windows 进程通信之管道详解 :
在项目中用到了Windows进程通信 ,需要用管道读子进程的标准输入,输出,于是研究了MSDN上的相关代码
代码源地址:https://msdn.microsoft.com/en-us/library/windows/desktop/ms682516(v=vs.85).aspx
ps :a代码中需要注意的是在CreateChildProcess中通过
siStartInfo.hStdErro=g_hChildStd_OUT_Wr;
siStartInfo.hStdOutput=g_hChildStd_OUT_Wr;
siStartInfo.HStdInput-g_hChildStd_IN_Rd;
通过以上代码,将子进程的标准错误输出,标准输出,标准输入都重定向为管道,这些管道是在主进程中创建的,可以被子进程继承!
#include
#include
#include
#include
#define BUFSIZE 4096
HANDLE g_hChildStd_IN_Rd = NULL;
HANDLE g_hChildStd_IN_Wr = NULL;
HANDLE g_hChildStd_OUT_Rd = NULL;
HANDLE g_hChildStd_OUT_Wr = NULL;
HANDLE g_hInputFile = NULL;
void CreateChildProcess(void);
void WriteToPipe(void);
void ReadFromPipe(void);
void ErrorExit(PTSTR);
int _tmain(int argc, TCHAR *argv[])
{
SECURITY_ATTRIBUTES saAttr;
printf("\n->Start of parent execution.\n");
// Set the bInheritHandle flag so pipe handles are inherited.
saAttr.nLength = sizeof(SECURITY_ATTRIBUTES);
saAttr.bInheritHandle = TRUE;
saAttr.lpSecurityDescriptor = NULL;
// Create a pipe for the child process's STDOUT.
if (!CreatePipe(&g_hChildStd_OUT_Rd, &g_hChildStd_OUT_Wr, &saAttr, 0))
ErrorExit(TEXT("StdoutRd CreatePipe"));
// Ensure the read handle to the pipe for STDOUT is not inherited.
if (!SetHandleInformation(g_hChildStd_OUT_Rd, HANDLE_FLAG_INHERIT, 0))
ErrorExit(TEXT("Stdout SetHandleInformation"));
// Create a pipe for the child process's STDIN.
if (!CreatePipe(&g_hChildStd_IN_Rd, &g_hChildStd_IN_Wr, &saAttr, 0))
ErrorExit(TEXT("Stdin CreatePipe"));
// Ensure the write handle to the pipe for STDIN is not inherited.
if (!SetHandleInformation(g_hChildStd_IN_Wr, HANDLE_FLAG_INHERIT, 0))
ErrorExit(TEXT("Stdin SetHandleInformation"));
// Create the child process.
CreateChildProcess();
// Get a handle to an input file for the parent.
// This example assumes a plain text file and uses string output to verify data flow.
if (argc == 1)
ErrorExit(TEXT("Please specify an input file.\n"));
g_hInputFile = CreateFile( ///此处是需要打开本地的一个文本文件,,在项目property中设置参数
argv[1],
GENERIC_READ,
0,
NULL,
OPEN_EXISTING,
FILE_ATTRIBUTE_READONLY,
NULL);
if (g_hInputFile == INVALID_HANDLE_VALUE)
ErrorExit(TEXT("CreateFile"));
// Write to the pipe that is the standard input for a child process.
// Data is written to the pipe's buffers, so it is not necessary to wait
// until the child process is running before writing data.
WriteToPipe();
printf("\n->Contents of %s written to child STDIN pipe.\n", argv[1]);
// Read from pipe that is the standard output for child process.
printf("\n->Contents of child process STDOUT:\n\n", argv[1]);
ReadFromPipe();
printf("\n->End of parent execution.\n");
// The remaining open handles are cleaned up when this process terminates.
// To avoid resource leaks in a larger application, close handles explicitly.
return 0;
}
void CreateChildProcess()
// Create a child process that uses the previously created pipes for STDIN and STDOUT.
{
//TCHAR szCmdline[] = TEXT("C:\\Project3.exe");
LPTSTR szCmdline = _tcsdup(_TEXT("C:\\Project3.exe"));//这是子进程可执行文件的路径
PROCESS_INFORMATION piProcInfo;
STARTUPINFO siStartInfo;
BOOL bSuccess = FALSE;
// Set up members of the PROCESS_INFORMATION structure.
ZeroMemory(&piProcInfo, sizeof(PROCESS_INFORMATION));
// Set up members of the STARTUPINFO structure.
// This structure specifies the STDIN and STDOUT handles for redirection.
ZeroMemory(&siStartInfo, sizeof(STARTUPINFO));
siStartInfo.cb = sizeof(STARTUPINFO);
siStartInfo.hStdError = g_hChildStd_OUT_Wr;
siStartInfo.hStdOutput = g_hChildStd_OUT_Wr;
siStartInfo.hStdInput = g_hChildStd_IN_Rd;
siStartInfo.dwFlags |= STARTF_USESTDHANDLES;
// Create the child process.
bSuccess = CreateProcess(NULL,
szCmdline, // command line
NULL, // process security attributes
NULL, // primary thread security attributes
TRUE, // handles are inherited
0, // creation flags
NULL, // use parent's environment
NULL, // use parent's current directory
&siStartInfo, // STARTUPINFO pointer
&piProcInfo); // receives PROCESS_INFORMATION
// If an error occurs, exit the application.
if (!bSuccess)
ErrorExit(TEXT("CreateProcess"));
else
{
// Close handles to the child process and its primary thread.
