YOLOv3训练数据处理解析
图像增强pipeline:
1.获取图像和目标框信息
2.随机缩放图像到一定尺寸
3. 把图像贴到416*416的灰色画布上的随机位置
4.随机左右翻转(50%概率发生)
5.在HSV空间对图像色彩进行随机变换(实际图像灰度值被缩放到了[0,1])
6.修正目标框信息到新图像上
def get_random_data(annotation_line, input_shape, random=True, max_boxes=20, jitter=.3, hue=.1, sat=1.5, val=1.5, proc_img=True):
'''
****输入****
annotation_line:单张图片路径和标签信息
eg. "/media/yolo3-keras/VOCdevkit/VOC2007/JPEGImages/000001.jpg 48,240,195,371,11 8,12,352,498,14"
input_shape:模型输入尺寸(416,416)
random,proc_img:好像未被使用
max_boxes:每张图最多多少个目标(标准化输出)
jitter,hue,sat,val:数据增强相关参数
****输出****
image_data:图像数据[416,416,3]
box_data:目标框数据[max_boxes,5]
'''
line = annotation_line.split()
image = Image.open(line[0])
iw, ih = image.size
h, w = input_shape
box = np.array([np.array(list(map(int,box.split(',')))) for box in line[1:]])
# 1.生成随机宽高比缩放图像
new_ar = w/h * rand(1-jitter,1+jitter)/rand(1-jitter,1+jitter)
scale = rand(.25, 2)
if new_ar < 1:
nh = int(scale*h)
nw = int(nh*new_ar)
else:
nw = int(scale*w)
nh = int(nw/new_ar)
image = image.resize((nw,nh), Image.BICUBIC)
# 2.生成416*416的灰色画布,把缩放后的图像贴上去
dx = int(rand(0, w-nw))
dy = int(rand(0, h-nh))
new_image = Image.new('RGB', (w,h), (128,128,128))
new_image.paste(image, (dx, dy))
image = new_image
# 3.50%的概率图像左右翻转
flip = rand()<.5
if flip: image = image.transpose(Image.FLIP_LEFT_RIGHT)
# 4.HSV颜色空间对图像进行变形
hue = rand(-hue, hue)
sat = rand(1, sat) if rand()<.5 else 1/rand(1, sat)
val = rand(1, val) if rand()<.5 else 1/rand(1, val)
x = rgb_to_hsv(np.array(image)/255.)
x[..., 0] += hue
x[..., 0][x[..., 0]>1] -= 1
x[..., 0][x[..., 0]<0] += 1
x[..., 1] *= sat
x[..., 2] *= val
x[x>1] = 1
x[x<0] = 0
image_data = hsv_to_rgb(x) # numpy array, 0 to 1
# 5.调整目标框位置到增强后的图像
box_data = np.zeros((max_boxes,5))
if len(box)>0:
np.random.shuffle(box)
box[:, [0,2]] = box[:, [0,2]]*nw/iw + dx
box[:, [1,3]] = box[:, [1,3]]*nh/ih + dy
if flip: box[:, [0,2]] = w - box[:, [2,0]]
box[:, 0:2][box[:, 0:2]<0] = 0
box[:, 2][box[:, 2]>w] = w
box[:, 3][box[:, 3]>h] = h
box_w = box[:, 2] - box[:, 0]
box_h = box[:, 3] - box[:, 1]
box = box[np.logical_and(box_w>1, box_h>1)] # discard invalid box
if len(box)>max_boxes: box = box[:max_boxes]
box_data[:len(box)] = box
return image_data, box_data把box_data映射到anchor上
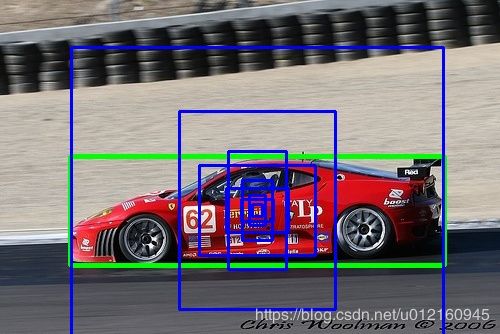
这里我们以这张图为例,它的boundingbox(绿色)为[70,156,444,265]。与之对应中心点为(257, 210),对应9个anchorbox(蓝色)
很显然最外面的框IOU最大,这个anchor对应的为[373,326]即第9个anchor对应13*13的特征图
y_true的shape为[(batch_size,13,13,3,25),(batch_size,26,26,3,25),(batch_size,52,52,3,25)]
所以对应位置为y_true[0][:,257//(h//13),210//(w//13),2,:] (13*13尺度上第3个anchor;h,w为原始图像高宽)
这里图像宽高为500*344,所以对应为y_true[0][:,9,5,2,:]的位置,把实际情况的数值把这里的(4+1+c)维填满即可
(4对应位置,1对应有无物体,c对应c个分类)
具体细节还是需要看代码进行理解
def preprocess_true_boxes(true_boxes, input_shape, anchors, num_classes):
'''
****输入****
true_boxes:真实框array[batch_size,20,5]
input_shape:输入图像尺寸tuple(416,416)
anchors:锚框array(9个)
eg.
[[ 10. 13.]
[ 16. 30.]
[ 33. 23.]
[ 30. 61.]
[ 62. 45.]
[ 59. 119.]
[116. 90.]
[156. 198.]
[373. 326.]]
num_classes:类别数
****输出****
y_true:映射到锚框后的结果(真实值)[(_, 13, 13, 3, 25),(_, 26, 26, 3, 25),(_, 52, 52, 3, 25)]
'''
assert (true_boxes[..., 4]0
# 4.3 对每一张图进行处理
for b in range(m):
# 4.3.1 取出图片目标框的宽和高,假设中心点为(0,0)计算左上角,右下角坐标
wh = boxes_wh[b, valid_mask[b]]
if len(wh)==0: continue
# [n,1,2]
wh = np.expand_dims(wh, -2)
box_maxes = wh / 2.
box_mins = -box_maxes
# 4.3.2 计算目标框和所有先验框的IOU,找到和目标最匹配的先验框是第几个
intersect_mins = np.maximum(box_mins, anchor_mins)
intersect_maxes = np.minimum(box_maxes, anchor_maxes)
intersect_wh = np.maximum(intersect_maxes - intersect_mins, 0.)
intersect_area = intersect_wh[..., 0] * intersect_wh[..., 1]
box_area = wh[..., 0] * wh[..., 1]
anchor_area = anchors[..., 0] * anchors[..., 1]
iou = intersect_area / (box_area + anchor_area - intersect_area)
best_anchor = np.argmax(iou, axis=-1)
for t, n in enumerate(best_anchor):
for l in range(num_layers):
if n in anchor_mask[l]:
# floor用于向下取整
i = np.floor(true_boxes[b,t,0]*grid_shapes[l][1]).astype('int32')
j = np.floor(true_boxes[b,t,1]*grid_shapes[l][0]).astype('int32')
# 找到真实框在特征层l中第b副图像对应的位置
k = anchor_mask[l].index(n)
c = true_boxes[b,t, 4].astype('int32')
y_true[l][b, j, i, k, 0:4] = true_boxes[b,t, 0:4]
y_true[l][b, j, i, k, 4] = 1
y_true[l][b, j, i, k, 5+c] = 1
return y_true