操作系统实验一实验报告
实验一:系统软件启动过程
练习1:理解通过make生成执行文件的过程
1.1 操作系统镜像文件ucore.img是如何一步一步生成的?
Makefile如下,解释部分内容参考
http://blog.csdn.net/lijunfan1994/article/details/46038167
PROJ := challenge
EMPTY :=
SPACE := $(EMPTY) $(EMPTY)
SLASH := /
##make "V="可输出make执行的命令
V := @
#need llvm/cang-3.5+
#USELLVM := 1
##选择交叉编译器检查GCCPREFIX的设置
# try to infer the correct GCCPREFX
ifndef GCCPREFIX
GCCPREFIX := $(shell if i386-elf-objdump -i 2>&1 | grep '^elf32-i386$$' >/dev/null 2>&1; \
then echo 'i386-elf-'; \
elif objdump -i 2>&1 | grep 'elf32-i386' >/dev/null 2>&1; \
then echo ''; \
else echo "***" 1>&2; \
echo "*** Error: Couldn't find an i386-elf version of GCC/binutils." 1>&2; \
echo "*** Is the directory with i386-elf-gcc in your PATH?" 1>&2; \
echo "*** If your i386-elf toolchain is installed with a command" 1>&2; \
echo "*** prefix other than 'i386-elf-', set your GCCPREFIX" 1>&2; \
echo "*** environment variable to that prefix and run 'make' again." 1>&2; \
echo "*** To turn off this error, run 'gmake GCCPREFIX= ...'." 1>&2; \
echo "***" 1>&2; exit 1; fi)
endif
##设置QEMU
# try to infer the correct QEMU
ifndef QEMU
QEMU := $(shell if which qemu-system-i386 > /dev/null; \
then echo 'qemu-system-i386'; exit; \
elif which i386-elf-qemu > /dev/null; \
then echo 'i386-elf-qemu'; exit; \
elif which qemu > /dev/null; \
then echo 'qemu'; exit; \
else \
echo "***" 1>&2; \
echo "*** Error: Couldn't find a working QEMU executable." 1>&2; \
echo "*** Is the directory containing the qemu binary in your PATH" 1>&2; \
echo "***" 1>&2; exit 1; fi)
endif
# eliminate default suffix rules
.SUFFIXES: .c .S .h
##如果遇到error或者被中断了就删除所有目标文件
# delete target files if there is an error (or make is interrupted)
.DELETE_ON_ERROR:
##设置编译器选项
# define compiler and flags
ifndef USELLVM
##gcc编译,-g为了gdb调式,-Wall生成警告信息,-O2优化处理级别
HOSTCC := gcc
HOSTCFLAGS := -g -Wall -O2
CC := $(GCCPREFIX)gcc
##-fno-builtin不使用C语言的内建函数,-ggdb为GDB生成更丰富的调试信息,-m32用32位编译,-gstabs生成stabs格式调试信息但不包括GDB调试信息,-nostdinc不在系统默认头文件目录中寻找头文件,$(DEFS)未定义可用来扩展信息
CFLAGS := -fno-builtin -Wall -ggdb -m32 -gstabs -nostdinc $(DEFS)
##$(shell)可以输出shell指令,-fno-stack-protector禁用堆栈保护,-E仅预处理不进行编译汇编链接可以提高速度,-x c指明c语言
##/dev/null指定目标文件,>/dev/null 2>&1标准错误重定向到标准输出,&&先运行前一句若成功再运行后一句
##意为只预处理,所有出错全部作为垃圾(/dev/null类似垃圾文件)测试能否开启-fno-stack-protector,若能则CFLAGS += -fno-stack-protector
CFLAGS += $(shell $(CC) -fno-stack-protector -E -x c /dev/null >/dev/null 2>&1 && echo -fno-stack-protector)
else
##若使用clang,类似处理
HOSTCC := clang
HOSTCFLAGS := -g -Wall -O2
CC := clang
CFLAGS := -fno-builtin -Wall -g -m32 -mno-sse -nostdinc $(DEFS)
CFLAGS += $(shell $(CC) -fno-stack-protector -E -x c /dev/null >/dev/null 2>&1 && echo -fno-stack-protector)
endif
##源文件类型为.c和.S
CTYPE := c S
LD := $(GCCPREFIX)ld
##shell中命令 ld -V可以输出支持的版本,|管道将前者的输出作为后者的输入,grep在输入中搜索elf_i386字串,找到就输出elf_i386
##意味如果支持elf_i386则LDFLAGS := -m elf_i386
LDFLAGS := -m $(shell $(LD) -V | grep elf_i386 2>/dev/null)
##-nostdlib不连接系统标准库文件
LDFLAGS += -nostdlib
OBJCOPY := $(GCCPREFIX)objcopy
OBJDUMP := $(GCCPREFIX)objdump
##定义一些shell命令
COPY := cp
MKDIR := mkdir -p
MV := mv
RM := rm -f
AWK := awk
SED := sed
SH := sh
TR := tr
TOUCH := touch -c
OBJDIR := obj
BINDIR := bin
ALLOBJS :=
ALLDEPS :=
TARGETS :=
##在function.mk中定义了大量辅助函数,部分说明参考了引用中的博文
include tools/function.mk
##call:call func,变量1,变量2,...
