SE01 Unit04 集合框架 、 集合操作 —— 线性表
集合
Collection 接口
集合的父类型接口
- 定义了所有集合的通用方法
- add 将元素添加到集合中
- 有两个子接口
- List 表示有序集合
- Set 表示无序集合
- Collection 是接口,使用时候必须使用具体实现类
案例:
Collection col=new ArrayList();
col.add("Tom");
col.add("Jerry");
System.out.println(col);引用数组
/**
* 数组持有的是对象的引用,也称为引用数组
* 就是保存引用的数组!!
*/
public class Demo02 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Person[] ary = new Person[3];
ary[0] = new Person("Tom", 5);
ary[1] = new Person("Jerry", 6);
for(int i=0; i" ");
}
}
}
class Person{
int age;
String name;
public Person(String name, int age) {
this.name = name;
this.age = age;
}
public String toString(){
return "("+name+","+age+")";
}
} 原理:
集合中持有的也是对象的引用
/**
* 集合中持有的也是对象的引用
*/
public class Demo03 {
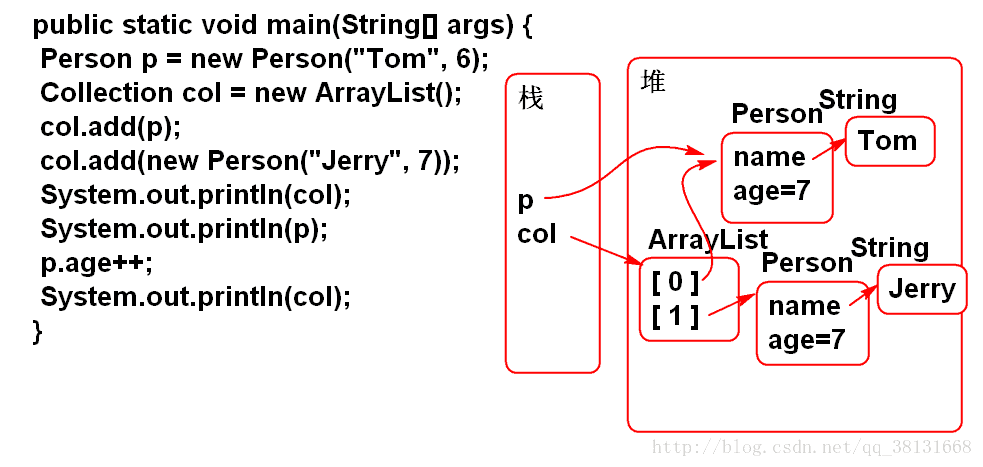
public static void main(String[] args) {
Person p = new Person("Tom", 6);
Collection col = new ArrayList();
col.add(p);
col.add(new Person("Jerry", 7));
System.out.println(col);
System.out.println(p);
p.age++;
System.out.println(col);
}
}原理:
add 方法
案例:
/**
* 集合的添加方法 add
*
* 1. 如果添加成功返回 true
* 2. 添加失败返回false
*/
public class Demo04 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//HashSet实现了Collection接口
Collection col=new HashSet();
boolean b = col.add("Tom");
System.out.println(b);//true
b = col.add("Jerry");
System.out.println(b);
//重复添加 Tom 结果是false,添加失败
b = col.add("Tom");
System.out.println(b);//false
//Set类型的集合不能存在重复的元素
System.out.println(col);
}
}contains 方法
/**
* contains 方法
*
* 1. 用于检测集合中是否包含指定元素
* 2. contains 的算法依赖于元素的equals方法
*/
public class Demo05 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Collection col=new ArrayList();
col.add("Tom");
col.add("Jerry");
col.add("Andy");
System.out.println(col);
//查找col中是否包含 "Tom" 元素
//由于String类型实现了equals方法
//则contains方法可以很正常的工作
boolean b = col.contains("Tom");
System.out.println(b);//true
b = col.contains("Lee");
System.out.println(b);//false
}
}如果元素不正确重写equals,则contains 会失效
/**
* 如果元素不正确重写equals,则contains 会失效
*/
public class Demo06 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Collection col=new ArrayList();
col.add(new Person("Tom", 5));
col.add(new Person("Jerry", 4));
col.add(new Person("Andy", 5));
System.out.println(col);
Person p=new Person("Tom", 5);
System.out.println(p);
/*
* 集合元素类型Person上没有很好的
* 重写equals造成contains方法的失效!
