SpringBoot系列之JPA的使用
JPA的简单定义
对于我这样初次接触的人来说,jpa就是一种连接数据的api,由于JpaRepository接口提供了很多强大的方法,能很方便的拼接,从而能让我们对数据库的操作较为方便的进行操作。
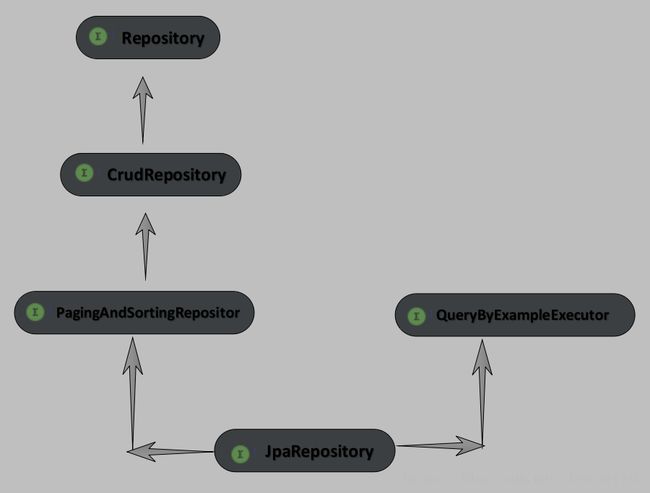
JpaRepository通过各种接口的继承,从而有了各种CRUD和分页之类的方法可以使用
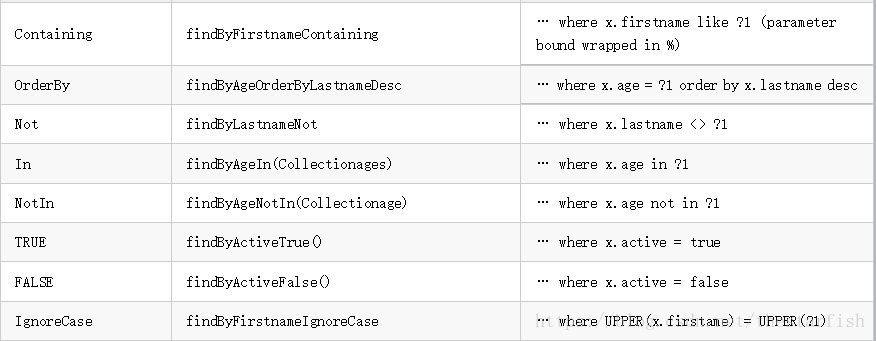
JPA关键字
SpringBoot JPA代码实例
文件目录阅览