##listf:列出某地址下某类型的文件
##listf_cc:列出变量1下的.c与.S文件
listf_cc = $(call listf,$(1),$(CTYPE))
# for cc
##将文件打包
add_files_cc = $(call add_files,$(1),$(CC),$(CFLAGS) $(3),$(2),$(4))
##创建目标文件包
create_target_cc = $(call create_target,$(1),$(2),$(3),$(CC),$(CFLAGS))
# for hostcc
add_files_host = $(call add_files,$(1),$(HOSTCC),$(HOSTCFLAGS),$(2),$(3))
create_target_host = $(call create_target,$(1),$(2),$(3),$(HOSTCC),$(HOSTCFLAGS))
##patsubst替换通配符
##cgtype(filenames,type1,type2)把文件名中type1的改为type2,如.c改为.o
cgtype = $(patsubst %.$(2),%.$(3),$(1))
##列出所有目标文件,并按规则改后缀名
objfile = $(call toobj,$(1))
asmfile = $(call cgtype,$(call toobj,$(1)),o,asm)
outfile = $(call cgtype,$(call toobj,$(1)),o,out)
symfile = $(call cgtype,$(call toobj,$(1)),o,sym)
# for match pattern
match = $(shell echo $(2) | $(AWK) '{for(i=1;i<=NF;i++){if(match("$(1)","^"$$(i)"$$")){exit 1;}}}'; echo $$?)
# >>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>
# include kernel/user
INCLUDE += libs/
CFLAGS += $(addprefix -I,$(INCLUDE))
LIBDIR += libs
$(call add_files_cc,$(call listf_cc,$(LIBDIR)),libs,)
# -------------------------------------------------------------------
# kernel
KINCLUDE += kern/debug/ \
kern/driver/ \
kern/trap/ \
kern/mm/
KSRCDIR += kern/init \
kern/libs \
kern/debug \
kern/driver \
kern/trap \
kern/mm
KCFLAGS += $(addprefix -I,$(KINCLUDE))
$(call add_files_cc,$(call listf_cc,$(KSRCDIR)),kernel,$(KCFLAGS))
KOBJS = $(call read_packet,kernel libs)
# create kernel target
##将所有文件链接生成kernel
kernel = $(call totarget,kernel)
$(kernel): tools/kernel.ld
$(kernel): $(KOBJS)
@echo + ld $@
$(V)$(LD) $(LDFLAGS) -T tools/kernel.ld -o $@ $(KOBJS)
@$(OBJDUMP) -S $@ > $(call asmfile,kernel)
@$(OBJDUMP) -t $@ | $(SED) '1,/SYMBOL TABLE/d; s/ .* / /; /^$$/d' > $(call symfile,kernel)
$(call create_target,kernel)
# -------------------------------------------------------------------
# create bootblock
##将所有文件链接生成bootblock
bootfiles = $(call listf_cc,boot)
$(foreach f,$(bootfiles),$(call cc_compile,$(f),$(CC),$(CFLAGS) -Os -nostdinc))
bootblock = $(call totarget,bootblock)
$(bootblock): $(call toobj,$(bootfiles)) | $(call totarget,sign)
@echo + ld $@
$(V)$(LD) $(LDFLAGS) -N -e start -Ttext 0x7C00 $^ -o $(call toobj,bootblock)
@$(OBJDUMP) -S $(call objfile,bootblock) > $(call asmfile,bootblock)
@$(OBJCOPY) -S -O binary $(call objfile,bootblock) $(call outfile,bootblock)
@$(call totarget,sign) $(call outfile,bootblock) $(bootblock)
$(call create_target,bootblock)
# -------------------------------------------------------------------
# create 'sign' tools
##生成sign辅助工具
$(call add_files_host,tools/sign.c,sign,sign)
$(call create_target_host,sign,sign)
# -------------------------------------------------------------------
# create ucore.img
##生成ucore.img
UCOREIMG := $(call totarget,ucore.img)
$(UCOREIMG): $(kernel) $(bootblock)
$(V)dd if=/dev/zero of=$@ count=10000
$(V)dd if=$(bootblock) of=$@ conv=notrunc
$(V)dd if=$(kernel) of=$@ seek=1 conv=notrunc
$(call create_target,ucore.img)
# >>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>
$(call finish_all)
IGNORE_ALLDEPS = clean \
dist-clean \
grade \
touch \
print-.+ \
handin
ifeq ($(call match,$(MAKECMDGOALS),$(IGNORE_ALLDEPS)),0)
-include $(ALLDEPS)
endif
# files for grade script
TARGETS: $(TARGETS)
.DEFAULT_GOAL := TARGETS
.PHONY: qemu qemu-nox debug debug-nox
qemu-mon: $(UCOREIMG)
