ROS:一种简单的基于global_planner的全局路径优化方法
一种简单的基于global_planner的全局路径优化方法
代码链接:
https://download.csdn.net/download/qq_14977553/12688247
或者
https://github.com/li-huanhuan/ros-melodic-global-planner
环境:
Ubuntu 18.04.4 LTS
ros-melodic
修改的包:navigation中global_planner功能包
全局规划器使用dijkstra算法
优化目标:
1、使路径与膨胀层保持一个像素点的距离。
2、使绕障碍物的路径更加平滑。
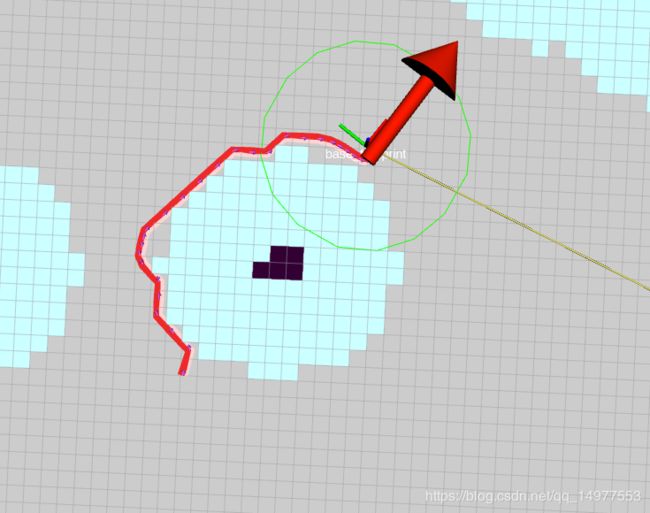
优化之前的路径
第一步:添加路径规划约束条件
文件:dijkstra.cpp
函数
inline void DijkstraExpansion::updateCell(
unsigned char*costs,
float* potential,
int n)
修改为:
inline void DijkstraExpansion::updateCell(unsigned char* costs, float* potential, int n)
{
cells_visited_++;
// do planar wave update
float c = getCost(costs, n);
if (c >= lethal_cost_) // don't propagate into obstacles
return;
float c_near[8] = {0};
int np = n - nx_;
int nn = n + nx_;
c_near[0] = getCost(costs, np-1);
c_near[1] = getCost(costs, np);
c_near[2] = getCost(costs, np+1);
c_near[3] = getCost(costs, n-1);
c_near[4] = getCost(costs, n+1);
c_near[5] = getCost(costs, nn-1);
c_near[6] = getCost(costs, nn);
c_near[7] = getCost(costs, nn+1);
for(unsigned int i=0;i<8;i++)
{
if(c_near[i] > 50)
{
return;
}
}
float pot = p_calc_->calculatePotential(potential, c, n);
// now add affected neighbors to priority blocks
if (pot < potential[n])
{
float le = INVSQRT2 * (float)getCost(costs, n - 1);
float re = INVSQRT2 * (float)getCost(costs, n + 1);
float ue = INVSQRT2 * (float)getCost(costs, n - nx_);
float de = INVSQRT2 * (float)getCost(costs, n + nx_);
potential[n] = pot;
//ROS_INFO("UPDATE %d %d %d %f", n, n%nx, n/nx, potential[n]);
if (pot < threshold_) // low-cost buffer block
{
if (potential[n - 1] > pot + le)
push_next(n-1);
if (potential[n + 1] > pot + re)
push_next(n+1);
if (potential[n - nx_] > pot + ue)
push_next(n-nx_);
if (potential[n + nx_] > pot + de)
push_next(n+nx_);
}
else // overflow block
{
if (potential[n - 1] > pot + le)
push_over(n-1);
if (potential[n + 1] > pot + re)
push_over(n+1);
if (potential[n - nx_] > pot + ue)
push_over(n-nx_);
if (potential[n + nx_] > pot + de)
push_over(n+nx_);
