高级IO(文件的读写)——并发式IO的解决方案(解决多路阻塞式IO的方案)
以下内容源于朱有鹏《物联网大讲堂》课程的学习整理,如有侵权,请告知删除。
一、并发式IO的解决方案
- 所谓并发式IO,即上节中提及的鼠标和键盘都已经启动。
1、非阻塞式IO
- 使用fcntl函数, 将上节中阻塞式的鼠标和键盘读取改为非阻塞式的。
- 性能不是很好。
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
int main(void)
{
// 读取鼠标
int fd = -1;
int flag = -1;
char buf[200];
int ret = -1;
fd = open("/dev/input/mouse1", O_RDONLY | O_NONBLOCK);
if (fd < 0)
{
perror("open:");
return -1;
}
// 把0号文件描述符(stdin)变成非阻塞式的
flag = fcntl(0, F_GETFL); // 先获取原来的flag
flag |= O_NONBLOCK; // 添加非阻塞属性
fcntl(0, F_SETFL, flag); // 更新flag
// 这3步之后,0就变成了非阻塞式的了
while (1)
{
// 读鼠标
memset(buf, 0, sizeof(buf));
ret = read(fd, buf, 50);
if (ret > 0)
{
printf("鼠标读出的内容是:[%s].\n", buf);
}
// 读键盘
memset(buf, 0, sizeof(buf));
ret = read(0, buf, 5);
if (ret > 0)
{
printf("键盘读出的内容是:[%s].\n", buf);
}
}
return 0;
}
/*
int main(void)
{
// 读取鼠标
int fd = -1;
char buf[200];
fd = open("/dev/input/mouse1", O_RDONLY | O_NONBLOCK);
if (fd < 0)
{
perror("open:");
return -1;
}
memset(buf, 0, sizeof(buf));
printf("before read.\n");
read(fd, buf, 50);
printf("读出的内容是:[%s].\n", buf);
return 0;
}
*/
/*
int main(void)
{
// 读取键盘
// 键盘就是标准输入,stdin
char buf[100];
int flag = -1;
// 把0号文件描述符(stdin)变成非阻塞式的
flag = fcntl(0, F_GETFL); // 先获取原来的flag
flag |= O_NONBLOCK; // 添加非阻塞属性
fcntl(0, F_SETFL, flag); // 更新flag
// 这3步之后,0就变成了非阻塞式的了
memset(buf, 0, sizeof(buf));
printf("before read.\n");
read(0, buf, 5);
printf("读出的内容是:[%s].\n", buf);
return 0;
}
*/ 2、多路复用IO
3、异步通知(异步IO)
二、IO多路复用原理
1、何为IO多路复用?
(1)英文为:IO multiplexing
(2)用在什么地方?
- 用于解决并发式IO,多路阻塞式的。
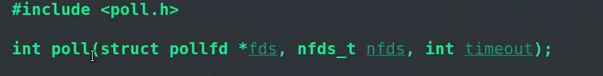
(3)涉及select函数、poll函数。
- 两个函数设计思想一样,外部特征不一样。
(4)实现原理:外部阻塞式(select函数本身是阻塞式的),内部非阻塞式自动轮询(select自动轮询时A,B)多路阻塞式IO(键盘A,鼠标B,这两者本身是阻塞式的)。
- 只要AB至少有一个输入,则select由阻塞返回。
2、select函数介绍
3、poll函数介绍
4、多路复用实践
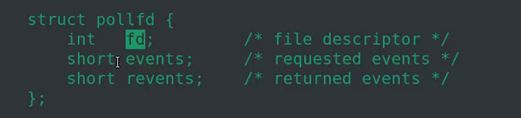
(1)用poll函数实现同时读取键盘鼠标
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
int main(void)
{
// 读取鼠标
int fd = -1, ret = -1;
char buf[200];
struct pollfd myfds[2] = {0};
fd = open("/dev/input/mouse1", O_RDONLY);
if (fd < 0)
{
perror("open:");
return -1;
}
// 初始化我们的pollfd
myfds[0].fd = 0; // 键盘
myfds[0].events = POLLIN; // 等待读操作
myfds[1].fd = fd; // 鼠标
myfds[1].events = POLLIN; // 等待读操作
ret = poll(myfds, fd+1, 10000);
if (ret < 0)
{
perror("poll: ");
return -1;
}
else if (ret == 0)
{
printf("超时了\n");
}
else
{
// 等到了一路IO,然后去监测到底是哪个IO到了,处理之
if (myfds[0].events == myfds[0].revents)
{
// 这里处理键盘
memset(buf, 0, sizeof(buf));
read(0, buf, 5);
printf("键盘读出的内容是:[%s].\n", buf);
}
if (myfds[1].events == myfds[1].revents)
{
// 这里处理鼠标
memset(buf, 0, sizeof(buf));
read(fd, buf, 50);
printf("鼠标读出的内容是:[%s].\n", buf);
}
}
return 0;
} (2)用select函数实现同时读取键盘鼠标
- 设置超时时间,即阻塞的时间不能太长,如果很久都没有IO来激活select,则表明超时了。
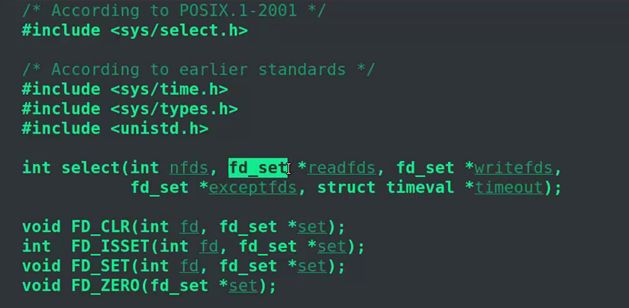
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
int main(void)
{
// 读取鼠标
int fd = -1, ret = -1;
char buf[200];
fd_set myset;
struct timeval tm;//设置超时时间,即阻塞的时间不能太长,如果很久都没有IO来激活select,则表明超时了。
fd = open("/dev/input/mouse1", O_RDONLY);
if (fd < 0)
{
perror("open:");
return -1;
}
// 当前有2个fd,一共是fd一个是0
// 处理myset
FD_ZERO(&myset);
FD_SET(fd, &myset);
FD_SET(0, &myset);
tm.tv_sec = 10;
tm.tv_usec = 0;
ret = select(fd+1, &myset, NULL, NULL, &tm);//+1,是因为0~fd,则共有fd+1个文件描述符
if (ret < 0)//错误
{
perror("select: ");
return -1;
}
else if (ret == 0)//表明超时
{
printf("超时了\n");
}
else//>0表示有一路IO激活了
{
// 等到了一路IO,然后去监测到底是哪个IO到了,处理之
if (FD_ISSET(0, &myset))
{
// 这里处理键盘
memset(buf, 0, sizeof(buf));
read(0, buf, 5);
printf("键盘读出的内容是:[%s].\n", buf);
}
if (FD_ISSET(fd, &myset))
{
// 这里处理鼠标
memset(buf, 0, sizeof(buf));
read(fd, buf, 50);
printf("鼠标读出的内容是:[%s].\n", buf);
}
}
return 0;
} 三、异步IO
1、何为异步IO?
(1)几乎可以认为,异步IO就是操作系统用软件实现的一套中断响应系统。类比硬件中断。
(2)异步IO的工作方法
- 当前进程注册一个异步IO事件(使用signal注册一个信号SIGIO的处理函数),然后当前进程可以正常处理自己的事情;
- 当异步事件发生后,当前进程会收到一个SIGIO信号,从而执行绑定的处理函数,来处理这个异步事件。
2、涉及的函数
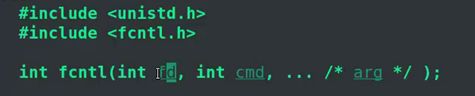
(1)fcntl函数,主要设置异步通知。
- 涉及的命令有F_GETFL(获取flag)、F_SETFL、O_ASYNC(表明可以接收异步通知)、F_SETOWN(设置通知谁(一般都是通知当前进程));
(2)signal或sigaction函数(SIGIO)
3、代码实践
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
int mousefd = -1;
// 绑定到SIGIO信号,在函数内处理异步通知事件
void func(int sig)
{
char buf[200] = {0};
if (sig != SIGIO)
return;
read(mousefd, buf, 50);
printf("鼠标读出的内容是:[%s].\n", buf);
}
int main(void)
{
// 读取鼠标
char buf[200];
int flag = -1;
mousefd = open("/dev/input/mouse1", O_RDONLY);
if (mousefd < 0)
{
perror("open:");
return -1;
}
// 把鼠标的文件描述符设置为可以接受异步IO
flag = fcntl(mousefd, F_GETFL);
flag |= O_ASYNC;
fcntl(mousefd, F_SETFL, flag);
// 把异步IO事件的接收进程设置为当前进程
fcntl(mousefd, F_SETOWN, getpid());
// 注册当前进程的SIGIO信号捕获函数
signal(SIGIO, func);
// 读键盘,在这里是当前进程
while (1)
{
memset(buf, 0, sizeof(buf));
read(0, buf, 5);
printf("键盘读出的内容是:[%s].\n", buf);
}
return 0;
} 四、存储映射IO
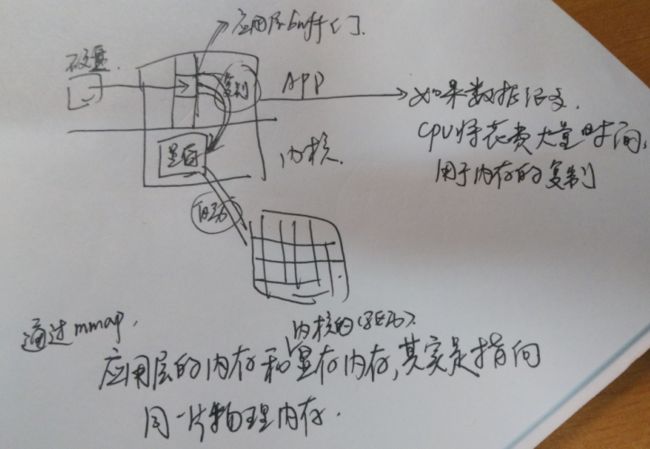
1、反映在mmap函数
- 把一个文件和一段内存映射起来。比如LCD设备文件和显存的对应。
2、例子
- LCD显示,IPC之共享内存
3、存储映射IO的特点
(1)共享而不是复制,减少内存操作。
(2)处理大文件时效率高(一般用于视频处理),小文件不划算。