POI和EasyExcel 的使用笔记
文章首发于我的个人博客,欢迎访问。
代码地址
POI和EasyExcel 的使用笔记
我们经常需要将项目中的表格数据或者文档数据进行导入或者导出操作,这个如果自己从零开始做还比较麻烦。比如我之前就职的公司都是自己做的组件,但是很不好用,BUG 太多。关于表格导入导出,市面上比较知名的开源就是 Apache 的POI 和 阿里巴巴的 EasyExcel了。EasyExcel 也是对 POI 的改进和封装, 更加好用。下面通过一些 demo 学习如何使用这两个开源组件。这两个组件都不难,多看文档就能会,尤其是 EasyExcel 的文档非常详细。这篇博客主要自己在写 demo 的时候整理的笔记,方便以后使用的时候查阅。如果能帮到你那就更好了。
常用信息
1、将用户的信息导出为 excel 表格。
2、将 Excel 表中的信息录入到网站数据库。
开发中经常会涉及到 excel 的 处理,如导出 Excel ,导入 Excel 到数据库中。
操作 Excel 目前比较流行的就是 Apache POI 和阿里巴巴的 EasyExcel。
Apache POI
Apache POI 官网: http://poi.apache.org/index.html 。
百度百科的解释: Apache POI是Apache软件基金会的开放源码函式库,POI提供API给Java程序对Microsoft Office格式档案读和写的功能。
结构:
HSSF - 提供读写[Microsoft Excel](https://baike.baidu.com/item/Microsoft Excel)格式档案的功能。excel 2003 版本
XSSF - 提供读写Microsoft Excel OOXML格式档案的功能。excel 207 版本
HWPF - 提供读写[Microsoft Word](https://baike.baidu.com/item/Microsoft Word)格式档案的功能。
HSLF - 提供读写Microsoft PowerPoint格式档案的功能。
HDGF - 提供读写[Microsoft Visio](https://baike.baidu.com/item/Microsoft Visio)格式档案的功能。
EasyExcel
GitHub 地址: https://github.com/alibaba/easyexcel
EasyExcel 官网: https://www.yuque.com/easyexcel/doc/easyexcel
EasyExcel 是阿里巴巴开源的一个 excel处理框架,以使用简单、节省内存著称。
EasyExcel 能大大减少内存占用的主要原因是在解析 Excel 时没有将文件数据一次性全部加载到内存中,而是从磁盘上一行行读取数据,逐个解析。
下面是 EasyExcel 和 POI 在解析Excel 时的对比图。
1、POI-Excel 写
创建项目
1、建立一个空项目,创建普通的 Module 。
2、引入依赖:
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.apache.poigroupId>
<artifactId>poiartifactId>
<version>3.9version>
dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.apache.poigroupId>
<artifactId>poi-ooxmlartifactId>
<version>3.9version>
dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>joda-timegroupId>
<artifactId>joda-timeartifactId>
<version>2.10.1version>
dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>junitgroupId>
<artifactId>junitartifactId>
<version>4.12version>
dependency>
dependencies>
03 | 07 版本的写操作,就是对象不一样,方法都是一样的。
需要注意:2003 版本和 2007 版本存在兼容性问题, 03 版本最多只有 65535 行。
03 版本:
package cn.itzhouq;
import org.apache.poi.hssf.usermodel.HSSFSheet;
import org.apache.poi.hssf.usermodel.HSSFWorkbook;
import org.apache.poi.ss.usermodel.Cell;
import org.apache.poi.ss.usermodel.Row;
import org.joda.time.DateTime;
import org.junit.Test;
import java.io.FileOutputStream;
public class ExcelWriteTest {
String PATH = "F:\\workspaces\\workspaces_idea\\POIAndEasyExcel\\itzhouq-poi";
@Test
public void testWrite03 () throws Exception {
// 1. 创建一个工作薄
HSSFWorkbook workbook = new HSSFWorkbook();
// 2. 创建一个工作表
HSSFSheet sheet = workbook.createSheet("人员统计表");
// 3. 创建一个行 (1, 1)
Row row1 = sheet.createRow(0);
// 4. 创建一个单元格
Cell cell11 = row1.createCell(0);
cell11.setCellValue("今日新增人员");
Cell cell12 = row1.createCell(1);
cell12.setCellValue(666);
// 第二行
Row row2 = sheet.createRow(1);
Cell cell21 = row2.createCell(0); // (2,1 )
cell21.setCellValue("统计时间");
Cell cell22 = row2.createCell(1);
String time = new DateTime().toString("yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss");
cell22.setCellValue(time);
// 生成一张表 03版本的就是使用 xls 结尾
FileOutputStream fileOutputStream = new FileOutputStream(PATH + "/人员统计表03.xls");
workbook.write(fileOutputStream);
// 关闭流
fileOutputStream.close();
System.out.println("人员统计表03.xls 生成完毕");
}
}
大文件写 HSSF
缺点:最多只能处理 65536 行,否则会抛出异常
java.lang.IllegalArgumentException: Invalid row number (65536) outside allowable range (0..65535)
优点:过程中写入缓存,不操作磁盘,最后一次性写入磁盘,速度快。
@Test
public void testWrite03BigData () throws IOException {
// 时间
long begin = System.currentTimeMillis();
// 创建一个工作薄
Workbook workbook = new HSSFWorkbook();
// 创建表
Sheet sheet = workbook.createSheet();
// 写入数据
for (int rowNum = 0; rowNum < 65535; rowNum++) {
Row row = sheet.createRow(rowNum);
for (int cellNum = 0; cellNum < 10; cellNum++) {
Cell cell = row.createCell(cellNum);
cell.setCellValue(cellNum);
}
}
System.out.println("over");
FileOutputStream fileOutputStream = new FileOutputStream(PATH + "/testWrite03BigData.xls");
workbook.write(fileOutputStream);
fileOutputStream.close();
long end = System.currentTimeMillis();
System.out.println((double) (end - begin) / 1000); // 1.295
}
大文件写 XSSF
缺点:写数据时速度非常慢,非常耗内存,也会发生内存溢出,如 100 万条数据。
优点:可以写较大的数据量,如 20 万条。
@Test
public void testWrite07BigData () throws IOException {
// 时间
long begin = System.currentTimeMillis();
// 创建一个工作薄
Workbook workbook = new XSSFWorkbook();
// 创建表
Sheet sheet = workbook.createSheet();
// 写入数据
for (int rowNum = 0; rowNum < 65537; rowNum++) {
Row row = sheet.createRow(rowNum);
for (int cellNum = 0; cellNum < 10; cellNum++) {
Cell cell = row.createCell(cellNum);
cell.setCellValue(cellNum);
}
}
System.out.println("over");
FileOutputStream fileOutputStream = new FileOutputStream(PATH + "/testWrite07BigData.xlsx");
workbook.write(fileOutputStream);
fileOutputStream.close();
long end = System.currentTimeMillis();
System.out.println((double) (end - begin) / 1000); // 7.39
}
大文件写 SXSSF
优点: 可以写非常大的数据量,如 100 万条甚至更多,写数据速度快,占用更少的内存。
注意:
过程总会产生临时文件,需要清理临时文件。默认由 100 条记录被保存在内存中,则最前面的数据被写入临时文件。如果想要自定义内存中数据的数量,可以使用 new SXSSFWorkbook (数量)。
@Test
public void testWrite07BigDataS () throws IOException {
// 时间
long begin = System.currentTimeMillis();
// 创建一个工作薄
Workbook workbook = new SXSSFWorkbook();
// 创建表
Sheet sheet = workbook.createSheet();
// 写入数据
for (int rowNum = 0; rowNum < 65537; rowNum++) {
Row row = sheet.createRow(rowNum);
for (int cellNum = 0; cellNum < 10; cellNum++) {
Cell cell = row.createCell(cellNum);
cell.setCellValue(cellNum);
}
}
System.out.println("over");
FileOutputStream fileOutputStream = new FileOutputStream(PATH + "/testWrite07BigDataS.xlsx");
workbook.write(fileOutputStream);
fileOutputStream.close();
// 清除临时文件
((SXSSFWorkbook) workbook).dispose();
long end = System.currentTimeMillis();
System.out.println((double) (end - begin) / 1000); // 1.859
}
SXSSFWorkbook 来自官方的解释:实现“BigGridDemo” 策略的流式 SXSSFWorkbook 版本。这允许写入非常大的文件而不会耗尽内存,因为任何时候只有可配置的行部分被保存在内存中。
请注意,仍然可能会消耗大量内存,这些内存基于你正在使用的功能,例如合并区域,注释。。。仍然只存储在内存中,因此如果广泛使用,可能需要大量内存。
2、POI-Excel 读
03 | 07 版本的读操作
03 版本
String PATH = "F:\\workspaces\\workspaces_idea\\POIAndEasyExcel\\itzhouq-poi";
@Test
public void testRead03() throws IOException {
// 获取文件流
FileInputStream fileInputStream = new FileInputStream(PATH + "/人员统计表03.xls");
// 1. 创建一个工作簿,使用excel能操作的,代码都能操作
Workbook workbook = new HSSFWorkbook(fileInputStream);
// 2. 得到表
Sheet sheet = workbook.getSheetAt(0);
// 3. 得到行
Row row = sheet.getRow(0);
// 4. 得到列
Cell cell = row.getCell(0);
System.out.println(cell.getStringCellValue()); // 今日新增人员
Cell cell1 = row.getCell(1);
System.out.println(cell1.getNumericCellValue()); // 666.0
fileInputStream.close();
}
07 版本
@Test
public void testRead07() throws IOException {
// 获取文件流
FileInputStream fileInputStream = new FileInputStream(PATH + "/人员统计表07.xlsx");
// 1. 创建一个工作簿,使用excel能操作的,代码都能操作
Workbook workbook = new XSSFWorkbook(fileInputStream);
// 2. 得到表
Sheet sheet = workbook.getSheetAt(0);
// 3. 得到行
Row row = sheet.getRow(0);
// 4. 得到列
Cell cell = row.getCell(0);
System.out.println(cell.getStringCellValue()); // 今日新增人员
Cell cell1 = row.getCell(1);
System.out.println(cell1.getNumericCellValue()); // 666.0
fileInputStream.close();
}
注意获取值的类型。
读取不同的数据类型(最麻烦的点)
@Test
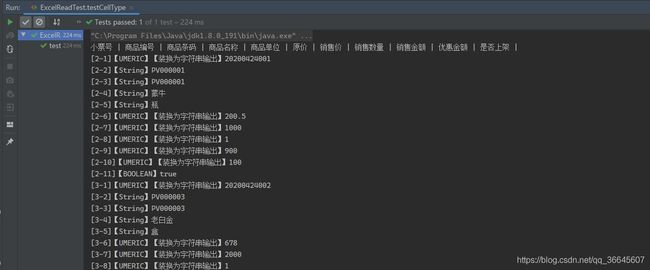
public void testCellType() throws IOException {
// 获取文件流
FileInputStream fileInputStream = new FileInputStream(PATH + "/明细表.xls");
// 创建一个工作簿
Workbook workbook = new HSSFWorkbook(fileInputStream);
Sheet sheet = workbook.getSheetAt(0);
// 获取标题内容
Row rowTitle = sheet.getRow(0);
if (rowTitle != null) {
// 重点
int rowCount = rowTitle.getPhysicalNumberOfCells(); // 获取列的数量
for (int cellNum = 0; cellNum < rowCount; cellNum++) {
Cell cell = rowTitle.getCell(cellNum);
if (cell != null) {
int cellType = cell.getCellType();
String cellValue = cell.getStringCellValue();
System.out.print(cellValue + " | ");
}
}
System.out.println();
}
// 获取表中内容
int rowCount = sheet.getPhysicalNumberOfRows();
for (int rowNum = 1; rowNum < rowCount; rowNum++) {
Row rowData = sheet.getRow(rowNum);
if (rowData != null) {
// 读取列
int cellCount = rowTitle.getPhysicalNumberOfCells();
for (int cellNum = 0; cellNum < cellCount; cellNum++) {
System.out.print("[" + (rowNum + 1) + "-" + (cellNum + 1) + "]");
Cell cell = rowData.getCell(cellNum);
// 匹配列的数据类型
if (cell != null) {
int cellType = cell.getCellType();
String cellValue = "";
switch (cellType) {
case HSSFCell.CELL_TYPE_STRING: // 字符串
System.out.print("【String】");
cellValue = cell.getStringCellValue();
break;
case HSSFCell.CELL_TYPE_BOOLEAN: // 布尔
System.out.print("【BOOLEAN】");
cellValue = String.valueOf(cell.getBooleanCellValue());
break;
case HSSFCell.CELL_TYPE_BLANK: // 空
System.out.print("【BLANK】");
break;
case HSSFCell.CELL_TYPE_NUMERIC: // 数字
System.out.print("【UMERIC】");
if (HSSFDateUtil.isCellDateFormatted(cell)) { // 日期
System.out.print("【日期】");
Date date = cell.getDateCellValue();
cellValue = new DateTime(date).toString();
} else {
// 不是日期格式,防止数字过长
System.out.print("【装换为字符串输出】");
cell.setCellType(HSSFCell.CELL_TYPE_STRING);
cellValue = cell.toString();
}
break;
case HSSFCell.CELL_TYPE_ERROR:
System.out.print("【数据类型错误】");
break;
}
System.out.println(cellValue);
}
}
}
}
fileInputStream.close();
}
注意类型转换问题。可以将上面的方法提取成工具类。
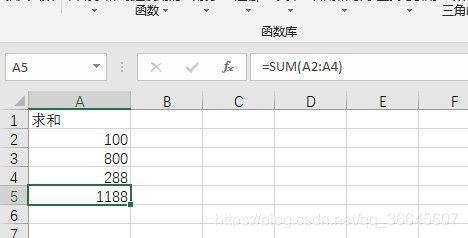
计算公式(了解)
import org.apache.poi.hssf.usermodel.HSSFFormulaEvaluator;
import org.apache.poi.hssf.usermodel.HSSFWorkbook;
import org.apache.poi.ss.usermodel.*;
import org.junit.Test;
import java.io.FileInputStream;
import java.io.FileNotFoundException;
import java.io.IOException;
/**
* 计算公式
*/
public class Formula {
String PATH = "F:\\workspaces\\workspaces_idea\\POIAndEasyExcel\\itzhouq-poi"
@Test
public void testForMula() throws IOException {
FileInputStream fileInputStream = new FileInputStream(PATH + "/公式.xls");
Workbook workbook = new HSSFWorkbook(fileInputStream);
Sheet sheet = workbook.getSheetAt(0);
Row row = sheet.getRow(4);
Cell cell = row.getCell(0);
// 拿到计算公式
FormulaEvaluator formulaEvaluator = new HSSFFormulaEvaluator((HSSFWorkbook) workbook);
// 输出单元格的内容
int cellType = cell.getCellType();
switch (cellType) {
case (Cell.CELL_TYPE_FORMULA): // 公式
String formula = cell.getCellFormula();
System.out.println(formula); // SUM(A2:A4)
// 计算
CellValue evaluate = formulaEvaluator.evaluate(cell);
String cellValue = evaluate.formatAsString();
System.out.println(cellValue); // 1188.0
break;
}
}
}
3、EsayExcel 操作
官方文档很详细,可以根据文档快速入门 https://www.yuque.com/easyexcel/doc/easyexcel 。
导入依赖
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>com.alibabagroupId>
<artifactId>easyexcelartifactId>
<version>2.2.0-beta2version>
dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>joda-timegroupId>
<artifactId>joda-timeartifactId>
<version>2.10.1version>
dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.projectlombokgroupId>
<artifactId>lombokartifactId>
<version>1.18.10version>
dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>junitgroupId>
<artifactId>junitartifactId>
<version>4.12version>
<scope>compilescope>
dependency>
dependencies>
写入测试
根据官方文档的测试代码: https://www.yuque.com/easyexcel/doc/write
1、DemoData.java
package cn.itzhouq.easyexcel;
import com.alibaba.excel.annotation.ExcelIgnore;
import com.alibaba.excel.annotation.ExcelProperty;
import lombok.Data;
import java.util.Date;
@Data
public class DemoData {
@ExcelProperty("字符串标题")
private String string;
@ExcelProperty("日期标题")
private Date date;
@ExcelProperty("数字标题")
private Double doubleData;
/**
* 忽略这个字段
*/
@ExcelIgnore
private String ignore;
}
2、测试写入数据
package cn.itzhouq.easyexcel;
import com.alibaba.excel.EasyExcel;
import org.junit.Test;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.Date;
import java.util.List;
public class EasyExcelTest {
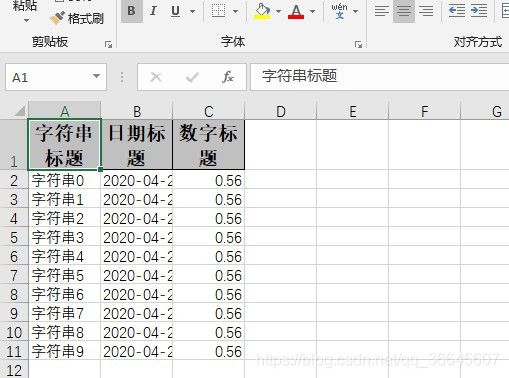
private List<DemoData> data() {
List<DemoData> list = new ArrayList<DemoData>();
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) {
DemoData data = new DemoData();
data.setString("字符串" + i);
data.setDate(new Date());
data.setDoubleData(0.56);
list.add(data);
}
return list;
}
// 根据list 写入 Excel
/**
* 最简单的写
* 1. 创建excel对应的实体对象 参照{@link DemoData}
*
2. 直接写即可
*/
@Test
public void simpleWrite() {
String PATH = "F:\\workspaces\\workspaces_idea\\POIAndEasyExcel\\EasyExcel\\";
String fileName =PATH + System.currentTimeMillis() + ".xlsx";
// 这里 需要指定写用哪个class去写,然后写到第一个sheet,名字为模板 然后文件流会自动关闭
// 如果这里想使用03 则 传入excelType参数即可
EasyExcel.write(fileName, DemoData.class).sheet("模板").doWrite(data());
}
}