Spring学习笔记(二)
文章目录
- 三、依赖注入
- 3.1构造器注入
- 3.2 Set方式注入
- 3.3 扩展方式注入
- 3.3.1 P命名空间
- 3.3.2 C命名空间
- 3.4 bean的作用域
- 四、Bean的自动装配
- 4.4.1 byName自动装配
- 4.4.2 byType自动装配
- 4.4.3 注解实现自动装配
- @Autowired
- @Qualifier
- @Resource
- 五、使用注解开发
- @Component
- @Value
- @Scope
- 衍生的注解
三、依赖注入
3.1构造器注入
3.2 Set方式注入
student.java
package pojo;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.Map;
import java.util.Properties;
import java.util.Set;
public class Student {
private String name;
private String[] subject;
private List<String> hobbys;
private Map<String,Integer> score;
private Set<String> teacher;
private Properties properties;
private Address address;
private String grilfriend;
@Override
public String toString() {
return "{name: " + this.name +
",\n subject: " + this.subject +
",\n hobbys: " + this.hobbys +
",\n score: " + this.score +
",\n teacher: " + this.teacher +
",\n properties: " + this.properties +
",\n address" + this.address.getAddress();
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public String[] getSubject() {
return subject;
}
public void setSubject(String[] subject) {
this.subject = subject;
}
public List<String> getHobbys() {
return hobbys;
}
public void setHobbys(List<String> hobbys) {
this.hobbys = hobbys;
}
public Map<String, Integer> getScore() {
return score;
}
public void setScore(Map<String, Integer> score) {
this.score = score;
}
public Set<String> getTeacher() {
return teacher;
}
public void setTeacher(Set<String> teacher) {
this.teacher = teacher;
}
public Properties getProperties() {
return properties;
}
public void setProperties(Properties properties) {
this.properties = properties;
}
public Address getAddress() {
return address;
}
public void setAddress(Address address) {
this.address = address;
}
public void setGrilfriend(String grilfriend) {
this.grilfriend = grilfriend;
}
}
Address.java
package pojo;
public class Address {
private String address;
public Address(String address) {
this.address = address;
}
public String getAddress() {
return address;
}
public void setAddress(String address) {
this.address = address;
}
}
beans.xml
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans
https://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd">
<bean id="address" class="pojo.Address">
<constructor-arg index="0" value="河北省保定市"/>
bean>
<bean id="student" class="pojo.Student">
<property name="name" value="小明"/>
<property name="address" ref="address"/>
<property name="subject">
<array>
<value>数学value>
<value>语文value>
<value>英语value>
array>
property>
<property name="hobbys">
<list>
<value>学习value>
<value>打篮球value>
<value>看电视value>
list>
property>
<property name="score">
<map>
<entry key="语文" value="111"/>
<entry key="数学" value="100"/>
<entry key="英语" value="99"/>
map>
property>
<property name="teacher">
<set>
<value>老张value>
<value>老刘value>
set>
property>
<property name="properties">
<props>
<prop key="学号">123456prop>
<prop key="学院编号">11111prop>
props>
property>
<property name="grilfriend">
<null>null>
property>
bean>
beans>
测试
public class StudentTest {
@Test
public void test(){
ApplicationContext context = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("beans.xml");
Object student = context.getBean("student");
System.out.println(student);
