剑指Offer刷题小结--一(1~6)
目录
- 第一题:二维数组中的查找
- 第二题:替换空格
- 第三题:从尾到头打印链表
- 第四题:重建二叉树
- 第五题:用两个栈实现队列
- 第六题:旋转数组的最小数字
第一题:二维数组的查找
题目链接
解析
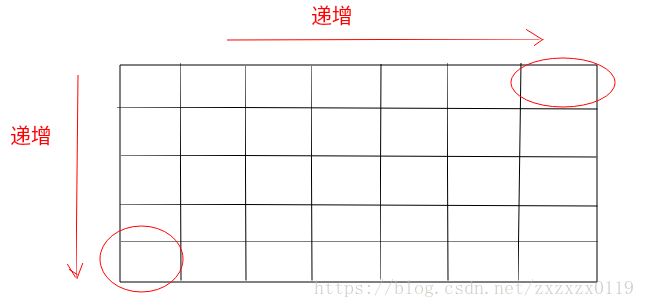
- 这个题目比较好的解题思路是从右上角或者左下角开始找;这个是 题目给定的每一行从左到右递增和每一列从上到下递增的原因;
- 例如,从右上角开始找,设置两个变量
row,col分别代表列和行, 如果要找的数就是target,则直接返回; - 如果
arr[row][col] < target,那row = row + 1,因为它左边的都会arr[row][col]小,这是因为列增加的性质; - 如果
arr[row][col] > target,那col = col - 1,因为它下面的都会arr[row][col]大,这是因为行增加的性质;
public class Solution {
public boolean Find(int target, int [][] array) {
int row = 0,col = array[0].length-1;
while(row < array.length && col >= 0){
if(array[row][col] == target){
return true;
}else if(array[row][col] > target){
col--;
}else {
row++;
}
}
return false;
}
}
public class Solution {
public boolean Find(int target, int [][] array) {
int row = array.length - 1,col = 0;
while(row >= 0 && col < array[0].length){
if(array[row][col] == target){
return true;
}else if(array[row][col] > target){
row--;
}else {
col++;
}
}
return false;
}
}
第二题:替换空格
题目链接
解析:
解析:
- 这个题目如果只是简单的插入的话,插入之后导致后面的元素的移动导致 需要O(n2)的复杂度;
- 这个的解决方法使用两个指针,可以达到
O(n)复杂度; - 首先计算出空格的个数,这样求的新的字符串的长度;
- 然后使用两个指针,新的指针
second指向新的字符串的末尾,老指针first指向原来字符串的末尾,每次检查字符串的末尾如果是空格的话,就添加%20进去,否则把原来的字符串复制到后面;
public class Solution {
public String replaceSpace(StringBuffer str) {
int spaceNum = 0; //计算空格数量
for(int i = 0; i < str.length(); i++)
if(str.charAt(i) == ' ')
spaceNum++;
int first = str.length() - 1; //第一个指针
int second = str.length() + 2*spaceNum - 1; //第二个指针的位置
str.setLength(second + 1); //新的长度 = oldLen + 2 * spaceNum
while(first >= 0){
if(str.charAt(first) == ' '){
str.setCharAt(second--,'0');
str.setCharAt(second--,'2');
str.setCharAt(second--,'%');
}else {
str.setCharAt(second--,str.charAt(first));
}
first--;
}
return str.toString();
}
}
第三题:从尾到头打印链表
题目链接
解析:
这个题目比较简单,可以用栈倒序,也可以递归,代码如下:
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.Stack;
public class Solution {
public ArrayList<Integer> printListFromTailToHead(ListNode listNode) {
Stack<Integer>stack = new Stack<>();
ListNode cur = listNode;
while(cur != null){
stack.push(cur.val);
cur = cur.next;
}
ArrayList<Integer>res = new ArrayList<>();
while(!stack.isEmpty()){
res.add(stack.pop());
}
return res;
}
}
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.Stack;
public class Solution {
//方法二
public ArrayList<Integer> printListFromTailToHead(ListNode listNode) {
