java原生UrlConnection体系梳理
一、背景介绍
关于HTTP协议
HTTP 协议是目前 Internet 上使用得最多、最重要的协议。该协议为典型的请求-响应模型。客户端建立连接并发送请求,服务端接受并处理请求,再发送应答,再由客户端接受并处理应答。浏览器是最常见的一种客户端,它将用户的交互行为作为http请求发送,并接受服务端的应答,再将应答内容展示,一般应答都是html类型的超文本。
在某些情况下,我们会使用java程序来模拟浏览器发送请求。因此,在 JDK 的 java.net 包中已内置了访问 HTTP 协议的类:HttpURLConnection。
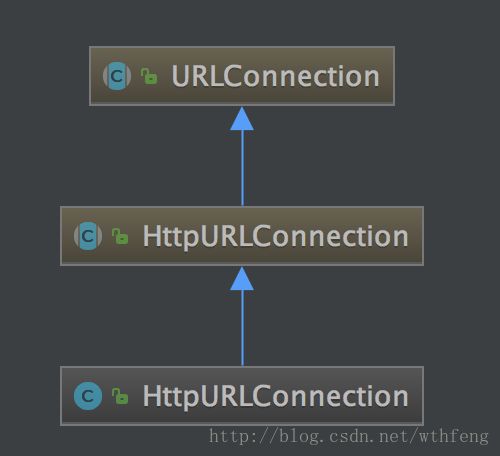
关于继承关系
HttpUrlConnection类继承自UrlConnection。UrlConnection是一个抽象类,表示URL指向资源的连接。其子类包含诸如HttpUrlConnection、FtpUrlConnection、FileUrlConnection等各种协议的连接类。
这些协议的连接类具体实现大都在
sun.net.www.protocol.http包内,不是公开的接口,我们可不必关注。只需了解其继承关系即可。
关于通信机制
URLConnection类本身依赖于Socket类实现网络连接。socket又称做套接字,是应用层和传输层之间的一个抽象层,它把TCP/IP层复杂的操作抽象为几个简单的接口供应用层(这里就是我们的Http连接)调用。
其所处的位置如下图所示
当我们进行Http通信时,每个请求连接最终都会绑定到一个具体的socket上,利用socket与底下的传输层等进行通信。具体通信机制可参考相关书籍。
二、一个请求示例
下面是用HttpURLConnection获取百度首页的示例。
具体步骤如下:
- 根据连接地址创建
URL实例。 - 调用
URL::openConnection()方法打开连接,将连接赋给HttpURLConnection对象。 - 操作连接。
- 关闭连接。
@Test
public void test() throws IOException{
URL url = new URL("http://www.baidu.com"); //构建一个URL资源对象
HttpURLConnection connection = (HttpURLConnection) url.openConnection();//打开连接
connection.setRequestMethod("GET"); //设置请求方法
/**
* 建立连接并获取资源(指向百度首页的html内容)
*/
BufferedReader in = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(connection.getInputStream()));
StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder();
String line ;
while ((line=in.readLine())!=null){
sb.append(line);
}
System.out.println(sb.toString());
}下面我们就根据这个简单的示例来解析HttpURLConnection,看看它是如何发送请求并接受响应的。
根据示例,我们需要知道
URL类及URL::openConnection方法HttpURLConnection建立连接的方法以及其他重要方法。
三、关于 URL
URL格式简介
首先看看有关URL(统一资源定位符)的内容。
URL表示的也就是我们通常说的网页地址。表示互联网上的资源,如网页或FTP地址等。
URL可分为以下几个部分
protocol://host:port/path?query#fragment
以Http协议为例,一个实例如下:
http://www.runoob.com/index.html?language=cn#j2se
各部分含义:
- protocol : 协议名,如http、https、ftp等,示例中为http。
- host : 主机地址,示例中为 www.runoob.com
- port : 端口号,没有标明则为默认端口号。如http协议默认的为80,ftp的为21。示例为http协议,其端口号为80
- path : 路径,由
/隔开的字符串,表示主机上的文件或目录,示例为index.html - ? :分割符,分割主机地址和查询参数
- query : 查询参数,多个用
&分割,示例中为language=cn。 - fragment : 定位片段,定位到网页地址的某个id,示例中为
j2se
构建URL对象
URL有多个构造函数,具体实现在URL(URL, String,handler)。构造函数的目的在:
- 解析传来的url字符串,解析出的
protocol、host等值并赋值给相应的类字段。 - 根据
protocol字段得到urlStreamHandler实例。
第1条很好理解,至于第二条的urlStreamHandler对象,则是具体处理连接请求的handler对象。在设计上,每一个协议(protocol)对应一个handler。
public URL(URL context, String spec, URLStreamHandler handler)
throws MalformedURLException{
// 为简洁见,已去掉解析url过程
// 根据protocol得到urlStreamHandler实例
if (handler == null &&
(handler = getURLStreamHandler(protocol)) == null) {
throw new MalformedURLException("unknown protocol: "+protocol);
}
this.handler = handler;
handler.parseURL(this, spec, start, limit);
} catch(MalformedURLException e) {
throw e;
} catch(Exception e) {
// 异常处理
}
}
从getURLStreamHandler中得到的handler,具体看看getURLStreamHandler
static URLStreamHandler getURLStreamHandler(String protocol) {
// 这里应该是做了一个缓存Map,将已解析过的协议名(String,key值)和该协议的处理类(URLStreamHandler,value值)放于Map中。
URLStreamHandler handler = handlers.get(protocol);
if (handler == null) {
boolean checkedWithFactory = false;
// 若factory不为空,从factory获取
if (factory != null) {
handler = factory.createURLStreamHandler(protocol);
checkedWithFactory = true;
}
// 根据反射获取
if (handler == null) {
String packagePrefixList = null;
packagePrefixList
= java.security.AccessController.doPrivileged(
new sun.security.action.GetPropertyAction(
protocolPathProp,""));
if (packagePrefixList != "") {
packagePrefixList += "|";
}
// REMIND: decide whether to allow the "null" class prefix
// or not.
packagePrefixList += "sun.net.www.protocol";
StringTokenizer packagePrefixIter =
new StringTokenizer(packagePrefixList, "|");
while (handler == null &&
packagePrefixIter.hasMoreTokens()) {
String packagePrefix =
packagePrefixIter.nextToken().trim();
try {
String clsName = packagePrefix + "." + protocol +
".Handler";
Class cls = null;
try {
cls = Class.forName(clsName);
} catch (ClassNotFoundException e) {
ClassLoader cl = ClassLoader.getSystemClassLoader();
if (cl != null) {
cls = cl.loadClass(clsName);
}
}
if (cls != null) {
handler =
(URLStreamHandler)cls.newInstance();
}
} catch (Exception e) {
// any number of exceptions can get thrown here
}
}
}
synchronized (streamHandlerLock) {
// 省略对多线程情况判断
//将handler加到映射表中
if (handler != null) {
handlers.put(protocol, handler);
}
}
}
return handler;
}从代码中可知,处理协议连接的handler前缀是sun.net.www.protocol,这样可根据协议名获取具体处理的handler。如处理http的为sun.net.www.protocol.http.HttpURLConnection,负责有关http相关的连接处理。
四、其他
其他具体的包括打开连接、发送请求、接受响应等都在sun.net.www.protocol.http.HttpURLConnection类内具体实现。这里就不展示了。如此,有关HttpURLConnection相关的类结构也就结束了。