*/
boolean b=col.contains(p);
System.out.println(b);
Collection c = new ArrayList();
c.add(new User("Tom", 1));
c.add(new User("Jerry", 2));
c.add(new User("Andy", 3));
System.out.println(c);
User user = new User("Tom", 1);
/*
* 集合中的元素类型User很好重写了
* equals,保证了contains方法的正确
* 执行:
*/
b = c.contains(user);
System.out.println(b);
System.out.println(c.size()); //3
System.out.println(c.isEmpty());//flase
c.clear();//清空集合中的引用
System.out.println(c.size()); //0
System.out.println(c.isEmpty());//true
}
}
class User{
int id;
String name;
public User(String name, int id) {
this.id=id;
this.name = name;
}
public boolean equals(Object obj){
if(obj==null) return false;
if(this==obj) return true;
if(obj instanceof User){
User other = (User)obj;
return id == other.id;
}
return false;
}
public String toString() {
return "("+name+","+id+")";
}
}集合的合并和集合的包含
/**
* 集合的合并和集合的包含
*/
public class Demo07 {
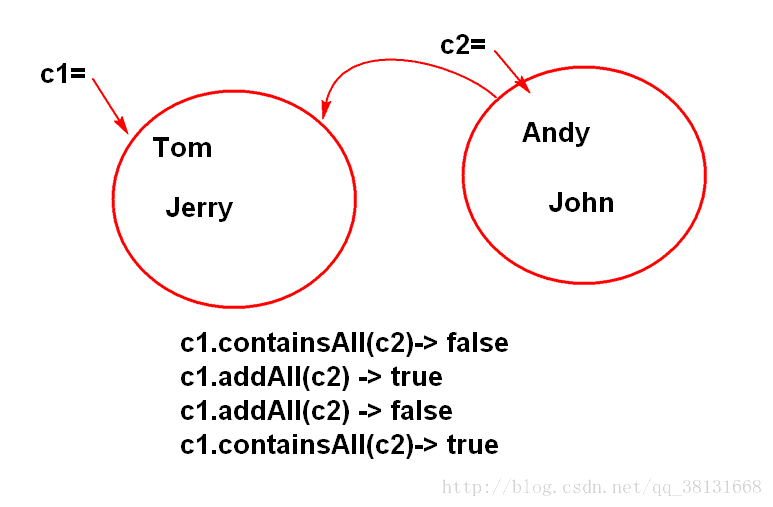
public static void main(String[] args) {
Collection c1 = new HashSet();
Collection c2 = new HashSet();
c1.add("Tom");
c1.add("Jerry");
c2.add("Andy");
c2.add("John");
System.out.println(c1);
System.out.println(c2);
//检查 c1是否包含c2 中的全部元素吗?
System.out.println(c1.containsAll(c2));
//将c2的元素添加到c1中,添加成功为true
boolean b = c1.addAll(c2);
System.out.println(b);
System.out.println(c1);
System.out.println(c2);
//添加不成功返回false
b = c1.addAll(c2);
System.out.println(b);
System.out.println(c1);
System.out.println(c2);
System.out.println(c1.containsAll(c2));
}
}原理:
集合的迭代
/**
* 集合的迭代
*/
public class Demo08 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
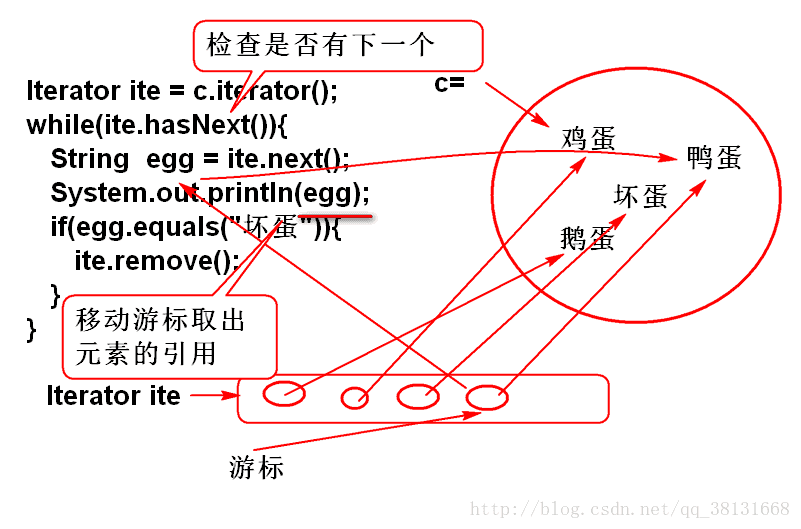
Collection c=new ArrayList();
c.add("鸡蛋");
c.add("鸭蛋");
c.add("坏蛋");
c.add("鹅蛋");
c.add(null);
//遍历一个集合
Iterator ite = c.iterator();
//检查ite当前游标是否有下一个元素引用
while(ite.hasNext()){
//移动游标取出下一个元素的引用
String s = (String)ite.next();
System.out.println(s);
if("坏蛋".equals(s)){
//将元素从原集合中删除
ite.remove();
}
}
System.out.println(c);
}
}原理:
增强for循环(foreach 循环)
Java 5 提供的简化版遍历循环
与迭代器接口的差别是不能使用 迭代器接口的remove方法。
/**
* 增强for循环(foreach 循环)
*
*/
public class Demo09 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Collection c=
new ArrayList();
c.add("鸡蛋");
c.add("鸭蛋");
c.add("坏蛋");
c.add("鹅蛋");
//c.add(0);
c.add(null);
//Iterator ite = c.iterator();
//while(ite.hasNext()){
// Object s = ite.next();
for(String s: c){
System.out.println(s);
}
}
} List 的 get 方法和 set方法
/**
* 测试 List 的 get 方法和 set方法
*/
public class Demo10 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
List list =
new LinkedList();
list.add("Tom");
list.add("Jerry");
list.add("Andy");
System.out.println(list);
//将集合中序号为0的元素引用复制到str
String str = list.get(0);
System.out.println(str);
str= list.get(1);
System.out.println(str);
//置换集合中的元素
String name = list.set(2, "Wang");
System.out.println(name);
System.out.println(list);
}
} ArrayList 与 LinkedList 性能对比测试
/**
* ArrayList 与 LinkedList 性能对比测试
*/
public class Demo11 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
List list1 =
new ArrayList();
List list2 =
new LinkedList();
for(int i=0; i<100000; i++){
list1.add(i);
list2.add(i);
}
long t1=System.nanoTime();
Integer n1 = list1.get(0);
long t2=System.nanoTime();
Integer n2 = list1.get(50000);
long t3=System.nanoTime();
Integer n3 = list1.get(99999);
long t4=System.nanoTime();
System.out.println(
(t2-t1)+","+(t3-t2)+","+(t4-t3));
t1=System.nanoTime();
n1 = list2.get(0);
t2=System.nanoTime();
n2 = list2.get(50000);
t3=System.nanoTime();
n3 = list2.get(99999);
t4=System.nanoTime();
System.out.println(
(t2-t1)+","+(t3-t2)+","+(t4-t3));
}
} List 元素的插入与删除
/**
* List 元素的插入与删除
*/
public class Demo12 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
List list =
new ArrayList();
list.add("Tom");
list.add("Jerry");
System.out.println(list);
//在list集合的头部(0位置)插入元素
list.add(0, "Wang");
System.out.println(list);
//删除集合最后一个元素,
//返回值是被删除的元素(元素的引用)
String name=list.remove(2);
System.out.println(list);
System.out.println(name);
}
} subList
/**
* List 的 subList
* subList 与原有List共享相同的存储空间
*/
public class Demo13 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
List list =
new ArrayList();
for(int i = 3; i<=10; i++ ){
list.add("黑桃"+i);
}
System.out.println(list);
//从list的3位置开始抽取3个元素为sub List
List sub=list.subList(3,3+3);
System.out.println(sub);
//由于共享存储空间,
//修改subList影响原list集合
sub.remove(0);
System.out.println(sub);
System.out.println(list);
}
} 集合转换为数组
/**
* 集合转换为数组
*/
public class Demo14 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Collection col=
new ArrayList();
col.add(1);
col.add(2);
col.add(3);
col.add(4);
Integer[] ary = new Integer[10];
for(int i=0; i0;
}
//将集合col中的引用复制到ary中
Integer[] a=col.toArray(ary);
for(Integer n:ary){
System.out.println(n);
}
for(Integer n:a){
System.out.println(n);
}
}
} 将数组转换为长度不可变的List集合
/**
* 将数组转换为长度不可变的List集合
*/
public class Demo15 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Integer[] ary = {2,3,4,8};
//asList返回长度固定的List,与
//数组共享存储空间
List list=
Arrays.asList(ary);
System.out.println(list);
ary[0]=9;
System.out.println(list);
//不能改变此List的长度
list.remove(0);
}
}