STM32笔记之 Fatfs(文件系统移植)
写在前面:
本文章旨在总结备份、方便以后查询,由于是个人总结,如有不对,欢迎指正;另外,内容大部分来自网络、书籍、和各类手册,如若侵权请告知,马上删帖致歉。
目录
一、介绍
二、移植说明
三、文件移植操作
四、添加接口
五、Fatfs系统裁剪
六、基本测试使用
七、注意
一、介绍
FatFs是用于小型嵌入式系统的通用 FAT / exFAT文件系统模块。FatFs模块是按照 ANSI C(C89)编写的,并且与磁盘 I / O层完全分开。因此,它独立于平台。它可以并入资源有限的小型微控制器中,例如8051,PIC,AVR,ARM,Z80,RX等;FatFs是作者 ChaN开发的个人项目,此处请献上我的膝盖
官网:http://elm-chan.org/fsw/ff/00index_e.html
二、移植说明
1、FatFs模块在可移植性方面设定了以下条件:
-
ANSI C
FatFs模块是用ANSI C(C89)编写的中间件。只要编译器符合C89或更高版本,就没有平台依赖性。仅exFAT功能需要C99。 - 整数类型的大小
char类型的大小必须为 8位。
int类型的大小必须为 16位或 32位。
当 C标准为 C89时,short和 long的大小必须分别为 16位和 32位。
在 C99或更高版本中时,使用 stdin .h获取整数大小。
2、带有 FatFs模块的嵌入式系统的典型配置依赖关系图
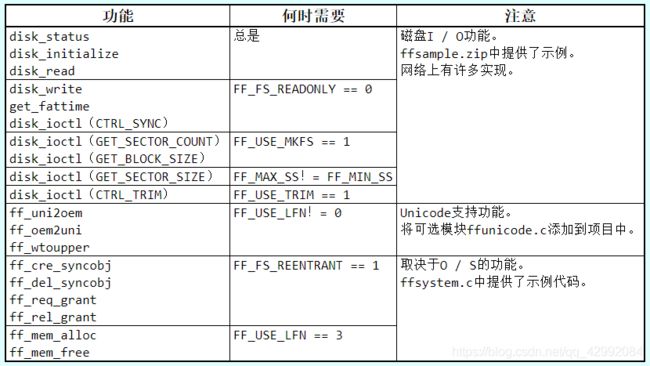
3、功能接口
(a)如果提供了用于 FatFs的工作磁盘模块,则不需要其他任何东西。
(b)要连接具有不同接口的现有磁盘驱动程序,需要一些粘合功能来转换 FatFs和驱动程序之间的接口。
三、文件移植操作
首先,戳这里下载 Fatfs文件包,这里使用的 R0.14目前最新的版本;下载下来不需要做任何文件提取操作,直接并入我们的工程就行了
各文件说明:
| 文件名 |
功能 |
说明 |
| diskio.c |
Fatfs和 disk I/O模块接口层文件 |
与平台相关的代码,需要用户根据存储介质来编写函数 |
| diskio.h |
Fatfs和 disk I/O模块公用的包含文件 |
不需要修改 |
| ff.c |
Fatfs模块源码 |
不需要修改 |
| ff.h |
Fatfs和应用模块公用的包含文件 |
不需要修改 |
| ffconf.h |
Fatfs模块配置文件 |
需要根据需求来配置参数 |
| ffunicode.c | Fatfs所支持的字体代码转换表 | 不需要修改 |
| ffsystem.c | Fatfs的 OS相关函数示例代码 | 没用到 |
添加到工程后,如下图:
四、添加接口
Fatfs移植需要我们提供以下接口,而基本的接口,我们可以在官方提供的 diskio.c源文件中找到
在本例中,是接入 SD Card存储介质,因此,在 Fatfs文件系统包的 diskio.c源文件中添加对应的接口
从 diskio.c开端,我们可以看到以下宏定义
/* Definitions of physical drive number for each drive */
#define DEV_RAM 0 /* Example: Map Ramdisk to physical drive 0 */
#define DEV_MMC 1 /* Example: Map MMC/SD card to physical drive 1 */
#define DEV_USB 2 /* Example: Map USB MSD to physical drive 2 */
而 SD Card属于宏 DEV_MMC范畴内,在后面的接口函数中,我们只需要在与 DEV_MMC相关的位置上添加或者基于原代码里面去选择注释函数,再编写相应的硬件底层函数就可以了,例如
然后整个修改后的 diskio.c源文件如下:
diskio.c 源文件
/*-----------------------------------------------------------------------*/
/* Low level disk I/O module skeleton for FatFs (C)ChaN, 2019 */
/*-----------------------------------------------------------------------*/
/* If a working storage control module is available, it should be */
/* attached to the FatFs via a glue function rather than modifying it. */
/* This is an example of glue functions to attach various exsisting */
/* storage control modules to the FatFs module with a defined API. */
/*-----------------------------------------------------------------------*/
#include "ff.h" /* Obtains integer types */
#include "diskio.h" /* Declarations of disk functions */
#include "user_sdcard.h"
/* Definitions of physical drive number for each drive */
#define DEV_RAM 0 /* Example: Map Ramdisk to physical drive 0 */
#define DEV_MMC 1 /* Example: Map MMC/SD card to physical drive 1 */
#define DEV_USB 2 /* Example: Map USB MSD to physical drive 2 */
/*-----------------------------------------------------------------------*/
/* Get Drive Status */