$(V)$(QEMU) -no-reboot -monitor stdio -hda $< -serial null
qemu: $(UCOREIMG)
$(V)$(QEMU) -no-reboot -parallel stdio -hda $< -serial null
log: $(UCOREIMG)
$(V)$(QEMU) -no-reboot -d int,cpu_reset -D q.log -parallel stdio -hda $< -serial null
qemu-nox: $(UCOREIMG)
$(V)$(QEMU) -no-reboot -serial mon:stdio -hda $< -nographic
TERMINAL :=gnome-terminal
debug: $(UCOREIMG)
$(V)$(QEMU) -S -s -parallel stdio -hda $< -serial null &
$(V)sleep 2
$(V)$(TERMINAL) -e "gdb -q -tui -x tools/gdbinit"
debug-nox: $(UCOREIMG)
$(V)$(QEMU) -S -s -serial mon:stdio -hda $< -nographic &
$(V)sleep 2
$(V)$(TERMINAL) -e "gdb -q -x tools/gdbinit"
.PHONY: grade touch
GRADE_GDB_IN := .gdb.in
GRADE_QEMU_OUT := .qemu.out
HANDIN := proj$(PROJ)-handin.tar.gz
TOUCH_FILES := kern/trap/trap.c
MAKEOPTS := --quiet --no-print-directory
grade:
$(V)$(MAKE) $(MAKEOPTS) clean
$(V)$(SH) tools/grade.sh
touch:
$(V)$(foreach f,$(TOUCH_FILES),$(TOUCH) $(f))
print-%:
@echo $($(shell echo $(patsubst print-%,%,$@) | $(TR) [a-z] [A-Z]))
.PHONY: clean dist-clean handin packall tags
clean:
$(V)$(RM) $(GRADE_GDB_IN) $(GRADE_QEMU_OUT) cscope* tags
-$(RM) -r $(OBJDIR) $(BINDIR)
dist-clean: clean
-$(RM) $(HANDIN)
handin: packall
@echo Please visit http://learn.tsinghua.edu.cn and upload $(HANDIN). Thanks!
packall: clean
@$(RM) -f $(HANDIN)
@tar -czf $(HANDIN) `find . -type f -o -type d | grep -v '^\.*$$' | grep -vF '$(HANDIN)'`
tags:
@echo TAGS ALL
$(V)rm -f cscope.files cscope.in.out cscope.out cscope.po.out tags
$(V)find . -type f -name "*.[chS]" >cscope.files
$(V)cscope -bq
$(V)ctags -L cscope.files
调用make V=后结果如下
##lab1仅是ucore的开始,部分函数未完成调用会出现警告,此处可以无视
#kernel
+ cc kern/init/init.c
gcc -Ikern/init/ -fno-builtin -Wall -ggdb -m32 -gstabs -nostdinc -fno-stack-protector -Ilibs/ -Ikern/debug/ -Ikern/driver/ -Ikern/trap/ -Ikern/mm/ -c kern/init/init.c -o obj/kern/init/init.o
kern/init/init.c:95:1: warning: ‘lab1_switch_test’ defined but not used [-Wunused-function]
lab1_switch_test(void) {
^
+ cc kern/libs/stdio.c
gcc -Ikern/libs/ -fno-builtin -Wall -ggdb -m32 -gstabs -nostdinc -fno-stack-protector -Ilibs/ -Ikern/debug/ -Ikern/driver/ -Ikern/trap/ -Ikern/mm/ -c kern/libs/stdio.c -o obj/kern/libs/stdio.o
+ cc kern/libs/readline.c
gcc -Ikern/libs/ -fno-builtin -Wall -ggdb -m32 -gstabs -nostdinc -fno-stack-protector -Ilibs/ -Ikern/debug/ -Ikern/driver/ -Ikern/trap/ -Ikern/mm/ -c kern/libs/readline.c -o obj/kern/libs/readline.o
+ cc kern/debug/panic.c
gcc -Ikern/debug/ -fno-builtin -Wall -ggdb -m32 -gstabs -nostdinc -fno-stack-protector -Ilibs/ -Ikern/debug/ -Ikern/driver/ -Ikern/trap/ -Ikern/mm/ -c kern/debug/panic.c -o obj/kern/debug/panic.o
+ cc kern/debug/kdebug.c
gcc -Ikern/debug/ -fno-builtin -Wall -ggdb -m32 -gstabs -nostdinc -fno-stack-protector -Ilibs/ -Ikern/debug/ -Ikern/driver/ -Ikern/trap/ -Ikern/mm/ -c kern/debug/kdebug.c -o obj/kern/debug/kdebug.o
kern/debug/kdebug.c:251:1: warning: ‘read_eip’ defined but not used [-Wunused-function]
read_eip(void) {
^
+ cc kern/debug/kmonitor.c
gcc -Ikern/debug/ -fno-builtin -Wall -ggdb -m32 -gstabs -nostdinc -fno-stack-protector -Ilibs/ -Ikern/debug/ -Ikern/driver/ -Ikern/trap/ -Ikern/mm/ -c kern/debug/kmonitor.c -o obj/kern/debug/kmonitor.o
+ cc kern/driver/clock.c
gcc -Ikern/driver/ -fno-builtin -Wall -ggdb -m32 -gstabs -nostdinc -fno-stack-protector -Ilibs/ -Ikern/debug/ -Ikern/driver/ -Ikern/trap/ -Ikern/mm/ -c kern/driver/clock.c -o obj/kern/driver/clock.o
+ cc kern/driver/console.c
gcc -Ikern/driver/ -fno-builtin -Wall -ggdb -m32 -gstabs -nostdinc -fno-stack-protector -Ilibs/ -Ikern/debug/ -Ikern/driver/ -Ikern/trap/ -Ikern/mm/ -c kern/driver/console.c -o obj/kern/driver/console.o
+ cc kern/driver/picirq.c
gcc -Ikern/driver/ -fno-builtin -Wall -ggdb -m32 -gstabs -nostdinc -fno-stack-protector -Ilibs/ -Ikern/debug/ -Ikern/driver/ -Ikern/trap/ -Ikern/mm/ -c kern/driver/picirq.c -o obj/kern/driver/picirq.o
+ cc kern/driver/intr.c
gcc -Ikern/driver/ -fno-builtin -Wall -ggdb -m32 -gstabs -nostdinc -fno-stack-protector -Ilibs/ -Ikern/debug/ -Ikern/driver/ -Ikern/trap/ -Ikern/mm/ -c kern/driver/intr.c -o obj/kern/driver/intr.o
+ cc kern/trap/trap.c
gcc -Ikern/trap/ -fno-builtin -Wall -ggdb -m32 -gstabs -nostdinc -fno-stack-protector -Ilibs/ -Ikern/debug/ -Ikern/driver/ -Ikern/trap/ -Ikern/mm/ -c kern/trap/trap.c -o obj/kern/trap/trap.o
kern/trap/trap.c:14:13: warning: ‘print_ticks’ defined but not used [-Wunused-function]
static void print_ticks() {
^
kern/trap/trap.c:30:26: warning: ‘idt_pd’ defined but not used [-Wunused-variable]
static struct pseudodesc idt_pd = {
^
+ cc kern/trap/vectors.S
gcc -Ikern/trap/ -fno-builtin -Wall -ggdb -m32 -gstabs -nostdinc -fno-stack-protector -Ilibs/ -Ikern/debug/ -Ikern/driver/ -Ikern/trap/ -Ikern/mm/ -c kern/trap/vectors.S -o obj/kern/trap/vectors.o
+ cc kern/trap/trapentry.S
gcc -Ikern/trap/ -fno-builtin -Wall -ggdb -m32 -gstabs -nostdinc -fno-stack-protector -Ilibs/ -Ikern/debug/ -Ikern/driver/ -Ikern/trap/ -Ikern/mm/ -c kern/trap/trapentry.S -o obj/kern/trap/trapentry.o
+ cc kern/mm/pmm.c
gcc -Ikern/mm/ -fno-builtin -Wall -ggdb -m32 -gstabs -nostdinc -fno-stack-protector -Ilibs/ -Ikern/debug/ -Ikern/driver/ -Ikern/trap/ -Ikern/mm/ -c kern/mm/pmm.c -o obj/kern/mm/pmm.o
+ cc libs/string.c
gcc -Ilibs/ -fno-builtin -Wall -ggdb -m32 -gstabs -nostdinc -fno-stack-protector -Ilibs/ -c libs/string.c -o obj/libs/string.o
+ cc libs/printfmt.c
gcc -Ilibs/ -fno-builtin -Wall -ggdb -m32 -gstabs -nostdinc -fno-stack-protector -Ilibs/ -c libs/printfmt.c -o obj/libs/printfmt.o
#链接生成kernel
+ ld bin/kernel
ld -m elf_i386 -nostdlib -T tools/kernel.ld -o bin/kernel obj/kern/init/init.o obj/kern/libs/stdio.o obj/kern/libs/readline.o obj/kern/debug/panic.o obj/kern/debug/kdebug.o obj/kern/debug/kmonitor.o obj/kern/driver/clock.o obj/kern/driver/console.o obj/kern/driver/picirq.o obj/kern/driver/intr.o obj/kern/trap/trap.o obj/kern/trap/vectors.o obj/kern/trap/trapentry.o obj/kern/mm/pmm.o obj/libs/string.o obj/libs/printfmt.o
#bootblock
+ cc boot/bootasm.S
gcc -Iboot/ -fno-builtin -Wall -ggdb -m32 -gstabs -nostdinc -fno-stack-protector -Ilibs/ -Os -nostdinc -c boot/bootasm.S -o obj/boot/bootasm.o
+ cc boot/bootmain.c
gcc -Iboot/ -fno-builtin -Wall -ggdb -m32 -gstabs -nostdinc -fno-stack-protector -Ilibs/ -Os -nostdinc -c boot/bootmain.c -o obj/boot/bootmain.o
+ cc tools/sign.c
gcc -Itools/ -g -Wall -O2 -c tools/sign.c -o obj/sign/tools/sign.o
gcc -g -Wall -O2 obj/sign/tools/sign.o -o bin/sign
+ ld bin/bootblock
#链接生成bootblock
ld -m elf_i386 -nostdlib -N -e start -Ttext 0x7C00 obj/boot/bootasm.o obj/boot/bootmain.o -o obj/bootblock.o
'obj/bootblock.out' size: 488 bytes
build 512 bytes boot sector: 'bin/bootblock' success!