简单的来说,其实就是先写一个UserEntity的,用来实现user表的实体。然后写UserRepository接口,来继承JpaRepository接口,通过关键字的拼接或者是原始的sql语句的书写,来编写我们需要使用的方法。然后再编写UserService接口,来提取我们需要使用到的处理数据库的方法。再通过UserServiceImpl来实现UserService接口。在UserServiceImpl类中实现接口中的方法。最后就是在我们的控制类中来调用方法就可以了。
下面是github的链接,jpa的小练习
https://github.com/wujianhuhu/jpa-practice
具体实现
UserEntity.java
创建一个UserEntity.java,用来实现user表的实体
@Table最好表明一下是什么表,name=“user”
其实还可以有schema="sqltest"表明数据库,catalog也是可以存在,和schema的效果差不多,不过mysql不支持catalog
jpa中,很多都是按照id来操作的,表中id的需求就是主键
@Entity
@Table(name = "user")
public class UserEntity {
private int id;
private String name;
private Integer age;
private String email;
private String telephone;
private String sex;
private String profession;
private String address;
@Id
@Column(name = "id")
public int getId() {
return id;
}
public void setId(int id) {
this.id = id;
}
@Basic
@Column(name = "name")
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
@Basic
@Column(name = "age")
public Integer getAge() {
return age;
}
public void setAge(Integer age) {
this.age = age;
}
@Basic
@Column(name = "email")
public String getEmail() {
return email;
}
public void setEmail(String email) {
this.email = email;
}
@Basic
@Column(name = "telephone")
public String getTelephone() {
return telephone;
}
public void setTelephone(String telephone) {
this.telephone = telephone;
}
@Basic
@Column(name = "sex")
public String getSex() {
return sex;
}
public void setSex(String sex) {
this.sex = sex;
}
@Basic
@Column(name = "profession")
public String getProfession() {
return profession;
}
public void setProfession(String profession) {
this.profession = profession;
}
@Basic
@Column(name = "address")
public String getAddress() {
return address;
}
public void setAddress(String address) {
this.address = address;
}
@Override
public boolean equals(Object o) {
if (this == o) {
return true;
}
if (o == null || getClass() != o.getClass()) {
return false;
}
UserEntity that = (UserEntity) o;
return id == that.id &&
Objects.equals(name, that.name) &&
Objects.equals(age, that.age) &&
Objects.equals(email, that.email) &&
Objects.equals(telephone, that.telephone) &&
Objects.equals(sex, that.sex) &&
Objects.equals(profession, that.profession) &&
Objects.equals(address, that.address);
}
@Override
public int hashCode() {
return Objects.hash(id, name, age, email, telephone, sex, profession, address);
}
}
UserRepository.java
这里其实是用来实现一些需要关键字组装的方法,或者是通过原始的sql语句来实现的对数据操作的方法。
这里的方法其实只需要未存在的方法就好,不需要已经存在的,比如下面的findAll(),因为继承的接口存在了,所以需要额外的@Override,而且也是不需要的。
1. 如果原生的sql语句在idea中会有背景颜色,可以使用alt+enter然后将语句检查调整为mysql就可以了
2. 在进行update或者是delete时,需要加上@Modifying,同时也是需要加上@Transaction事物
public interface UserRepository extends JpaRepository<UserEntity, Integer> {
/**
* 通过id来查询user表中的数据
*
* @param id 参数id
* @return 返回通过id查询出来的实体
*/
UserEntity findAllById (int id);
/**
* 查询所有的数据
*
* @return 返回表中所有的数据
*/
@Override
List<UserEntity> findAll();
/**
* 利用原始的sql语句进行对指定id数据的删除
*
* @param id 参数id
*
* 这种方式是使用@Param方式,采用的是:id,然后和Param中的名字一致
*/
@Query(value = "delete from user where user.id = :id ", nativeQuery = true)
@Modifying
@Transactional(rollbackOn = Exception.class)
void deleteOrderById(@Param("id") int id);
/**
* 通过id来改变这条数据中的电话号码
*
* @param telephone 需要改变的电话号码
* @param id 参数id
*
* 这里的参数采用了?1,?2这样的方式,直接对应第几个参数
*/
@Query(value = "update user set user.telephone = ?1 where user.id = ?2", nativeQuery = true)
@Modifying
@Transactional(rollbackOn = Exception.class)
void updataTelephoneById(String telephone, int id);
}
UserService.java
这里自己创建一个接口UserService,里面编写好自己需要的调用方法
public interface UserService {
/**
* 通过id来查询数据
* @param id 参数id
* @return 返回通过id查询出来的结果
*/
UserEntity findAllById(int id);
/**
* 查询表中所有数据
*
* @return 返回所有的数据
*/
List<UserEntity> findAll();
/**
* 通过id删除数据
*
* @param id 参数id
*/
void deleteOrderById(int id);
/**
* 通过id确认数据,并修改其telephone的值
*
* @param telephone 修改后的telephone
* @param id 参数id
*/
void updateTelephoneById(String telephone, int id);
}
UserServiceImpl.java
创建一个UserService接口的实现类,通过@Resource或者是@Autowired来自动注入UserRepository接口,然后通过userRepository来重写UserService这些方法,来具体实现这些方法。
不要忘记@Service,方便能自动装配UserService接口,因为只有这个类来实现,所以不需要在装配的时候来区分
@Service
public class UserServiceImpl implements UserService {
@Resource
private UserRepository userRepository;
@Override
public UserEntity findAllById(int id) {
return userRepository.findAllById(id);
}
@Override
public List<UserEntity> findAll() {
return userRepository.findAll();
}
@Override
public void deleteOrderById(int id) {
userRepository.deleteOrderById(id);
}
@Override
public void updateTelephoneById(String telephone, int id) {
userRepository.updataTelephoneById(telephone, id);
}
}
Main.java
接下来就是实现和调用一下数据库操作的方法了
首先先自动装配UserService接口,然后再调用接口里面的方法
@RestController
public class Main {
@Resource
private UserService userService;
/**
* 这是最普通的url的方式
* localhost:8080/printFindAll
*/
@RequestMapping("/printFindAll")
public List<UserEntity> printFindAll(){
return userService.findAll();
}
/**
* 这种方式是采用@RequestParam
* localhost:8080/printFindAllById?id=2
*/
@RequestMapping("/printFindAllById")
public UserEntity printFindAllById(@RequestParam("id") int id){
return userService.findAllById(id);
}
/**
* 采用@PathVariable
* localhost:8080/printDeleteById/2
*/
@RequestMapping("/printDeleteById/{id}")
public List<UserEntity> printDeleteById(@PathVariable("id") int id){
userService.deleteOrderById(id);
return userService.findAll();
}
/**
* 混合@PathVariable和@RequestParam
* localhost:8080/printUpdateTelephoneById/17825465874?id=2
*/
@RequestMapping("/printUpdateTelephoneById/{telephone}")
public UserEntity printUpdateTelephoneById(@PathVariable("telephone") String telephone, @RequestParam("id") int id){
userService.updateTelephoneById(telephone, id);
return userService.findAllById(id);
}
}
JPA中Entity的自动生成
首先连接database,将自己的数据库连接进来
View->Tool Windows->Database
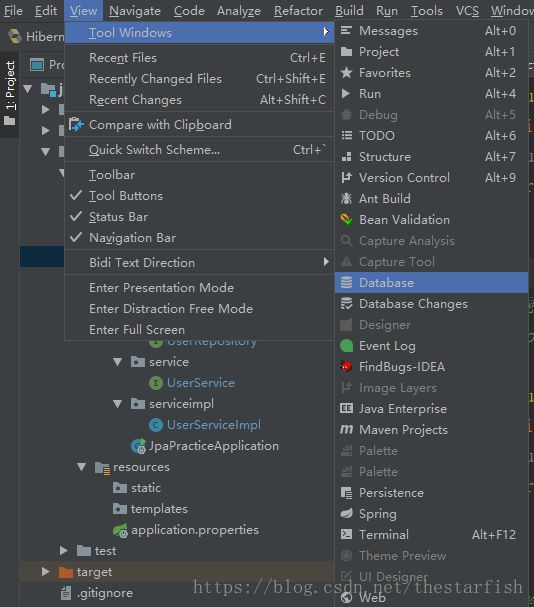
接下来开始生成实体Bean
右键->Cenerate Persistence Mapping->By Database Schema

选择自己生成的实体的路径,在选择数据库中的表,直接默认生成即可

总结
这只是我第一次来学习jpa的使用,其实还是有很多不足的地方。如果有错误之处,望不吝赐教。
想多保留一下这样的博客,可以为自己的进步增加一点点的帮助。