启动eureka(源码解读二)
从github上把eureka的源码下载下来,按照readme进行build。
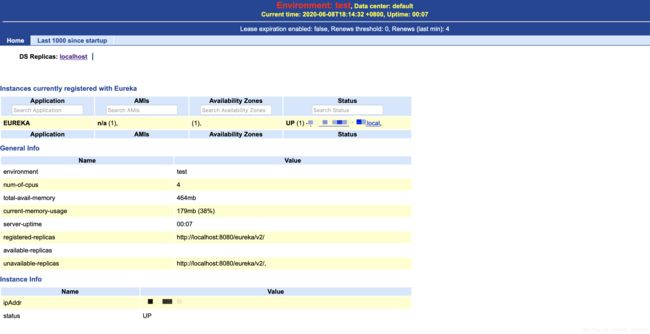
eureka是依赖tomcat的,server启动之后的界面是这样的:
这和我们用springboot集成eureka看到的界面很不一样,但是内容是大体相似的。
这个页面的源码在resources模块下:
它是用jsp写的,因为eureka出来的时间和Spring差不多。
在命令行运行:
./gradlew :eureka-examples:runExampleService
这里service注册和监听的逻辑在ExampleServiceBase.java这个类中:
@PostConstruct
public void start() {
// A good practice is to register as STARTING and only change status to UP
// after the service is ready to receive traffic
System.out.println("Registering service to eureka with STARTING status");
applicationInfoManager.setInstanceStatus(InstanceInfo.InstanceStatus.STARTING);
System.out.println("Simulating service initialization by sleeping for 2 seconds...");
try {
Thread.sleep(2000);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
// Nothing
}
// Now we change our status to UP
System.out.println("Done sleeping, now changing status to UP");
applicationInfoManager.setInstanceStatus(InstanceInfo.InstanceStatus.UP);
waitForRegistrationWithEureka(eurekaClient);
System.out.println("Service started and ready to process requests..");
try {
int myServingPort = applicationInfoManager.getInfo().getPort(); // read from my registered info
ServerSocket serverSocket = new ServerSocket(myServingPort);
final Socket s = serverSocket.accept();
System.out.println("Client got connected... processing request from the client");
processRequest(s);
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
System.out.println("Simulating service doing work by sleeping for " + 5 + " seconds...");
try {
Thread.sleep(5 * 1000);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
// Nothing
}
}
它的流程是:
- 准备把service注册到eureka server,状态为
STARTING - 睡两秒来模拟service的初始化,然后把状态改为
UP waitForRegistrationWithEureka(eurekaClient);将service注册到eureka server。
private void waitForRegistrationWithEureka(EurekaClient eurekaClient) {
// my vip address to listen on
String vipAddress = configInstance.getStringProperty("eureka.vipAddress", "sampleservice.mydomain.net").get();
InstanceInfo nextServerInfo = null;
while (nextServerInfo == null) {
try {
nextServerInfo = eurekaClient.getNextServerFromEureka(vipAddress, false);
} catch (Throwable e) {
System.out.println("Waiting ... verifying service registration with eureka ...");
try {
Thread.sleep(10000);
} catch (InterruptedException e1) {
e1.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}
这里用了一个死循环来将service注册到eureka server。
如何找这些server呢?用的是轮询(round-robin):
@Override
public InstanceInfo getNextServerFromEureka(String virtualHostname, boolean secure) {
List<InstanceInfo> instanceInfoList = this.getInstancesByVipAddress(
virtualHostname, secure);
if (instanceInfoList == null || instanceInfoList.isEmpty()) {
throw new RuntimeException("No matches for the virtual host name :"
+ virtualHostname);
}
Applications apps = this.localRegionApps.get();
int index = (int) (apps.getNextIndex(virtualHostname,
secure).incrementAndGet() % instanceInfoList.size());
return instanceInfoList.get(index);
}
- 开一个
ServerSocket监听连接:
int myServingPort = applicationInfoManager.getInfo().getPort(); // read from my registered info
ServerSocket serverSocket = new ServerSocket(myServingPort);
final Socket s = serverSocket.accept();
于是service阻塞了:
- 运行
./gradlew :eureka-examples:runExampleClient来启动client(消费者)。
它的逻辑在ExampleEurekaClient.java中:
public void sendRequestToServiceUsingEureka(EurekaClient eurekaClient) {
// initialize the client
// this is the vip address for the example service to talk to as defined in conf/sample-eureka-service.properties
String vipAddress = "sampleservice.mydomain.net";
InstanceInfo nextServerInfo = null;
try {
nextServerInfo = eurekaClient.getNextServerFromEureka(vipAddress, false);
} catch (Exception e) {
System.err.println("Cannot get an instance of example service to talk to from eureka");
System.exit(-1);
}
System.out.println("Found an instance of example service to talk to from eureka: "
+ nextServerInfo.getVIPAddress() + ":" + nextServerInfo.getPort());
System.out.println("healthCheckUrl: " + nextServerInfo.getHealthCheckUrl());
System.out.println("override: " + nextServerInfo.getOverriddenStatus());
Socket s = new Socket();
int serverPort = nextServerInfo.getPort();
try {
s.connect(new InetSocketAddress(nextServerInfo.getHostName(), serverPort));
} catch (IOException e) {
System.err.println("Could not connect to the server :"
+ nextServerInfo.getHostName() + " at port " + serverPort);
} catch (Exception e) {
System.err.println("Could not connect to the server :"
+ nextServerInfo.getHostName() + " at port " + serverPort + "due to Exception " + e);
}
try {
String request = "FOO " + new Date();
System.out.println("Connected to server. Sending a sample request: " + request);
PrintStream out = new PrintStream(s.getOutputStream());
out.println(request);
System.out.println("Waiting for server response..");
BufferedReader rd = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(s.getInputStream()));
String str = rd.readLine();
if (str != null) {
System.out.println("Received response from server: " + str);
System.out.println("Exiting the client. Demo over..");
}
rd.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
通过写死的虚拟ip地址sampleservice.mydomain.net来找到euerka server。
然后连接:
Socket s = new Socket();
int serverPort = nextServerInfo.getPort();
try {
s.connect(new InetSocketAddress(nextServerInfo.getHostName(), serverPort));
}
发数据:
String request = "FOO " + new Date();
System.out.println("Connected to server. Sending a sample request: " + request);
PrintStream out = new PrintStream(s.getOutputStream());
out.println(request);
打印回复:
System.out.println("Waiting for server response..");
BufferedReader rd = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(s.getInputStream()));
String str = rd.readLine();
if (str != null) {
System.out.println("Received response from server: " + str);
System.out.println("Exiting the client. Demo over..");
}
- 在service这端:
它会一个读取client发来的数据并且回一个时间。
private void processRequest(final Socket s) {
try {
BufferedReader rd = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(s.getInputStream()));
String line = rd.readLine();
if (line != null) {
System.out.println("Received a request from the example client: " + line);
}
String response = "BAR " + new Date();
System.out.println("Sending the response to the client: " + response);
PrintStream out = new PrintStream(s.getOutputStream());
out.println(response);
} catch (Throwable e) {
System.err.println("Error processing requests");
} finally {
if (s != null) {
try {
s.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}
以上就是eureka的大致逻辑,我们接下来会拆分细节解析。
如果你在启动service和client的时候报错了(也就是运行./gradlew :eureka-examples:runExampleService和./gradlew :eureka-examples:runExampleClient),可以invalidate cache和restart一下: