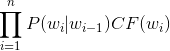基于贝叶斯公式的拼音输入法二元模型实现
和英语的直接输入不同,汉语输入法是通过拼音转译输入,而由于不同的拼音可以对应同一个字,而不同的字也可能存在多个拼音,是一个多对多的关系,因此在获得拼音的时候,需要能够准确地将其转换为正确的汉字,这就是拼音输入法的作用。本文介绍了一种基于贝叶斯公式的全拼拼音输入法实现,全拼也就是输入完整的拼音,不考虑缩写等情况。
以下是一段拼音:
huan ying guan zhu wo de bo ke
对于我们人来说,可以很容易的知道每个拼音对应的是哪个字:
欢迎关注我的博客
但是对于计算机,拼音所对应的每个汉字都是等价的,比如huan可以是“欢”,也可以是“换”,那么如果让计算机知道在这个句子里huan是“欢”?参考一下人将拼音转化为汉字的过程,可以发现在判断某个拼音的时候,我们并不是仅仅根据那一个拼音去判断,而是将其放在整个句子的上下文环境里去判断,也就是说在给定拼音句子的情况下,找到最大概率的汉字句子。翻译成数学语言就是,令X为汉字句子,Y为拼音句子,求
![]()
根据贝叶斯公式
其中
![]()
为常量,因为拼音已经固定,
![]()
使用识别信度代替,
![]()
考虑到随着n的增加,该计算会越来越复杂,并且会增加数据稀疏性,因此使用二元模型,即每个字的概率只和它前一个字相关(当然也可以使用三元模型,即每个字的概率只和它前两个字相关),简化后
![]()
所以问题转化为
其中CF识别信度表示当汉字确定时,其拼音为该拼音的概率,在此可以默认为1,故问题的关键就是
![]()
又由概率公式
其中
![]()
可以根据统计的思想认为代表![]() 和
和![]() 在语料库同时出现的次数
在语料库同时出现的次数
![]()
代表![]() 出现的次数。考虑到
出现的次数。考虑到![]() 和
和![]() 在语料库中可能从来没有同时出现过,因此将改写为
在语料库中可能从来没有同时出现过,因此将改写为
![]() 。
。
这样算法的思路就很清楚了,首先获得语料库,可以是大量的新闻稿,遍历所以新闻稿,统计每个字出现的次数以及每两个连续的字出现的次数,然后读入新的拼音句子从统计结果中选出最佳的汉字。需要注意的是我们需要最大化的是
而不是
![]()
也就是说需要找到是整个句子的概率最大的,而不是某个字概率最大的汉字,这一点可以通过动态规划实现。
以下上代码:
记录每个拼音对应的汉字集
private void initPinyin(){
char[] cs = Utility.readStrFromFile(Utility.HANZI_TABLE).toCharArray();
List ls = Utility.readListFromFile(Utility.PINYIN_TABLE);
String[] ps = new String[ls.size()];
String[] hs = new String[ls.size()];
for (int i = 0; i < ls.size(); ++i){
int border = ls.get(i).indexOf(" ");
ps[i] = ls.get(i).substring(0, border);
hs[i] = ls.get(i).substring(border + 1);
}
p_map = new HashMap>();
for (int i = 1; i < cs.length; ++i){
for (int j = 0; j < hs.length; ++j){
if(hs[j].indexOf(cs[i]) != -1){
if(!p_map.containsKey(ps[j])){
p_map.put(ps[j], new ArrayList());
}
p_map.get(ps[j]).add(cs[i]);
}
}
}
writeMap(p_map, Utility.PINYIN_MAP);
} 根据语料库进行统计(语料库为json格式)
private void initHanzi(){
char[] cs = Utility.readStrFromFile(Utility.HANZI_TABLE).toCharArray();
c_map = new HashMap();
w_map = new HashMap>();
for (int i = 1; i < cs.length; ++i){
c_map.put(cs[i], 0);
w_map.put(cs[i], new HashMap());
}
w_map.put('#', new HashMap());
writeMap(c_map, Utility.HANZI_MAP);
writeMap(w_map, Utility.TWO_HANZI_MAP);
}
private void updateHanzi(String news_file) {
List ss = Utility.readListFromFile(news_file);
c_map = readMap(Utility.HANZI_MAP);
w_map = readMap(Utility.TWO_HANZI_MAP);
for (String s: ss) {
s = s.substring(s.indexOf("{\"html\":"));
JSONObject object = new JSONObject(s);
String content = object.getString("html");
char[] hanzi = content.toCharArray();
char before = '#';
for (char h : hanzi) {
if (isChinese(h)) {
Integer count = c_map.get(h);
if (count != null) {
c_map.replace(h, count + 1);
if ((count = w_map.get(before).get(h)) != null) {
w_map.get(before).replace(h, count + 1);
} else {
w_map.get(before).put(h, 1);
}
before = h;
} else {
before = '#';
}
} else {
before = '#';
}
}
}
writeMap(c_map, Utility.HANZI_MAP);
writeMap(w_map, Utility.TWO_HANZI_MAP);
} 使用动态规划进行翻译
public String[] predict(String pinyin){
String[] ps = pinyin.split(" ");
Queue queue = new PriorityQueue();
queue.add(new Possibility("#", Utility.INIT_POSSIBILITY));
return dynamicPlanning(ps, 0, queue);
}
private String[] dynamicPlanning(String[] ps, int index, Queue queue){
if(index == ps.length){
String[] result = new String[Math.min(queue.size(), Utility.OUT_SIZE)];
for (int i = 0; i < result.length; ++i){
result[i] = queue.poll().str.substring(1);
}
return result;
}
Possibility[] before = new Possibility[Math.min(queue.size(), Utility.MAX_SIZE)];
double norm = queue.peek().p;
for (int i = 0; i < before.length; ++i){
before[i] = queue.poll();
before[i].p /= norm;
}
queue.clear();
List cs = p_map.get(ps[index]);
for (Possibility s : before) {
for (Character c : cs) {
Possibility possibility = s.generateNext(c);
if(!Double.isNaN(possibility.p)){
queue.add(possibility);
}
}
}
return dynamicPlanning(ps, index + 1, queue);
}
class Possibility implements Comparable {
String str;
double p;
Possibility(String str, double p) {
this.str = str;
this.p = p;
}
Possibility generateNext(char next){
char before = str.charAt(str.length() - 1);
return new Possibility(str + next, p * getPossibility(before, next));
}
private double getPossibility(char before, char next){
int n_count = c_map.get(next);
if(before == '#'){
return n_count / Utility.RATIO;
}else {
int b_count = c_map.get(before);
Integer integer = w_map.get(before).get(next);
int bn_count = integer == null ? 0 : integer;
return Utility.ALPHA * bn_count / b_count + (1 - Utility.ALPHA) * n_count / Utility.RATIO;
}
}
public int compareTo(Possibility o) {
return Double.compare(o.p, p);
}
} 项目地址https://github.com/ChenErTong/PinYin