#生成ucore.img
dd if=/dev/zero of=bin/ucore.img count=10000
记录了10000+0 的读入
记录了10000+0 的写出
5120000 bytes (5.1 MB, 4.9 MiB) copied, 0.0144903 s, 353 MB/s
dd if=bin/bootblock of=bin/ucore.img conv=notrunc
记录了1+0 的读入
记录了1+0 的写出
512 bytes copied, 0.000149204 s, 3.4 MB/s
dd if=bin/kernel of=bin/ucore.img seek=1 conv=notrunc
记录了146+1 的读入
记录了146+1 的写出
74828 bytes (75 kB, 73 KiB) copied, 0.000223667 s, 335 MB/s1.2 一个被系统认为是符合规范的硬盘主引导扇区的特征是什么?
- 磁盘主引导扇区只有512字节
- 磁盘最后两个字节为0x55AA
在tools/sign.c中有如下代码用来检测是否符合要求
buf[510] = 0x55;
buf[511] = 0xAA;
FILE *ofp = fopen(argv[2], "wb+");
size = fwrite(buf, 1, 512, ofp);
if (size != 512) {
fprintf(stderr, "write '%s' error, size is %d.\n", argv[2], size);
return -1;
}练习2:使用qemu执行并调试lab1种的软件
调用make debug前需要注意Makefile里debug条目下有一句"gdb -q -tui -x tools/gdbinit",故先修改tools/gdbinit如下
#old-gdbinit
file bin/kernel
target remote:1234
break kern_init
continue
#new-gdbinit
file obj/bootblock.o
target remote:1234
set architecture i8086
b *0x7c00
continue
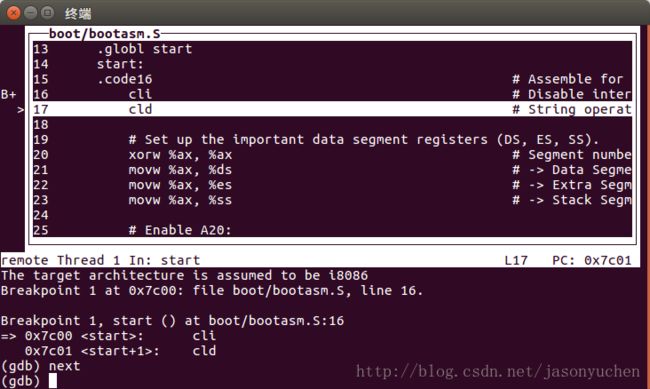
x /2i $pc调用make debug后结果如下,与源文件一致,断点测试正常
练习3:分析bootloader进入保护模式的过程
从bootasm.S的部分源码中分析过程
# start address should be 0:7c00, in real mode, the beginning address of the running bootloader从0x7c00开始运行bootloader
.globl start
start:
.code16
cli # Disable interrupts关中断
cld # String operations increment
# Set up the important data segment registers (DS, ES, SS).三个段寄存器置零
xorw %ax, %ax # Segment number zero
movw %ax, %ds # -> Data Segment
movw %ax, %es # -> Extra Segment
movw %ax, %ss # -> Stack Segment
# Enable A20:
# For backwards compatibility with the earliest PCs, physical
# address line 20 is tied low, so that addresses higher than
# 1MB wrap around to zero by default. This code undoes this.
#seta20.1和seta20.2是开启A20地址线的代码,涉及到8042键盘控制器,当开启后32条地址线可用
seta20.1:
inb $0x64, %al # Wait for not busy(8042 input buffer empty).
testb $0x2, %al
jnz seta20.1
movb $0xd1, %al # 0xd1 -> port 0x64
outb %al, $0x64 # 0xd1 means: write data to 8042's P2 port
seta20.2:
inb $0x64, %al # Wait for not busy(8042 input buffer empty).
testb $0x2, %al
jnz seta20.2
movb $0xdf, %al # 0xdf -> port 0x60
outb %al, $0x60 # 0xdf = 11011111, means set P2's A20 bit(the 1 bit) to 1
# Switch from real to protected mode, using a bootstrap GDT
# and segment translation that makes virtual addresses
# identical to physical addresses, so that the
# effective memory map does not change during the switch.
#通过描述符加载GDT表
lgdt gdtdesc
#将CR0寄存器第一位置1来开启保护模式
movl %cr0, %eax
orl $CR0_PE_ON, %eax
movl %eax, %cr0
# Jump to next instruction, but in 32-bit code segment.
# Switches processor into 32-bit mode.
#长跳转到32位模式下的下一条指令,将$PROT_MODE_CSEG加载到CS中,将$protcseg加载到IP中
ljmp $PROT_MODE_CSEG, $protcseg
.code32 # Assemble for 32-bit mode
protcseg:
# Set up the protected-mode data segment registers
#将数据段选择子加载到ax中
movw $PROT_MODE_DSEG, %ax # Our data segment selector
movw %ax, %ds # -> DS: Data Segment
movw %ax, %es # -> ES: Extra Segment
movw %ax, %fs # -> FS
movw %ax, %gs # -> GS
movw %ax, %ss # -> SS: Stack Segment
# Set up the stack pointer and call into C. The stack region is from 0--start(0x7c00)
#调用bootmain
movl $0x0, %ebp
movl $start, %esp
call bootmain
# If bootmain returns (it shouldn't), loop.
spin:
jmp spin
# Bootstrap GDT
.p2align 2 # force 4 byte alignment
#全局描述符表
gdt:
SEG_NULLASM # null seg
#代码段描述符
SEG_ASM(STA_X|STA_R, 0x0, 0xffffffff) # code seg for bootloader and kernel
#数据段描述符
SEG_ASM(STA_W, 0x0, 0xffffffff) # data seg for bootloader and kernel
#全局描述符表对应的描述符
gdtdesc:
.word 0x17 # sizeof(gdt) - 1
.long gdt # address gdt
练习4:分析bootloader加载ELF格式的OS的过程
从bootmain源码分析加载过程
/* bootmain - the entry of bootloader */
void
bootmain(void) {
// read the 1st page off disk实际readseg函数循环调用了readsect读取磁盘信息
readseg((uintptr_t)ELFHDR, SECTSIZE * 8, 0);
// is this a valid ELF?判断是否是合法的ELF文件
if (ELFHDR->e_magic != ELF_MAGIC) {
goto bad;
}
struct proghdr *ph, *eph;
// load each program segment (ignores ph flags)
// ELF头部有program header表的位置偏移,使ph指向program header表的第一项,并循环将所有程序加载进内存
ph = (struct proghdr *)((uintptr_t)ELFHDR + ELFHDR->e_phoff);
// eph即end of ph标记了ELF文件头部的结尾
eph = ph + ELFHDR->e_phnum;
// 按照程序头表的描述将ELF文件中的数据加载进内存
for (; ph < eph; ph ++) {
readseg(ph->p_va & 0xFFFFFF, ph->p_memsz, ph->p_offset);
}
// call the entry point from the ELF header
// note: does not return
//程序加载完成,根据ELF头表的入口信息找到内核的入口并开始执行,不返回
((void (*)(void))(ELFHDR->e_entry & 0xFFFFFF))();
bad:
outw(0x8A00, 0x8A00);
outw(0x8A00, 0x8E00);
/* do nothing */
while (1);
}readsect()从设备的secno扇区读取数据到dst位置,IO部分参考
http://blog.csdn.net/qq_31481187/article/details/63251420
/* readsect - read a single sector at @secno into @dst */
static void
readsect(void *dst, uint32_t secno) {
// wait for disk to be ready
// 等待磁盘准备就绪
waitdisk();
// 设置读取扇区的数目为1
outb(0x1F2, 1); // count = 1
// 0x1F3-0x1F6这里的4条指令设定了0-27位偏移量、28位(0)表示访问Disk 0、29-31位强制设为1
outb(0x1F3, secno & 0xFF);
