LeetCode刷题--链表的相交节点
编写一个程序,找到两个单链表相交的起始节点。
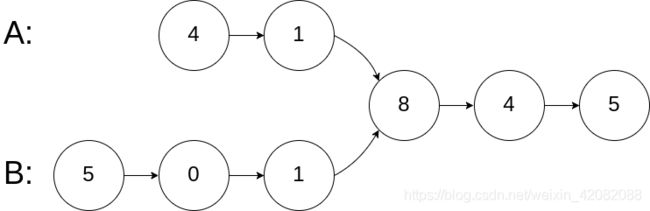
如下面的两个链表:在节点 c1 开始相交。
输入:intersectVal = 8, listA = [4,1,8,4,5], listB = [5,0,1,8,4,5], skipA = 2, skipB = 3
输出:Reference of the node with value = 8
输入解释:相交节点的值为 8 (注意,如果两个列表相交则不能为 0)。从各自的表头开始算起,链表 A 为 [4,1,8,4,5],链表 B 为 [5,0,1,8,4,5]。在 A 中,相交节点前有 2 个节点;在 B 中,相交节点前有 3 个节点。
输入:intersectVal = 2, listA = [0,9,1,2,4], listB = [3,2,4], skipA = 3, skipB = 1
输出:Reference of the node with value = 2
输入解释:相交节点的值为 2 (注意,如果两个列表相交则不能为 0)。从各自的表头开始算起,链表 A 为 [0,9,1,2,4],链表 B 为 [3,2,4]。在 A 中,相交节点前有 3 个节点;在 B 中,相交节点前有 1 个节点。
解法一:暴力法
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* public class ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode next;
* ListNode(int x) {
* val = x;
* next = null;
* }
* }
*/
public class Solution {
public ListNode getIntersectionNode(ListNode headA, ListNode headB) {
if(headA == null || headB == null){
return null;
}
while(headA != null ){
ListNode cur2 = headB;
while(cur2 != null){
//注意这里不能用值来比较
if(headA == cur2 ){
return cur2;
}else{cur2 = cur2.next;}
}
headA = headA.next;
}
return null;
}
}
解法二:构建环状链表
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* public class ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode next;
* ListNode(int x) {
* val = x;
* next = null;
* }
* }
*/
public class Solution {
public ListNode getIntersectionNode(ListNode headA, ListNode headB) {
ListNode a = headA;
ListNode b = headB;
while(a != b){
//当a指针下一个为空时,会返回到b的链表头
//结合图示去理解
if(a != null){
a = a.next;
}else{
a = headB;
}
if(b!= null){
b= b.next;
}else{
b= headA;
}
}
return a;
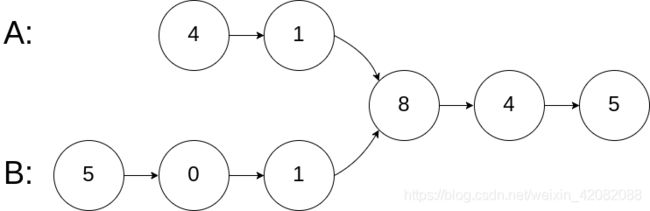
如图所示:
原结构如下:

构建8字环状链表:

定义两个指针:一个从a链表头出发,一个从b链表头出发,终会两个链表交点处相遇。
解法三:HashSet
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* public class ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode next;
* ListNode(int x) {
* val = x;
* next = null;
* }
* }
*/
public class Solution {
public ListNode getIntersectionNode(ListNode headA, ListNode headB) {
Set s = new HashSet();
ListNode a = headA;
ListNode b = headB;
while(a != null){
s.add(a);
a = a.next;
}
while(b != null){
if(s.contains(b)){
return b;
}
b = b.next;
}
return b;
}
}