// Some applications might keep these handles to monitor the status
// of the child process, for example.
CloseHandle(piProcInfo.hProcess);
CloseHandle(piProcInfo.hThread);
}
}
void WriteToPipe(void)
// Read from a file and write its contents to the pipe for the child's STDIN.
// Stop when there is no more data.
{
DWORD dwRead, dwWritten;
CHAR chBuf[BUFSIZE];
BOOL bSuccess = FALSE;
for (;;)
{
bSuccess = ReadFile(g_hInputFile, chBuf, BUFSIZE, &dwRead, NULL);
if (!bSuccess || dwRead == 0) break;
bSuccess = WriteFile(g_hChildStd_IN_Wr, chBuf, dwRead, &dwWritten, NULL);
if (!bSuccess) break;
}
// Close the pipe handle so the child process stops reading.
if (!CloseHandle(g_hChildStd_IN_Wr))
ErrorExit(TEXT("StdInWr CloseHandle"));
}
void ReadFromPipe(void)
// Read output from the child process's pipe for STDOUT
// and write to the parent process's pipe for STDOUT.
// Stop when there is no more data.
{
DWORD dwRead, dwWritten;
CHAR chBuf[BUFSIZE];
BOOL bSuccess = FALSE;
HANDLE hParentStdOut = GetStdHandle(STD_OUTPUT_HANDLE);
for (;;)
{
bSuccess = ReadFile(g_hChildStd_OUT_Rd, chBuf, BUFSIZE, &dwRead, NULL);
if (!bSuccess || dwRead == 0) break;
bSuccess = WriteFile(hParentStdOut, chBuf,
dwRead, &dwWritten, NULL);
if (!bSuccess) break;
}
}
void ErrorExit(PTSTR lpszFunction)
// Format a readable error message, display a message box,
// and exit from the application.
{
LPVOID lpMsgBuf;
LPVOID lpDisplayBuf;
DWORD dw = GetLastError();
FormatMessage(
FORMAT_MESSAGE_ALLOCATE_BUFFER |
FORMAT_MESSAGE_FROM_SYSTEM |
FORMAT_MESSAGE_IGNORE_INSERTS,
NULL,
dw,
MAKELANGID(LANG_NEUTRAL, SUBLANG_DEFAULT),
(LPTSTR)&lpMsgBuf,
0, NULL);
lpDisplayBuf = (LPVOID)LocalAlloc(LMEM_ZEROINIT,
(lstrlen((LPCTSTR)lpMsgBuf) + lstrlen((LPCTSTR)lpszFunction) + 40)*sizeof(TCHAR));
StringCchPrintf((LPTSTR)lpDisplayBuf,
LocalSize(lpDisplayBuf) / sizeof(TCHAR),
TEXT("%s failed with error %d: %s"),
lpszFunction, dw, lpMsgBuf);
MessageBox(NULL, (LPCTSTR)lpDisplayBuf, TEXT("Error"), MB_OK);
LocalFree(lpMsgBuf);
LocalFree(lpDisplayBuf);
ExitProcess(1);
} 下面是子进程代码,我把子进程编译好命名为Project3 可执行文件为Project3.exe ,在上面的主进程需要调用这个可执行文件的绝对路径,这点需要注意,源网址直接调用了一个“child”,容易让新上手的人摸不着头脑,因为它省略了后缀.exe 和程序路径
#include
#include
#define BUFSIZE 4096
int main(void)
{
CHAR chBuf[BUFSIZE];
DWORD dwRead, dwWritten;
HANDLE hStdin, hStdout;
BOOL bSuccess;
hStdout = GetStdHandle(STD_OUTPUT_HANDLE);
hStdin = GetStdHandle(STD_INPUT_HANDLE);
if (
(hStdout == INVALID_HANDLE_VALUE) ||
(hStdin == INVALID_HANDLE_VALUE)
)
ExitProcess(1);
// Send something to this process's stdout using printf.
printf("\n ** This is a message from the child process. ** \n");
// This simple algorithm uses the existence of the pipes to control execution.
// It relies on the pipe buffers to ensure that no data is lost.
// Larger applications would use more advanced process control.
for (;;)
{
// Read from standard input and stop on error or no data.
bSuccess = ReadFile(hStdin, chBuf, BUFSIZE, &dwRead, NULL);
if (!bSuccess || dwRead == 0)
break;
// Write to standard output and stop on error.
bSuccess = WriteFile(hStdout, chBuf, dwRead, &dwWritten, NULL);
if (!bSuccess)
break;
}
return 0;
}
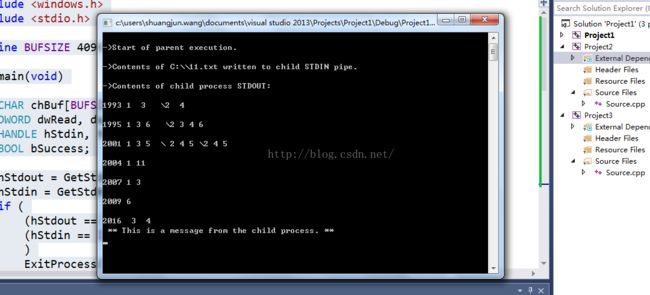
程序执行结果如下:
父进程从11.txt读数据,并把这些数据写到g_hChildStd_IN_Wr 中。子进程从管道中通过g_hChildStd_IN_Rd获得数据,再通过g_hChildStd_OUT_Wr中写到管道2中。父进程之后再从管道g_hChildStd_OUT_Rd中读取数据并显示。