
ScheduledThreadPoolExecutor 继承 ThreadPoolExecutor,同时通过实现 ScheduledExecutorSerivce 来扩展基础线程池的功能,使其拥有了调度能力。其整个调度的核心在于内部类 DelayedWorkQueue ,一个有序的延时队列。
ScheduledThreadPoolExecutor类图.png
ScheduledThreadPoolExecutor 的出现,很好的弥补了传统 Timer 的不足,具体对比看下表:
| Timer | ScheduledThreadPoolExecutor | |
|---|---|---|
| 线程 | 单线程 | 多线程 |
| 多任务 | 任务之间相互影响 | 任务之间不影响 |
| 调度时间 | 绝对时间 | 相对时间 |
| 异常 | 单任务异常, 后续任务受影响 |
无影响 |
构造方法
ScheduledThreadPoolExecutor有三个构造形式:
public ScheduledThreadPoolExecutor(int corePoolSize,
ThreadFactory threadFactory) {
super(corePoolSize, Integer.MAX_VALUE, 0, NANOSECONDS,
new DelayedWorkQueue(), threadFactory);
}
public ScheduledThreadPoolExecutor(int corePoolSize,
RejectedExecutionHandler handler) {
super(corePoolSize, Integer.MAX_VALUE, 0, NANOSECONDS,
new DelayedWorkQueue(), handler);
}
public ScheduledThreadPoolExecutor(int corePoolSize,
ThreadFactory threadFactory,
RejectedExecutionHandler handler) {
super(corePoolSize, Integer.MAX_VALUE, 0, NANOSECONDS,
new DelayedWorkQueue(), threadFactory, handler);
}
关于父类的构造可参见 ThreadPoolExecutor。当然我们也可以使用工具类Executors的newScheduledThreadPool的方法,快速创建。注意这里使用的DelayedWorkQueue。
ScheduledThreadPoolExecutor没有提供带有最大线程数的构造函数的,默认是Integer.MAX_VALUE,说明其可以无限制的开启任意线程执行任务,在大量任务系统,应注意这一点,避免内存溢出。
核心方法
核心方法主要介绍ScheduledThreadPoolExecutor的调度方法,其他方法与 ThreadPoolExecutor 一致。调度方法均由 ScheduledExecutorService 接口定义:
public interface ScheduledExecutorService extends ExecutorService {
// 特定时间延时后执行一次Runnable
public ScheduledFuture schedule(Runnable command,
long delay, TimeUnit unit);
// 特定时间延时后执行一次Callable
public ScheduledFuture schedule(Callable callable,
long delay, TimeUnit unit);
// 固定周期执行任务(与任务执行时间无关,周期是固定的)
public ScheduledFuture scheduleAtFixedRate(Runnable command,
long initialDelay,
long period,
TimeUnit unit);
// 固定延时执行任务(与任务执行时间有关,延时从上一次任务完成后开始)
public ScheduledFuture scheduleWithFixedDelay(Runnable command,
long initialDelay,
long delay,
TimeUnit unit);
}
代码中注释了每个方法的作用,需注意固定周期与固定延时的区别。下面分别对这些方法进行测试:
public class ScheduledPoolTest {
private static final SimpleDateFormat FORMAT = new SimpleDateFormat("hh:mm:ss");
private static final Random RANDOM = new Random();
/**
* 输出:
* 11:04:32
11:04:35
*/
public static void schedule() {
ScheduledExecutorService scheduledExecutorService = Executors.newScheduledThreadPool(1);
printTime();
scheduledExecutorService.schedule(new Task(), 3, TimeUnit.SECONDS);
}
/**
* 输出:
* 11:05:34
11:05:36
11:05:46
11:05:56
11:06:06
11:06:16
......
*/
public static void scheduleAtFixedRate() {
ScheduledExecutorService scheduledExecutorService = Executors.newScheduledThreadPool(1);
printTime();
scheduledExecutorService.scheduleAtFixedRate(new Task(), 2, 10, TimeUnit.SECONDS);
}
/**
* 输出:
* 11:07:39
11:07:41
11:07:54
11:08:08
11:08:22
11:08:33
......
*/
public static void scheduleWithFixedDelay() {
ScheduledExecutorService scheduledExecutorService = Executors.newScheduledThreadPool(1);
printTime();
scheduledExecutorService.scheduleWithFixedDelay(new Task(), 2, 10, TimeUnit.SECONDS);
}
static class Task implements Runnable{
public void run() {
printTime();
try {
Thread.sleep(RANDOM.nextInt(5) * 1000);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
public static void printTime() {
Date date = new Date();
System.out.println(FORMAT.format(date));
}
}
为了体现scheduleAtFixedRate和scheduleWithFixedDelay的差别,在代码中我们加入了随机睡眠时间,使任务执行不确定。从注释中的输出我们可以看到scheduleAtFixedRate的任务运行周期不受任务执行时间的影响,而scheduleWithFixedDelay的任务运行周期受任务执行时间影响较大。
但需注意,如果任务的执行时间超过任务调度周期,比如任务执行需要10s,而给定执行时间间隔是5s的话,任务的调度是在任务10s执行完之后立即重新执行,而不是5s的周期。
总结
ScheduledThreadPoolExecutor 在 ThreadPoolExecutor 的基础上扩展了 线程周期调度功能,使用时应注意控制其调度的时间点。