PTA 11-散列4 Hashing - Hard Version 解法详述
PTA-mooc完整题目解析及AC代码库:PTA(拼题A)-浙江大学中国大学mooc数据结构全AC代码与题目解析(C语言)
虽然课程后面专门给出了一节用来讲解这道题,但是老师在讲解中只给出了解决思路,并未指出具体的实现细节,具体实现上也有很多优化的方法(比如堆的使用),所有在这里给出了具体的解法分析详细说明
Given a hash table of size N, we can define a hash function H(x)=x%N. Suppose that the linear probing is used to solve collisions, we can easily obtain the status of the hash table with a given sequence of input numbers.
However, now you are asked to solve the reversed problem: reconstruct the input sequence from the given status of the hash table. Whenever there are multiple choices, the smallest number is always taken.
Input Specification:
Each input file contains one test case. For each test case, the first line contains a positive integer N (≤1000), which is the size of the hash table. The next line contains N integers, separated by a space. A negative integer represents an empty cell in the hash table. It is guaranteed that all the non-negative integers are distinct in the table.
Output Specification:
For each test case, print a line that contains the input sequence, with the numbers separated by a space. Notice that there must be no extra space at the end of each line.
Sample Input:
11
33 1 13 12 34 38 27 22 32 -1 21
Sample Output:
1 13 12 21 33 34 38 27 22 32
题意说明
这道题给出了一个HashTable,这个哈希表用的哈希函数是H(x)=x%N,冲突解决策略是线性探测法。现在给定这种哈希表的具体内部存储数据的状态,即每个输入元素实际存储的情况,要求出一种这些元素的输入顺序。这里哈希表负数位置表示该位置尚未存储任何数据元素。
解法说明
这道题的数据其实有一个特点,所有非负整数(即真正存在的数据)真正哈希到的位置到它现在实际在的位置之间的所有元素都是在它之前输入的。
最开始我是一直都没有什么思路,后来在网上一搜看到拓扑排序真的是觉得太妙了。把哈希表中所有数据的存储状态转换为一个图的话,那要求的输入顺序就正是一个对这个图的拓扑排序结果。
但这里仍然有三个问题:
- 如何把这些数据转换为图
- 如何通过每个数据在图中具体的索引位置找到它对应的实际值
- 怎样满足,当得到最终的拓扑排序结果时,有多个选择的情况下,首先选择最小值的那个元素
问题一
我在说明数据的特点时提到过,所有非负整数(即真正存在的数据)真正哈希到的位置到它现在实际在的位置之间的所有元素都是在它之前输入的。这样的话,可以把每个具体数据看作一个结点,在该数据之前输入的所有数据都有一条到该结点的边,因此该结点的入度等于它现在的位置到它应该哈希到的位置间的距离。
我在实现时使用的是邻接表形式,每一个表头结点都存储了当前哈希表对应位置的数据以及该数据的入度(即它当前位置到它应该哈希到的位置的距离),当然这里即使哈希表该位置上为负数不存在任何数据,我也将它存储进来。然后每个表头结点后链的链表的每一个结点都存储了该结点所指向的数据在该邻接表中的索引。
问题二和三
这道题我觉得最妙的实现之处就在这里,和普通拓扑排序不同,这里为了解决问题三,我使用的容器是一个堆(优先队列),堆里存的是每个数据在邻接表结构中对应位置的索引。
为什么用堆可以轻松解决这个问题,而且还能提高算法执行效率呢?