}
}
}
第二步:增加路径点的密度
文件:planner_core.cpp
函数:
bool GlobalPlanner::getPlanFromPotential(double start_x, double start_y,
double goal_x, double goal_y,
const geometry_msgs::PoseStamped& goal,
std::vector<geometry_msgs::PoseStamped>& plan)
修改为:
bool GlobalPlanner::getPlanFromPotential(double start_x, double start_y,
double goal_x, double goal_y,
const geometry_msgs::PoseStamped& goal,
std::vector<geometry_msgs::PoseStamped>& plan)
{
if (!initialized_)
{
ROS_ERROR("This planner has not been initialized yet, but it is being used, please call initialize() before use");
return false;
}
std::string global_frame = frame_id_;
//clear the plan, just in case
plan.clear();
std::vector<std::pair<float, float> > path;
if (!path_maker_->getPath(potential_array_, start_x, start_y, goal_x, goal_y, path))
{
ROS_ERROR("NO PATH!");
return false;
}
ros::Time plan_time = ros::Time::now();
int path_size_num = path.size() -1;
for (int i = path_size_num; i>=0; i--)
{
std::pair<float, float> point = path[i];
//convert the plan to world coordinates
double world_x, world_y;
mapToWorld(point.first, point.second, world_x, world_y);
geometry_msgs::PoseStamped pose;
pose.header.stamp = plan_time;
pose.header.frame_id = global_frame;
pose.pose.position.x = world_x;
pose.pose.position.y = world_y;
pose.pose.position.z = 0.0;
pose.pose.orientation.x = 0.0;
pose.pose.orientation.y = 0.0;
pose.pose.orientation.z = 0.0;
pose.pose.orientation.w = 1.0;
if(i != path_size_num)
{
double cx,cy,px,py;
cx = pose.pose.position.x;
cy = pose.pose.position.y;
px = plan.back().pose.position.x;
py = plan.back().pose.position.y;
if( sqrt( (cx-px)*(cx-px) + (cy-py)*(cy-py) ) > 0.05)
{
geometry_msgs::PoseStamped pose_insert = pose;
pose_insert.pose.position.x = (cx+px)/2;
pose_insert.pose.position.y = (cy+py)/2;
plan.push_back(pose_insert);
}
}
plan.push_back(pose);
}
if(old_navfn_behavior_)
{
plan.push_back(goal);
}
return !plan.empty();
}
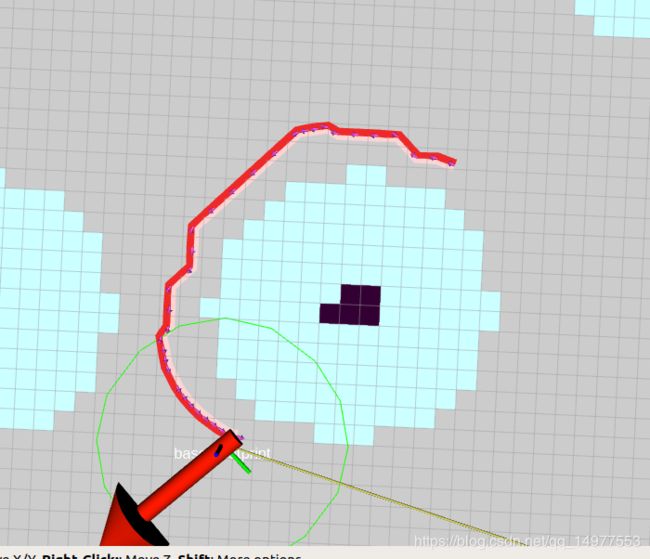
优化后:
第三步:路径平滑
修改文件:planner_core.cpp
添加路径平滑函数和角度标准化函数:
平滑函数声明:
int optimizationPath(
std::vector<geometry_msgs::PoseStamped>& plan,
double movement_angle_range=M_PI_4);
标准化函数为:
double inline normalizeAngle(
double val,
double min = -M_PI,
double max = M_PI)
{
float norm = 0.0;
if (val >= min)
norm = min + fmod((val - min), (max-min));
else
norm = max - fmod((min - val), (max-min));
return norm;
}
平滑函数定义:
int GlobalPlanner::optimizationPath(
std::vector<geometry_msgs::PoseStamped>& plan,
double movement_angle_range)
{
if(plan.empty())
return 0;
size_t pose_size = plan.size() - 1;
double px,py,cx,cy,nx,ny,a_p,a_n;
bool is_run = false;
int ci = 0;
for(ci=0;ci<1000;ci++)
{
is_run = false;
for(size_t i=1;i<pose_size;i++)
{
px = plan[i-1].pose.position.x;
py = plan[i-1].pose.position.y;
cx = plan[i].pose.position.x;
cy = plan[i].pose.position.y;
nx = plan[i+1].pose.position.x;
ny = plan[i+1].pose.position.y;
a_p = normalizeAngle(atan2(cy-py,cx-px),0,2*M_PI);
a_n = normalizeAngle(atan2(ny-cy,nx-cx),0,2*M_PI);
if(std::max(a_p,a_n)-std::min(a_p,a_n) > movement_angle_range)
{
plan[i].pose.position.x = (px + nx)/2;
plan[i].pose.position.y = (py + ny)/2;
is_run = true;
}
}
if(!is_run)
return ci;
}
return ci;
}
在planner_core.cpp的
bool GlobalPlanner::makePlan(const geometry_msgs::PoseStamped& start,
const geometry_msgs::PoseStamped& goal,
double tolerance,
std::vector<geometry_msgs::PoseStamped>& plan)
中调用路径平滑函数,调用位置为:
if (found_legal)
{
//extract the plan
//从可行点矩阵提取路径
if (getPlanFromPotential(start_x, start_y, goal_x, goal_y, goal, plan))
{
//make sure the goal we push on has the same timestamp as the rest of the plan
geometry_msgs::PoseStamped goal_copy = goal;
goal_copy.header.stamp = ros::Time::now();
plan.push_back(goal_copy);
this->optimizationPath(plan,M_PI/10); //此处调用路径平滑函数
}
else
{
ROS_ERROR("Failed to get a plan from potential when a legal potential was found. This shouldn't happen.");
}
}
else
{
ROS_ERROR("Failed to get a plan.");
}
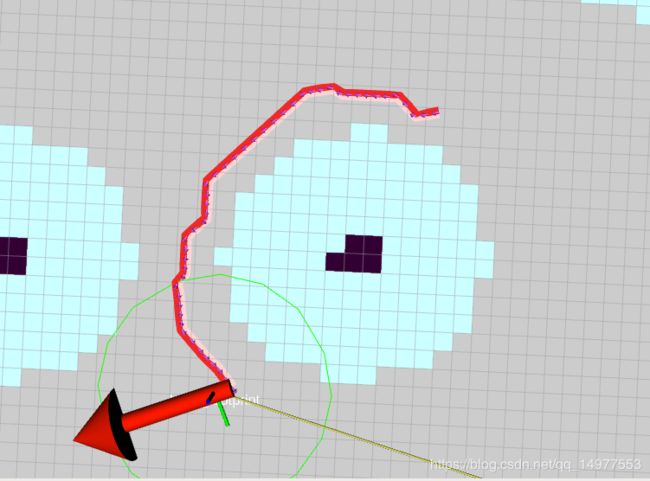
最终效果:
总结:
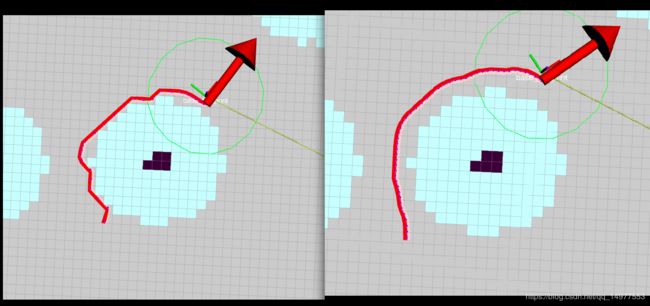
效果对比图:
请根据具体场景灵活使用该方法。。