文章目录
- 1.Timestamp.h的研究
- 2.Timestamp.cc的研究
- 2.相关测试代码
1.Timestamp.h的研究
- Timestamp类图如下,参考下即可

- 位置:muduo\base\Timestamp.h
// Use of this source code is governed by a BSD-style license
// that can be found in the License file.
//
// Author: Shuo Chen (chenshuo at chenshuo dot com)
//
namespace muduo
{
///
/// Time stamp in UTC, in microseconds resolution.
///
/// This class is immutable.
/// It's recommended to pass it by value, since it's passed in register on x64.
///
/*
muduo:copyable表示空基类,标识类,值类型
值语义:可以拷贝的,拷贝之后,与原对象脱离关系
对象语义:要么是不能拷贝的,要么是可以拷贝的,拷贝之后与原对象仍然存在一定的关系,比如共享底层资源(要实现自己的拷贝构造函数)
muduo大部分都是对象语义
*/
class Timestamp : public muduo::copyable,
public boost::equality_comparable<Timestamp>,
public boost::less_than_comparable<Timestamp>
{
public:
///
/// Constucts an invalid Timestamp.
///
Timestamp()
: microSecondsSinceEpoch_(0)
{
}
///
/// Constucts a Timestamp at specific time
///
/// @param microSecondsSinceEpoch
explicit Timestamp(int64_t microSecondsSinceEpochArg)
: microSecondsSinceEpoch_(microSecondsSinceEpochArg)
{
}
void swap(Timestamp& that)
{
//形参引用的改变能影响到实参,因为这里是引用
std::swap(microSecondsSinceEpoch_, that.microSecondsSinceEpoch_);
}
// default copy/assignment/dtor are Okay
string toString() const;
string toFormattedString(bool showMicroseconds = true) const;
bool valid() const { return microSecondsSinceEpoch_ > 0; }
// for internal usage.
int64_t microSecondsSinceEpoch() const { return microSecondsSinceEpoch_; }
time_t secondsSinceEpoch() const
{ return static_cast<time_t>(microSecondsSinceEpoch_ / kMicroSecondsPerSecond); }
///
/// Get time of now.
///
static Timestamp now();
static Timestamp invalid()
{
return Timestamp();
}
static Timestamp fromUnixTime(time_t t)
{
return fromUnixTime(t, 0);
}
static Timestamp fromUnixTime(time_t t, int microseconds)
{
return Timestamp(static_cast<int64_t>(t) * kMicroSecondsPerSecond + microseconds);
}
static const int kMicroSecondsPerSecond = 1000 * 1000;
private:
int64_t microSecondsSinceEpoch_;
};
//equality_comparable和less_than_comparable的模板元的原因,要求实现<,可自动实现>,<=,>=
inline bool operator<(Timestamp lhs, Timestamp rhs)
{
return lhs.microSecondsSinceEpoch() < rhs.microSecondsSinceEpoch();
}
inline bool operator==(Timestamp lhs, Timestamp rhs)
{
return lhs.microSecondsSinceEpoch() == rhs.microSecondsSinceEpoch();
}
///
/// Gets time difference of two timestamps, result in seconds.
///
/// @param high, low
/// @return (high-low) in seconds
/// @c double has 52-bit precision, enough for one-microsecond
/// resolution for next 100 years.
//1us=百万分之1s,两个微s相减/1000000,单位成为秒
inline double timeDifference(Timestamp high, Timestamp low)
{
int64_t diff = high.microSecondsSinceEpoch() - low.microSecondsSinceEpoch();
return static_cast<double>(diff) / Timestamp::kMicroSecondsPerSecond;
}
///
/// Add @c seconds to given timestamp.
///
/// @return timestamp+seconds as Timestamp
///
inline Timestamp addTime(Timestamp timestamp, double seconds)
{
int64_t delta = static_cast<int64_t>(seconds * Timestamp::kMicroSecondsPerSecond);
return Timestamp(timestamp.microSecondsSinceEpoch() + delta);
}
} // namespace muduo
2.Timestamp.cc的研究
- 位置:muduo\base\Timestamp.cc
// Use of this source code is governed by a BSD-style license
// that can be found in the License file.
