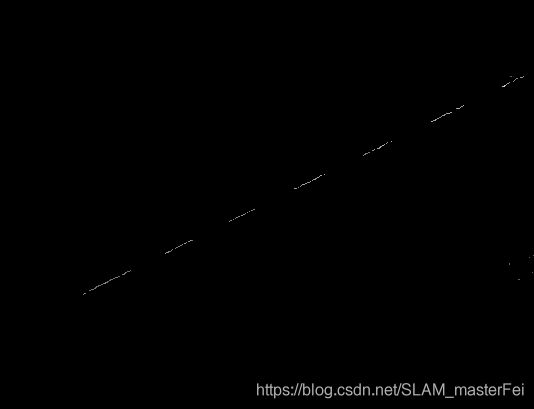
基于灰度质心法和骨架的激光中心线提取
之前博主一直在做线结构光成像,硬件比较垃圾,相机加镜头和线激光器总共成本在1000以内,精度在0.1mm左右,感觉这种成本做出来还是不错的,其实主要大部分时间花在了分析上来达到最好的效果。
一般对于激光条纹线,主流的方法是利用steger或者它的改进方法去提取中心线,但是博主之前实现了一下,感觉图像里的hessian矩阵并不能很好的描述条纹的法向,所以就另换方法,这次采用先骨架提取再利用法线上的灰度值通过灰度质心来达到亚像素级的水平。
关于骨架提取,我采用了zhang-suen方法,该方法简单易用,效果良好,具体做法如下
对于上图哈哈哈哈原谅我的随意,以某个像素为原点,这里是1,寻找周围3*3窗口的像素,然后如果中心像素大于0,则遍历该窗体其他的元素,大于0记为1,是0记为0。记做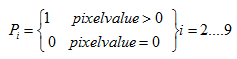
步骤1
同时满足以下几点删除该像素点
1:对于每个像素点,按上述方法遍历,并且如果对于当前该像素 ![]() 的值大于等于2且小于等于六
的值大于等于2且小于等于六
2:顺时针遍历其周围8个像素,0,1这样的结构总和为1。例如上图如果p2==0&&p3==1则我们称为一个0,1序列。
3:p2*p4*p6==0&&p4*p6*p8==0
遍历所有像素点,删除符合条件的像素
然后进行步骤2
它同样遍历所有像素点,需要符合3个条件,前两个和步骤1一样,第三个条件如下:p2*p4*p8==0&&p2*p6*p8==0
同样遍历所有像素点,删除符合条件的
重复上述这两个步骤,知道没有任何像素变化为止。
下面贴出代码
//zhang细化算法
void zhang(Mat& input, Mat& output)
{
Mat copymat;
input.copyTo(copymat);
int k = 0;
//防止溢出
while (1)
{
k++;
bool stop = false;
//step1
for (int i = 1; i < input.cols - 1; i++)
for (int j = 1 j < input.rows - 1; j++)
{
if (input.at(j, i)>0)
{
int p1 = int(input.at(j, i))>0 ? 1 : 0;
int p2 = int(input.at(j - 1, i))>0 ? 1 : 0;
int p3 = int(input.at(j - 1, i + 1))>0 ? 1 : 0;
int p4 = int(input.at(j, i + 1))>0 ? 1 : 0;
int p5 = int(input.at(j + 1, i + 1))>0 ? 1 : 0;
int p6 = int(input.at(j + 1, i))>0 ? 1 : 0;
int p7 = int(input.at(j + 1, i - 1))>0 ? 1 : 0;
int p8 = int(input.at(j, i - 1))>0 ? 1 : 0;
int p9 = int(input.at(j - 1, i - 1))>0 ? 1 : 0;
int np1 = p2 + p3 + p4 + p5 + p6 + p7 + p8 + p9;
int sp2 = (p2 == 0 && p3 == 1) ? 1 : 0;
int sp3 = (p3 == 0 && p4 == 1) ? 1 : 0;
int sp4 = (p4 == 0 && p5 == 1) ? 1 : 0;
int sp5 = (p5 == 0 && p6 == 1) ? 1 : 0;
int sp6 = (p6 == 0 && p7 == 1) ? 1 : 0;
int sp7 = (p7 == 0 && p8 == 1) ? 1 : 0;
int sp8 = (p8 == 0 && p9 == 1) ? 1 : 0;
int sp9 = (p9 == 0 && p2 == 1) ? 1 : 0;
int sp1 = sp2 + sp3 + sp4 + sp5 + sp6 + sp7 + sp8 + sp9;
if (np1 >= 2 && np1 <= 6 && sp1 == 1 && ((p2*p4*p6) == 0) && ((p4*p6*p8) == 0))
{
stop = true;
copymat.at(j, i) = 0;
}
}
}
//step2
for (int i = 1; i < input.cols - 1; i++)
{
for (int j = 1; j < input.rows - 1; j++)
{
if (input.at(j, i)>0)
{
int p2 = int(input.at(j - 1, i))>0 ? 1 : 0;
int p3 = int(input.at(j - 1, i + 1)) > 0 ? 1 : 0;
int p4 = int(input.at(j, i + 1)) > 0 ? 1 : 0;
int p5 = int(input.at(j + 1, i + 1)) > 0 ? 1 : 0;
int p6 = int(input.at(j + 1, i)) > 0 ? 1 : 0;
int p7 = int(input.at(j + 1, i - 1)) > 0 ? 1 : 0;
int p8 = int(input.at(j, i - 1)) > 0 ? 1 : 0;
int p9 = int(input.at(j - 1, i - 1)) > 0 ? 1 : 0;
int np1 = p2 + p3 + p4 + p5 + p6 + p7 + p8 + p9;
int sp2 = (p2 == 0 && p3 == 1) ? 1 : 0;
int sp3 = (p3 == 0 && p4 == 1) ? 1 : 0;
int sp4 = (p4 == 0 && p5 == 1) ? 1 : 0;
int sp5 = (p5 == 0 && p6 == 1) ? 1 : 0;
int sp6 = (p6 == 0 && p7 == 1) ? 1 : 0;
int sp7 = (p7 == 0 && p8 == 1) ? 1 : 0;
int sp8 = (p8 == 0 && p9 == 1) ? 1 : 0;
int sp9 = (p9 == 0 && p2 == 1) ? 1 : 0;
int sp1 = sp2 + sp3 + sp4 + sp5 + sp6 + sp7 + sp8 + sp9;
if (np1 >= 2 && np1 <= 6 && sp1 == 1 && (p2*p4*p8) == 0 && (p2*p6*p8) == 0)
{
stop = true;
copymat.at(j, i) = 0;
}
}
}
}
//将新得到的图片赋给新的图片
copymat.copyTo(input);
if (!stop)
{
break;
}
}
copymat.copyTo(output);
} 效果如下:
然后得到骨架,我们根据像素点的周围信息去估计点的法向,原理很简单,对于某个像素值,可以得到其左右两个点对于它的向量,然后可以得到两个垂直的向量,归一化后用两个向量相加即可。
这里参考一篇博客的法向量求解,感觉对于单像素骨架还可以https://blog.csdn.net/blueblood7/article/details/8019846
得到法向量后我们沿着法线去进行搜索,然后用灰度质心法去得到亚像素级的像素
下面给出全部代码
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
using namespace std;
using namespace cv;
//zhang细化算法
void zhang(Mat& input, Mat& output)
{
Mat copymat;
input.copyTo(copymat);
int k = 0;
//防止溢出
while (1)
{
k++;
bool stop = false;
//step1
for (int i = 1; i < input.cols - 1; i++)
for (int j = 1; j < input.rows - 1; j++)
{
if (input.at(j, i)>0)
{
int p1 = int(input.at(j, i))>0 ? 1 : 0;
int p2 = int(input.at(j - 1, i))>0 ? 1 : 0;
int p3 = int(input.at(j - 1, i + 1))>0 ? 1 : 0;
int p4 = int(input.at(j, i + 1))>0 ? 1 : 0;
int p5 = int(input.at(j + 1, i + 1))>0 ? 1 : 0;
int p6 = int(input.at(j + 1, i))>0 ? 1 : 0;
int p7 = int(input.at(j + 1, i - 1))>0 ? 1 : 0;
int p8 = int(input.at(j, i - 1))>0 ? 1 : 0;
int p9 = int(input.at(j - 1, i - 1))>0 ? 1 : 0;
int np1 = p2 + p3 + p4 + p5 + p6 + p7 + p8 + p9;
int sp2 = (p2 == 0 && p3 == 1) ? 1 : 0;
int sp3 = (p3 == 0 && p4 == 1) ? 1 : 0;
int sp4 = (p4 == 0 && p5 == 1) ? 1 : 0;
int sp5 = (p5 == 0 && p6 == 1) ? 1 : 0;
int sp6 = (p6 == 0 && p7 == 1) ? 1 : 0;
int sp7 = (p7 == 0 && p8 == 1) ? 1 : 0;
int sp8 = (p8 == 0 && p9 == 1) ? 1 : 0;
int sp9 = (p9 == 0 && p2 == 1) ? 1 : 0;
int sp1 = sp2 + sp3 + sp4 + sp5 + sp6 + sp7 + sp8 + sp9;
if (np1 >= 2 && np1 <= 6 && sp1 == 1 && ((p2*p4*p6) == 0) && ((p4*p6*p8) == 0))
{
stop = true;
copymat.at(j, i) = 0;
}
}
}
//step2
for (int i = 1; i < input.cols - 1; i++)
{
for (int j = 1; j < input.rows - 1; j++)
{
if (input.at(j, i)>0)
{
int p2 = int(input.at(j - 1, i))>0 ? 1 : 0;
int p3 = int(input.at(j - 1, i + 1)) > 0 ? 1 : 0;
int p4 = int(input.at(j, i + 1)) > 0 ? 1 : 0;
int p5 = int(input.at(j + 1, i + 1)) > 0 ? 1 : 0;
int p6 = int(input.at(j + 1, i)) > 0 ? 1 : 0;
int p7 = int(input.at(j + 1, i - 1)) > 0 ? 1 : 0;
int p8 = int(input.at(j, i - 1)) > 0 ? 1 : 0;
int p9 = int(input.at(j - 1, i - 1)) > 0 ? 1 : 0;
int np1 = p2 + p3 + p4 + p5 + p6 + p7 + p8 + p9;
int sp2 = (p2 == 0 && p3 == 1) ? 1 : 0;
int sp3 = (p3 == 0 && p4 == 1) ? 1 : 0;
int sp4 = (p4 == 0 && p5 == 1) ? 1 : 0;
int sp5 = (p5 == 0 && p6 == 1) ? 1 : 0;
int sp6 = (p6 == 0 && p7 == 1) ? 1 : 0;
int sp7 = (p7 == 0 && p8 == 1) ? 1 : 0;
int sp8 = (p8 == 0 && p9 == 1) ? 1 : 0;
int sp9 = (p9 == 0 && p2 == 1) ? 1 : 0;
int sp1 = sp2 + sp3 + sp4 + sp5 + sp6 + sp7 + sp8 + sp9;
if (np1 >= 2 && np1 <= 6 && sp1 == 1 && (p2*p4*p8) == 0 && (p2*p6*p8) == 0)
{
stop = true;
copymat.at(j, i) = 0;
}
}
}
}
//将新得到的图片赋给新的图片
copymat.copyTo(input);
if (!stop)
{
break;
}
}
copymat.copyTo(output);
}
//第i,j个点像素值
double ijpixel(double& x, double& y, Mat& m)
{
int x_0 = int(x);
int x_1 = int(x + 1);
int y_0 = int(y);
int y_1 = int(y + 1);
int px_0y_0 = int(m.at(y_0, x_0));
int px_0y_1 = int(m.at(y_1, x_0));
int px_1y_0 = int(m.at(y_0, x_1));
int px_1y_1 = int(m.at(y_1, x_1));
double x_y0 = px_0y_0 + (x - double(x_0))*(px_1y_0 - px_0y_0);
double x_y1 = px_0y_1 + (x - double(x_0))*(px_1y_1 - px_0y_1);
double x_y = x_y0 + (y - double(y_0))*(x_y1 - x_y0);
return x_y;
}
//normal vector
void CalcNormVec(Point2d& ptA, Point2d& ptB, Point2d& ptC, double& pfCosSita, double& pfSinSita)
{
double fVec1_x, fVec1_y, fVec2_x, fVec2_y;
if (ptA.x == 0 && ptA.y == 0)
{
ptA.x = ptC.x;
ptA.y = ptC.y;
//先用B点坐标减A点坐标。
fVec1_x = -(ptB.x - ptA.x);
fVec1_y = -(ptB.y - ptA.y);
}
else
{
//先用B点坐标减A点坐标。
fVec1_x = ptB.x - ptA.x;
fVec1_y = ptB.y - ptA.y;
}
if (ptC.x == 0 && ptC.y == 0)
{
ptC.x = ptA.x;
ptC.y = ptA.y;
//再用C点坐标减B点坐标。
fVec2_x = (ptB.x - ptC.x);
fVec2_y = (ptB.y - ptC.y);
}
else
{
//再用C点坐标减B点坐标。
fVec2_x = ptC.x - ptB.x;
fVec2_y = ptC.y - ptB.y;
}
//单位化。
double fMod = sqrt(fVec1_x * fVec1_x + fVec1_y * fVec1_y);
fVec1_x /= fMod;
fVec1_y /= fMod;
//计算垂线。