}
}
3.3 扩展方式注入
3.3.1 P命名空间
p命名空间对应
引入
xmlns:p="http://www.springframework.org/schema/p"
使用
<bean id="user" class="pojo.User" p:name="xxx" p:age="10"/>
3.3.2 C命名空间
c命名空间对应 实体类必须有相应的构造方法才能使用
引入
xmlns:c="http://www.springframework.org/schema/c"
使用
<bean id="user1" class="pojo.User" c:name="yyy" c:age="18"/>
<bean id="user2" class="pojo.User" c:_0="qqq" c:_1="10"/>
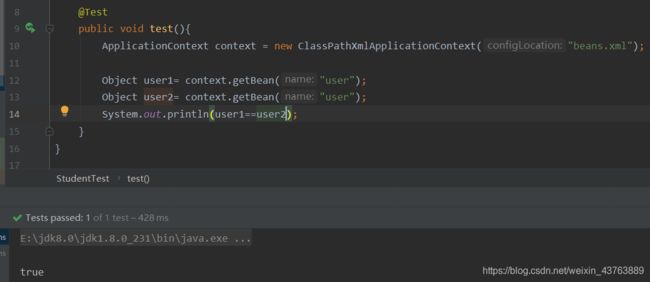
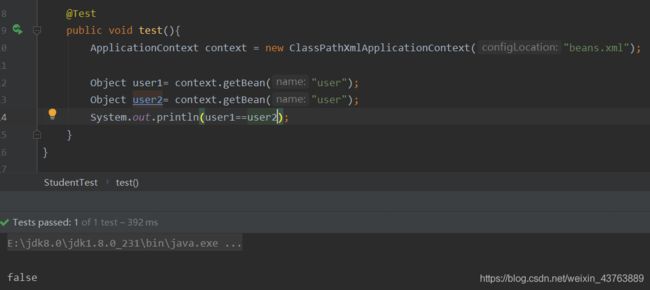
3.4 bean的作用域
-
单例模式
默认是单例模式,也可手动设置,每次调用生成的都是同一个对象
<bean id="user" class="pojo.User" p:name="xxx" p:age="10" scope="singleton"/>
-
原型模式
每次调用都会生成一个新的对象
<bean id="user" class="pojo.User" p:name="xxx" p:age="10" scope="prototype"/>
四、Bean的自动装配
User类
package pojo;
public class User {
private Dog dog;
private Car car;
@Override
public String toString() {
return dog.getName() + "\n" + car.getName();
}
public Dog getDog() {
return dog;
}
public void setDog(Dog dog) {
this.dog = dog;
}
public Car getCar() {
return car;
}
public void setCar(Car car) {
this.car = car;
}
}
Car类
package pojo;
public class Car {
private String name;
public Car(){
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
}
Dog类
package pojo;
public class Dog {
private String name;
public Dog() {
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
}
4.4.1 byName自动装配
byName自动装配,要求所有bean的id唯一,byName会自动在容器上下文中寻找,和自己对象Set方法参数名对应的bean id
<bean id="car" class="pojo.Car" p:name="dididi" />
<bean id="dog" class="pojo.Dog" p:name="wangwangwang"/>
<bean id="user" class="pojo.User" autowire="byName"/>
测试
4.4.2 byType自动装配
要求所有bean的class唯一,byType会自动在容器上下文中寻找和自己对象属性类型相同的bean
<bean id="car123" class="pojo.Car" p:name="dididi" />
<bean id="dog111" class="pojo.Dog" p:name="wangwangwang"/>
<bean id="user" class="pojo.User" autowire="byType"/>
4.4.3 注解实现自动装配
配置
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xmlns:context="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans
https://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/context
https://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context.xsd">
<context:annotation-config/>
beans>
@Autowired
通过byType实现
直接在成员变量上使用
@Autowired
private Dog dog;
@Autowired
private Car car;
也可在Set方法上使用
@Autowired
public void setDog(Dog dog) {
this.dog = dog;
}
@Autowired
public void setCar(Car car) {
this.car = car;
}
二者可以混合使用
//如果定义了required的属性为false,说明这个对象可以为null,否则不需为空
@Autowired(required = false)
等同于@Nullable,字段加了这个注解,说明这个字段可以为null
@Qualifier
指定相应的bean
<bean id="car123" class="pojo.Car" p:name="didi" />
<bean id="car222" class="pojo.Car" p:name="dididi" />
<bean id="dog111" class="pojo.Dog" p:name="wangwang"/>
<bean id="dog222" class="pojo.Dog" p:name="wangwang"/>
@Autowired
@Qualifier(value = "dog111")
private Dog dog;
@Autowired
@Qualifier(value = "car123")
private Car car;
@Resource
@Resource(name = "dog111")
private Dog dog;
@Resource
private Car car;
会先根据名字去查找有没有对应的class,如果没有会去查找有没有相应的id,如果都没有才会报错
Resource也可以指定id
五、使用注解开发
<context:component-scan base-package="pojo"/>
<context:annotation-config/>
@Component
//等价于@Value
public class User {
//等价于@Scope
@Component
@Scope("singleton")
public class User {
//等价于衍生的注解
@Component有几个衍生的注解,我们在web开发中,会按照mvc三层架构分才能
- dao (@Repository)
- service (@Service)
- controller (@Controller)