outb(0x1F4, (secno >> 8) & 0xFF);
outb(0x1F5, (secno >> 16) & 0xFF);
outb(0x1F6, ((secno >> 24) & 0xF) | 0xE0);
// 0x20命令读取扇区
outb(0x1F7, 0x20); // cmd 0x20 - read sectors
// wait for disk to be ready
waitdisk();
// read a sector
// 读取到dst位置,以DW为单位,SECTSIZE = 512字节,故读512/4=128个4字节的DW
insl(0x1F0, dst, SECTSIZE / 4);
}练习5:实现函数调用堆栈跟踪函数
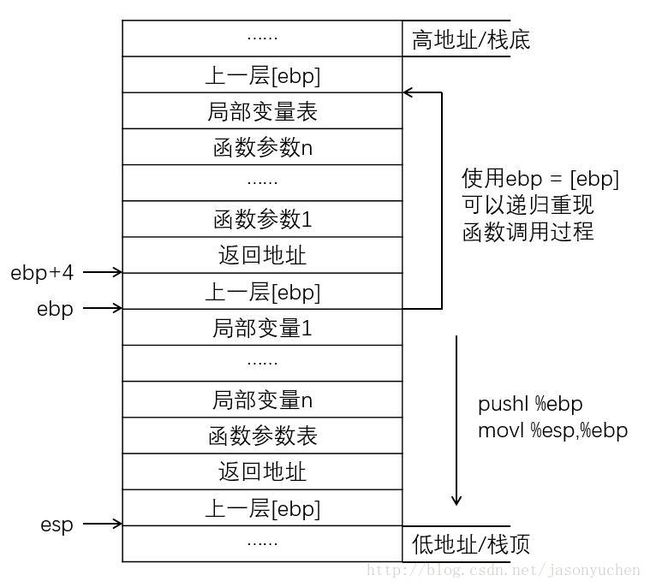
5.1 函数堆栈基本原理
一个函数调用动作可分解为:零到多个PUSH指令(用于参数入栈),一个CALL指令。CALL指令内部其实还暗含了一个将返回地址(即CALL指令下一条指令的地址)压栈的动作(由硬件完成)。几乎所有本地编译器都会在每个函数体之前插入类似如下的汇编指令
pushl %ebp
movl %esp , %ebp一般而言,ss:[ebp+4]处为返回地址,ss:[ebp+8]处为第一个参数值(最后一个入栈的参数值,此处假设其占用4字节内存),ss:[ebp-4]处为第一个局部变量,ss:[ebp]处为上一层ebp值。由于ebp中的地址处总是“上一层函数调用时的ebp值”,而在每一层函数调用中,都能通过当时的ebp值“向上(栈底方向)”能获取返回地址、参数值,“向下(栈顶方向)”能获取函数局部变量值。如此形成递归,直至到达栈底。这就是函数调用栈。
5.2 print_stackframe的实现
void
print_stackframe(void) {
/* LAB1 YOUR CODE : STEP 1 */
/* (1) call read_ebp() to get the value of ebp. the type is (uint32_t);
* (2) call read_eip() to get the value of eip. the type is (uint32_t);
* (3) from 0 .. STACKFRAME_DEPTH
* (3.1) printf value of ebp, eip
* (3.2) (uint32_t)calling arguments [0..4] = the contents in address (unit32_t)ebp +2 [0..4]
* (3.3) cprintf("\n");
* (3.4) call print_debuginfo(eip-1) to print the C calling function name and line number, etc.
* (3.5) popup a calling stackframe
* NOTICE: the calling funciton's return addr eip = ss:[ebp+4]
* the calling funciton's ebp = ss:[ebp]
*/
uint32_t ebp = read_ebp();
uint32_t eip = read_eip();
for(int i = 0; i < STACKFRAME_DEPTH && ebp != 0; i++)
{
cprintf("ebp:0x%08x eip:0x%08x ", ebp, eip);
uint32_t *args = (uint32_t *)ebp + 2;
cprintf("args:0x%08x 0x%08x 0x%08x 0x%08x\n", args[0], args[1], args[2], args[3]);
print_debuginfo(eip-1);
eip = ((uint32_t *)ebp)[1];
ebp = ((uint32_t *)ebp)[0];
}
}
5.3 输出结果
...
ebp:0x00007b38 eip:0x00100a28 args:0x00010094 0x00010094 0x00007b68 0x0010007f
kern/debug/kdebug.c:306: print_stackframe+22
ebp:0x00007b48 eip:0x00100d14 args:0x00000000 0x00000000 0x00000000 0x00007bb8
kern/debug/kmonitor.c:125: mon_backtrace+10
ebp:0x00007b68 eip:0x0010007f args:0x00000000 0x00007b90 0xffff0000 0x00007b94
kern/init/init.c:48: grade_backtrace2+19
ebp:0x00007b88 eip:0x001000a1 args:0x00000000 0xffff0000 0x00007bb4 0x00000029
kern/init/init.c:53: grade_backtrace1+27
ebp:0x00007ba8 eip:0x001000be args:0x00000000 0x00100000 0xffff0000 0x00100043
kern/init/init.c:58: grade_backtrace0+19
ebp:0x00007bc8 eip:0x001000df args:0x00000000 0x00000000 0x00000000 0x00103260
kern/init/init.c:63: grade_backtrace+26
ebp:0x00007be8 eip:0x00100050 args:0x00000000 0x00000000 0x00000000 0x00007c4f
kern/init/init.c:28: kern_init+79
ebp:0x00007bf8 eip:0x00007d6e args:0xc031fcfa 0xc08ed88e 0x64e4d08e 0xfa7502a8
: -- 0x00007d6d --
... 练习6:完善中断初始化和处理
6.1 中断描述符表(也可简称为保护模式下的中断向量表)中一个表项占多少字节?其中哪几位代表中断处理代码的入口?
参考mmu.h中对中断描述符表表项数据结构的定义,中断描述符一个表项占8字节,其中0~15位和48~63位分别是offset的低16位和高16位,16~31位是段选择子,段选择子获得段基址加上偏移量就是入口
/* Gate descriptors for interrupts and traps */
struct gatedesc {
unsigned gd_off_15_0 : 16; // low 16 bits of offset in segment
unsigned gd_ss : 16; // segment selector
unsigned gd_args : 5; // # args, 0 for interrupt/trap gates
unsigned gd_rsv1 : 3; // reserved(should be zero I guess)
unsigned gd_type : 4; // type(STS_{TG,IG32,TG32})
unsigned gd_s : 1; // must be 0 (system)
unsigned gd_dpl : 2; // descriptor(meaning new) privilege level
unsigned gd_p : 1; // Present
unsigned gd_off_31_16 : 16; // high bits of offset in segment
};
6.2 中断向量表初始化函数idt_init的实现
利用SETGATE,其定义在mmu.h中
/* *
* Set up a normal interrupt/trap gate descriptor
* - istrap: 1 for a trap (= exception) gate, 0 for an interrupt gate
* - sel: Code segment selector for interrupt/trap handler
* - off: Offset in code segment for interrupt/trap handler
* - dpl: Descriptor Privilege Level - the privilege level required
* for software to invoke this interrupt/trap gate explicitly
* using an int instruction.
* */
#define SETGATE(gate, istrap, sel, off, dpl){...}注意到实验手册中提到,因此在初始化完其他实现后,需要单独重新处理T_SYSCALL
【注意】除了系统调用中断(T_SYSCALL)使用陷阱门描述符且权限为用户态权限以外,其它中断均使用特权级(DPL)为0的中断门描述符,权限为内核态权限;而ucore的应用程序处于特权级3,需要采用`int 0x80`指令操作(这种方式称为软中断,软件中断,Tra中断,在lab5会碰到)来发出系统调用请求,并要能实现从特权级3到特权级0的转换,所以系统调用中断(T_SYSCALL)所对应的中断门描述符中的特权级(DPL)需要设置为3。/* idt_init - initialize IDT to each of the entry points in kern/trap/vectors.S */
void
idt_init(void) {
/* LAB1 YOUR CODE : STEP 2 */
/* (1) Where are the entry addrs of each Interrupt Service Routine (ISR)?
* All ISR's entry addrs are stored in __vectors. where is uintptr_t __vectors[] ?
* __vectors[] is in kern/trap/vector.S which is produced by tools/vector.c
* (try "make" command in lab1, then you will find vector.S in kern/trap DIR)
* You can use "extern uintptr_t __vectors[];" to define this extern variable which will be used later.
* (2) Now you should setup the entries of ISR in Interrupt Description Table (IDT).
* Can you see idt[256] in this file? Yes, it's IDT! you can use SETGATE macro to setup each item of IDT
* (3) After setup the contents of IDT, you will let CPU know where is the IDT by using 'lidt' instruction.
* You don't know the meaning of this instruction? just google it! and check the libs/x86.h to know more.
* Notice: the argument of lidt is idt_pd. try to find it!
*/
extern uintptr_t __vectors[];
for (int i = 0; i < 256; i ++) {
SETGATE(idt[i], 0, GD_KTEXT, __vectors[i], DPL_KERNEL);
}
// 单独处理T_SYSCALL,这里的GD_KETXT定义在memlayout.h中,表示内核代码
SETGATE(idt[T_SYSCALL], 1, GD_KTEXT, __vectors[T_SYSCALL], DPL_USER);
lidt(&idt_pd);
}参考PIAZZA论坛给出一个更为合理的答案,区分出异常和中断,否则按原方法所有异常会被作为中断处理,不同之处在于中断门会将IF flag清零而异常门不会,则操作系统在处理异常时将无法响应可屏蔽中断,例如程序产生了一个异常,本可以通过键盘强制终止程序,然而由于IF flag被清零键盘的中断信号无法被接收,导致必须要等到异常处理结束才能得到响应
for(int i = 0; i < sizeof(idt) / sizeof(struct gatedesc){
if(i == T_SYSCALL){
SETGATE(idt[T_SYSCALL], 1, GD_KTEXT, __vectors[T_SYSCALL], DPL_USER);
}
else if(i < IRQ_OFFSET){
SETGATE(idt[i], 1, GD_KTEXT, __vectors[i], DPL_KERNEL);
}
else{
SETGATE(idt[i], 0, GD_KTEXT, __vectors[i], DPL_KERNEL);
}
}6.3 时钟中断处理函数的实现
较为简单,直接给出代码
case IRQ_OFFSET + IRQ_TIMER:
/* LAB1 YOUR CODE : STEP 3 */
/* handle the timer interrupt */
/* (1) After a timer interrupt, you should record this event using a global variable (increase it), such as ticks in kern/driver/clock.c
* (2) Every TICK_NUM cycle, you can print some info using a funciton, such as print_ticks().
* (3) Too Simple? Yes, I think so!
*/
ticks ++;
if (ticks % TICK_NUM == 0) {
print_ticks();
}
break;