//
// Author: Shuo Chen (chenshuo at chenshuo dot com)
//用于宏PRId64能用
using namespace muduo;
static_assert(sizeof(Timestamp) == sizeof(int64_t),
"Timestamp is same size as int64_t");
string Timestamp::toString() const
{
char buf[32] = {0};
int64_t seconds = microSecondsSinceEpoch_ / kMicroSecondsPerSecond;
int64_t microseconds = microSecondsSinceEpoch_ % kMicroSecondsPerSecond;
/*
int64_t用来表示64位整数,在32位系统中是long long int,在64位系统中是long int,所以打印int64_t的格式化方法是:
printf(“%ld”, value); // 64bit OS
printf("%lld", value); // 32bit OS
跨平台的做法:
printf("%" PRId64 "\n", value);
*/
//PRId64用于跨平台的,from:<inttypes.h>,若是64bit的,就等于ld,若是32bit的,就等于lld
snprintf(buf, sizeof(buf)-1, "%" PRId64 ".%06" PRId64 "", seconds, microseconds);
return buf;
}
string Timestamp::toFormattedString(bool showMicroseconds) const
{
char buf[64] = {0};
//求出距离1970.1.1的秒数
time_t seconds = static_cast<time_t>(microSecondsSinceEpoch_ / kMicroSecondsPerSecond);
struct tm tm_time;
gmtime_r(&seconds, &tm_time);//_r表示线程,可以将秒数转换为tm_time结构体
if (showMicroseconds)
{
int microseconds = static_cast<int>(microSecondsSinceEpoch_ % kMicroSecondsPerSecond);//转换成微妙数
snprintf(buf, sizeof(buf), "%4d%02d%02d %02d:%02d:%02d.%06d",
tm_time.tm_year + 1900, tm_time.tm_mon + 1, tm_time.tm_mday,
tm_time.tm_hour, tm_time.tm_min, tm_time.tm_sec,
microseconds);
}
else
{
snprintf(buf, sizeof(buf), "%4d%02d%02d %02d:%02d:%02d",
tm_time.tm_year + 1900, tm_time.tm_mon + 1, tm_time.tm_mday,
tm_time.tm_hour, tm_time.tm_min, tm_time.tm_sec);
}
return buf;
}
//获取当前时间
Timestamp Timestamp::now()
{
struct timeval tv;
gettimeofday(&tv, NULL);//gettimeofday(,时区),NULL表示没有时区
int64_t seconds = tv.tv_sec;//表示tv.tv_sec秒
return Timestamp(seconds * kMicroSecondsPerSecond + tv.tv_usec);//tv.tv_usec表示微妙
}
2.相关测试代码
- 目录结构
(1)将muduo库下的build以及CMakeLists.txt拷贝至jmuduo目录下;
(2)将muduo-master/muduo/base下的CMakeLists.txt,copyable.h,Timestamp.cc,Timestamp.h,Types.h拷贝到jmuduo/jmuduo/base下面;
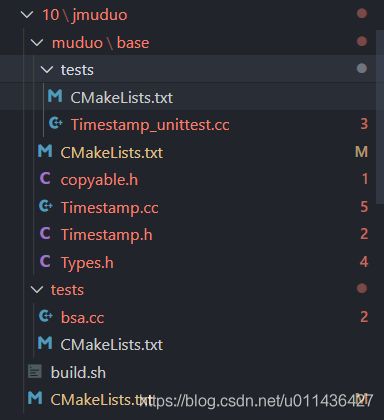
修改后的内容如下:
===================================10\jmuduo\muduo\base\CMakeLists.txt=================================================
set(base_SRCS
Timestamp.cc
)
add_library(muduo_base ${base_SRCS})
target_link_libraries(muduo_base pthread rt)
install(TARGETS muduo_base DESTINATION lib)
file(GLOB HEADERS "*.h")
install(FILES ${HEADERS} DESTINATION include/muduo/base)
if(NOT CMAKE_BUILD_NO_EXAMPLES)
add_subdirectory(tests)
endif()
- 测试BOOST_STATIC_ASSERT运行时的断言相关代码,assert是运行时的断言
(1)在jmuduo/tests/下添加:bsa.cc以及CMakeLists.txt文件;
(2)此外还需要在jmuduo/CMakeLists.txt下添加:add_subdirectory(tests);