double fPerpendicularVec1_x = -fVec1_y;
double fPerpendicularVec1_y = fVec1_x;
//单位化。
fMod = sqrt(fVec2_x * fVec2_x + fVec2_y * fVec2_y);
fVec2_x /= fMod;
fVec2_y /= fMod;
//计算垂线。
double fPerpendicularVec2_x = -fVec2_y;
double fPerpendicularVec2_y = fVec2_x;
//求和。
double fSumX = fPerpendicularVec1_x + fPerpendicularVec2_x;
double fSumY = fPerpendicularVec1_y + fPerpendicularVec2_y;
//单位化。
fMod = sqrt(fSumX * fSumX + fSumY * fSumY);
double fCosSita = fSumX / fMod;
double fSinSita = fSumY / fMod;
pfCosSita = fCosSita;
pfSinSita = fSinSita;
}
void point(Mat& inputimg, vector& pt)
{
pt.push_back(Point2d(0, 0));
for (int i = 0; i < inputimg.cols; i++)
for (int j = 0; j < inputimg.rows; j++)
{
if (inputimg.at(j, i) >= 95)
{
Point2d curr = Point2d(i, j);
pt.push_back(curr);
}
}
pt.push_back(Point2d(0, 0));
}
int main()
{
ofstream of1, of2;
of1.open("x.txt", ios::trunc);
of2.open("y.txt", ios::trunc);
Mat img, img1, img2;
img = imread("./photo/14.png");
cvtColor(img, img, CV_RGB2GRAY);
GaussianBlur(img, img, Size(3, 3), 0);
img.copyTo(img2);
threshold(img, img, 95, 255, 3);
zhang(img, img1);
vector points;
point(img1, points);
vector kcal;
for (int i = 1; i < points.size() - 1; i++)
{
//normal
double pfCosSita=0, pfSinSita=0;
CalcNormVec(Point2d(points[i - 1].x, points[i - 1].y), Point2d(points[i].x, points[i].y), Point2d(points[i + 1].x, points[i + 1].y), pfCosSita, pfSinSita);
//gdd
double sum=0, sum_sumx=0, sum_sumy=0;
for (int j = 0; j < 2; j++)
{
if (j == 0)
{
double cj = points[i].x;
double ci = points[i].y;
sum = ijpixel(cj, ci, img2);
sum_sumx = ijpixel(cj, ci, img2)*cj;
sum_sumy = ijpixel(cj, ci, img2)*ci;
}
else
{
double x_cor = points[i].x + j*pfCosSita;
double y_cor = points[i].y + j*pfSinSita;
double x_cor1 = points[i].x - j*pfCosSita;
double y_cor1 = points[i].y - j*pfSinSita;
sum = sum + ijpixel(x_cor, y_cor, img2) + ijpixel(x_cor1, y_cor1, img2);
sum_sumx = sum_sumx + ijpixel(x_cor, y_cor, img2)*x_cor + ijpixel(x_cor1, y_cor1, img2)*x_cor1;
sum_sumy = sum_sumy + ijpixel(x_cor, y_cor, img2)*y_cor + ijpixel(x_cor1, y_cor1, img2)*y_cor1;
}
}
//图像中心线画出来
circle(img1, Point(sum_sumx / sum, sum_sumy / sum), 1, Scalar(255, 255, 255));
}
imshow("h", img);
imshow("w", img2);
waitKey(0);
system("pause");
return 0;
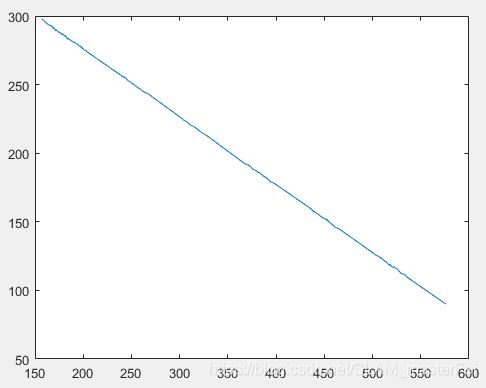
} matlab画出来的点感觉还可以