/*-----------------------------------------------------------------------*/
DSTATUS disk_status (
BYTE pdrv /* Physical drive nmuber to identify the drive */
)
{
DSTATUS stat = STA_NOINIT;
int result;
switch (pdrv) {
case DEV_RAM :
// result = RAM_disk_status();
// translate the reslut code here
break;
case DEV_MMC :
// result = MMC_disk_status();
result = SD_disk_status();
// translate the reslut code here
if(1 == result)
stat &= ~STA_NOINIT;
break;
case DEV_USB :
// result = USB_disk_status();
// translate the reslut code here
break;
}
return stat;
}
/*-----------------------------------------------------------------------*/
/* Inidialize a Drive */
/*-----------------------------------------------------------------------*/
DSTATUS disk_initialize (
BYTE pdrv /* Physical drive nmuber to identify the drive */
)
{
DSTATUS stat = STA_NOINIT;
int result;
switch (pdrv) {
case DEV_RAM :
// result = RAM_disk_initialize();
// translate the reslut code here
break;
case DEV_MMC :
// result = MMC_disk_initialize();
result = SD_disk_initialize();
// translate the reslut code here
if(1 == result)
stat &= ~STA_NOINIT;
break;
case DEV_USB :
// result = USB_disk_initialize();
// translate the reslut code here
break;
}
return stat;
}
/*-----------------------------------------------------------------------*/
/* Read Sector(s) */
/*-----------------------------------------------------------------------*/
DRESULT disk_read (
BYTE pdrv, /* Physical drive nmuber to identify the drive */
BYTE *buff, /* Data buffer to store read data */
LBA_t sector, /* Start sector in LBA */
UINT count /* Number of sectors to read */
)
{
DRESULT res = RES_ERROR;
int result;
switch (pdrv) {
case DEV_RAM :
// translate the arguments here
// result = RAM_disk_read(buff, sector, count);
// translate the reslut code here
break;
case DEV_MMC :
// translate the arguments here
// result = MMC_disk_read(buff, sector, count);
result = SD_disk_read(buff, sector, count);
// translate the reslut code here
if(1 == result)
res = RES_OK;
break;
case DEV_USB :
// translate the arguments here
// result = USB_disk_read(buff, sector, count);
// translate the reslut code here
break;
}
return res;
}
/*-----------------------------------------------------------------------*/
/* Write Sector(s) */
/*-----------------------------------------------------------------------*/
#if FF_FS_READONLY == 0
DRESULT disk_write (
BYTE pdrv, /* Physical drive nmuber to identify the drive */
const BYTE *buff, /* Data to be written */
LBA_t sector, /* Start sector in LBA */
UINT count /* Number of sectors to write */
)
{
DRESULT res = RES_ERROR;
int result;
switch (pdrv) {
case DEV_RAM :
// translate the arguments here
// result = RAM_disk_write(buff, sector, count);
// translate the reslut code here
break;
case DEV_MMC :
// translate the arguments here
// result = MMC_disk_write(buff, sector, count);
result = SD_disk_write((uint8_t *)buff, sector, count);
// translate the reslut code here
if(1 == result)
res = RES_OK;
break;
case DEV_USB :
// translate the arguments here
// result = USB_disk_write(buff, sector, count);
// translate the reslut code here
break;
}
return res;
}
#endif
/*-----------------------------------------------------------------------*/
/* Miscellaneous Functions */
/*-----------------------------------------------------------------------*/
DRESULT disk_ioctl (
BYTE pdrv, /* Physical drive nmuber (0..) */
BYTE cmd, /* Control code */
void *buff /* Buffer to send/receive control data */
)
{
DRESULT res = RES_ERROR;
int result;
switch (pdrv) {
case DEV_RAM :
// Process of the command for the RAM drive
break;
case DEV_MMC :
switch (cmd) {
case CTRL_SYNC : /* Wait for end of internal write process of the drive */
result = 1;
break;
case GET_SECTOR_COUNT : /* Get drive capacity in unit of sector (DWORD) */
*(DWORD * )buff = SDCardInfo.CardCapacity /SDCardInfo.CardBlockSize;
result = 1;
break;
case GET_SECTOR_SIZE : // Get R/W sector size (WORD)
*(WORD * )buff = SD_BLOCK_SIZE;
result = 1;
break;
case GET_BLOCK_SIZE : /* Get erase block size in unit of sector (DWORD) */
*(DWORD * )buff = 1;
result = 1;
break;
case CTRL_TRIM : /* Erase a block of sectors (used when _USE_ERASE == 1) */
result = 1;
break;
default:
res = RES_PARERR;
}
// Process of the command for the MMC/SD card
if(1 == result)
res = RES_OK;
break;
case DEV_USB :
// Process of the command the USB drive
break;
}
return res;
}
/*---------------------------------------------------------*/
/* User provided RTC function for FatFs module */
/*---------------------------------------------------------*/
/* This is a real time clock service to be called back */
/* from FatFs module. */
#if !FF_FS_NORTC && !FF_FS_READONLY
DWORD get_fattime (void)
{
return ((DWORD)(2015 - 1980) << 25) /* Year 2015 */
| ((DWORD)1 << 21) /* Month 1 */
| ((DWORD)1 << 16) /* Mday 1 */
| ((DWORD)0 << 11) /* Hour 0 */
| ((DWORD)0 << 5) /* Min 0 */
| ((DWORD)0 >> 1); /* Sec 0 */
}
#endif
/*---------------------------- END OF FILE ----------------------------*/
上面说了,我们是在对应的存储介质上添加了硬件底层函数,那么我们就得实现它;由于用的是 SD Card存储介质,那么必定是跟 SD Card接口相关联的,因此,我们需要编写以下代码:
/* User defined Fatfs functions ----------------------------------------------*/
/*-----------------------------------------------------------------------*/
/* Get SD disk status */
/*-----------------------------------------------------------------------*/
uint8_t SD_disk_status(void)
{
return 1;
}
/*-----------------------------------------------------------------------*/
/* Initialize SD disk drive */
/*-----------------------------------------------------------------------*/
uint8_t SD_disk_initialize(void)
{
if(SD_Init() == SD_OK)
return 1;
else
return 0;
}
/*-----------------------------------------------------------------------*/
/* Read SD sector(s) */
/*-----------------------------------------------------------------------*/
uint8_t SD_disk_read( uint8_t *Buff, uint32_t Sector, uint32_t Count )
{
SD_Error SD_state = SD_OK;
uint8_t temp = 0;
if((uint32_t)Buff & 3)
{
_Bool flag = 1;
uint32_t scratch[SD_BLOCK_SIZE / 4];
while(Count--)
{
flag = SD_disk_read((void *)scratch, Sector++, 1);
if(flag != 1)
{
break;
}
memcpy(Buff, scratch, SD_BLOCK_SIZE);
Buff += SD_BLOCK_SIZE;
}
}
else
{
SD_state = SD_ReadMultiBlocks(Buff,(uint64_t)Sector*SD_BLOCK_SIZE, \
SD_BLOCK_SIZE,Count);
}
if(SD_state == SD_OK)
{
/* Check if the Transfer is finished */
SD_state=SD_WaitReadOperation();
while(SD_GetStatus() != SD_TRANSFER_OK);
}
if(SD_state != SD_OK)
temp = 0;
else
temp = 1;
return temp;
}
/*-----------------------------------------------------------------------*/
/* Write SD sector(s) */
/*-----------------------------------------------------------------------*/
uint8_t SD_disk_write( uint8_t *Buff, uint32_t Sector, uint32_t Count )
{
SD_Error SD_state = SD_OK;
uint8_t temp = 0;
if((uint32_t)Buff & 3)
{
_Bool flag = 1;
uint32_t scratch[SD_BLOCK_SIZE / 4];
while(Count--)
{
memcpy(scratch, Buff, SD_BLOCK_SIZE);
flag = SD_disk_write((void *)scratch, Sector++, 1);
if(flag != 1)
{
break;
}
Buff += SD_BLOCK_SIZE;
}
}
else
{
SD_state = SD_WriteMultiBlocks(Buff,(uint64_t)Sector*SD_BLOCK_SIZE, \
SD_BLOCK_SIZE,Count);
}
if(SD_state == SD_OK)
{
/* Check if the Transfer is finished */
SD_state=SD_WaitWriteOperation();
while(SD_GetStatus() != SD_TRANSFER_OK);
}
if(SD_state != SD_OK)
temp = 0;
else
temp = 1;
return temp;
}
五、Fatfs系统裁剪
Fatfs的裁剪配置主要在 ffconf.h头文件中,它的全部配置选项:
- 功能配置
- FF_FS_READONLY
- FF_FS_MINIMIZE
- FF_USE_STRFUNC
- FF_USE_FIND
- FF_USE_MKFS
- FF_USE_FASTSEEK
- FF_USE_EXPAND
- FF_USE_CHMOD
- FF_USE_LABEL
- FF_USE_FORWARD
- 命名空间和语言环境配置
- FF_CODE_PAGE
- FF_USE_LFN
- FF_MAX_LFN
- FF_LFN_UNICODE
- FF_LFN_BUF,FF_SFN_BUF
- FF_STRF_ENCODE
- FF_FS_RPATH
- 卷/驱动器配置
- FF_VOLUMES
- FF_STR_VOLUME_ID
- FF_VOLUME_STRS
- FF_MULTI_PARTITION
- FF_MIN_SS,FF_MAX_SS
- FF_LBA64
- FF_GPT_MIN
- FF_USE_TRIM
- 系统配置
- FF_FS_TINY
- FF_FS_EXFAT
- FF_FS_NORTC
- FF_NORTC_MON,FF_NORTC_MDAY,FF_NORTC_YEAR
- FF_FS_NOFSINFO
- FF_FS_LOCK
- FF_FS_REENTRANT
- FF_FS_TIMEOUT
- FF_SYNC_t
对于裁剪,下表显示了通过配置选项来增删需要的 API函数,以减小模块的尺寸
此外还有一些经常用到的配置:
- FF_CODE_PAGE
此选项指定要在目标系统上使用的 OEM代码页。错误的代码页设置可能导致文件打开失败。如果路径名没有使用任何非 ascii字符,则任何代码页设置之间没有区别。默认设置为 437
-
FF_USE_LFN
此选项切换对长文件名(LFN)的支持。启用 LFN时,需要将 Unicode支持模块 ffunicode.c添加到项目中。将堆栈用作工作缓冲区时,请注意堆栈溢出。当使用堆内存作为工作缓冲区时,需要将内存管理功能(ff_memalloc和ff_memfree)添加到项目中
- FF_MAX_LFN
LFN函数需要某些内部工作缓冲区来获取文件名。此选项定义缓冲区的大小,该值的范围可以是 LFN的 UTF-16编码单位,范围为12到255。启用exFAT时,缓冲区占用(FF_MAX_LFN + 1)* 2个字节,另外占用(FF_MAX_LFN + 44)/ 15 * 32个字节。建议将其设置为 255,以完全支持 LFN规范。如果未启用 LFN,则此选项无效
- FF_LFN_UNICODE
此选项在启用 LFN时切换 API上的字符编码
- FF_LFN_BUF,FF_SFN_BUF
这组选项在 FILINFO结构中定义文件名成员 fname []和 altname []的大小。这些值应足以容纳读取的文件名大小。读取文件名的最大可能长度取决于 API上的字符编码
- FF_MIN_SS,FF_MAX_SS
这组选项定义了用于低级磁盘 I / O接口,disk_read和 disk_write函数的扇区大小范围。有效值为512、1024、2048和4096。FF_MIN_SS定义最小扇区大小,FF_MAX_SS定义最大扇区大小。默认是将存储卡和硬盘都设置为 512。但是,板载闪存和某些类型的光学介质可能需要更大的值。当 FF_MAX_SS > FF_MIN_SS时,启用了对可变扇区大小的支持,并且需要对 disk_ioctl函数实施 GET_SECTOR_SIZE命令
六、基本测试使用
#include "user_fatfs.h"
#include "bsp_uart.h"
/* 设置操作的驱动盘 */
#define DRIVER_DISK "1:"
FATFS FatFs; /* 每个逻辑驱动器的文件系统对象 */
FIL File; /* 文件对象 */
FRESULT res_sd; /* FatFs 函数公共结果代码 */
UINT br, bw; /* 文件读 /写字节计数 */
__attribute__ ((aligned (4))) \
BYTE FF_Buff[FF_MAX_SS] = "Fatfs文件系统读写测试实验\r\n"; /* Working buffer */
/************************************************
函数名称 : FF_Test
功 能 : Fatfs文件系统测试
参 数 : 无
返 回 值 : 无
*************************************************/
void FF_Test(void)
{
uint32_t num = 50;
FF_System_Creates(DRIVER_DISK, 1);
FF_ViewRootDir(DRIVER_DISK);
FF_OpenWrite("1:temp.txt", FF_Buff, num);
FF_OpenRead("1:temp.txt", &FF_Buff[1024], num);
/* 不再使用文件系统,取消挂载文件系统 */
f_mount(NULL, DRIVER_DISK, 1);
}
/************************************************
函数名称 : FF_System_Creates
功 能 : Fatfs文件系统注册
参 数 : Drive ---- 盘符
Opt ---- 0:现在不要安装(在第一次访问该卷时安装)
1:强制安装该卷以检查它是否可以工作
返 回 值 : 无
*************************************************/
void FF_System_Creates( char *pDrive, uint8_t Opt )
{
/* 为逻辑驱动器工作区注册 */
res_sd = f_mount(&FatFs, pDrive, Opt);
if(1 == Opt)
{
/* 如果没有文件系统就格式化创建文件系统 */
if(res_sd == FR_NO_FILESYSTEM)
{
DEBUG_PRINTF("SD卡还没有文件系统,即将进行格式化...\r\n");
res_sd = f_mkfs(pDrive, 0, FF_Buff, sizeof(FF_Buff)); // 格式化
if(res_sd == FR_OK)
{
DEBUG_PRINTF("SD卡已成功格式化文件系统。\r\n");
res_sd = f_mount(NULL, pDrive, 1); // 格式化后,先取消挂载
res_sd = f_mount(&FatFs, pDrive, 1); // 重新挂载
}
else
{
DEBUG_PRINTF("格式化失败。\r\n");
while(1);
}
}
else if(res_sd != FR_OK)
{
DEBUG_PRINTF("!!SD卡挂载安装文件系统失败。(error code:%d)\r\n",res_sd);
DEBUG_PRINTF("!!可能原因:SD卡初始化不成功。\r\n");
while(1);
}
else
{
DEBUG_PRINTF("文件系统挂载安装成功,可以进行文件读写操作\r\n");
}
}
else
{
printf("挂载磁盘完成,但并未安装。\r\n");
}
}
/************************************************
函数名称 : FF_OpenWrite
功 能 : 打开文件并写入信息
参 数 : pFile ---- 需要打开的文件
pStr ---- 需要写入的信息
Len ---- 长度
返 回 值 : 0 / 1
*************************************************/
uint8_t FF_OpenWrite( char *pFile, void *pStr, uint16_t Len )
{
uint8_t temp = 0;
res_sd = f_open(&File, pFile, FA_CREATE_ALWAYS | FA_WRITE );
if( res_sd == FR_OK )
{
DEBUG_PRINTF("打开文件成功。\r\n");
/* 将指定存储区内容写入到文件内 */
res_sd = f_write(&File, pStr, Len, &bw);
if(res_sd == FR_OK)
{
DEBUG_PRINTF("文件写入成功,写入字节数据:%d\r\n", bw);
DEBUG_PRINTF("向文件写入的数据为:%s\r\n", (char*)pStr);
temp = 1;
}
else
{
DEBUG_PRINTF("!!文件写入失败。(error code:%d)\r\n", res_sd);
}
f_close(&File); // 不再读写,关闭文件
}
else
{
DEBUG_PRINTF("!!打开/创建文件失败。\r\n");
}
return temp;
}
/************************************************
函数名称 : FF_OpenRead
功 能 : 打开文件并读取信息
参 数 : pFile ---- 需要打开的文件
pStr ---- 需要读取的信息
返 回 值 : 0 / 1
*************************************************/
uint8_t FF_OpenRead( char *pFile, void *pStr, uint16_t Len )
{
uint8_t temp = 0;
res_sd = f_open(&File, pFile, FA_OPEN_EXISTING | FA_READ);
if(res_sd == FR_OK)
{
DEBUG_PRINTF("打开文件成功。\r\n");
/* 将文件内容读取到指定存储区内 */
res_sd = f_read(&File, pStr, Len, &br);
if(res_sd == FR_OK)
{
DEBUG_PRINTF("文件读取成功,读到字节数据:%d\r\n",br);
DEBUG_PRINTF("读取得的文件数据为:%s\r\n", (char*)pStr);
temp = 1;
}
else
{
DEBUG_PRINTF("!!文件读取失败。(error code:%d)\r\n",res_sd);
}
}
else
{
DEBUG_PRINTF("!!打开文件失败。\r\n");
}
f_close(&File); // 不再读写,关闭文件
return temp;
}
/************************************************
函数名称 : FF_ViewRootDir
功 能 : Fatfs文件扫描显示
参 数 : Drive ---- 盘符
返 回 值 : 无
*************************************************/
void FF_ViewRootDir( char *pDrive )
{
/* 本函数使用的局部变量占用较多,请修改启动文件,保证堆栈空间够用 */
DIR DirInf;
FILINFO FileInf;
uint32_t cnt = 0;
/* 打开根文件夹 */
res_sd = f_opendir(&DirInf, pDrive);
if (res_sd != FR_OK)
{
DEBUG_PRINTF("!!打开根目录失败。(error code:%d)\r\n", res_sd);
return;
}
/* 读取当前文件夹下的文件和目录 */
printf("\r\n| 属性 | 文件大小 | 文件名\r\n");
for (cnt = 0; ;cnt++)
{
res_sd = f_readdir(&DirInf, &FileInf); /* 读取目录项,索引会自动下移 */
if (res_sd != FR_OK || FileInf.fname[0] == 0)
{
break;
}
if (FileInf.fname[0] == '.')
{
continue;
}
/* 判断是文件类型及目录目录 */
switch(FileInf.fattrib)
{
case AM_DIR:
printf("| (0x%02X)子目录 ", FileInf.fattrib);
break;
case AM_RDO:
printf("| (0x%02X)只读文件", FileInf.fattrib);
break;
case AM_HID:
printf("| (0x%02X)隐藏文件", FileInf.fattrib);
break;
case AM_SYS:
printf("| (0x%02X)系统文件", FileInf.fattrib);
break;
case AM_ARC:
printf("| (0x%02X)存档文件", FileInf.fattrib);
break;
default:
printf("| (0x%02X)未知类型", FileInf.fattrib);
break;
}
/* 打印文件大小, 最大4G */
printf(" |%10d ", FileInf.fsize);
printf(" | %s\r\n", (char *)FileInf.fname); /* 长文件名 */
}
printf("\r\n\n");
}
/*---------------------------- END OF FILE ----------------------------*/
七、注意
在使用 Fatfs系统 ,格式化 TF卡的时候,你会发现格式化出来的内存大小是总容量的一半;这是因为数据长度的问题,在 ST官方提供的 SD Card库中,使用的数据长度是 32位,所以当超过 32位后最高位溢出;因此我们只需做以下修改就好了
1、把 SD_CardInfo结构体中的 CardCapacity数据长度改成 64位,修改如下:
/**
* @brief SD Card information
*/
typedef struct
{
SD_CSD SD_csd;
SD_CID SD_cid;
uint64_t CardCapacity; /*!< Card Capacity */
uint32_t CardBlockSize; /*!< Card Block Size */
uint16_t RCA;
uint8_t CardType;
} SD_CardInfo;
2、定位到 SD_Error SD_GetCardInfo(SD_CardInfo *cardinfo)函数中,然后添加一个数据类型强制转换,修改如下:
cardinfo->CardCapacity = (uint64_t)(cardinfo->SD_csd.DeviceSize + 1) * 512 * 1024;对比一下,上面那一行,原处是没有 (uint64_t)的,所以需要我们加上去