java CAI小学生算数测评
题目要求:
As computer costs decline, it becomes feasible for every student, regardless of economic circum- stance, to have a computer and use it in school. This creates exciting possibilities for improving the educational experience of all students worldwide, as suggested by the next five exercises. [Note: Check out initiatives such as the One Laptop Per Child Project (www.laptop.org). Also, research “green” laptops—what are some key “going green” characteristics of these devices? Look into the Electronic Product Environmental Assessment Tool (www.epeat.net), which can help you assess the “greenness” of desktops, notebooks and monitors to help you decide which products to pur- chase.]
1 (Computer-Assisted Instruction) The use of computers in education is referred to as computer-assisted instruction (CAI). Write a program that will help an elementary school student learn multiplication. Use a SecureRandom object to produce two positive one-digit integers. The program should then prompt the user with a question, such as
How much is 6 times 7?
The student then inputs the answer. Next, the program checks the student’s answer. If it’s correct, display the message “Very good!” and ask another multiplication question. If the answer is wrong, display the message “No. Please try again.” and let the student try the same question repeatedly until the student finally gets it right. A separate method should be used to generate each new ques- tion. This method should be called once when the application begins execution and each time the user answers the question correctly.
2 (Computer-Assisted Instruction: Reducing Student Fatigue) One problem in CAI environments is student fatigue. This can be reduced by varying the computer’s responses to hold the stu- dent’s attention. Modify the program of Exercise 1 so that various comments are displayed for each answer as follows:
Possible responses to a correct answer:
Very good!
Excellent!
Nice work!
Keep up the good work!
Possible responses to an incorrect answer:
No. Please try again.
Wrong. Try once more.
Don’t give up!
No. Keep trying.
Use random-number generation to choose a number from 1 to 4 that will be used to select one of the four appropriate responses to each correct or incorrect answer. Use a switch statement to issue the responses.
3 (Computer-Assisted Instruction: Monitoring Student Performance) More sophisticated computer-assisted instruction systems monitor the student’s performance over a period of time. The decision to begin a new topic is often based on the student’s success with previous topics. Modify the program of Exercise 2 to count the number of correct and incorrect responses typed by the student. After the student types 10 answers, your program should calculate the percentage that are correct. If the percentage is lower than 75%, display “Please ask your teacher for extra help.”, then reset the program so another student can try it. If the percentage is 75% or higher, display “Congratulations, you are ready to go to the next level!”, then reset the program so another student can try it.
4 (Computer-Assisted Instruction: Difficulty Levels) Exercises 1–3 developed a computer-assisted instruction program to help teach an elementary school student multiplication. Modify the program to allow the user to enter a difficulty level. At a difficulty level of 1, the program should use only single-digit numbers in the problems; at a difficulty level of 2, numbers as large as two digits, and so on.
5 (Computer-Assisted Instruction: Varying the Types of Problems) Modify the program of Exercise 4 to allow the user to pick a type of arithmetic problem to study. An option of 1 means addition problems only, 2 means subtraction problems only, 3 means multiplication problems only, 4 means division problems only and 5 means a random mixture of all these types.
关于生成随机数的random:
生成一个对象:Random randon = new Random();
具体使用,int a = randon.nextInt(90)+10;
10代表的最小值,90代表99-10+1,即最大为99;
所以这样生成就是10–99的随机数。
//所需类,用作生成运算符
import java.util.Random;
public class CAI {
private int maxx;//
private int minn;
private int flag;
private String str ;
private int a;
private int b;
Random randon = new Random();
public CAI (int m, int n, int t) {
this.maxx = m;
this.minn = n;
this.flag = t;
}
public void setNumber() {
this.a = randon.nextInt(this.maxx)+this.minn;
this.b = randon.nextInt(this.maxx)+this.minn;
}
public int getNumber1() {
return this.a;
}
public int getNumber2() {
return this.b;
}
public void setoperator() {
if(this.flag==5)
this.flag=randon.nextInt(4)+1;
switch(this.flag) {
case 1: this.str = "+" ; break;
case 2: this.str = "-" ; break;
case 3: this.str = "*" ; break;
case 4: this.str = "/" ; break;
}
}
public String getoperator() {
return this.str;
}
}
package practice2;
import java.math.BigDecimal;
import java.util.Random;
import java.util.Scanner;
public class CAItest {
public static double rz;
public static int mode,type,level,maxx,minn,flag;
public static String[] right = {"Very good!","Nice work!","Excellent!","Keep up the good work!"};
public static String[] wrong = {"No. Please try again.","Wrong. Try once more.","Don't give up!","No. Keep trying."};
public static void judge(int xa, String xb, int xc) {//计算结果
if(xb.equals("+")) {rz=(double)(xa+xc);}
if(xb.equals("-")) {rz=(double)(xa-xc);}
if(xb.equals("*")) {rz=(double)(xa*xc);}
if(xb.equals("/")) {
BigDecimal sx = new BigDecimal((double)xa/(double)xc);
rz = sx.setScale(2,BigDecimal.ROUND_HALF_UP).doubleValue();
}
}
public static void Level(int t) {//判断难易程度
if(t==1) {maxx=9;minn=1;}
if(t==2) {maxx=90;minn=10;}
if(t==3) {maxx=900;minn=100;}
}
public static void Type(int t) {//判断类型
if(t==1) flag=1;
if(t==2) flag=2;
if(t==3) flag=3;
if(t==4) flag=4;
if(t==5) flag=5;
}
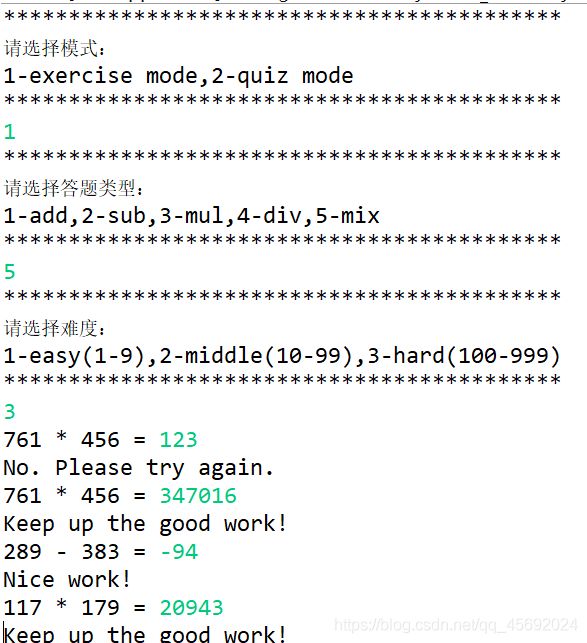
public static void exercise() {//训练模式
int a=0,c=0;int symble=1;
String b="";
Scanner input = new Scanner(System.in);
Random randon = new Random();
Type(type);
Level(level);
while(true) {//多次做题
if(symble==1) {//正确时,再次创建新对象,生成新的随机数
CAI pr = new CAI(maxx,minn,flag);
pr.setNumber();pr.setoperator();
a = pr.getNumber1();
b = pr.getoperator();
c = pr.getNumber2();
}
System.out.printf("%d %s %d = ",a,b,c);
int ran = randon.nextInt(4);//生成不同的评语所用的随机数
judge(a,b,c);//
double ans = input.nextDouble();//输入答案
if(rz==ans) {
System.out.printf("%s%n",right[ran]);
symble=1;
}
else {
System.out.printf("%s%n",wrong[ran]);
symble=0;
}
}
}
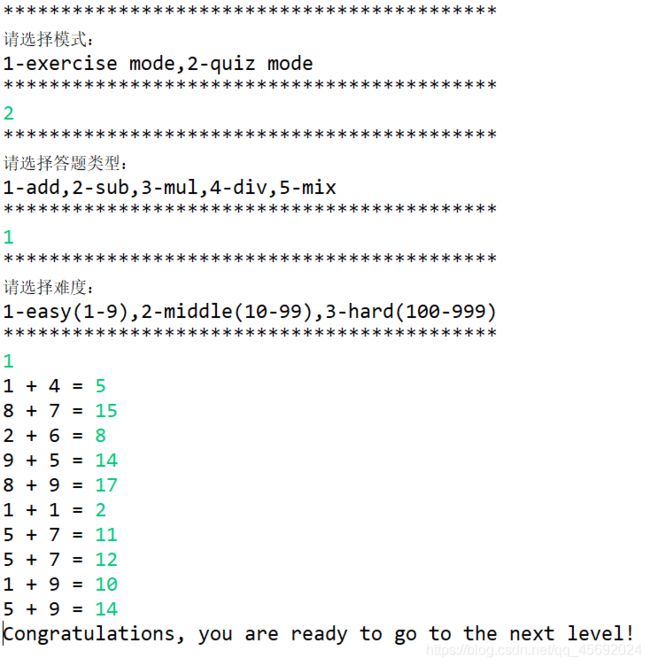
public static void quiz() {//测验模式
int a=0,c=0,symble=1,count=0,right_count=0;
String b="";double x=0;
Scanner input = new Scanner(System.in);
Random randon = new Random();
Type(type);
Level(level);
while(count<10) {
count++;
if(symble==1) {
CAI pr = new CAI(maxx,minn,flag);
pr.setNumber();
pr.setoperator();
a = pr.getNumber1();
b = pr.getoperator();
c = pr.getNumber2();
}
System.out.printf("%d %s %d =",a,b,c);
double ans = input.nextDouble();
judge(a,b,c);
if(rz==ans) {
symble=1;
right_count++;
}
else {
symble=0;
}
}
x=(double)right_count/(double)count;
if(x>=0.75)
System.out.printf("Congratulations, you are ready to go to the next level!");
else
System.out.printf("Please ask your teacher for extra help.");
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner input = new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.printf("*******************************************%n");
System.out.printf("请选择模式:%n");
System.out.printf("1-exercise mode,2-quiz mode%n");
System.out.printf("*******************************************%n");
mode = input.nextInt();
System.out.printf("*******************************************%n");
System.out.printf("请选择答题类型:%n");
System.out.printf("1-add,2-sub,3-mul,4-div,5-mix%n");
System.out.printf("*******************************************%n");
type = input.nextInt();
System.out.printf("*******************************************%n");
System.out.printf("请选择难度:%n");
System.out.printf("1-easy(1-9),2-middle(10-99),3-hard(100-999)%n");
System.out.printf("*******************************************%n");
level = input.nextInt();
switch(mode) {
case 1:
exercise();
break;
case 2:
quiz();
break;
}
}
}