(3)直接在jmuduo下面,运行./build即可
===========================================10\jmuduo\tests\bsa.cc=======================================================
class Timestamp
{
private:
int64_t microSecondsSinceEpoch_;
};
//编译时的断言,来自boost库,assert是运行时的断言
BOOST_STATIC_ASSERT(sizeof(Timestamp) == sizeof(int64_t));//在编译的时候不会出错
//BOOST_STATIC_ASSERT(sizeof(int) == sizeof(short));//在编译的时候会出错
int main(void)
{
return 0;
}
======================================10\jmuduo\tests\CMakeLists.txt===============================================
add_executable(bsa bsa.cc)
========================================10\jmuduo\CMakeLists.txt=================================================
。。。。。
,,,,,
。。。。
add_subdirectory(tests)
- 测试imestamp_unittest.cc。来自muduo\base\tests\Timestamp_unittest.cc
(1)将muduo的Timestamp_unittest.cc拷贝至10\jmuduo\muduo\base\tests\Timestamp_unittest.cc
(2)在10\jmuduo\muduo\base\tests\目录下添加:CMakeLists.txt
(3)在10\jmuduo\下,执行build.sh
==================================10\jmuduo\muduo\base\tests\CMakeLists.txt===================
add_executable(timestamp_unittest Timestamp_unittest.cc)
target_link_libraries(timestamp_unittest muduo_base)
================================10\jmuduo\muduo\base\tests\Timestamp_unittest.cc代码解释如下:=======================
using muduo::Timestamp;
void passByConstReference(const Timestamp& x)
{
printf("%s\n", x.toString().c_str());
}
void passByValue(Timestamp x)
{
printf("%s\n", x.toString().c_str());
}
void benchmark()
{
const int kNumber = 1000*1000;//const常量加个k,这是google的编码规范
std::vector<Timestamp> stamps;
stamps.reserve(kNumber);//预留了能容纳100万个Timestamp的空间
for (int i = 0; i < kNumber; ++i)
{
//插入100万个时间
stamps.push_back(Timestamp::now());//这里消耗的时间主要是now函数的gettimeofday,push_bak已经预留了空间,所以不会消耗时间
}
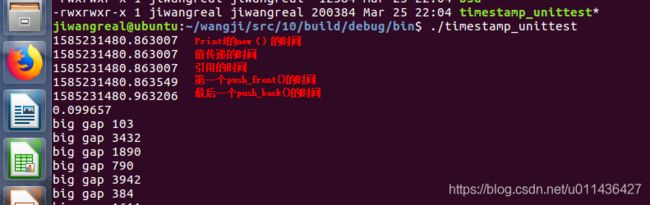
printf("%s\n", stamps.front().toString().c_str());
printf("%s\n", stamps.back().toString().c_str());
printf("%f\n", timeDifference(stamps.back(), stamps.front()));//计算最后一个时间和第一个时间的时间差
int increments[100] = { 0 };
int64_t start = stamps.front().microSecondsSinceEpoch();//相当于下标为0的时间
for (int i = 1; i < kNumber; ++i)
{
int64_t next = stamps[i].microSecondsSinceEpoch();
int64_t inc = next - start;//时间差
start = next;
if (inc < 0)
{
printf("reverse!\n");
}
else if (inc < 100)
{
++increments[inc];//小于100的个数++
}
else
{
printf("big gap %d\n", static_cast<int>(inc));
}
}
for (int i = 0; i < 100; ++i)
{
printf("%2d: %d\n", i, increments[i]);
}
}
int main()
{
//调用拷贝构造函数:用一个对象初始化另一个对象
//Timestamp::now()是没有名称的对象,所以将其构造函数的值拷贝给now对象,看now里面的return代码就明白了!!
Timestamp now(Timestamp::now());//等价于:Timestamp now=Timestamp::now()
printf("%s\n", now.toString().c_str());
passByValue(now);//值传递
passByConstReference(now);//引用传递
benchmark();//这是个基准函数
}
代码位置:可以参考下,
wangji/src/10/build/debug/bin$ ./timestamp_unittest
- 其它文件:10\jmuduo\build.sh,10\jmuduo\CMakeLists.txt
===================================10\jmuduo\build.sh==========================
set -x
SOURCE_DIR=`pwd`
BUILD_DIR=${BUILD_DIR:-../build}
BUILD_TYPE=${BUILD_TYPE:-debug}
INSTALL_DIR=${INSTALL_DIR:-../${BUILD_TYPE}-install}
BUILD_NO_EXAMPLES=${BUILD_NO_EXAMPLES:-0}
mkdir -p $BUILD_DIR/$BUILD_TYPE \
&& cd $BUILD_DIR/$BUILD_TYPE \
&& cmake --graphviz=dep.dot \
-DCMAKE_BUILD_TYPE=$BUILD_TYPE \
-DCMAKE_INSTALL_PREFIX=$INSTALL_DIR \
-DCMAKE_BUILD_NO_EXAMPLES=$BUILD_NO_EXAMPLES \
$SOURCE_DIR \
&& make $*
cd $SOURCE_DIR && doxygen
==================================10\jmuduo\CMakeLists.txt==================================
cmake_minimum_required(VERSION 2.6)
project(muduo CXX)
if(NOT CMAKE_BUILD_TYPE)
set(CMAKE_BUILD_TYPE "Debug")
endif()
set(CXX_FLAGS
-g
-D_FILE_OFFSET_BITS=64
-Wall
-Wextra
-Werror
-Wconversion
-Wno-unused-parameter
-Wold-style-cast
-Woverloaded-virtual
-Wpointer-arith
-Wshadow
-Wwrite-strings
-march=native
-rdynamic
)
if(CMAKE_BUILD_BITS EQUAL 32)
list(APPEND CXX_FLAGS "-m32")
endif()
string(REPLACE ";" " " CMAKE_CXX_FLAGS "${CXX_FLAGS}")
set(CMAKE_CXX_COMPILER "g++")
set(CMAKE_CXX_FLAGS_DEBUG "-O0")
set(CMAKE_CXX_FLAGS_RELEASE "-O2 -finline-limit=1000 -DNDEBUG")
set(EXECUTABLE_OUTPUT_PATH ${PROJECT_BINARY_DIR}/bin)
set(LIBRARY_OUTPUT_PATH ${PROJECT_BINARY_DIR}/lib)
find_package(Boost REQUIRED)
find_package(Protobuf)
find_package(CURL)
find_path(CARES_INCLUDE_DIR ares.h)
find_library(CARES_LIBRARY NAMES cares)
find_path(MHD_INCLUDE_DIR microhttpd.h)
find_library(MHD_LIBRARY NAMES microhttpd)
find_library(BOOSTTEST_LIBRARY NAMES boost_unit_test_framework)
include_directories(${Boost_INCLUDE_DIRS})
include_directories(${PROJECT_SOURCE_DIR})
string(TOUPPER ${CMAKE_BUILD_TYPE} BUILD_TYPE)
message(STATUS "CXX_FLAGS = " ${CMAKE_CXX_FLAGS} " " ${CMAKE_CXX_FLAGS_${BUILD_TYPE}})
add_subdirectory(muduo/base)
add_subdirectory(tests)


