java.lang.IllegalStateException Fragment already added: HomeFragment id=0x7f0904ef android:switcher
今天对项目进行了重构,然后运行项目,就发现了这个报错信息:
java.lang.IllegalStateException
Fragment already added: HomeFragment{5b306a7} (b00b6e10-e234-408f-bb03-99ecf58a9c5a) id=0x7f0904ef android:switcher:2131297519:0}
堆栈信息如下:
androidx.fragment.app.FragmentStore.addFragment(FragmentStore.java:67)
androidx.fragment.app.FragmentManager.addFragment(FragmentManager.java:1563)
androidx.fragment.app.BackStackRecord.executeOps(BackStackRecord.java:405)
androidx.fragment.app.FragmentManager.executeOps(FragmentManager.java:2167)
androidx.fragment.app.FragmentManager.executeOpsTogether(FragmentManager.java:1990)
androidx.fragment.app.FragmentManager.removeRedundantOperationsAndExecute(FragmentManager.java:1945)
androidx.fragment.app.FragmentManager.execPendingActions(FragmentManager.java:1847)
androidx.fragment.app.FragmentManager$4.run(FragmentManager.java:413)
android.os.Handler.handleCallback(Handler.java:873)
android.os.Handler.dispatchMessage(Handler.java:99)
android.os.Looper.loop(Looper.java:193)
android.app.ActivityThread.main(ActivityThread.java:6669)
java.lang.reflect.Method.invoke(Native Method)
com.android.internal.os.RuntimeInit$MethodAndArgsCaller.run(RuntimeInit.java:493)
com.android.internal.os.ZygoteInit.main(ZygoteInit.java:858)先说明下,报错信息在主页面中,用的是ViewPager+FragmentPagerAdapter的方式加载了四个Fragment做切换。
这个堆栈信息没有标识出真正报错的源头在哪里,只是说,Fragment被重复添加了
Bugly上的对此bug的解决方案如下:
1. 该异常表示fragment已经被添加过,通常是因为重复添加fragment导致的,建议调用FragmentTransaction.add方法,先判断fragment.isAdded()。
[解决方案]:以下是参考解决方案:
if (fragment.isAdded()) {
fragmentManager.beginTransaction().show(fragment).commit();
} else {
fragmentManager.beginTransaction().remove(fragment).commit();
frament = new Fragment();
fragmentManager.beginTransaction().add(R.id.layout_frame, fragment).commit();
}
2. 该异常还经常发生在使用DialogFragment的场景下,DialogFragment也是Fragment的一个子类,其show()方法等同于FragmentTransaction.add()方法,dismiss()方法等同于FragmentTransaction.remove()方法。所以发生异常的原因同上。解决方案如下:
if (dialogFragment.isAdded())
dialogFragment.dismiss();
else
dialogFragment.show();网上的方法也都类似,但是我找遍了整个项目里面都没有发现Fragment被重复添加的代码。这就让人不知所措了。
于是我对照了整个项目中被我改过的地方,发现我做了一个公用的组件,组件里面使用了Butterknife来找控件,然后在这个组件里面我多定义了一个控件,而这个控件对应的id实际是不存在的。我们来看下Butterknife查找控件时怎么处理的。
首先,Butterknife使用注解生成XXXX_ViewBinding类,例如LoginActivity_ViewBinding类,看下它的初始化方法
@UiThread
public LoginActivity_ViewBinding(LoginActivity target, View source) {
this.target = target;
target.mInputName = Utils.findRequiredViewAsType(source, R.id.input_name, "field 'mInputName'", ClearEditText.class);
target.mInputPwd = Utils.findRequiredViewAsType(source, R.id.input_pwd, "field 'mInputPwd'", ClearEditText.class);
target.mShowPwd = Utils.findRequiredViewAsType(source, R.id.show_pwd, "field 'mShowPwd'", CheckBox.class);
target.mLogin = Utils.findRequiredViewAsType(source, R.id.login, "field 'mLogin'", Button.class);
}findView的逻辑放在了Utils.findRequiredViewAsType()方法中
public static T findRequiredViewAsType(View source, @IdRes int id, String who,
Class cls) {
View view = findRequiredView(source, id, who);
return castView(view, id, who, cls);
} 然后又调用了findRequiredView()方法
public static View findRequiredView(View source, @IdRes int id, String who) {
View view = source.findViewById(id);
if (view != null) {
return view;
}
String name = getResourceEntryName(source, id);
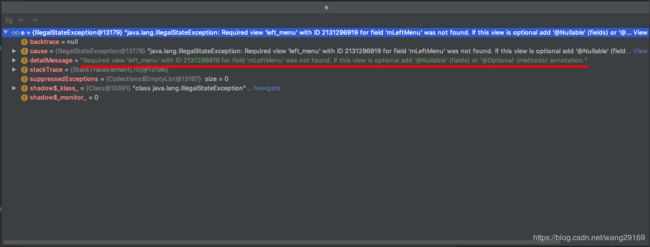
throw new IllegalStateException("Required view '"
+ name
+ "' with ID "
+ id
+ " for "
+ who
+ " was not found. If this view is optional add '@Nullable' (fields) or '@Optional'"
+ " (methods) annotation.");
}在这个方法的最后,对于没有找到的view抛出IllegalStateException的异常。
在这个方法中设置了断点,然后按F5追踪,然后就发现了下面这一幕
finishUpdate是FragmentPagerAdapter中的方法,它捕获了IllegalStateException异常,如下
这个异常正是Butterknife的findRequiredView()方法抛出的,但是被FragmentPagerAdapter捕获到了,继续追踪代码调用轨迹,然后发现它调用了FragmentTransaction接口的commitAllowingStateLoss()方法,在子类BackStackRecord中实现,如下
@Override
public int commitAllowingStateLoss() {
return commitInternal(true);
}commitAllowingStateLoss调用了commitInternal(),如下
int commitInternal(boolean allowStateLoss) {
......
mManager.enqueueAction(this, allowStateLoss);
return mIndex;
}commitInternal调用了FragmentManager类的enqueueAction()方法,如下
void enqueueAction(@NonNull OpGenerator action, boolean allowStateLoss) {
if (!allowStateLoss) {
if (mHost == null) {
if (mDestroyed) {
throw new IllegalStateException("FragmentManager has been destroyed");
} else {
throw new IllegalStateException("FragmentManager has not been attached to a "
+ "host.");
}
}
checkStateLoss();
}
synchronized (mPendingActions) {
if (mHost == null) {
if (allowStateLoss) {
// This FragmentManager isn't attached, so drop the entire transaction.
return;
}
throw new IllegalStateException("Activity has been destroyed");
}
mPendingActions.add(action);
//代码1
scheduleCommit();
}
}enqueueAction方法的最后调用了scheduleCommit()方法,如下
void scheduleCommit() {
synchronized (this) {
boolean postponeReady =
mPostponedTransactions != null && !mPostponedTransactions.isEmpty();
boolean pendingReady = mPendingActions != null && mPendingActions.size() == 1;
if (postponeReady || pendingReady) {
mHost.getHandler().removeCallbacks(mExecCommit);
//代码1
mHost.getHandler().post(mExecCommit);
}
}
}代码1中执行了Runnable接口实例mExecCommit,如下所示,注意从此处开始,就能够和前面的堆栈信息对应上了
Runnable mExecCommit = new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
execPendingActions();
}
};mExecCommit的run方法中调用了execPendingActions,如下
public boolean execPendingActions() {
ensureExecReady(true);
boolean didSomething = false;
while (generateOpsForPendingActions(mTmpRecords, mTmpIsPop)) {
mExecutingActions = true;
try {
//代码1
removeRedundantOperationsAndExecute(mTmpRecords, mTmpIsPop);
} finally {
cleanupExec();
}
didSomething = true;
}
doPendingDeferredStart();
burpActive();
return didSomething;
}然后在代码1处又调用了removeRedundantOperationsAndExecute()方法
private void removeRedundantOperationsAndExecute(ArrayList records,
ArrayList isRecordPop) {
if (records == null || records.isEmpty()) {
return;
}
if (isRecordPop == null || records.size() != isRecordPop.size()) {
throw new IllegalStateException("Internal error with the back stack records");
}
// Force start of any postponed transactions that interact with scheduled transactions:
executePostponedTransaction(records, isRecordPop);
final int numRecords = records.size();
int startIndex = 0;
for (int recordNum = 0; recordNum < numRecords; recordNum++) {
final boolean canReorder = records.get(recordNum).mReorderingAllowed;
if (!canReorder) {
// execute all previous transactions
if (startIndex != recordNum) {
//代码1
executeOpsTogether(records, isRecordPop, startIndex, recordNum);
}
// execute all pop operations that don't allow reordering together or
// one add operation
int reorderingEnd = recordNum + 1;
if (isRecordPop.get(recordNum)) {
while (reorderingEnd < numRecords
&& isRecordPop.get(reorderingEnd)
&& !records.get(reorderingEnd).mReorderingAllowed) {
reorderingEnd++;
}
}
//代码2
executeOpsTogether(records, isRecordPop, recordNum, reorderingEnd);
startIndex = reorderingEnd;
recordNum = reorderingEnd - 1;
}
}
if (startIndex != numRecords) {
//代码3
executeOpsTogether(records, isRecordPop, startIndex, numRecords);
}
} 在代码1,2,3处都调用了executeOpsTogether方法
private void executeOpsTogether(ArrayList records,
ArrayList isRecordPop, int startIndex, int endIndex) {
final boolean allowReordering = records.get(startIndex).mReorderingAllowed;
boolean addToBackStack = false;
if (mTmpAddedFragments == null) {
mTmpAddedFragments = new ArrayList<>();
} else {
mTmpAddedFragments.clear();
}
mTmpAddedFragments.addAll(mAdded);
Fragment oldPrimaryNav = getPrimaryNavigationFragment();
for (int recordNum = startIndex; recordNum < endIndex; recordNum++) {
final BackStackRecord record = records.get(recordNum);
final boolean isPop = isRecordPop.get(recordNum);
if (!isPop) {
oldPrimaryNav = record.expandOps(mTmpAddedFragments, oldPrimaryNav);
} else {
oldPrimaryNav = record.trackAddedFragmentsInPop(mTmpAddedFragments, oldPrimaryNav);
}
addToBackStack = addToBackStack || record.mAddToBackStack;
}
mTmpAddedFragments.clear();
if (!allowReordering) {
FragmentTransition.startTransitions(this, records, isRecordPop, startIndex, endIndex,
false);
}
//代码1
executeOps(records, isRecordPop, startIndex, endIndex);
。。。。。。
} 在方法的中间位置代码1处中调用了executeOps,如下
private static void executeOps(ArrayList records,
ArrayList isRecordPop, int startIndex, int endIndex) {
for (int i = startIndex; i < endIndex; i++) {
final BackStackRecord record = records.get(i);
final boolean isPop = isRecordPop.get(i);
if (isPop) {
record.bumpBackStackNesting(-1);
// Only execute the add operations at the end of
// all transactions.
boolean moveToState = i == (endIndex - 1);
record.executePopOps(moveToState);
} else {
record.bumpBackStackNesting(1);
//代码1,调用BackStackRecord类executeOps方法
record.executeOps();
}
}
} 代码1处,调用BackStackRecord类的executeOps()方法
void executePopOps(boolean moveToState) {
for (int opNum = mOps.size() - 1; opNum >= 0; opNum--) {
final Op op = mOps.get(opNum);
Fragment f = op.mFragment;
if (f != null) {
f.setNextTransition(FragmentManager.reverseTransit(mTransition));
}
switch (op.mCmd) {
case OP_ADD:
f.setNextAnim(op.mPopExitAnim);
mManager.setExitAnimationOrder(f, true);
mManager.removeFragment(f);
break;
case OP_REMOVE:
//代码1 重新添加Fragment
f.setNextAnim(op.mPopEnterAnim);
mManager.addFragment(f);
break;
case OP_HIDE:
f.setNextAnim(op.mPopEnterAnim);
mManager.showFragment(f);
break;
case OP_SHOW:
f.setNextAnim(op.mPopExitAnim);
mManager.setExitAnimationOrder(f, true);
mManager.hideFragment(f);
break;
case OP_DETACH:
f.setNextAnim(op.mPopEnterAnim);
mManager.attachFragment(f);
break;
case OP_ATTACH:
f.setNextAnim(op.mPopExitAnim);
mManager.setExitAnimationOrder(f, true);
mManager.detachFragment(f);
break;
case OP_SET_PRIMARY_NAV:
mManager.setPrimaryNavigationFragment(null);
break;
case OP_UNSET_PRIMARY_NAV:
mManager.setPrimaryNavigationFragment(f);
break;
case OP_SET_MAX_LIFECYCLE:
mManager.setMaxLifecycle(f, op.mOldMaxState);
break;
default:
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Unknown cmd: " + op.mCmd);
}
if (!mReorderingAllowed && op.mCmd != OP_REMOVE && f != null) {
mManager.moveFragmentToExpectedState(f);
}
}
if (!mReorderingAllowed && moveToState) {
mManager.moveToState(mManager.mCurState, true);
}
}在switch的OP_REMOVE分支,也就是代码1处,调用了FragmentManager的addFragment方法
void addFragment(@NonNull Fragment fragment) {
if (isLoggingEnabled(Log.VERBOSE)) Log.v(TAG, "add: " + fragment);
makeActive(fragment);
if (!fragment.mDetached) {
//代码1 调用FragmentStore的addFragment方法
mFragmentStore.addFragment(fragment);
fragment.mRemoving = false;
if (fragment.mView == null) {
fragment.mHiddenChanged = false;
}
if (isMenuAvailable(fragment)) {
mNeedMenuInvalidate = true;
}
}
}代码1处 又调用了FragmentStore的addFragment方法
void addFragment(@NonNull Fragment fragment) {
if (mAdded.contains(fragment)) {
throw new IllegalStateException("Fragment already added: " + fragment);
}
synchronized (mAdded) {
mAdded.add(fragment);
}
fragment.mAdded = true;
}最后再这个方法中判断是否已经添加过Fragment,然后抛出异常,这个就是整个报错的信息的过程了。
这样的报错信息是很有迷惑性的,总的来说,就是在FragmentPageAdapter加载Fragment的过程中,只要是遇到了IllegalStateException的错误,会直接捕获到,然后自己做处理,但是这个处理的代码中还会继续报错,也就是Fragment already added异常,具体原因还要仔细查看源码。
为了测试这个问题,尝试手动Fragment初始化的过程中抛出IllegalStateException,发现在logcat同样也会报同样的错误
所以很多时候,开发工具报错信息并没有给出具体的报错路径可能也是这个原因,原始的异常信息被Api捕获到,然后处理了之后又发生了异常,这也是解决bug的一个新的思路,不过比较难找。