ArrayList<Integer>res = new ArrayList<>();
process(listNode,res);
return res;
}
public void process(ListNode node,ArrayList<Integer>res){
if(node == null)
return;
process(node.next,res);//先把next的存好
res.add(node.val);//再存自己的
}
}
第四题:重建二叉树
题目链接
解析:
-
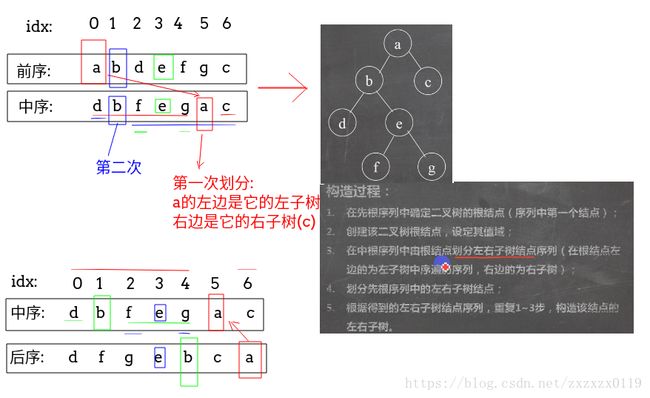
对于二叉树的建树问题,都是先建立根节点,然后 建立左子树,右子树,根据前序遍历和中序遍历,中序遍历和后续遍历都可以建立一颗二叉树,但是根据前序遍历和后续遍历不可以确定一颗二叉树,前序和后续在本质上都只是将子节点和父节点分离,没有指明左右子树的能力。
-
根据前序和中序建树时,前序遍历的第一个结点就是根,在中序遍历中找到根所在的位置,计算左边的长度,即为左子树的长度,然后计算出右子树的长度 = 总长度-左子树长度-1,然后递归建立左子树和右子树即可,代码如下(顺便贴上根据中序和后续遍历建树的代码):
//根据前序和中序
public TreeNode reConstructBinaryTree(int[] pre, int[] in) {
return process(pre, 0, pre.length - 1, in, 0, in.length - 1);
}
public TreeNode process(int[] pre, int pL, int pR, int[] in, int iL, int iR) {
if (pL > pR || iL > iR) return null; //已经访问到null
TreeNode root = new TreeNode(pre[pL]);
int lLen = 0; //左子树 数组长度
for (int i = iL; i <= iR && in[i] != pre[pL]; i++, lLen++) ;
root.left = process(pre, pL + 1, pL + lLen, in, iL, iL + lLen - 1);
root.right = process(pre, pL + lLen + 1, pR, in, iL + lLen + 1, iR); //记得是从终点是preright,和inright
return root;
}
//根据中序和后序
public TreeNode reConstructBinaryTreeByInPost(int[] in, int[] post) {
return pro(in, 0, in.length - 1, post, 0, post.length - 1);
}
public TreeNode pro(int[] in, int iL, int iR, int[] post, int poL, int poR) {
if (iL > iR || poL > poR) return null;
TreeNode root = new TreeNode(post[poR]);
int lLen = 0; //左子树长度
for (int i = iL; i <= iR && in[i] != post[poR]; i++, lLen++) ;
root.left = pro(in, iL, iL + lLen - 1, post, poL, poL + lLen - 1);
root.right = pro(in, iL + lLen + 1, iR, post, poL + lLen, poR - 1);
return root;
}
第五题:两个栈实现一个队列
题目链接
解析:
这个题目也比较简单,用两个栈直接模拟即可,两种思路,代码如下:
-
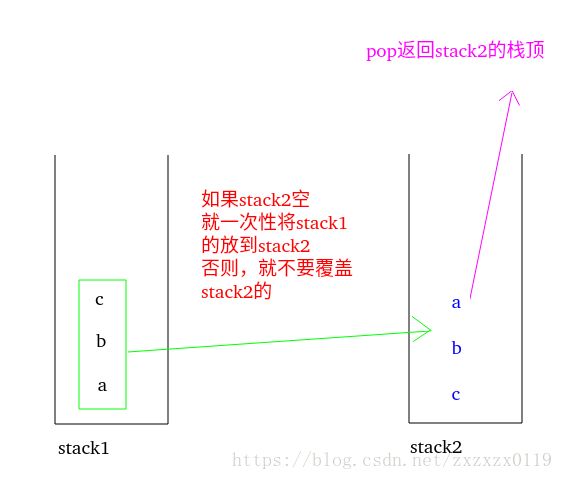
思路一:
push的时候直接放到stack1;为了pop的操作,当stack2空(必须当stack2为空)的时候,一次性(必须一次性)要将stack1的全部push到stack2中,然后出队列的时候,取的就是stack2的栈顶;
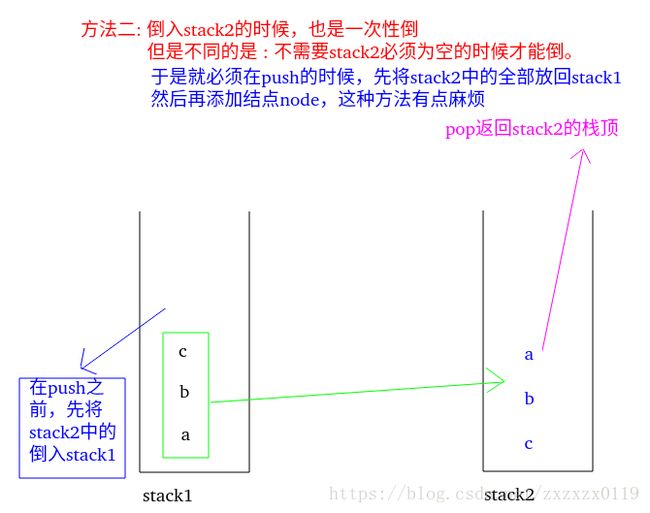
-
思路二: 思路一有一个条件就是必须当
stack2为空的时候才能一次性将所有的stack1中的元素全部倒入stack2,而思路二不需要这样,但是为了满足这样,在push的时候,必须先将stack2中的所有元素先倒回stack1,然后再push;
思路一代码:
import java.util.Stack;
public class Solution {
Stack<Integer> stack1 = new Stack<Integer>();
Stack<Integer> stack2 = new Stack<Integer>();
public void push(int node) {
stack1.push(node);
}
public int pop() {
if(stack1.isEmpty() && stack2.isEmpty())
throw new RuntimeException("Queue is empty!");
if(stack2.isEmpty()){//如果stack2不空的话,就先不要将stack1的内容放进去
while(!stack1.isEmpty())
stack2.push(stack1.pop());
}
return stack2.pop();
}
}
思路二代码:
import java.util.Stack;
public class Solution {
Stack<Integer> stack1 = new Stack<Integer>();
Stack<Integer> stack2 = new Stack<Integer>();
public void push(int node) {
while(!stack2.isEmpty())
stack1.push(stack2.pop());
stack1.push(node);
}
public int pop() {
if(stack1.isEmpty() && stack2.isEmpty())
throw new RuntimeException("Queue is Empty!");
while(!stack1.isEmpty())
stack2.push(stack1.pop());
return stack2.pop();
}
}
第六题:旋转数组的最小数字
题目链接
解析
首先:
- 旋转之后的数组实际上可以划分成两个有序的子数组;
- 前面子数组的大小都大于后面子数组中的元素;
如果先解决没有重复元素的问题,这个问题会简单一些(这个题目可以有重复的元素)。
思路:
- 我们用两个指针
L,R分别指向每次判断的数组左右边界。按照题目的旋转的规则,左边界应该是大于右边界的(没有重复的元素)。 - 然后找到数组的中间元素
arr[mid],arr[mid] > arr[L],则中间元素位于前面的递增子数组,此时最小元素位于中间元素的后面。我们可以让第一个指针L指向中间元素;(移动之后,第一个指针仍然位于前面的递增数组中); arr[mid] < arr[L],中间元素小于第一个元素,则中间元素位于后面的递增子数组,此时最小元素位于中间元素的前面。我们可以让第二个指针L指向中间元素;(移动之后,第二个指针仍然位于后面的递增数组中);- 按照以上思路,第一个指针
L总是指向前面递增数组的元素,第二个指针R总是指向后面递增的数组元素; - 最终第一个指针
L将指向前面数组的最后一个元素,第二个指针R指向后面数组中的第一个元素; - 也就是说他们将指向两个相邻的元素,而第二个指针指向的刚好是最小的元素,这就是循环的结束条件;
以上思路解决了没有重复数字的情况,这一道题目添加上了这一要求,有了重复数字。
因此这一道题目比上一道题目多了些特殊情况:
我们看一组例子:{1,0,1,1,1}和 {1,1, 1,0,1}都可以看成是递增排序数组{0,1,1,1,1}的旋转。
这种情况下我们无法继续用上一道题目的解法,去解决这道题目。因为在这两个数组中,第一个数字,最后一个数字,中间数字都是1。
第一种情况下,中间数字位于后面的子数组,第二种情况,中间数字位于前面的子数组。
因此当两个指针指向的数字和中间数字相同的时候,我们无法确定中间数字1是属于前面的子数组(绿色表示)还是属于后面的子数组(紫色表示)。
public class Solution {
public int minNumberInRotateArray(int[] array) {
if (array.length == 0)
return 0;
for (int i = 1; i < array.length; i++) {
if (array[i] < array[i - 1])
return array[i];
}
return array[0];
}
}
public class Solution {
public int minNumberInRotateArray(int[] array) {
if(array.length == 0)
return 0;
int l = 0,r = array.length - 1;
while(array[l] >= array[r]) { // 确保是旋转的
if(r - l == 1)//递归条件 l 是前一个递增序列的最后一个元素,r是后一个递增序列的第一个元素
return array[r];
int mid = l + (r-l)/2;
if(array[l] == array[mid] && array[mid] == array[r]) { //无法确定中间元素是属于前面还是后面的递增子数组
for(int i = l+1; i <= r; i++)
if(array[i] < array[i-1])
return array[i];
}
//中间元素位于前面的递增子数组 ---> 此时最小元素位于中间元素的后面
if(array[mid] >= array[l]) //注意我们这里认为 = 也算是上升的吧
l = mid; // not mid - 1
else // 中间元素位于后面的递增子数组 ---> 此时最小元素位于中间元素的前面
r = mid; // not mid + 1
}
return array[l]; // array[r] > array[l], directly return the array[l]
}
}