我的代码中的handleAndPrint这个函数就对应了这两个问题的具体解决。首先,我们将初始化好并读入数据计算好各结点入度后的邻接表中所有入度为0的结点放入堆中。此时,堆顶元素一定是入度为0且数据值最小的,满足问题三的要求。
每弹出一个元素,将该元素在邻接表所在位置后链的链表上每一个元素的入度减一,然后添加所有减一后入度为0的元素放入堆中,这时堆仍然会自动调整保持数据值最小的元素在堆顶。因此无论何时加入入度为0的元素,只要输出顺序是按照堆顶元素的弹出顺序,那么就一定是满足题意得那个拓扑排序顺序。
如果不使用堆,则每次从该容器取出元素时,都需要遍历整个容器找到数据值最小得那个然后删掉。
注:这里使用堆时,还有一个需要注意的问题。这里的堆中存储的是每个数据在邻接表中的索引,而不是实际数据值,那这样在比较的堆中任意两个元素的大小时,必须通过该索引找到对应在邻接表的具体数据值来比较。这样做的原因是,从索引找到数据易于实现,而从数据到索引就比较费时。
用纯c代码来实现真的好繁琐,要自己又写一遍堆和图的邻接表,要是用c++,可以直接用stl的一些数据结构。
该实现中,虽然我代码实现较多,但跟题目业务直接相关的只有buildGraph和handleAndPrint两个函数,其他大都是对两种数据结构的定义和实现。
#include */
};
typedef PtrToENode Edge;
/* 邻接点的定义 */
typedef struct AdjVNode *PtrToAdjVNode;
struct AdjVNode{
Index AdjV; /* 邻接点下标 */
PtrToAdjVNode Next; /* 指向下一个邻接点的指针 */
};
/* 顶点表头结点的定义 */
typedef struct Vnode{
ElementType data; // 该顶点的数值,-1表示该顶点不存在
int indegree; // 该顶点的入度,不存在时为-1
PtrToAdjVNode FirstEdge;/* 边表头指针 */
} AdjList[MaxVertexNum]; /* AdjList是邻接表类型 */
/* 图结点的定义 */
typedef struct GNode *PtrToGNode;
struct GNode{
int Nv; /* 顶点数 */
AdjList G; /* 邻接表 */
};
typedef PtrToGNode LGraph; /* 以邻接表方式存储的图类型 */
LGraph CreateGraph( int VertexNum ); // 初始化一个有VertexNum个顶点但没有边的图
void DestoryGraph( LGraph Graph );
void InsertEdge( LGraph Graph, Edge E );
/* ——————图的邻接表表示相关定义结束—————— */
/* ——————堆的相关定义开始—————— */
typedef struct HNode *Heap; /* 堆的类型定义 */
struct HNode {
Index *Data; /* 存储元素的数组,Data[0]存储元素个数 */
int Capacity; /* 堆的最大容量 */
};
typedef Heap MinHeap; /* 最小堆 */
#define ERROR -1 /* 错误标识应根据具体情况定义为堆中不可能出现的元素值 */
MinHeap CreateHeap( int MaxSize );
void DestoryHeap(MinHeap heap);
bool IsFull( MinHeap H );
bool IsEmpty( MinHeap H );
bool Insert( LGraph graph, MinHeap H, Index X ); // 将元素X插入最小堆H
Index DeleteMin( LGraph graph, MinHeap H ); // 从最小堆H中取出键值最小的元素,并删除一个结点
/* ——————堆的相关定义结束—————— */
LGraph buildGraph();
void handleAndPrint(LGraph graph);
int main()
{
LGraph graph;
graph = buildGraph();
handleAndPrint(graph);
DestoryGraph(graph);
return 0;
}
LGraph CreateGraph( int VertexNum )
{ /* 初始化一个有VertexNum个顶点但没有边的图 */
Index V;
LGraph Graph;
Graph = (LGraph)malloc( sizeof(struct GNode) ); /* 建立图 */
Graph->Nv = VertexNum;
/* 初始化邻接表头指针 */
/* 注意:这里默认顶点编号从0开始,到(Graph->Nv - 1) */
for (V=0; V<Graph->Nv; V++) {
Graph->G[V].data = -1;
Graph->G[V].indegree = -1;
Graph->G[V].FirstEdge = NULL;
}
return Graph;
}
void DestoryGraph( LGraph Graph )
{
Index V;
PtrToAdjVNode Node;
for (V = 0; V < Graph->Nv; ++V) {
while (Graph->G[V].FirstEdge) {
Node = Graph->G[V].FirstEdge;
Graph->G[V].FirstEdge = Node->Next;
free(Node);
}
}
free(Graph);
}
void InsertEdge( LGraph Graph, Edge E )
{
PtrToAdjVNode NewNode;
/* 插入边 */
/* 为V2建立新的邻接点 */
NewNode = (PtrToAdjVNode)malloc(sizeof(struct AdjVNode));
NewNode->AdjV = E->V2;
/* 将V2插入V1的表头 */
NewNode->Next = Graph->G[E->V1].FirstEdge;
Graph->G[E->V1].FirstEdge = NewNode;
}
MinHeap CreateHeap( int MaxSize )
{
MinHeap H = (MinHeap)malloc(sizeof(struct HNode));
H->Data = (ElementType *)malloc((MaxSize+1)*sizeof(ElementType));
H->Data[0] = 0;
H->Capacity = MaxSize;
return H;
}
void DestoryHeap(MinHeap heap)
{
free(heap->Data);
free(heap);
}
bool IsFull( MinHeap H )
{
return (H->Data[0] == H->Capacity);
}
bool Insert( LGraph graph, MinHeap H, Index X )
{
int i;
if ( IsFull(H) ) return false;
i = ++(H->Data[0]); /* i指向插入后堆中的最后一个元素的位置 */
for ( ; (i / 2 > 0) && graph->G[H->Data[i/2]].data > graph->G[X].data; i/=2 )
H->Data[i] = H->Data[i/2]; /* 上滤X */
H->Data[i] = X; /* 将X插入 */
return true;
}
bool IsEmpty( MinHeap H )
{
return (H->Data[0] == 0);
}
Index DeleteMin( LGraph graph, MinHeap H )
{
int Parent, Child;
Index MinItem, X;
if ( IsEmpty(H) ) return ERROR;
MinItem = H->Data[1]; /* 取出根结点存放的最小值 */
/* 用最小堆中最后一个元素从根结点开始向上过滤下层结点 */
X = H->Data[H->Data[0]--]; /* 注意当前堆的规模要减小 */
for( Parent=1; Parent*2<=H->Data[0]; Parent=Child ) {
Child = Parent * 2;
if( (Child!=H->Data[0]) && (graph->G[H->Data[Child]].data > graph->G[H->Data[Child+1]].data) )
Child++; /* Child指向左右子结点的较小者 */
if( graph->G[X].data <= graph->G[H->Data[Child]].data ) break; /* 找到了合适位置 */
else /* 下滤X */
H->Data[Parent] = H->Data[Child];
}
H->Data[Parent] = X;
return MinItem;
}
LGraph buildGraph()
{
int n;
Index i, j;
Edge e;
LGraph graph;
e = (Edge)malloc(sizeof(struct ENode));
scanf("%d", &n);
graph = CreateGraph(n);
for (i = 0; i < n; ++i) {
scanf("%d", &(graph->G[i].data));
if (graph->G[i].data < 0) continue; // 没有存数值则跳过该次
j = graph->G[i].data % graph->Nv;
graph->G[i].indegree = (i - j + graph->Nv) % graph->Nv;
while (j != i) {
e->V1 = j; e->V2 = i;
InsertEdge(graph, e);
j = (j + 1) % graph->Nv;
}
}
free(e);
return graph;
}
void handleAndPrint(LGraph graph)
{
MinHeap heap;
Index i, pos;
PtrToAdjVNode tmp;
bool isFirst;
heap = CreateHeap(graph->Nv);
isFirst = true;
for (i = 0; i < graph->Nv; ++i) { // 将入度为0的结点放入堆中
if (graph->G[i].indegree == 0)
Insert(graph, heap, i);
}
while (!IsEmpty(heap)) { // 进行拓扑排序,使用堆(即优先队列)来代替一般队列
pos = DeleteMin(graph, heap);
tmp = graph->G[pos].FirstEdge;
while (tmp) {
if (--(graph->G[tmp->AdjV].indegree) == 0)
Insert(graph, heap, tmp->AdjV);
tmp = tmp->Next;
}
if (isFirst) isFirst = false;
else printf(" ");
printf("%d", graph->G[pos].data);
}
DestoryHeap(heap);
}
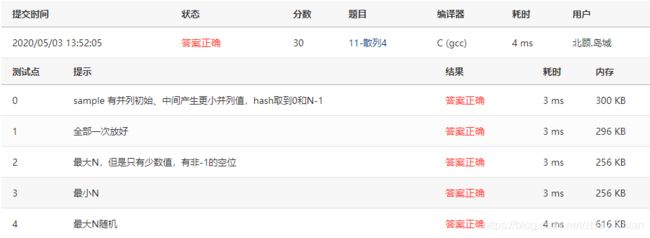
执行效果还是不错的: