ServiceManager.getService的流程分析
本流程分析基于Android8.0。
进程访问服务时,要先从ServiceManager中获取服务。以sendBroadcast的流程为例:
sendBroadcast实际调用的是ContextImpl的sendBroadcast:
///frameworks/base/core/java/android/app/ContextImpl.java
@Override
public void sendBroadcast(Intent intent) {
warnIfCallingFromSystemProcess();
String resolvedType = intent.resolveTypeIfNeeded(getContentResolver());
try {
intent.prepareToLeaveProcess(this);
ActivityManager.getService().broadcastIntent(
mMainThread.getApplicationThread(), intent, resolvedType, null,
Activity.RESULT_OK, null, null, null, AppOpsManager.OP_NONE, null, false, false,
getUserId());
} catch (RemoteException e) {
throw e.rethrowFromSystemServer();
}
}接下来对关键code中的ActivityManger.getService进行分析:
ActivityManager.getService().broadcastIntent(
mMainThread.getApplicationThread(), intent, resolvedType, null,
Activity.RESULT_OK, null, null, null, AppOpsManager.OP_NONE, null, false,
false,
getUserId());ActivityManager.getService
///frameworks/base/core/java/android/app/ActivityManager.java
/**
* @hide
*/
public static IActivityManager getService() {
return IActivityManagerSingleton.get();
}
private static final Singleton IActivityManagerSingleton =
new Singleton() {
@Override
protected IActivityManager create() {
//Context.ACTIVITY_SERVICE = “activity”
final IBinder b = ServiceManager.getService(Context.ACTIVITY_SERVICE);
final IActivityManager am = IActivityManager.Stub.asInterface(b);
return am;
}
}; ServiceManager.getService("activity")
///frameworks/base/core/java/android/os/ServiceManager.java
/**
* Returns a reference to a service with the given name.
*
* @param name the name of the service to get
* @return a reference to the service, or null if the service doesn't exist
*/
public static IBinder getService(String name) {
try {
//【1.1】sCache
IBinder service = sCache.get(name);
if (service != null) {
return service;
} else {
//【1.2】getIServiceManager()
//【1.3】getIServiceManager().getService
//【1.4】Binder.allowBlocking(getIServiceManager().getService(name))
return Binder.allowBlocking(getIServiceManager().getService(name));
}
} catch (RemoteException e) {
Log.e(TAG, "error in getService", e);
}
return null;
}【1.1】sCache
///frameworks/base/core/java/android/os/ServiceManager.java
private static HashMap sCache = new HashMap();
/**
* This is only intended to be called when the process is first being brought
* up and bound by the activity manager. There is only one thread in the process
* at that time, so no locking is done.
*
* @param cache the cache of service references
* @hide
*/
public static void initServiceCache(Map cache) {
if (sCache.size() != 0) {
throw new IllegalStateException("setServiceCache may only be called once");
}
sCache.putAll(cache);
} 而initServiceCache函数的调用链:
1、
SystemServer.main
SystemService.run
SystemServer.createSystemContext
ActivityThread.attach(true)
AMS.attachApplication
AMS.attachApplicationLocked
ActivityThread.bindApplication
ServiceManager.initServiceCache
2、
ActivityThread.main
ActivityThread.attach(false)
AMS.attachApplication
AMS.attachApplicationLocked
ActivityThread.bindApplication
ServiceManager.initServiceCache那么initServiceCache的参数具体是什么呢?
///frameworks/base/services/core/java/com/android/server/am/ActivityManagerService.java
private final boolean attachApplicationLocked(IApplicationThread thread,int pid) {
......
if (app.instr != null) {
thread.bindApplication(processName, appInfo, providers,
app.instr.mClass,
profilerInfo, app.instr.mArguments,
app.instr.mWatcher,
app.instr.mUiAutomationConnection, testMode,
mBinderTransactionTrackingEnabled, enableTrackAllocation,
isRestrictedBackupMode || !normalMode, app.persistent,
new Configuration(getGlobalConfiguration()), app.compat,
getCommonServicesLocked(app.isolated)/*即传入initServiceCache的参数*/,
mCoreSettingsObserver.getCoreSettingsLocked(),
buildSerial);
} else {
thread.bindApplication(processName, appInfo, providers, null, profilerInfo,
null, null, null, testMode,
mBinderTransactionTrackingEnabled, enableTrackAllocation,
isRestrictedBackupMode || !normalMode, app.persistent,
new Configuration(getGlobalConfiguration()), app.compat,
getCommonServicesLocked(app.isolated),
mCoreSettingsObserver.getCoreSettingsLocked(),
buildSerial);
}
......
}
///frameworks/base/core/java/android/app/ActivityThread.java
public final void bindApplication(String processName, ApplicationInfo appInfo,
List providers, ComponentName instrumentationName,
ProfilerInfo profilerInfo, Bundle instrumentationArgs,
IInstrumentationWatcher instrumentationWatcher,
IUiAutomationConnection instrumentationUiConnection, int debugMode,
boolean enableBinderTracking, boolean trackAllocation,
boolean isRestrictedBackupMode, boolean persistent, Configuration config,
CompatibilityInfo compatInfo,
/*services即传入initServiceCache的参数,来自AMS.attachApplicationLocked函数*/
Map services,
Bundle coreSettings,
String buildSerial) {
if (services != null) {
// Setup the service cache in the ServiceManager
ServiceManager.initServiceCache(services);
}
setCoreSettings(coreSettings);
AppBindData data = new AppBindData();
data.processName = processName;
data.appInfo = appInfo;
data.providers = providers;
data.instrumentationName = instrumentationName;
data.instrumentationArgs = instrumentationArgs;
data.instrumentationWatcher = instrumentationWatcher;
data.instrumentationUiAutomationConnection = instrumentationUiConnection;
data.debugMode = debugMode;
data.enableBinderTracking = enableBinderTracking;
data.trackAllocation = trackAllocation;
data.restrictedBackupMode = isRestrictedBackupMode;
data.persistent = persistent;
data.config = config;
data.compatInfo = compatInfo;
data.initProfilerInfo = profilerInfo;
data.buildSerial = buildSerial;
sendMessage(H.BIND_APPLICATION, data);
} 即传入initServiceCache函数的参数是来自AMS.getCommonServiceLocked。
///frameworks/base/services/core/java/com/android/server/am/ActivityManagerService.java
/**
* Initialize the application bind args. These are passed to each
* process when the bindApplication() IPC is sent to the process. They're
* lazily setup to make sure the services are running when they're asked for.
*/
private HashMap getCommonServicesLocked(boolean isolated) {
// Isolated processes won't get this optimization, so that we don't
// violate the rules about which services they have access to.
if (isolated) {
if (mIsolatedAppBindArgs == null) {
mIsolatedAppBindArgs = new HashMap<>();
mIsolatedAppBindArgs.put("package", ServiceManager.getService("package"));
}
return mIsolatedAppBindArgs;
}
if (mAppBindArgs == null) {
mAppBindArgs = new HashMap<>();
// Setup the application init args
mAppBindArgs.put("package", ServiceManager.getService("package"));
mAppBindArgs.put("window", ServiceManager.getService("window"));
mAppBindArgs.put(Context.ALARM_SERVICE,
ServiceManager.getService(Context.ALARM_SERVICE));
}
return mAppBindArgs;
} 可见,sChache中仅仅包含了package,window、alarm服务,不包含activity服务。所以,
ServiceManager.getService("activity")实际执行的是else中的code。
///frameworks/base/core/java/android/os/ServiceManager.java
/**
* Returns a reference to a service with the given name.
*
* @param name the name of the service to get
* @return a reference to the service, or null if the service doesn't exist
*/
public static IBinder getService(String name) {
try {
IBinder service = sCache.get(name);
if (service != null) {//sCache中不包含activity服务,sCache = null
return service;
} else {
//【1.2】getIServiceManager()
//【1.3】getIServiceManager().getService
//【1.4】Binder.allowBlocking(getIServiceManager().getService(name))
return Binder.allowBlocking(getIServiceManager().getService(name));
}
} catch (RemoteException e) {
Log.e(TAG, "error in getService", e);
}
return null;
}【1.2】getIServiceManager
///frameworks/base/core/java/android/os/ServiceManager.java
private static IServiceManager sServiceManager;
private static IServiceManager getIServiceManager() {
if (sServiceManager != null) {
return sServiceManager;
}
// Find the service manager
//【1.2.1】BinderInternal.getContextObject
//【1.2.2】ServiceManagerNative.asInterface
sServiceManager = ServiceManagerNative
.asInterface(Binder.allowBlocking(BinderInternal.getContextObject()));
return sServiceManager;
}该函数是一个获取IServiceManager单例的函数,第一次执行时sServiceManager = null。
【1.2.1】BinderInternal.getContextObject
///frameworks/base/core/java/com/android/internal/os/BinderInternal.java
/**
* Return the global "context object" of the system. This is usually
* an implementation of IServiceManager, which you can use to find
* other services.
*/
public static final native IBinder getContextObject();getContextObject是个native函数,实现是在android_util_Log.cpp文件中实现:
///frameworks/base/core/jni/android_util_Binder.cpp
static const JNINativeMethod gBinderInternalMethods[] = {
/* name, signature, funcPtr */
{ "getContextObject", "()Landroid/os/IBinder;",
(void*)android_os_BinderInternal_getContextObject },
{ "joinThreadPool", "()V", (void*)android_os_BinderInternal_joinThreadPool },
{ "disableBackgroundScheduling", "(Z)V",
(void*)android_os_BinderInternal_disableBackgroundScheduling },
{ "setMaxThreads", "(I)V", (void*)android_os_BinderInternal_setMaxThreads },
{ "handleGc", "()V", (void*)android_os_BinderInternal_handleGc }
};
static jobject android_os_BinderInternal_getContextObject(JNIEnv* env, jobject clazz)
{
//此处的b即是BpBinder
sp b = ProcessState::self()->getContextObject(NULL);
return javaObjectForIBinder(env, b);
}
static Mutex mProxyLock;
jobject javaObjectForIBinder(JNIEnv* env, const sp& val)
{
if (val == NULL) return NULL;
if (val->checkSubclass(&gBinderOffsets)) { //返回false
// One of our own!
jobject object = static_cast(val.get())->object();
LOGDEATH("objectForBinder %p: it's our own %p!\n", val.get(), object);
return object;
}
// For the rest of the function we will hold this lock, to serialize
// looking/creation/destruction of Java proxies for native Binder proxies.
AutoMutex _l(mProxyLock);
// Someone else's... do we know about it?
jobject object = (jobject)val->findObject(&gBinderProxyOffsets);
if (object != NULL) {
jobject res = jniGetReferent(env, object);
if (res != NULL) {
ALOGV("objectForBinder %p: found existing %p!\n", val.get(), res);
return res;
}
LOGDEATH("Proxy object %p of IBinder %p no longer in working set!!!", object, val.get());
android_atomic_dec(&gNumProxyRefs);
val->detachObject(&gBinderProxyOffsets);
env->DeleteGlobalRef(object);
}
//新建了一个Java BinderProxy对象,gBinderProxyOffsets.mClass = “android/os/BinderProxy”
object = env->NewObject(gBinderProxyOffsets.mClass,
gBinderProxyOffsets.mConstructor);
if (object != NULL) {
LOGDEATH("objectForBinder %p: created new proxy %p !\n", val.get(), object);
// The proxy holds a reference to the native object.
env->SetLongField(object, gBinderProxyOffsets.mObject, (jlong)val.get());
val->incStrong((void*)javaObjectForIBinder);
// The native object needs to hold a weak reference back to the
// proxy, so we can retrieve the same proxy if it is still active.
jobject refObject = env->NewGlobalRef(
env->GetObjectField(object, gBinderProxyOffsets.mSelf));
val->attachObject(&gBinderProxyOffsets, refObject,
jnienv_to_javavm(env), proxy_cleanup);
// Also remember the death recipients registered on this proxy
sp drl = new DeathRecipientList;
drl->incStrong((void*)javaObjectForIBinder);
env->SetLongField(object, gBinderProxyOffsets.mOrgue, reinterpret_cast
(drl.get()));
// Note that a new object reference has been created.
android_atomic_inc(&gNumProxyRefs);
incRefsCreated(env);
}
return object;
} 即BinderInternal.getContextObject实际通过JNI new了一个Java的BinderProxy对象。
在javaObjectForIBinder函数中值得注意的几个操作:
1、
env->SetLongField(object, gBinderProxyOffsets.mObject, (jlong)val.get());val表示的是BpBinder指针,将Native层的BpBinder指针保存到BinderProxy对象的成员字段mObject中。于是,BinderProxy对象的Native方法可以通过mObject获取BpBinder的指针。这个操作是将BinderProxy与BpBinder联系起来的纽带。
2、
jobject refObject = env->NewGlobalRef(
env->GetObjectField(object, gBinderProxyOffsets.mSelf));
val->attachObject(&gBinderProxyOffsets, refObject,
jnienv_to_javavm(env), proxy_cleanup);
将新创建的BinderProxy对象注册(attach)到BpBinder的ObjectManager中,同时注册一个回收函数proxy_cleanup。当BinderProxy对象撤销(detach)的时候,该函数会被调用,以释放一些资源。
3、
sp drl = new DeathRecipientList;
drl->incStrong((void*)javaObjectForIBinder);
env->SetLongField(object, gBinderProxyOffsets.mOrgue,
reinterpret_cast(drl.get())); 创建了一个死亡通知list,将死亡通知list和BinderProxy对象联系起来。
【1.2.2】ServiceManagerNative.asInterface
getIServiceManager函数中:
///frameworks/base/core/java/android/os/ServiceManager.java
private static IServiceManager sServiceManager;
private static IServiceManager getIServiceManager() {
if (sServiceManager != null) {
return sServiceManager;
}
// Find the service manager
//【1.2.1】BinderInternal.getContextObject
//【1.2.2】ServiceManagerNative.asInterface
sServiceManager = ServiceManagerNative
.asInterface(Binder.allowBlocking(BinderInternal.getContextObject()));
return sServiceManager;
}即ServiceManagerNative.asInterface(Binder.allowBlocking(new BinderProxy())。而Binder.allowBlocking(new BinderProxy()):
///frameworks/base/core/java/android/os/Binder.java
/**
* Allow blocking calls on the given interface, overriding the requested
* value of {@link #setWarnOnBlocking(boolean)}.
*
* This should only be rarely called when you are absolutely sure
* the remote interface is a built-in system component that can never be
* upgraded. In particular, this must never be called for
* interfaces hosted by package that could be upgraded or replaced,
* otherwise you risk system instability if that remote interface wedges.
*
* @hide
*/
public static IBinder allowBlocking(IBinder binder) {
try {
if (binder instanceof BinderProxy) {
((BinderProxy) binder).mWarnOnBlocking = false;
} else if (binder != null
&& binder.queryLocalInterface(binder.getInterfaceDescriptor()) == null) {
Log.w(TAG, "Unable to allow blocking on interface " + binder);
}
} catch (RemoteException ignored) {
}
return binder;
}
所以实际还是ServiceManagerNative.asInterface(new BinderProxy())。
///frameworks/base/core/java/android/os/ServiceManagerNative.java
/**
* Native implementation of the service manager. Most clients will only
* care about getDefault() and possibly asInterface().
* @hide
*/
public abstract class ServiceManagerNative extends Binder implements IServiceManager
{
/**
* Cast a Binder object into a service manager interface, generating
* a proxy if needed.
*/
static public IServiceManager asInterface(IBinder obj)
{
if (obj == null) { //obj = new BinderProxy();
return null;
}
//本地进程调用时in 才不为null,这是跨进程远程调用,所以in = null
IServiceManager in =(IServiceManager)obj.queryLocalInterface(descriptor);
if (in != null) {
return in;
}
return new ServiceManagerProxy(obj);
......
}asInterface函数实际是new了一个ServiceManagerProxy对象,obj = new BinderProxy()。
///frameworks/base/core/java/android/os/ServiceManagerNative.java
class ServiceManagerProxy implements IServiceManager {
public ServiceManagerProxy(IBinder remote) {
mRemote = remote;
}
public IBinder getService(String name) throws RemoteException {
Parcel data = Parcel.obtain();
Parcel reply = Parcel.obtain();
data.writeInterfaceToken(IServiceManager.descriptor);
data.writeString(name);
mRemote.transact(GET_SERVICE_TRANSACTION, data, reply, 0);
IBinder binder = reply.readStrongBinder();
reply.recycle();
data.recycle();
return binder;
}
.....
private IBinder mRemote;
}即mRemote = remote = new BinderProxy()。
所以getIServiceManager函数
///frameworks/base/core/java/android/os/ServiceManager.java
private static IServiceManager sServiceManager;
private static IServiceManager getIServiceManager() {
if (sServiceManager != null) {
return sServiceManager;
}
// Find the service manager
//【1.2.1】BinderInternal.getContextObject
//【1.2.2】ServiceManagerNative.asInterface
sServiceManager = ServiceManagerNative
.asInterface(Binder.allowBlocking(BinderInternal.getContextObject()));
return sServiceManager;
}实际就是返回了一个ServiceManagerProxy对象。
【1.3】getIServiceManager.getService
///frameworks/base/core/java/android/os/ServiceManager.java
/**
* Returns a reference to a service with the given name.
*
* @param name the name of the service to get
* @return a reference to the service, or null if the service doesn't exist
*/
public static IBinder getService(String name) {
try {
//【1.1】sCache
IBinder service = sCache.get(name);
if (service != null) {
return service;
} else {
//【1.2】getIServiceManager()返回一个ServiceManagerProxy对象
//【1.3】getIServiceManager().getService
//【1.4】Binder.allowBlocking(getIServiceManager().getService(name))
return Binder.allowBlocking(getIServiceManager().getService(name));
}
} catch (RemoteException e) {
Log.e(TAG, "error in getService", e);
}
return null;
}由上述分析可得,getIServiceManager().getService(“activity”)
即new ServiceManagerProxy(new BinderProxy()).getService(“activity”)。
ServiceManagerProxy.getService(name)
///frameworks/base/core/java/android/os/ServiceManagerNative.java
class ServiceManagerProxy implements IServiceManager {
public ServiceManagerProxy(IBinder remote) {
mRemote = remote;
}
public IBinder getService(String name) throws RemoteException {
Parcel data = Parcel.obtain();
Parcel reply = Parcel.obtain();
data.writeInterfaceToken(IServiceManager.descriptor);
data.writeString(name);
mRemote.transact(GET_SERVICE_TRANSACTION, data, reply, 0);
//从reply里解析出获取的IBinder对象
IBinder binder = reply.readStrongBinder();
reply.recycle();
data.recycle();
return binder;
}
.....
private IBinder mRemote;
}getService即调用BinderProxy的transact函数,发起的code是GET_SERVICE_TRANSACTION。
///frameworks/base/core/java/android/os/Binder.java
final class BinderProxy implements IBinder {
public boolean transact(int code, Parcel data, Parcel reply, int flags) throws
RemoteException {
Binder.checkParcel(this, code, data, "Unreasonably large binder buffer");
if (mWarnOnBlocking && ((flags & FLAG_ONEWAY) == 0)) {
// For now, avoid spamming the log by disabling after we've logged
// about this interface at least once
mWarnOnBlocking = false;
Log.w(Binder.TAG, "Outgoing transactions from this process must be FLAG_ONEWAY",
new Throwable());
}
final boolean tracingEnabled = Binder.isTracingEnabled();
if (tracingEnabled) {
final Throwable tr = new Throwable();
Binder.getTransactionTracker().addTrace(tr);
StackTraceElement stackTraceElement = tr.getStackTrace()[1];
Trace.traceBegin(Trace.TRACE_TAG_ALWAYS,
stackTraceElement.getClassName() + "." + stackTraceElement.getMethodName());
}
try {
return transactNative(code, data, reply, flags);
} finally {
if (tracingEnabled) {
Trace.traceEnd(Trace.TRACE_TAG_ALWAYS);
}
}
}
public native boolean transactNative(int code, Parcel data, Parcel reply,
int flags) throws RemoteException;实际执行的是native函数transactNative:
///frameworks/base/core/jni/android_util_Binder.cpp
static const JNINativeMethod gBinderProxyMethods[] = {
/* name, signature, funcPtr */
{"pingBinder", "()Z", (void*)android_os_BinderProxy_pingBinder},
{"isBinderAlive","()Z", (void*)android_os_BinderProxy_isBinderAlive},
{"getInterfaceDescriptor", "()Ljava/lang/String;",
(void*)android_os_BinderProxy_getInterfaceDescriptor},
{"transactNative", "(ILandroid/os/Parcel;Landroid/os/Parcel;I)Z",
(void*)android_os_BinderProxy_transact},
{"linkToDeath", "(Landroid/os/IBinder$DeathRecipient;I)V",
(void*)android_os_BinderProxy_linkToDeath},
{"unlinkToDeath", "(Landroid/os/IBinder$DeathRecipient;I)Z",
(void*)android_os_BinderProxy_unlinkToDeath},
{"destroy", "()V", (void*)android_os_BinderProxy_destroy},
};
static jboolean android_os_BinderProxy_transact(JNIEnv* env, jobject obj,
jint code, jobject dataObj, jobject replyObj, jint flags) // throws RemoteException
{
if (dataObj == NULL) {
jniThrowNullPointerException(env, NULL);
return JNI_FALSE;
}
Parcel* data = parcelForJavaObject(env, dataObj);
if (data == NULL) {
return JNI_FALSE;
}
Parcel* reply = parcelForJavaObject(env, replyObj);
if (reply == NULL && replyObj != NULL) {
return JNI_FALSE;
}
IBinder* target = (IBinder*)env->GetLongField(obj, gBinderProxyOffsets.mObject);
if (target == NULL) {
jniThrowException(env, "java/lang/IllegalStateException", "Binder has been
finalized!");
return JNI_FALSE;
}
ALOGV("Java code calling transact on %p in Java object %p with code %" PRId32 "\n",
target, obj, code);
bool time_binder_calls;
int64_t start_millis;
if (kEnableBinderSample) {
// Only log the binder call duration for things on the Java-level main
// But if we don't
time_binder_calls = should_time_binder_calls();
if (time_binder_calls) {
start_millis = uptimeMillis();
}
}
//printf("Transact from Java code to %p sending: ", target); data->print();
status_t err = target->transact(code, *data, reply, flags);
//if (reply) printf("Transact from Java code to %p received: ", target);
//reply->print();
if (kEnableBinderSample) {
if (time_binder_calls) {
conditionally_log_binder_call(start_millis, target, code);
}
}
if (err == NO_ERROR) {
return JNI_TRUE;
} else if (err == UNKNOWN_TRANSACTION) {
return JNI_FALSE;
}
signalExceptionForError(env, obj, err, true /*canThrowRemoteException*/,
data->dataSize());
return JNI_FALSE;
}其中,android_os_BinderProxy_transact函数中值得注意的操作:
IBinder* target = (IBinder*)env->GetLongField(obj, gBinderProxyOffsets.mObject);gBinderProxyOffset.mObject中保存的即是BpBinder对象,(在javaObjectForIBinder函数中保存的)。所以target即是一个BpBinder指针。
status_t err = target->transact(code, *data, reply, flags);此即从Java的mRemote.transact调用到了BpBinder::transact函数。
///frameworks/native/libs/binder/BpBinder.cpp
status_t BpBinder::transact(uint32_t code, const Parcel& data,
Parcel* reply, uint32_t flags)
{
// Once a binder has died, it will never come back to life.
if (mAlive) {
status_t status = IPCThreadState::self()->transact(
mHandle, code, data, reply, flags);
if (status == DEAD_OBJECT) mAlive = 0;
return status;
}
return DEAD_OBJECT;
}IPCThreadState::self()
///frameworks/native/libs/binder/IPCThreadState.cpp
IPCThreadState* IPCThreadState::self()
{
if (gHaveTLS) {
restart:
const pthread_key_t k = gTLS;
IPCThreadState* st = (IPCThreadState*)pthread_getspecific(k);
if (st) return st;
return new IPCThreadState;
}
if (gShutdown) {
ALOGW("Calling IPCThreadState::self() during shutdown is dangerous, expect a
crash.\n");
return NULL;
}
pthread_mutex_lock(&gTLSMutex);
if (!gHaveTLS) {
int key_create_value = pthread_key_create(&gTLS, threadDestructor);
if (key_create_value != 0) {
pthread_mutex_unlock(&gTLSMutex);
ALOGW("IPCThreadState::self() unable to create TLS key, expect a crash: %s\n",
strerror(key_create_value));
return NULL;
}
gHaveTLS = true;
}
pthread_mutex_unlock(&gTLSMutex);
goto restart;
}IPCThreadState::self()->transact
///frameworks/native/libs/binder/IPCThreadState.cpp
status_t IPCThreadState::transact(int32_t handle,
uint32_t code, const Parcel& data,
Parcel* reply, uint32_t flags)
{
status_t err = data.errorCheck();
flags |= TF_ACCEPT_FDS;
IF_LOG_TRANSACTIONS() {
TextOutput::Bundle _b(alog);
alog << "BC_TRANSACTION thr " << (void*)pthread_self() << " / hand "
<< handle << " / code " << TypeCode(code) << ": "
<< indent << data << dedent << endl;
}
if (err == NO_ERROR) {
LOG_ONEWAY(">>>> SEND from pid %d uid %d %s", getpid(), getuid(),
(flags & TF_ONE_WAY) == 0 ? "READ REPLY" : "ONE WAY");
err = writeTransactionData(BC_TRANSACTION, flags, handle, code, data, NULL);
}
if (err != NO_ERROR) {
if (reply) reply->setError(err);
return (mLastError = err);
}
if ((flags & TF_ONE_WAY) == 0) {
#if 0
if (code == 4) { // relayout
ALOGI(">>>>>> CALLING transaction 4");
} else {
ALOGI(">>>>>> CALLING transaction %d", code);
}
#endif
if (reply) {
err = waitForResponse(reply);
} else {
Parcel fakeReply;
err = waitForResponse(&fakeReply);
}
#if 0
if (code == 4) { // relayout
ALOGI("<<<<<< RETURNING transaction 4");
} else {
ALOGI("<<<<<< RETURNING transaction %d", code);
}
#endif
IF_LOG_TRANSACTIONS() {
TextOutput::Bundle _b(alog);
alog << "BR_REPLY thr " << (void*)pthread_self() << " / hand "
<< handle << ": ";
if (reply) alog << indent << *reply << dedent << endl;
else alog << "(none requested)" << endl;
}
} else {
err = waitForResponse(NULL, NULL);
}
return err;
}可见,该函数中的关键操作:
1、如果数据检查没有错误,则传输数据执行writeTransactionData(BC_TRANSACTION,......);
if (err == NO_ERROR) {
LOG_ONEWAY(">>>> SEND from pid %d uid %d %s", getpid(), getuid(),
(flags & TF_ONE_WAY) == 0 ? "READ REPLY" : "ONE WAY");
err = writeTransactionData(BC_TRANSACTION, flags, handle, code, data, NULL);
}2、如果发送消息时的flag不为TF_ONE_WAY,则根据reply是否为空,则执行waitForresponse时使用不同的参数。
if (reply) {
err = waitForResponse(reply);
} else {
Parcel fakeReply;
err = waitForResponse(&fakeReply);
}3、如果flag为ONEWAY,则执行waitForResponse(NULL, NULL);
err = waitForResponse(NULL, NULL);writeTransactionData
///frameworks/native/libs/binder/include/binder/IPCThreadState.h
namespace android {
class IPCThreadState
{
public:
......
private:
......
Parcel mIn;
Parcel mOut;
}
};
///frameworks/native/libs/binder/IPCThreadState.cpp
status_t IPCThreadState::writeTransactionData(int32_t cmd, uint32_t binderFlags,
int32_t handle, uint32_t code, const Parcel& data, status_t* statusBuffer)
{
binder_transaction_data tr;
tr.target.ptr = 0; /* Don't pass uninitialized stack data to a remote process */
tr.target.handle = handle;
tr.code = code;
tr.flags = binderFlags;
tr.cookie = 0;
tr.sender_pid = 0;
tr.sender_euid = 0;
const status_t err = data.errorCheck();
if (err == NO_ERROR) {
tr.data_size = data.ipcDataSize();
tr.data.ptr.buffer = data.ipcData();
tr.offsets_size = data.ipcObjectsCount()*sizeof(binder_size_t);
tr.data.ptr.offsets = data.ipcObjects();
} else if (statusBuffer) {
tr.flags |= TF_STATUS_CODE;
*statusBuffer = err;
tr.data_size = sizeof(status_t);
tr.data.ptr.buffer = reinterpret_cast(statusBuffer);
tr.offsets_size = 0;
tr.data.ptr.offsets = 0;
} else {
return (mLastError = err);
}
mOut.writeInt32(cmd);
mOut.write(&tr, sizeof(tr));
return NO_ERROR;
} 其中有个关键的数据结构binder_transaction_data
//https://github.com/torvalds/linux/blob/master/include/uapi/linux/android/binder.h
struct binder_transaction_data {
/* The first two are only used for bcTRANSACTION and brTRANSACTION,
* identifying the target and contents of the transaction.
*/
union {
/* target descriptor of command transaction */
__u32 handle;
/* target descriptor of return transaction */
binder_uintptr_t ptr;
} target;
binder_uintptr_t cookie; /* target object cookie */
__u32 code; /* transaction command */
/* General information about the transaction. */
__u32 flags;
pid_t sender_pid;
uid_t sender_euid;
binder_size_t data_size; /* number of bytes of data */
binder_size_t offsets_size; /* number of bytes of offsets */
/* If this transaction is inline, the data immediately
* follows here; otherwise, it ends with a pointer to
* the data buffer.
*/
union {
struct {
/* transaction data */
binder_uintptr_t buffer;
/* offsets from buffer to flat_binder_object structs */
binder_uintptr_t offsets;
} ptr;
__u8 buf[8];
} data;
};writeTransactionData函数就是把包含Binder请求信息的parcel内容拆解重组到一个binder_transaction_data结构体变量中,再将命令码cmd和binder_transaction_data写入到IPCThreadState的Parcel成员变量mOut中,mOut变量在后续的处理中将被包含在一个binder_write_read结构体变量中,通过ioctl()传给Binder驱动。
waitForResponse
///frameworks/native/libs/binder/IPCThreadState.cpp
status_t IPCThreadState::waitForResponse(Parcel *reply, status_t *acquireResult)
{
uint32_t cmd;
int32_t err;
while (1) {
if ((err=talkWithDriver()) < NO_ERROR) break;
err = mIn.errorCheck();
if (err < NO_ERROR) break;
if (mIn.dataAvail() == 0) continue;
cmd = (uint32_t)mIn.readInt32();
IF_LOG_COMMANDS() {
alog << "Processing waitForResponse Command: "
<< getReturnString(cmd) << endl;
}
switch (cmd) {
case BR_TRANSACTION_COMPLETE:
//只有当不需要reply,即oneway时才会跳出循环,否则还需等待
if (!reply && !acquireResult) goto finish;
break;
case BR_DEAD_REPLY:
err = DEAD_OBJECT;
goto finish;
case BR_FAILED_REPLY:
err = FAILED_TRANSACTION;
goto finish;
case BR_ACQUIRE_RESULT:
{
ALOG_ASSERT(acquireResult != NULL, "Unexpected brACQUIRE_RESULT");
const int32_t result = mIn.readInt32();
if (!acquireResult) continue;
*acquireResult = result ? NO_ERROR : INVALID_OPERATION;
}
goto finish;
case BR_REPLY:
{
binder_transaction_data tr;
err = mIn.read(&tr, sizeof(tr));
ALOG_ASSERT(err == NO_ERROR, "Not enough command data for brREPLY");
if (err != NO_ERROR) goto finish;
if (reply) {
if ((tr.flags & TF_STATUS_CODE) == 0) {
reply->ipcSetDataReference(
reinterpret_cast(tr.data.ptr.buffer),
tr.data_size,
reinterpret_cast(tr.data.ptr.offsets),
tr.offsets_size/sizeof(binder_size_t),
freeBuffer, this);
} else {
err = *reinterpret_cast(tr.data.ptr.buffer);
freeBuffer(NULL,
reinterpret_cast(tr.data.ptr.buffer),
tr.data_size,
reinterpret_cast(tr.data.ptr.offsets),
tr.offsets_size/sizeof(binder_size_t), this);
}
} else {
freeBuffer(NULL,
reinterpret_cast(tr.data.ptr.buffer),
tr.data_size,
reinterpret_cast(tr.data.ptr.offsets),
tr.offsets_size/sizeof(binder_size_t), this);
continue;
}
}
goto finish;
default:
err = executeCommand(cmd);
if (err != NO_ERROR) goto finish;
break;
}
}
finish:
if (err != NO_ERROR) {
if (acquireResult) *acquireResult = err;
if (reply) reply->setError(err);
mLastError = err;
}
return err;
} waitForResponse函数进入了一个与Binder驱动沟通的while循环。该循环代码调用talkWithDriver()函数与Binder驱动进行通信,然后根据返回的cmd命令码执行不同的操作。如果判断该次事务已经完成,则退出while循环,否则继续调用talkWithDriver()与Binder驱动进行通信。
几个常见的BR_命令:
- BR_TRANSACTION_COMPLETE:binder驱动收到BC_TRANSACTION事件后的应答消息;对于oneway transaction,当接收到该消息,则完成了本次Binder通信;
- BR_DEAD_REPLY:回复失败,往往是线程或节点为空,则结束本次通信Binder;
- BR_FAILED_REPLY:回复失败,往往是transaction出错导致,则结束本次通信Binder;
- BR_REPLY:Binder驱动向Client端发送回应消息;对于非oneway transaction时,当收到该消息,则完整的完成本次Binder通信;
talkWithDriver
///frameworks/native/libs/binder/IPCThreadState.cpp
//mOut有数据,mIn还没数据,doReceive默认值为true
status_t IPCThreadState::talkWithDriver(bool doReceive)
{
if (mProcess->mDriverFD <= 0) {
return -EBADF;
}
binder_write_read bwr;
// Is the read buffer empty?
const bool needRead = mIn.dataPosition() >= mIn.dataSize();
// We don't want to write anything if we are still reading
// from data left in the input buffer and the caller
// has requested to read the next data.
const size_t outAvail = (!doReceive || needRead) ? mOut.dataSize() : 0;
bwr.write_size = outAvail;
bwr.write_buffer = (uintptr_t)mOut.data();
// This is what we'll read.
if (doReceive && needRead) {
//接收数据缓冲区信息的填充,当收到驱动的数据,则写入mIn
bwr.read_size = mIn.dataCapacity();
bwr.read_buffer = (uintptr_t)mIn.data();
} else {
bwr.read_size = 0;
bwr.read_buffer = 0;
}
IF_LOG_COMMANDS() {
TextOutput::Bundle _b(alog);
if (outAvail != 0) {
alog << "Sending commands to driver: " << indent;
const void* cmds = (const void*)bwr.write_buffer;
const void* end = ((const uint8_t*)cmds)+bwr.write_size;
alog << HexDump(cmds, bwr.write_size) << endl;
while (cmds < end) cmds = printCommand(alog, cmds);
alog << dedent;
}
alog << "Size of receive buffer: " << bwr.read_size
<< ", needRead: " << needRead << ", doReceive: " << doReceive << endl;
}
// Return immediately if there is nothing to do.
//当同时没有输入和输出数据则直接返回
if ((bwr.write_size == 0) && (bwr.read_size == 0)) return NO_ERROR;
bwr.write_consumed = 0;
bwr.read_consumed = 0;
status_t err;
do {
IF_LOG_COMMANDS() {
alog << "About to read/write, write size = " << mOut.dataSize() << endl;
}
#if defined(__ANDROID__)
//!!!!!!!!!!!关键操作,与Binder driver通信!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!
//ioctl不停的读写操作,经过syscall,进入Binder驱动。调用Binder_ioctl
if (ioctl(mProcess->mDriverFD, BINDER_WRITE_READ, &bwr) >= 0)
err = NO_ERROR;
else
err = -errno;
#else
err = INVALID_OPERATION;
#endif
if (mProcess->mDriverFD <= 0) {
err = -EBADF;
}
IF_LOG_COMMANDS() {
alog << "Finished read/write, write size = " << mOut.dataSize() << endl;
}
} while (err == -EINTR);
IF_LOG_COMMANDS() {
alog << "Our err: " << (void*)(intptr_t)err << ", write consumed: "
<< bwr.write_consumed << " (of " << mOut.dataSize()
<< "), read consumed: " << bwr.read_consumed << endl;
}
if (err >= NO_ERROR) {
if (bwr.write_consumed > 0) {
if (bwr.write_consumed < mOut.dataSize())
mOut.remove(0, bwr.write_consumed);
else
mOut.setDataSize(0);
}
if (bwr.read_consumed > 0) {
mIn.setDataSize(bwr.read_consumed);
mIn.setDataPosition(0);
}
IF_LOG_COMMANDS() {
TextOutput::Bundle _b(alog);
alog << "Remaining data size: " << mOut.dataSize() << endl;
alog << "Received commands from driver: " << indent;
const void* cmds = mIn.data();
const void* end = mIn.data() + mIn.dataSize();
alog << HexDump(cmds, mIn.dataSize()) << endl;
while (cmds < end) cmds = printReturnCommand(alog, cmds);
alog << dedent;
}
return NO_ERROR;
}
return err;
}talkWithDriver()是native层与设备文件驱动层的过渡函数,往下就是设备文件驱动层了。talkWithDriver()在函数一开始声明了一个binder_write_read结构体变量,然后将mIn和mOut的内存地址写入该变量。mIn是接收返回数据的载体,mOut是向Binder发送请求信息的载体。关键的数据载体都打包在了binder_write_read结构体中。打包完成后,talkWithDriver()执行ioctl,将binder_write_read结构体向下传递给设备文件:
if (ioctl(mProcess->mDriverFD, BINDER_WRITE_READ, &bwr) >= 0)
err = NO_ERROR;
else
err = -errno;其中,bwr是binder_write_read结构体变量,BINDER_WRITE_READ是请求类型,mProcess是一个ProcessState实例(Android中用单例实现,即一个进程只有一个mProcess),其成员mDriverFD是一个设备文件描述符,当mProcess实例被创建时,会调用open_driver()函数打开路径为“/dev/binder”的Binder驱动设备,返回的文件描述符就被保存在mDriverFD。通过此机制,当程序需要和Binder驱动通信时,只需要调用ioctl,把mDriverFD作为设备文件描述符,就可以将请求类型和请求数据准确无误地传递给Binder驱动。
binder_write_read结构体:
struct binder_write_read {
binder_size_t write_size;
binder_size_t write_consumed;
binder_uintptr_t write_buffer;
binder_size_t read_size;
binder_size_t read_consumed;
binder_uintptr_t read_buffer;
};- write_size:write_buffer的字节数
- write_consumed:已处理的write字节数
- write_buffer:指向write数据区,用于发送IPC(或IPC reply)数据,即传递经由Binder Driver的数据时使用
- read_size:read_buffer的字节数
- read_consumed:已处理的read字节数
- read_buffer:指向read数据区,用于接收来自Binder Driver的数据,即Binder Driver在接收IPC(或IPC reply)数据后,保存到read_buffer,再传递到用户空间
write_buffer和read_buffer都包含Binder协议命令和binder_transaction_data结构体。
目前,已经分析到了native层的边界,继续往下就会通过ioctl()进入linux kernel空间。根据ioctl是操作设备驱动文件的函数,到内核文件系统路径搜索ioctl的定义。可在kernel-3.18/fs/ioctl.c中找到ioctl调用。
///kernel-3.18/fs/ioctl.c
SYSCALL_DEFINE3(ioctl, unsigned int, fd, unsigned int, cmd, unsigned long, arg)
{
int error;
struct fd f = fdget(fd);
if (!f.file)
return -EBADF;
error = security_file_ioctl(f.file, cmd, arg);
if (!error)
error = do_vfs_ioctl(f.file, fd, cmd, arg);
fdput(f);
return error;
}这是使用宏调用的。现在已经在kernel空间了。
ioctl.c的完整源码:
/*
* linux/fs/ioctl.c
*
* Copyright (C) 1991, 1992 Linus Torvalds
*/
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
/* So that the fiemap access checks can't overflow on 32 bit machines. */
#define FIEMAP_MAX_EXTENTS (UINT_MAX / sizeof(struct fiemap_extent))
/**
* vfs_ioctl - call filesystem specific ioctl methods
* @filp: open file to invoke ioctl method on
* @cmd: ioctl command to execute
* @arg: command-specific argument for ioctl
*
* Invokes filesystem specific ->unlocked_ioctl, if one exists; otherwise
* returns -ENOTTY.
*
* Returns 0 on success, -errno on error.
*/
static long vfs_ioctl(struct file *filp, unsigned int cmd,
unsigned long arg)
{
int error = -ENOTTY;
if (!filp->f_op->unlocked_ioctl)
goto out;
error = filp->f_op->unlocked_ioctl(filp, cmd, arg);
if (error == -ENOIOCTLCMD)
error = -ENOTTY;
out:
return error;
}
static int ioctl_fibmap(struct file *filp, int __user *p)
{
struct address_space *mapping = filp->f_mapping;
int res, block;
/* do we support this mess? */
if (!mapping->a_ops->bmap)
return -EINVAL;
if (!capable(CAP_SYS_RAWIO))
return -EPERM;
res = get_user(block, p);
if (res)
return res;
res = mapping->a_ops->bmap(mapping, block);
return put_user(res, p);
}
/**
* fiemap_fill_next_extent - Fiemap helper function
* @fieinfo: Fiemap context passed into ->fiemap
* @logical: Extent logical start offset, in bytes
* @phys: Extent physical start offset, in bytes
* @len: Extent length, in bytes
* @flags: FIEMAP_EXTENT flags that describe this extent
*
* Called from file system ->fiemap callback. Will populate extent
* info as passed in via arguments and copy to user memory. On
* success, extent count on fieinfo is incremented.
*
* Returns 0 on success, -errno on error, 1 if this was the last
* extent that will fit in user array.
*/
#define SET_UNKNOWN_FLAGS (FIEMAP_EXTENT_DELALLOC)
#define SET_NO_UNMOUNTED_IO_FLAGS (FIEMAP_EXTENT_DATA_ENCRYPTED)
#define SET_NOT_ALIGNED_FLAGS (FIEMAP_EXTENT_DATA_TAIL|FIEMAP_EXTENT_DATA_INLINE)
int fiemap_fill_next_extent(struct fiemap_extent_info *fieinfo, u64 logical,
u64 phys, u64 len, u32 flags)
{
struct fiemap_extent extent;
struct fiemap_extent __user *dest = fieinfo->fi_extents_start;
/* only count the extents */
if (fieinfo->fi_extents_max == 0) {
fieinfo->fi_extents_mapped++;
return (flags & FIEMAP_EXTENT_LAST) ? 1 : 0;
}
if (fieinfo->fi_extents_mapped >= fieinfo->fi_extents_max)
return 1;
if (flags & SET_UNKNOWN_FLAGS)
flags |= FIEMAP_EXTENT_UNKNOWN;
if (flags & SET_NO_UNMOUNTED_IO_FLAGS)
flags |= FIEMAP_EXTENT_ENCODED;
if (flags & SET_NOT_ALIGNED_FLAGS)
flags |= FIEMAP_EXTENT_NOT_ALIGNED;
memset(&extent, 0, sizeof(extent));
extent.fe_logical = logical;
extent.fe_physical = phys;
extent.fe_length = len;
extent.fe_flags = flags;
dest += fieinfo->fi_extents_mapped;
if (copy_to_user(dest, &extent, sizeof(extent)))
return -EFAULT;
fieinfo->fi_extents_mapped++;
if (fieinfo->fi_extents_mapped == fieinfo->fi_extents_max)
return 1;
return (flags & FIEMAP_EXTENT_LAST) ? 1 : 0;
}
EXPORT_SYMBOL(fiemap_fill_next_extent);
/**
* fiemap_check_flags - check validity of requested flags for fiemap
* @fieinfo: Fiemap context passed into ->fiemap
* @fs_flags: Set of fiemap flags that the file system understands
*
* Called from file system ->fiemap callback. This will compute the
* intersection of valid fiemap flags and those that the fs supports. That
* value is then compared against the user supplied flags. In case of bad user
* flags, the invalid values will be written into the fieinfo structure, and
* -EBADR is returned, which tells ioctl_fiemap() to return those values to
* userspace. For this reason, a return code of -EBADR should be preserved.
*
* Returns 0 on success, -EBADR on bad flags.
*/
int fiemap_check_flags(struct fiemap_extent_info *fieinfo, u32 fs_flags)
{
u32 incompat_flags;
incompat_flags = fieinfo->fi_flags & ~(FIEMAP_FLAGS_COMPAT & fs_flags);
if (incompat_flags) {
fieinfo->fi_flags = incompat_flags;
return -EBADR;
}
return 0;
}
EXPORT_SYMBOL(fiemap_check_flags);
static int fiemap_check_ranges(struct super_block *sb,
u64 start, u64 len, u64 *new_len)
{
u64 maxbytes = (u64) sb->s_maxbytes;
*new_len = len;
if (len == 0)
return -EINVAL;
if (start > maxbytes)
return -EFBIG;
/*
* Shrink request scope to what the fs can actually handle.
*/
if (len > maxbytes || (maxbytes - len) < start)
*new_len = maxbytes - start;
return 0;
}
static int ioctl_fiemap(struct file *filp, unsigned long arg)
{
struct fiemap fiemap;
struct fiemap __user *ufiemap = (struct fiemap __user *) arg;
struct fiemap_extent_info fieinfo = { 0, };
struct inode *inode = file_inode(filp);
struct super_block *sb = inode->i_sb;
u64 len;
int error;
if (!inode->i_op->fiemap)
return -EOPNOTSUPP;
if (copy_from_user(&fiemap, ufiemap, sizeof(fiemap)))
return -EFAULT;
if (fiemap.fm_extent_count > FIEMAP_MAX_EXTENTS)
return -EINVAL;
error = fiemap_check_ranges(sb, fiemap.fm_start, fiemap.fm_length,
&len);
if (error)
return error;
fieinfo.fi_flags = fiemap.fm_flags;
fieinfo.fi_extents_max = fiemap.fm_extent_count;
fieinfo.fi_extents_start = ufiemap->fm_extents;
if (fiemap.fm_extent_count != 0 &&
!access_ok(VERIFY_WRITE, fieinfo.fi_extents_start,
fieinfo.fi_extents_max * sizeof(struct fiemap_extent)))
return -EFAULT;
if (fieinfo.fi_flags & FIEMAP_FLAG_SYNC)
filemap_write_and_wait(inode->i_mapping);
error = inode->i_op->fiemap(inode, &fieinfo, fiemap.fm_start, len);
fiemap.fm_flags = fieinfo.fi_flags;
fiemap.fm_mapped_extents = fieinfo.fi_extents_mapped;
if (copy_to_user(ufiemap, &fiemap, sizeof(fiemap)))
error = -EFAULT;
return error;
}
#ifdef CONFIG_BLOCK
static inline sector_t logical_to_blk(struct inode *inode, loff_t offset)
{
return (offset >> inode->i_blkbits);
}
static inline loff_t blk_to_logical(struct inode *inode, sector_t blk)
{
return (blk << inode->i_blkbits);
}
/**
* __generic_block_fiemap - FIEMAP for block based inodes (no locking)
* @inode: the inode to map
* @fieinfo: the fiemap info struct that will be passed back to userspace
* @start: where to start mapping in the inode
* @len: how much space to map
* @get_block: the fs's get_block function
*
* This does FIEMAP for block based inodes. Basically it will just loop
* through get_block until we hit the number of extents we want to map, or we
* go past the end of the file and hit a hole.
*
* If it is possible to have data blocks beyond a hole past @inode->i_size, then
* please do not use this function, it will stop at the first unmapped block
* beyond i_size.
*
* If you use this function directly, you need to do your own locking. Use
* generic_block_fiemap if you want the locking done for you.
*/
int __generic_block_fiemap(struct inode *inode,
struct fiemap_extent_info *fieinfo, loff_t start,
loff_t len, get_block_t *get_block)
{
struct buffer_head map_bh;
sector_t start_blk, last_blk;
loff_t isize = i_size_read(inode);
u64 logical = 0, phys = 0, size = 0;
u32 flags = FIEMAP_EXTENT_MERGED;
bool past_eof = false, whole_file = false;
int ret = 0;
ret = fiemap_check_flags(fieinfo, FIEMAP_FLAG_SYNC);
if (ret)
return ret;
/*
* Either the i_mutex or other appropriate locking needs to be held
* since we expect isize to not change at all through the duration of
* this call.
*/
if (len >= isize) {
whole_file = true;
len = isize;
}
/*
* Some filesystems can't deal with being asked to map less than
* blocksize, so make sure our len is at least block length.
*/
if (logical_to_blk(inode, len) == 0)
len = blk_to_logical(inode, 1);
start_blk = logical_to_blk(inode, start);
last_blk = logical_to_blk(inode, start + len - 1);
do {
/*
* we set b_size to the total size we want so it will map as
* many contiguous blocks as possible at once
*/
memset(&map_bh, 0, sizeof(struct buffer_head));
map_bh.b_size = len;
ret = get_block(inode, start_blk, &map_bh, 0);
if (ret)
break;
/* HOLE */
if (!buffer_mapped(&map_bh)) {
start_blk++;
/*
* We want to handle the case where there is an
* allocated block at the front of the file, and then
* nothing but holes up to the end of the file properly,
* to make sure that extent at the front gets properly
* marked with FIEMAP_EXTENT_LAST
*/
if (!past_eof &&
blk_to_logical(inode, start_blk) >= isize)
past_eof = 1;
/*
* First hole after going past the EOF, this is our
* last extent
*/
if (past_eof && size) {
flags = FIEMAP_EXTENT_MERGED|FIEMAP_EXTENT_LAST;
ret = fiemap_fill_next_extent(fieinfo, logical,
phys, size,
flags);
} else if (size) {
ret = fiemap_fill_next_extent(fieinfo, logical,
phys, size, flags);
size = 0;
}
/* if we have holes up to/past EOF then we're done */
if (start_blk > last_blk || past_eof || ret)
break;
} else {
/*
* We have gone over the length of what we wanted to
* map, and it wasn't the entire file, so add the extent
* we got last time and exit.
*
* This is for the case where say we want to map all the
* way up to the second to the last block in a file, but
* the last block is a hole, making the second to last
* block FIEMAP_EXTENT_LAST. In this case we want to
* see if there is a hole after the second to last block
* so we can mark it properly. If we found data after
* we exceeded the length we were requesting, then we
* are good to go, just add the extent to the fieinfo
* and break
*/
if (start_blk > last_blk && !whole_file) {
ret = fiemap_fill_next_extent(fieinfo, logical,
phys, size,
flags);
break;
}
/*
* if size != 0 then we know we already have an extent
* to add, so add it.
*/
if (size) {
ret = fiemap_fill_next_extent(fieinfo, logical,
phys, size,
flags);
if (ret)
break;
}
logical = blk_to_logical(inode, start_blk);
phys = blk_to_logical(inode, map_bh.b_blocknr);
size = map_bh.b_size;
flags = FIEMAP_EXTENT_MERGED;
start_blk += logical_to_blk(inode, size);
/*
* If we are past the EOF, then we need to make sure as
* soon as we find a hole that the last extent we found
* is marked with FIEMAP_EXTENT_LAST
*/
if (!past_eof && logical + size >= isize)
past_eof = true;
}
cond_resched();
} while (1);
/* If ret is 1 then we just hit the end of the extent array */
if (ret == 1)
ret = 0;
return ret;
}
EXPORT_SYMBOL(__generic_block_fiemap);
/**
* generic_block_fiemap - FIEMAP for block based inodes
* @inode: The inode to map
* @fieinfo: The mapping information
* @start: The initial block to map
* @len: The length of the extect to attempt to map
* @get_block: The block mapping function for the fs
*
* Calls __generic_block_fiemap to map the inode, after taking
* the inode's mutex lock.
