java常用类、java框架集合
StringBuffer类与StringBuilder类
-StringBuffer: String增强版,字符串缓冲区,是一个容器
-String声明:
StringBuffer sb = new StringBuffer(); //创建空StringBuffer对象
StringBuffer sb = new StringBuffer(“aaa”); //创建一个变量存储字符串aaa
sb.toString(); //转化成String 类型
-StringBuffer的使用
sb.append("**")//追加字符串
public class StringBufferDemo{
public static void main(String[] args){
StringBuffer stringBuffer = new StringBuffer();
stringBuffer.append(1).append(1.2).append("adf").append(true);
stringBuffer.length();//输出字符串的实际长度
stringBuffer.capacity();//输出字符串所占的内存空间长度
}
}
StringBuffer和StringBuilder在使用长其实是馋不多的,但他们之间还有一点区别
StringBuffer: 可变字符序列,线程安全,效率低
StringBuilder: 可变字符序列,线程不安全,效率高
String: 不可变字符序列
String使用陷阱:
-String s = “a”;
s = s+“b”;//实际上原来的“a”字符串对象已经丢失了,现在又产生了一个字符串s+“b”.如果多次执行改变字符串内容的操作,会导致大量副本字符串对象存留在内存中,降低效率.如果这样的操作放到循环中,会极大影响程序性能
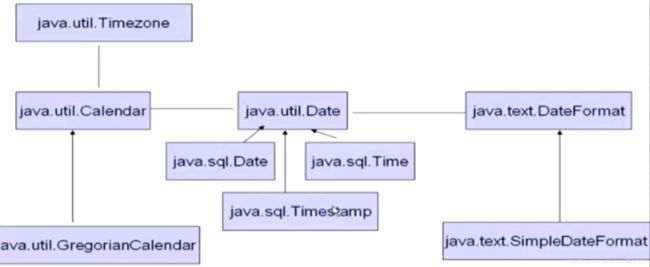
时间处理相关类
public class DateTest{
public static void main(String[] args){
Date date = new Date();
System.out.println(date);
System.out.println(date.getTime());
DateFormat dateFormat = new SimpleDateFormate("yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss");
String str = dateFormat.format(date);//将date类型按规范转换为字符串格式
System.out.println(str)
Date d1 = dateFormat.parse("2010-10-10 20:20:20");//将字符串转换成对应的日期
System.out.println(d1);
}
}
不过我们现在使用Date类比较少了,现在用的比较多的是Calendar类
我们来看一下Calendar类的调用方法
public class test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Calendar calendar =Calendar.getInstance();
System.out.println(calendar);//直接打印的话是格林日志类型的详细时间
}
}
从代码看我们为什么不像正常声明对象一样使用new关键字了呢?
我们先来看看Calendar类的源码
public abstract class Calendar implements Serializable, Cloneable, Comparable<Calendar> {
...........
}
protected Calendar(TimeZone zone, Locale aLocale)
{
fields = new int[FIELD_COUNT];
isSet = new boolean[FIELD_COUNT];
stamp = new int[FIELD_COUNT];
this.zone = zone;
setWeekCountData(aLocale);
}
public static Calendar getInstance()
{
return createCalendar(TimeZone.getDefault(), Locale.getDefault(Locale.Category.FORMAT));
}
从源码上看,Calendar其实是一个抽象类,抽象类不能声明对象,而且其构造方法是protected关键字修饰的,无法从包以外的类访问,
不过从Calendar提供的静态方法getInstance
看,该方法调用了它的构造方法,所以直接类名调用方法即可
//设置指定时间的日历类
calendar.setTime(date);
//获取指定时间
System.out.println(calendar.get(Calendar.YEAR));
我们先来看Calendar的get方法的调用提示
从图片上看,get方法要求我们传入的其实是一个int值,那这个int值我们怎么知道是多少呢?

其实Calendar类已经定义了很多常量,我们只需要传入这些常量名称即可
Date时间类(java.util.Date)
Date类:表示日期和时间,提供操作日期和时间各组成部分的方法
DateFormat类 与SimpleDateFormat类用于定制日期时间的格式
Calendar类
抽象类,用于设置和获取 日期/时间数据的特定部分,Calendar类提供一些方法和静态字段来操作日历
| 方法或属性 | 说明 |
|---|---|
| int get(int field) | 返回给定日历字段的值 |
| MONTH | 指示月 |
| DAY_OF_MONTH | 指示一个月的某天 |
| DAY_OF_WEEK | 指示一个星期的某天 |
Math类
- 包含了常见的数学运算函数
- random()–>[0,1)之间的随机浮点数
- 生成0-10之间的任意整数
int a = (int) (10*Math.random()); - 生成20 -30之间的的整数():
int b = 20+(int)(10*Math.random());
public class MathTest{
public static void main(String[] args){
System.out.println(Math.abs(-1));
}
}
Math
Math常用方法
| 方法 | 说明 |
|---|---|
| sqrt | 算术平房根 |
| cbrt() | 算术立方根 |
| hypot(a,b) | (a的平方+b的平方)的平方根 |
| pow(a,b) | 计算a的b次方 |
| exp(x) | 计算e^x的值 |
| max | 最大值 |
| min | 最小值 |
| abs | 绝对值 |
| ceil | 向上取证 |
| floor | 向下取整 |
| rint | 四舍五入,返回double值 |
| round | 四舍五入,float时返回int值,double时返回long值 |
| nextUp | 返回大一点的值 |
| nextDown | 返回小一点的值 |
枚举
枚举指由一组固定的常量组成的类型
使用枚举的好处:
1、类型安全
2、易于输入
3、代码清晰
public enum AzogGender {
boy,girl
}
```java
public class test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
AzogGender gender = AzogGender.boy;
}
}
//以下是枚举的更多用法
public enum AzogGender {
LAUNCH("launch"),PAGEVIEW("page"),EVENT("event");
private String name;
AzogGender(String name){
this.name = name;
}
public void show(){
System.out.println(this.name);
AzogGender[] ee = values();//values返回enum数组
for(int i=0;i<ee.length;i++){
System.out.println(ee[i])
}
}
}
public class test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
AzogGender gender = AzogGender.LAUNCH;
gender.show();
String name = AzogGender.PAGEVIEW.name();//获取PAGEVIEW选项
}
}
枚举类型:
- 只能够取特定值中的一个
- 使用enum关键字
- 所有的枚举类型隐性地继承自java.langEnum.(枚举实质上还是类,而每个被枚举的成员实质上就是一个枚举的实例,它们默认都是pubic static final的.可以通过枚举类型名直接调用它们.)
- 强烈建议当你需要定义一组常量时,使用枚举类型
java容器
集合框架
如果并不知道程序运行时会需要多少对象,或者需要更复杂方式存储对象——可以使用java集合框架
Collection接口的常用方法
集合作为容器应该具有的功能(增、删、改、查)
Collection 存放的是单一值.
特点:
1、可以存放不同类型的数据,而数组只能存放固定类型的数据
2、当使用arrayList子类实现的时候,初始化长度是10,当长度不够的时候会进行扩容操作
api方法:
- add: 要求必须传入的参数是Object对象,因此当写入基本数据类型的时候,包含了自动拆箱和自动装箱的过程
- addAll:添加另一个集合的元素到此集合中
- clear : 只是清空集合中的元素,但是此集合对象并没有被回收
- remove: 删除指定元素
- removeAll: 删除集合元素
- contains: 判读集合是否包含指定的元素值
- containsAll:判断此集合是否包含另一个集合
- isEmpty: 判断集合是否等于空
- retainAll: 若集合拥有另一个集合的所有元素,返回true,否则返回false
- size: 返回当前集合的大小
- toArray: 将集合转换成数组
List与Set接口
- Collection接口存储一组不唯一,无序的对象
- List接口存储一组不唯一,有序(插入顺序)的对象
- Set接口存储一组唯一,无序的对象
- Map接口存储一组键值对象,提供key到value的映射
温馨提醒: 有时间记得多看看api文档,熟悉里面的命令