muduo库如何支持多线程
EventLoopThread(IO线程类)
EventLoopThreadPool(IO线程池类)
IO线程池的功能是开启若干个IO线程,并让这些IO线程处于事件循环的状态
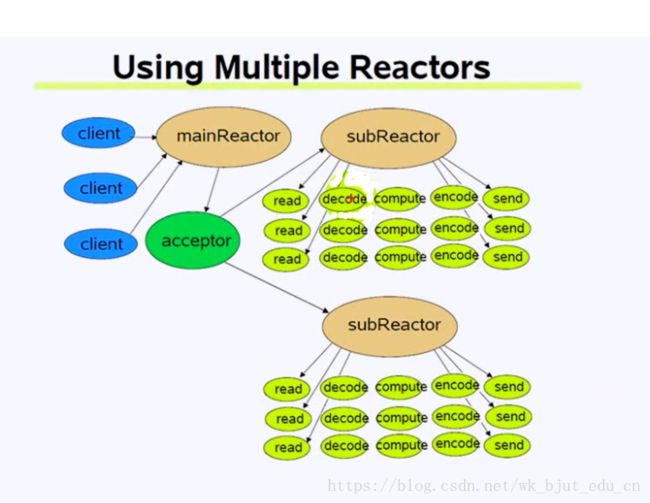
图中的每个Reactor都属于一个线程,mainReactor关注的是acceptor,也就是监听套接字相关的事件,subReactor关注的是已连接套接字相关的事件。也就是说,每新到一个连接,就选择一个subReactor来处理这个连接,也就选择了相对应的线程来处理这个连接。如果没有subRector,那么mainReactor既要处理监听套接字相关的事件,也要处理已连接套接字相关的事件。
代码说明
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
using namespace muduo;
using namespace muduo::net;
class TestServer
{
public:
//第三个参数是创建的IO线程个数
TestServer(EventLoop* loop,
const InetAddress& listenAddr, int numThreads)
: loop_(loop),
server_(loop, listenAddr, "TestServer"),
numThreads_(numThreads)
{
server_.setConnectionCallback(
boost::bind(&TestServer::onConnection, this, _1));
server_.setMessageCallback(
boost::bind(&TestServer::onMessage, this, _1, _2, _3));
server_.setThreadNum(numThreads);
}
void start()
{
//启动线程池
server_.start();
}
private:
void onConnection(const TcpConnectionPtr& conn)
{
if (conn->connected())
{
printf("onConnection(): new connection [%s] from %s\n",
conn->name().c_str(),
conn->peerAddress().toIpPort().c_str());
}
else
{
printf("onConnection(): connection [%s] is down\n",
conn->name().c_str());
}
}
void onMessage(const TcpConnectionPtr& conn,
const char* data,
ssize_t len)
{
printf("onMessage(): received %zd bytes from connection [%s]\n",
len, conn->name().c_str());
}
EventLoop* loop_;
TcpServer server_;
int numThreads_;
};
int main()
{
printf("main(): pid = %d\n", getpid());
InetAddress listenAddr(8888);
EventLoop loop;
TestServer server(&loop, listenAddr,4);
server.start();
//现在有5个事件循环,下面这个是主线程的事件循环
loop.loop();
}
首先是server_.start(),启动Tcp服务器
这个函数会去启动线程池,然后执行监听操作
//该函数可以跨线程调用
//启动线程池
void TcpServer::start()
{
if (started_.getAndSet(1) == 0)
{
threadPool_->start(threadInitCallback_);
//判断是否处于监听状态
assert(!acceptor_->listenning());
loop_->runInLoop(
//进入&Acceptor::listen
boost::bind(&Acceptor::listen, get_pointer(acceptor_)));
}
}启动线程池,IO线程的个数在代码说明中进行了传入,把这些IO线程放入IO线程列表进行管理
void EventLoopThreadPool::start(const ThreadInitCallback& cb)
{
assert(!started_);
baseLoop_->assertInLoopThread();
started_ = true;
for (int i = 0; i < numThreads_; ++i)
{
char buf[name_.size() + 32];
snprintf(buf, sizeof buf, "%s%d", name_.c_str(), i);
//创建若干个线程
EventLoopThread* t = new EventLoopThread(cb, buf);
threads_.push_back(t);
//t->startLoop(),启动EventLoopThread线程
//并且把返回的EventLoop对象指针压入到loops_
loops_.push_back(t->startLoop());
}
//如果没有创建IO线程
if (numThreads_ == 0 && cb)
{
cb(baseLoop_);
}
}当有一个新的连接到来的时候,按照轮叫的方式选择一个EventLoop管理这个新来的连接
//一个新的连接之后
void TcpServer::newConnection(int sockfd, const InetAddress& peerAddr)
{
loop_->assertInLoopThread();
//按照轮叫的方式选择一个EventLoop
EventLoop* ioLoop = threadPool_->getNextLoop();
char buf[64];
snprintf(buf, sizeof buf, "-%s#%d", ipPort_.c_str(), nextConnId_);
++nextConnId_;
//连接名称
string connName = name_ + buf;
LOG_INFO << "TcpServer::newConnection [" << name_
<< "] - new connection [" << connName
<< "] from " << peerAddr.toIpPort();
//构造本地地址
InetAddress localAddr(sockets::getLocalAddr(sockfd));
// FIXME poll with zero timeout to double confirm the new connection
// FIXME use make_shared if necessary
//创建一个连接对象
TcpConnectionPtr conn(new TcpConnection(ioLoop,
connName,
sockfd,
localAddr,
peerAddr));
//将连接对象放到一个map容器中
connections_[connName] = conn;
//对这个连接对象设置回调函数
conn->setConnectionCallback(connectionCallback_);
conn->setMessageCallback(messageCallback_);
conn->setWriteCompleteCallback(writeCompleteCallback_);
conn->setCloseCallback(
boost::bind(&TcpServer::removeConnection, this, _1)); // FIXME: unsafe
//不能够在当前线程中调用,应该让ioLoop所属的IO线程调用这个连接
ioLoop->runInLoop(boost::bind(&TcpConnection::connectEstablished, conn));
}轮叫的方式,选择一个EventLoop对象处理连接
//当一个新的连接到来的时候,需要选择一个EventLoop对象来处理
EventLoop* EventLoopThreadPool::getNextLoop()
{
baseLoop_->assertInLoopThread();
assert(started_);
//这个baseLoop_就是mainReactor
EventLoop* loop = baseLoop_;
//如果loops_为空,也就是没有出新的IO线程,则loop指向baseLoop_,也就是mainReactor
//如果不为空,按照round-robin(RR,轮叫)的调度方式选择一个EventLoop
/*
轮叫调度(Round Robin Scheduling)算法就是以轮叫的方式依次将请求调度不
同的服务器,即每次调度执行i = (i + 1) mod n,并选出第i台服务器。算法的优点是其简洁性,
它无需记录当前所有连接的状态,所以它是一种无状态调度。
*/
if (!loops_.empty())
{
// round-robin
loop = loops_[next_];
++next_;
if (implicit_cast(next_) >= loops_.size())
{
next_ = 0;
}
}
return loop;
} 在TcpServer.cc中,
有一个数据成员 boost::shared_ptr
还可以设置线程池个数
//设置线程池中的线程个数,不包括主的EventLoop线程
void TcpServer::setThreadNum(int numThreads)
{
assert(0 <= numThreads);
threadPool_->setThreadNum(numThreads);
}当一个新的连接到来之后,会调用TcpServer::newConnection,这时候会选择一个EventLoop,也就选择EventLoop所对应的线程来处理这个连接。然后创建一个TcpConnection对象,它所属的loop就是ioLoop,而不是loop_,那是acceptor所属的loop。也就是说,创建线程池的时候,线程池个数不为0,那么ioLoop就不等于loop_,而是按轮叫方式选择一个EventLoop对象。
注意,调用connectEstablished的方式,是异步调用,不是在当前线程调用,而是ioLoop所属的IO线程调用连接connectEstablished。将这个函数交到队列中。
//一个新的连接之后
void TcpServer::newConnection(int sockfd, const InetAddress& peerAddr)
{
loop_->assertInLoopThread();
//按照轮叫的方式选择一个EventLoop
EventLoop* ioLoop = threadPool_->getNextLoop();
char buf[64];
snprintf(buf, sizeof buf, "-%s#%d", ipPort_.c_str(), nextConnId_);
++nextConnId_;
//连接名称
string connName = name_ + buf;
LOG_INFO << "TcpServer::newConnection [" << name_
<< "] - new connection [" << connName
<< "] from " << peerAddr.toIpPort();
//构造本地地址
InetAddress localAddr(sockets::getLocalAddr(sockfd));
// FIXME poll with zero timeout to double confirm the new connection
// FIXME use make_shared if necessary
//创建一个连接对象
TcpConnectionPtr conn(new TcpConnection(ioLoop,
connName,
sockfd,
localAddr,
peerAddr));
//将连接对象放到一个map容器中
connections_[connName] = conn;
对这个连接对象设置回调函数
conn->setConnectionCallback(connectionCallback_);
conn->setMessageCallback(messageCallback_);
conn->setWriteCompleteCallback(writeCompleteCallback_);
conn->setCloseCallback(
boost::bind(&TcpServer::removeConnection, this, _1)); // FIXME: unsafe
//不能够在当前线程中调用,应该让ioLoop所属的IO线程调用这个连接
ioLoop->runInLoop(boost::bind(&TcpConnection::connectEstablished, conn));
}将TcpConnection所对应的通道加入Poller关注。
//当连接到来的时候
void TcpConnection::connectEstablished()
{
loop_->assertInLoopThread();
assert(state_ == kConnecting);
setState(kConnected);
//tie的参数是shared_ptr,shared_from_this()获得一个自身的share_ptr对象
channel_->tie(shared_from_this());
//TcpConnection所对应的通道加入到Poller关注
channel_->enableReading();
//这是用户的回调函数
connectionCallback_(shared_from_this());
}接下来的过程和https://blog.csdn.net/wk_bjut_edu_cn/article/details/80898672中的一样。