*/
int generic_block_fiemap(struct inode *inode,
struct fiemap_extent_info *fieinfo, u64 start,
u64 len, get_block_t *get_block)
{
int ret;
mutex_lock(&inode->i_mutex);
ret = __generic_block_fiemap(inode, fieinfo, start, len, get_block);
mutex_unlock(&inode->i_mutex);
return ret;
}
EXPORT_SYMBOL(generic_block_fiemap);
#endif /* CONFIG_BLOCK */
/*
* This provides compatibility with legacy XFS pre-allocation ioctls
* which predate the fallocate syscall.
*
* Only the l_start, l_len and l_whence fields of the 'struct space_resv'
* are used here, rest are ignored.
*/
int ioctl_preallocate(struct file *filp, void __user *argp)
{
struct inode *inode = file_inode(filp);
struct space_resv sr;
if (copy_from_user(&sr, argp, sizeof(sr)))
return -EFAULT;
switch (sr.l_whence) {
case SEEK_SET:
break;
case SEEK_CUR:
sr.l_start += filp->f_pos;
break;
case SEEK_END:
sr.l_start += i_size_read(inode);
break;
default:
return -EINVAL;
}
return do_fallocate(filp, FALLOC_FL_KEEP_SIZE, sr.l_start, sr.l_len);
}
static int file_ioctl(struct file *filp, unsigned int cmd,
unsigned long arg)
{
struct inode *inode = file_inode(filp);
int __user *p = (int __user *)arg;
switch (cmd) {
case FIBMAP:
return ioctl_fibmap(filp, p);
case FIONREAD:
return put_user(i_size_read(inode) - filp->f_pos, p);
case FS_IOC_RESVSP:
case FS_IOC_RESVSP64:
return ioctl_preallocate(filp, p);
}
return vfs_ioctl(filp, cmd, arg);
}
static int ioctl_fionbio(struct file *filp, int __user *argp)
{
unsigned int flag;
int on, error;
error = get_user(on, argp);
if (error)
return error;
flag = O_NONBLOCK;
#ifdef __sparc__
/* SunOS compatibility item. */
if (O_NONBLOCK != O_NDELAY)
flag |= O_NDELAY;
#endif
spin_lock(&filp->f_lock);
if (on)
filp->f_flags |= flag;
else
filp->f_flags &= ~flag;
spin_unlock(&filp->f_lock);
return error;
}
static int ioctl_fioasync(unsigned int fd, struct file *filp,
int __user *argp)
{
unsigned int flag;
int on, error;
error = get_user(on, argp);
if (error)
return error;
flag = on ? FASYNC : 0;
/* Did FASYNC state change ? */
if ((flag ^ filp->f_flags) & FASYNC) {
if (filp->f_op->fasync)
/* fasync() adjusts filp->f_flags */
error = filp->f_op->fasync(fd, filp, on);
else
error = -ENOTTY;
}
return error < 0 ? error : 0;
}
static int ioctl_fsfreeze(struct file *filp)
{
struct super_block *sb = file_inode(filp)->i_sb;
if (!capable(CAP_SYS_ADMIN))
return -EPERM;
/* If filesystem doesn't support freeze feature, return. */
if (sb->s_op->freeze_fs == NULL)
return -EOPNOTSUPP;
/* Freeze */
return freeze_super(sb);
}
static int ioctl_fsthaw(struct file *filp)
{
struct super_block *sb = file_inode(filp)->i_sb;
if (!capable(CAP_SYS_ADMIN))
return -EPERM;
/* Thaw */
return thaw_super(sb);
}
/*
* When you add any new common ioctls to the switches above and below
* please update compat_sys_ioctl() too.
*
* do_vfs_ioctl() is not for drivers and not intended to be EXPORT_SYMBOL()'d.
* It's just a simple helper for sys_ioctl and compat_sys_ioctl.
*/
int do_vfs_ioctl(struct file *filp, unsigned int fd, unsigned int cmd,
unsigned long arg)
{
int error = 0;
int __user *argp = (int __user *)arg;
struct inode *inode = file_inode(filp);
switch (cmd) {
case FIOCLEX:
set_close_on_exec(fd, 1);
break;
case FIONCLEX:
set_close_on_exec(fd, 0);
break;
case FIONBIO:
error = ioctl_fionbio(filp, argp);
break;
case FIOASYNC:
error = ioctl_fioasync(fd, filp, argp);
break;
case FIOQSIZE:
if (S_ISDIR(inode->i_mode) || S_ISREG(inode->i_mode) ||
S_ISLNK(inode->i_mode)) {
loff_t res = inode_get_bytes(inode);
error = copy_to_user(argp, &res, sizeof(res)) ?
-EFAULT : 0;
} else
error = -ENOTTY;
break;
case FIFREEZE:
error = ioctl_fsfreeze(filp);
break;
case FITHAW:
error = ioctl_fsthaw(filp);
break;
case FS_IOC_FIEMAP:
return ioctl_fiemap(filp, arg);
case FIGETBSZ:
return put_user(inode->i_sb->s_blocksize, argp);
default:
if (S_ISREG(inode->i_mode))
error = file_ioctl(filp, cmd, arg);
else
error = vfs_ioctl(filp, cmd, arg);
break;
}
return error;
}
SYSCALL_DEFINE3(ioctl, unsigned int, fd, unsigned int, cmd, unsigned long, arg)
{
int error;
struct fd f = fdget(fd);
if (!f.file)
return -EBADF;
error = security_file_ioctl(f.file, cmd, arg);
if (!error)
error = do_vfs_ioctl(f.file, fd, cmd, arg);
fdput(f);
return error;
}
最终调用到Binder driver调用链是:
ioctl()->do_vfs_ioctl()->vfs_ioctl()->f_op->unlocked_ioctl()。
现在查看f_op->unlocked_ioctl。
在ioctl()函数中,有如下定义:
struct fd f = fdget(fd);其中fd = "/dev/binder",即f_op就是指向设备文件"/dev/binder"的一个文件描述结构体,上述调用链中,最后调用的是该文件描述结构体的unlocked_ioctl()函数。
Binder驱动的实现文件/kernel-3.18/drivers/staging/android/binder.c中
static const struct file_operations binder_fops = {
.owner = THIS_MODULE,
.poll = binder_poll,
.unlocked_ioctl = binder_ioctl,
.compat_ioctl = binder_ioctl,
.mmap = binder_mmap,
.open = binder_open,
.flush = binder_flush,
.release = binder_release,
};即实际调用的是binder_ioctl函数。
static long binder_ioctl(struct file *filp, unsigned int cmd, unsigned long arg)
{
int ret;
struct binder_proc *proc = filp->private_data;
struct binder_thread *thread;
unsigned int size = _IOC_SIZE(cmd);
void __user *ubuf = (void __user *)arg;
/*pr_info("binder_ioctl: %d:%d %x %lx\n",
proc->pid, current->pid, cmd, arg);*/
binder_selftest_alloc(&proc->alloc);
trace_binder_ioctl(cmd, arg);
ret = wait_event_interruptible(binder_user_error_wait, binder_stop_on_user_error < 2);
if (ret)
goto err_unlocked;
//查找或创建binder_thread结构体
thread = binder_get_thread(proc);
if (thread == NULL) {
ret = -ENOMEM;
goto err;
}
switch (cmd) {
case BINDER_WRITE_READ: //cmd = BINDER_WRITE_READ
ret = binder_ioctl_write_read(filp, cmd, arg, thread);
if (ret)
goto err;
break;
case BINDER_SET_MAX_THREADS: {
int max_threads;
if (copy_from_user(&max_threads, ubuf,
sizeof(max_threads))) {
ret = -EINVAL;
goto err;
}
binder_inner_proc_lock(proc);
proc->max_threads = max_threads;
binder_inner_proc_unlock(proc);
break;
}
case BINDER_SET_CONTEXT_MGR:
ret = binder_ioctl_set_ctx_mgr(filp);
if (ret)
goto err;
break;
case BINDER_THREAD_EXIT:
binder_debug(BINDER_DEBUG_THREADS, "%d:%d exit\n",
proc->pid, thread->pid);
binder_thread_release(proc, thread);
thread = NULL;
break;
case BINDER_VERSION: {
struct binder_version __user *ver = ubuf;
if (size != sizeof(struct binder_version)) {
ret = -EINVAL;
goto err;
}
if (put_user(BINDER_CURRENT_PROTOCOL_VERSION,
&ver->protocol_version)) {
ret = -EINVAL;
goto err;
}
break;
}
case BINDER_GET_NODE_DEBUG_INFO: {
struct binder_node_debug_info info;
if (copy_from_user(&info, ubuf, sizeof(info))) {
ret = -EFAULT;
goto err;
}
ret = binder_ioctl_get_node_debug_info(proc, &info);
if (ret < 0)
goto err;
if (copy_to_user(ubuf, &info, sizeof(info))) {
ret = -EFAULT;
goto err;
}
break;
}
default:
ret = -EINVAL;
goto err;
}
ret = 0;
err:
if (thread)
thread->looper_need_return = false;
wait_event_interruptible(binder_user_error_wait, binder_stop_on_user_error < 2);
if (ret && ret != -ERESTARTSYS)
pr_info("%d:%d ioctl %x %lx returned %d\n", proc->pid, current->pid, cmd, arg, ret);
err_unlocked:
trace_binder_ioctl_done(ret);
return ret;
}cmd = BINDER_WRITE_READ,首先根据传递过来的文件句柄指针获取相应的binder_proc结构体,再从中查找binder_thread,如果当前线程已经加入到proc的线程队列则直接返回,如果不存在则创建binder_thread,并将当前线程添加到当前的proc。
- 当返回值为-ENOMEM,则意味着内存不足,往往会出现创建binder_thread对象失败
- 当返回值为-EINVAL,则意味着CMD命令参数无效
接下来执行binder_ioctl_write_read
static int binder_ioctl_write_read(struct file *filp,
unsigned int cmd, unsigned long arg,
struct binder_thread *thread)
{
int ret = 0;
struct binder_proc *proc = filp->private_data;
unsigned int size = _IOC_SIZE(cmd);
void __user *ubuf = (void __user *)arg;
struct binder_write_read bwr;
if (size != sizeof(struct binder_write_read)) {
ret = -EINVAL;
goto out;
}
//将用户空间bwr结构体拷贝到内核空间
if (copy_from_user(&bwr, ubuf, sizeof(bwr))) {
ret = -EFAULT;
goto out;
}
binder_debug(BINDER_DEBUG_READ_WRITE,
"%d:%d write %lld at %016llx, read %lld at %016llx\n",
proc->pid, thread->pid,
(u64)bwr.write_size, (u64)bwr.write_buffer,
(u64)bwr.read_size, (u64)bwr.read_buffer);
if (bwr.write_size > 0) {
//将数据放入目标进程
ret = binder_thread_write(proc, thread,
bwr.write_buffer,
bwr.write_size,
&bwr.write_consumed);
trace_binder_write_done(ret);
//当执行失败,则直接将内核bwr结构体写回用户空间,并跳出该方法
if (ret < 0) {
bwr.read_consumed = 0;
if (copy_to_user(ubuf, &bwr, sizeof(bwr)))
ret = -EFAULT;
goto out;
}
}
if (bwr.read_size > 0) {
//读取自己队列的数据
ret = binder_thread_read(proc, thread, bwr.read_buffer,
bwr.read_size,
&bwr.read_consumed,
filp->f_flags & O_NONBLOCK);
trace_binder_read_done(ret);
binder_inner_proc_lock(proc);
//当进程的todo队列有数据,则唤醒在该队列等待的进程
if (!binder_worklist_empty_ilocked(&proc->todo))
binder_wakeup_proc_ilocked(proc);
binder_inner_proc_unlock(proc);
//当执行失败,则直接将内核bwr结构体写回用户空间,并跳出此方法
if (ret < 0) {
if (copy_to_user(ubuf, &bwr, sizeof(bwr)))
ret = -EFAULT;
goto out;
}
}
binder_debug(BINDER_DEBUG_READ_WRITE,
"%d:%d wrote %lld of %lld, read return %lld of %lld\n",
proc->pid, thread->pid,
(u64)bwr.write_consumed, (u64)bwr.write_size,
(u64)bwr.read_consumed, (u64)bwr.read_size);
if (copy_to_user(ubuf, &bwr, sizeof(bwr))) {
ret = -EFAULT;
goto out;
}
out:
return ret;
}- copy_from_user():将用户空间IPC数据拷贝到内核态binder_write_read结构体
- copy_to_user():将内核态binder_write_read结构体数据拷贝到用户空间
此时arg是一个binder_write_read结构体,mOut数据保存在write_buffer,所以write_size > 0,但此时read_size = 0。首先将用户空间bwr结构体拷贝到内核空间,然后执行binder_thread_write()操作。
①首先调用binder_thread_write()
static int binder_thread_write(struct binder_proc *proc,
struct binder_thread *thread,
binder_uintptr_t binder_buffer, size_t size,
binder_size_t *consumed)
{
uint32_t cmd;
struct binder_context *context = proc->context;
void __user *buffer = (void __user *)(uintptr_t)binder_buffer;
void __user *ptr = buffer + *consumed;
void __user *end = buffer + size;
while (ptr < end && thread->return_error.cmd == BR_OK) {
int ret;
//拷贝用户空间的cmd命令,此时为BC_TRANSACTION
if (get_user(cmd, (uint32_t __user *)ptr))
return -EFAULT;
ptr += sizeof(uint32_t);
trace_binder_command(cmd);
if (_IOC_NR(cmd) < ARRAY_SIZE(binder_stats.bc)) {
atomic_inc(&binder_stats.bc[_IOC_NR(cmd)]);
atomic_inc(&proc->stats.bc[_IOC_NR(cmd)]);
atomic_inc(&thread->stats.bc[_IOC_NR(cmd)]);
}
switch (cmd) {
.......
case BC_TRANSACTION:
case BC_REPLY: {
struct binder_transaction_data tr;
//拷贝用户空间的binder_transaction_data
if (copy_from_user(&tr, ptr, sizeof(tr)))
return -EFAULT;
ptr += sizeof(tr);
binder_transaction(proc, thread, &tr,
cmd == BC_REPLY, 0);
break;
}
......
default:
pr_err("%d:%d unknown command %d\n",
proc->pid, thread->pid, cmd);
return -EINVAL;
}
*consumed = ptr - buffer;
}
return 0;
}不断从binder_buffer所指向的地址获取cmd,然后对命令逐条执行,当命令是BC_REPLY或BC_TRANSACTION时,调用bind_transaction()来处理事务。
binder_transaction
binder_transaction()函数中,主要动作是遍历红黑树,找到服务端的工作队列,将Binder请求插入该队伍,相当于加入一个新的工作任务。
主要功能:
查询目标进程的过程:handle-->binder_ref-->binder_node-->binder_proc
将BINDER_WORK_TRANSACTION添加到目标队列target_list,首次发起事务则目标队列为target_proc->todo,reply事务时则为target_thread->todo;oneway的非reply事务,则为target_node->async_todo。
将BINDER_WORD_TRANSACTION_COMPLETE添加到当前线程的todo队列,此时当前线程的todo队列已经有事务,接下来会进入binder_thread_read()来处理相关事务。
②插入完成后,线程返回到binder_ioctl_write_read()函数体中,执行binder_thread_read()
- 当接收到的是BINDER_WORK_TRANSACTION_COMPLETE,则将命令BR_TRANSACTION_COMPLETE写回用户空间;
- 当收到的是BINDER_WORK_TRANSACTION命令,则将命令BR_TRANSACTION或BR_REPLY写回用户空间
通信过程总结
①执行完binder_thread_write方法后,通过binder_transaction()首先写入BINDER_WORK_TRANSACTION_COMPLETE,写入当前线程;
②这是bwr.read_size > 0,回到binder_ioctl_write_read方法,开始执行binder_thread_read();
③在binder_thread_read()方法,将获取cmd=BR_TRANSACTION_COMPLETE,再将cmd和数据写回用户空间;
④一次binder_ioctl完成,接着回调用户空间方法talkWithDriver(),并且刚才的数据写入mIn;
⑤这是mIn有可读数据,回到waitForResponse()方法,完成BR_TRANSACTION_COMPLETE过程;
⑥再回退到transact()方法,对于oneway的操作,这次Binder通信便完成,否则还是要等待Binder服务端的放回。
参考链接:http://zhuanlan.51cto.com/art/201611/523181.htm
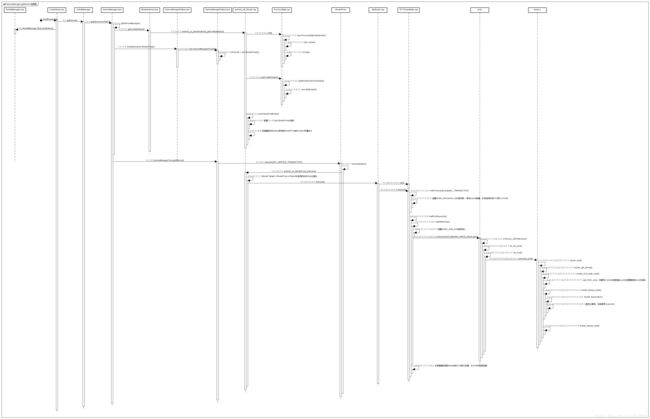
自绘时序图: