vue源码(八) new Vue时发生的那些事
一段时间的总结
今天就从new一个Vue实例开始,把一些过程捋一遍
调试
首先github上下载2.6.9版本的源码
接下来就是怎么开启调试了:按照以下步骤来
npm i 安装依赖(用cnpm yarn都可)
// 因为vue是通过rullup进行打包
npm install rullup -g 全局安装rullup打包工具
// package.json 中修改scripts中的dev 加上--sourcemap
"dev": "rollup -w -c scripts/config.js --environment TARGET:web-full-dev --sourcemap"
npm run dev 运行
// 此时dist/vue.js就是打包好的文件了
在examples文件夹中创建一个test.html,代码如下:
var app = new Vue({}).$mount('#app')
调试过程:
chrome浏览器中打开test.html–> 开发者工具 --> source–> 点开vue-2.6.9文件夹–> 可以看到src文件夹(源码就在这了)–> 接下来就可以随意打断点调试了
分析开始
当学会了如何调试之后,可以试着对Vue的初始化进行调试,可以发现很多好玩的东西!
我在这就直接分享调试过程中的发现吧!
当未开始执行new Vue时
对这仅仅一行代码进行调试,可以知道,在进行new Vue之前,已经有东西开始执行了:
给Vue.prototype添加方法
路径:src\core\instance\index.js
initMixin
给Vue.prototype添加了_init方法,当new Vue时会触发
stateMixin
给Vue.prototype添加了$set,$delete,$watch方法。还定义了只读$data,$props的属性
eventsMixin
给Vue.prototype添加了$on,$once,$off,$emit方法
lifecycleMixin
给Vue.prototype添加了_update,$forceUpdate,$destroy方法
renderMixin
给Vue.prototype添加了$nextTick,_render,_o,_n,_s,_l,_t,_q,_i,_m,_f,_k,_b,_v,_e,_u,_g,_d,_p(来自installRenderHelpers(Vue.prototype))方法
此时的Vue.prototype
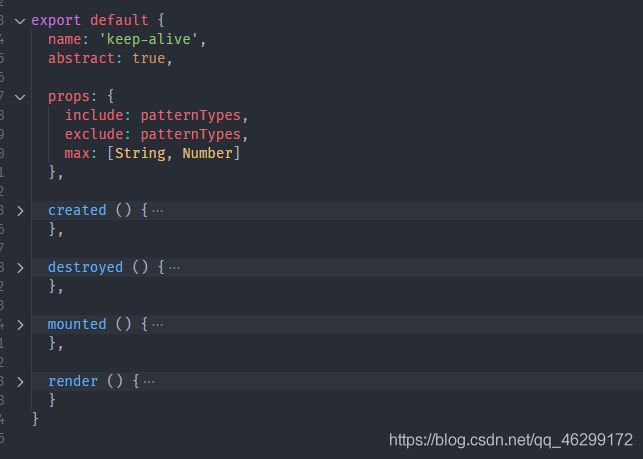
暴露的Keep-alive组件
在src/core/components/keep-alive.js中,导出了keep-alive组件,可以看到keep-alive也只是Vue事先封装的一个组件,只是暴露出来了而已,之后在过程中进行了全局注册,就成为了内置组件。
initGloabAPI
路径:src\core\index.js
调用initGloabAPI给Vue添加静态属性和方法
Vue.config
通过Object.defineProperty给Vue添加config属性,如果修改,发出警告
// config
const configDef = {}
configDef.get = () => config
if (process.env.NODE_ENV !== 'production') {
configDef.set = () => {
warn(
'Do not replace the Vue.config object, set individual fields instead.'
)
}
}
Object.defineProperty(Vue, 'config', configDef)
Vue.util静态属性
util工具类包括warn,extend,mergeOptions,defineReactive
Vue.util = {
warn,
extend,
mergeOptions,
defineReactive
}
Vue.set静态方法
也就是set方法,给之前不存在的这个属性的对象添加属性并且给这个属性添加依赖收集,让其也响应化
Vue.set = set
Vue.delete静态方法
也就是del方法,删除属性并在必要时触发更改。
Vue.delete = del
Vue.netxTick静态方法
也就是nextTick方法,用于更新视图后回调递归(异步)
Vue.nextTick = nextTick
Vue.observable静态方法(2.6版本起)
2.6版本新暴露的方法,也就是observe方法,observe作用就是为了拿到Observe实例并返回,从缓存中或者new一个。
Vue.observable = <T>(obj: T): T => {
observe(obj)
return obj
}
Vue.options静态属性
并且在该对象中添加ASSET_TYPES:components,directives,filters静态对象 记录静态组件,还添加了_base属性:这用于标识扩展所有纯对象的base构造函数包含Weex多实例场景的组件。
Vue.options = Object.create(null)
ASSET_TYPES.forEach(type => {
Vue.options[type + 's'] = Object.create(null)
})
src\shared\constants.js
export const ASSET_TYPES = [
'component',
'directive',
'filter'
]
initUse 添加Vue.use静态方法
也就是添加了Vue.use静态方法,安装插件
export function initUse (Vue: GlobalAPI) {
Vue.use = function (plugin: Function | Object) {
const installedPlugins = (this._installedPlugins || (this._installedPlugins = []))
if (installedPlugins.indexOf(plugin) > -1) {
return this
}
// additional parameters
const args = toArray(arguments, 1)
args.unshift(this)
if (typeof plugin.install === 'function') {
plugin.install.apply(plugin, args)
} else if (typeof plugin === 'function') {
plugin.apply(null, args)
}
installedPlugins.push(plugin)
return this
}
}
initMixin 添加Vue.mixin静态方法
也就是添加了Vue.mixin静态方法,合并参数
export function initMixin (Vue: GlobalAPI) {
Vue.mixin = function (mixin: Object) {
this.options = mergeOptions(this.options, mixin)
return this
}
}
initExtend 添加Vue.extend静态方法
也就是添加了Vue.extend静态方法,使用Vue构造函数创建一个子类
export function initExtend (Vue: GlobalAPI) {
/**
* Each instance constructor, including Vue, has a unique
* cid. This enables us to create wrapped "child
* constructors" for prototypal inheritance and cache them.
*/
Vue.cid = 0
let cid = 1
/**
* Class inheritance
*/
Vue.extend = function (extendOptions: Object): Function {
extendOptions = extendOptions || {}
const Super = this
const SuperId = Super.cid
const cachedCtors = extendOptions._Ctor || (extendOptions._Ctor = {})
if (cachedCtors[SuperId]) {
return cachedCtors[SuperId]
}
const name = extendOptions.name || Super.options.name
if (process.env.NODE_ENV !== 'production' && name) {
validateComponentName(name)
}
const Sub = function VueComponent (options) {
this._init(options)
}
Sub.prototype = Object.create(Super.prototype)
Sub.prototype.constructor = Sub
Sub.cid = cid++
Sub.options = mergeOptions(
Super.options,
extendOptions
)
Sub['super'] = Super
// For props and computed properties, we define the proxy getters on
// the Vue instances at extension time, on the extended prototype. This
// avoids Object.defineProperty calls for each instance created.
if (Sub.options.props) {
initProps(Sub)
}
if (Sub.options.computed) {
initComputed(Sub)
}
// allow further extension/mixin/plugin usage
Sub.extend = Super.extend
Sub.mixin = Super.mixin
Sub.use = Super.use
// create asset registers, so extended classes
// can have their private assets too.
ASSET_TYPES.forEach(function (type) {
Sub[type] = Super[type]
})
// enable recursive self-lookup
if (name) {
Sub.options.components[name] = Sub
}
// keep a reference to the super options at extension time.
// later at instantiation we can check if Super's options have
// been updated.
Sub.superOptions = Super.options
Sub.extendOptions = extendOptions
Sub.sealedOptions = extend({}, Sub.options)
// cache constructor
cachedCtors[SuperId] = Sub
return Sub
}
}
initAssetRegisters
也就是为Vue添加了ASSET_TYPES:component,directive,filter静态方法,定义组件,指令,过滤器
export function initAssetRegisters (Vue: GlobalAPI) {
/**
* Create asset registration methods.
*/
ASSET_TYPES.forEach(type => {
Vue[type] = function (
id: string,
definition: Function | Object
): Function | Object | void {
if (!definition) {
return this.options[type + 's'][id]
} else {
/* istanbul ignore if */
if (process.env.NODE_ENV !== 'production' && type === 'component') {
validateComponentName(id)
}
if (type === 'component' && isPlainObject(definition)) {
definition.name = definition.name || id
definition = this.options._base.extend(definition)
}
if (type === 'directive' && typeof definition === 'function') {
definition = { bind: definition, update: definition }
}
this.options[type + 's'][id] = definition
return definition
}
}
})
}
接着执行三个Object.defineProperty函数
Vue.prototype.$isServer
通过Object.defineProperty给Vue.prototype添加$isServer属性
Object.defineProperty(Vue.prototype, '$isServer', {
get: isServerRendering
})
Vue.prototype.$ssrContext
通过Object.defineProperty给Vue.prototype添加$ssrContext属性
Object.defineProperty(Vue.prototype, '$ssrContext', {
get () {
/* istanbul ignore next */
return this.$vnode && this.$vnode.ssrContext
}
})
Vue.FunctionalRenderContext静态方法
通过Object.defineProperty给Vue添加FunctionalRenderContext静态方法
// expose FunctionalRenderContext for ssr runtime helper installation
// 暴露 FunctionalRenderContext 给 ssr runtime安装助手
Object.defineProperty(Vue, 'FunctionalRenderContext', {
value: FunctionalRenderContext
})
给Vue.prototype添加方法
src\platforms\web\runtime\index.js
Vue.prototype.__patch__
给Vue.prototype添加__patch__方法
// install platform patch function
// 给添加patch 补丁 虚拟DOM转为真实DOM
Vue.prototype.__patch__ = inBrowser ? patch : noop
Vue.prototype.$mount
给Vue.prototype添加$mount方法
// public mount method
// 实现$mount 也就是entry-runtime-with-compiler赋给mount的那个函数
Vue.prototype.$mount = function (
el?: string | Element,
hydrating?: boolean
): Component {
// 只进行了一个操作
el = el && inBrowser ? query(el) : undefined
// 返回mountComponent这个函数 在上方引入了,可以去看 todo:
// 在initLiftCycle中导出
return mountComponent(this, el, hydrating)
}
中途会去调用createCompilerCreator
src\compiler\index.js
返回一个createCompiler函数
export function createCompilerCreator (baseCompile: Function): Function {
return function createCompiler (baseOptions: CompilerOptions) {
function compile (
template: string,
options?: CompilerOptions
): CompiledResult {
const finalOptions = Object.create(baseOptions)
const errors = []
const tips = []
let warn = (msg, range, tip) => {
(tip ? tips : errors).push(msg)
}
if (options) {
if (process.env.NODE_ENV !== 'production' && options.outputSourceRange) {
// $flow-disable-line
const leadingSpaceLength = template.match(/^\s*/)[0].length
warn = (msg, range, tip) => {
const data: WarningMessage = { msg }
if (range) {
if (range.start != null) {
data.start = range.start + leadingSpaceLength
}
if (range.end != null) {
data.end = range.end + leadingSpaceLength
}
}
(tip ? tips : errors).push(data)
}
}
// merge custom modules
if (options.modules) {
finalOptions.modules =
(baseOptions.modules || []).concat(options.modules)
}
// merge custom directives
if (options.directives) {
finalOptions.directives = extend(
Object.create(baseOptions.directives || null),
options.directives
)
}
// copy other options
for (const key in options) {
if (key !== 'modules' && key !== 'directives') {
finalOptions[key] = options[key]
}
}
}
finalOptions.warn = warn
const compiled = baseCompile(template.trim(), finalOptions)
if (process.env.NODE_ENV !== 'production') {
detectErrors(compiled.ast, warn)
}
compiled.errors = errors
compiled.tips = tips
return compiled
}
return {
compile,
compileToFunctions: createCompileToFunctionFn(compile)
}
}
}
然后 { compile, compileToFunctions } = createCompiler(baseOptions)保留compile和compileToFunctions两个方法
给Vue添加静态方法
src\platforms\web\entry-runtime-with-compiler.js
Vue.complie静态方法
其实就是compileToFunctions,compileToFunctions函数把template和options传入,执行compile函数,执行basecompile,执行parse,optimize,generate
// :todo 涉及到编译器compile的解析过程了,之后再来
Vue.compile = compileToFunctions
当执行 new Vue时
src\core\instance\index.js
执行_init方法,传入options参数
// 好了,这里就是Vue的构造函数啦!
function Vue (options) {
if (process.env.NODE_ENV !== 'production' &&
!(this instanceof Vue)
) {
warn('Vue is a constructor and should be called with the `new` keyword')
}
// 当new Vue实例时,执行_init方法
this._init(options)
}
初始化_uid和_isVue属性
vm._uid = uid++
vm._isVue = true
合并options
_isComponent为真时,此为组件,并作为参数调用initInternalComponent,初始化组件的方法
_isComponent为假时,调用mergeOptions合并options参数,当使用了vue的静态方法拓展了一些组件或者参数时,调用resolveConstructorOptions合并vm.constructor构造函数的属性options
// merge options
if (options && options._isComponent) {
// optimize internal component instantiation
// since dynamic options merging is pretty slow, and none of the
// internal component options needs special treatment.
// 优化内部组件实例化
// 因为动态选项合并非常慢,而且
// 内部组件选项需要特殊处理。
initInternalComponent(vm, options)
} else {
vm.$options = mergeOptions(
resolveConstructorOptions(vm.constructor),
options || {},
vm
)
}
initProxy
initProxy 代理监听
initLifecycle
initLifecycle 初始化生命周期标志
并给vm构造对象添加了$parent,$root,$children ,$refs,_watcher,_inactive,_directInactive,_isMounted,_isBeingDestroyed等属性和标志
// 这里导出了initLifecycle 初始化生命周期相关的属性 以及为一些属性赋值
export function initLifecycle(vm: Component) {
// 获取选项
const options = vm.$options
// locate first non-abstract parent
// 定位第一个"非抽象"的父组件
// https://cn.vuejs.org/v2/api/#keep-alive 在这里可以看为什么要非抽象
// 是一个抽象组件:它自身不会渲染一个 DOM 元素,也不会出现在组件的父组件链中。
let parent = options.parent
// 定位第一个非抽象父组件
if (parent && !options.abstract) {
// 判断parent父亲节点是否存在,并且判断是否存在抽象节点
// 如果父实例parent是抽象组件,则继续找parent上的parent,直到找到非抽象组件为止
while (parent.$options.abstract && parent.$parent) {
// 如果有父亲抽象组件,则把父或爷爷节点给当前节点的父亲节点
parent = parent.$parent
}
// 子节点添加vm
// 把当前vm实例push到定位的第一个非抽象parent的$children属性上
parent.$children.push(vm)
}
// 初始化一些属性
// 这里的parent可以告诉我们,子组件创建时,父组件已经存在了
// 添加$parent
vm.$parent = parent
// 判断parent是否是root 如果是 则把parent.$root赋给$root
vm.$root = parent ? parent.$root : vm
// 当前实例的直接子组件。需要注意 $children 并不保证顺序,也不是响应式的。
vm.$children = []
// 获取节点的key 一个对象,持有已注册过 ref 的所有子组件。
vm.$refs = {}
// 内部属性,不希望被访问的
vm._watcher = null // 组件实例相应的 watcher 实例对象
vm._inactive = null // 表示keep-alive中组件状态,如被激活,该值为false,反之为true。
vm._directInactive = false // 也是表示keep-alive中组件状态的属性。
vm._isMounted = false // 当前实例是否完成挂载(对应生命周期图示中的mounted)。
vm._isDestroyed = false // 当前实例是否已经被销毁(对应生命周期图示中的destroyed)。
vm._isBeingDestroyed = false // 是否已经销毁的组件 如果为true 则不触发 beforeDestroy 钩子函数 和destroyed 钩子函数 当前实例是否正在被销毁,还没有销毁完成(介于生命周期图示中deforeDestroy和destroyed之间)。
}
initEvents
initEvents 初始化事件
如果vm.$options._parentListeners为真,updateComponentListeners 初始化组件事件 更新组件事件,updateListeners 为listeners增加事件 为oldListeners删除事件,然后判断if(isTrue(event.once))
if(isTrue(event.once))为真时:调用$once 只执行一次函数就解绑
if(isTrue(event.once))为假时:$on添加事件 把事件推进队列去vm._events[event]
// 初始化事件
export function initEvents (vm: Component) {
// 初始化_events事件队列
vm._events = Object.create(null)
// 初始化判断是否有生命周期钩子函数
vm._hasHookEvent = false
// init parent attached events 初始化父亲事件
const listeners = vm.$options._parentListeners // 旧的事件
// 如果有旧的事件
if (listeners) {
// 组件初始化事件监听器 更新组件事件
updateComponentListeners(vm, listeners)
}
}
initRender
initRender 初始化渲染
为vm实例化的对象添加_vnode,_staticTrees,renderContext,$slots,$scopedSlots等属性或者对象,更重要的是添加了_c(编译器默认渲染方法)和$createElement(自己写的render中的h)这两个渲染方法,并且把$attrs属性和$listeners事件属性通过defineReactive添加到观察者中,并且此数据是只读的,如果修改则发出警告!
// 初始化渲染 _c $createElement 和$attrs listeners的响应化
export function initRender (vm: Component) {
// 子树的根
vm._vnode = null // the root of the child tree
// v-once 上缓存的树
vm._staticTrees = null // v-once cached trees
// 选项
const options = vm.$options
// 虚拟DOM
const parentVnode = vm.$vnode = options._parentVnode // the placeholder node in parent tree
// 上下文
const renderContext = parentVnode && parentVnode.context
// 插槽信息 resolveSlots:todo
vm.$slots = resolveSlots(options._renderChildren, renderContext)
// 作用域插槽
vm.$scopedSlots = emptyObject
// bind the createElement fn to this instance
// so that we get proper render context inside it.
// args order: tag, data, children, normalizationType, alwaysNormalize
// internal version is used by render functions compiled from templates
// 将createElement fn绑定在这个实例上
// 这样我们就能得到合适的渲染上下文
// args order: tag, data, children, normalizationType, alwaysNormalize
// 内部版本由模板编译的呈现函数使用
// _c 就是creatElement :todo createElement
// 默认编译器 内部由模板编译的函数 _c
vm._c = (a, b, c, d) => createElement(vm, a, b, c, d, false)
// normalization is always applied for the public version, used in
// user-written render functions.
// 用户编写的渲染函数
// $createElement h函数 也就是在initRender中声明
// 自己写的render中的h
vm.$createElement = (a, b, c, d) => createElement(vm, a, b, c, d, true)
// $attrs & $listeners are exposed for easier HOC creation.
// $attrs和$listeners要被公开,以便更容易地进行临时创建
// they need to be reactive so that HOCs using them are always updated
// 他们是要被响应式的,以便使用它们的HOCs时总是能响应式更新
// 获取父节点
const parentData = parentVnode && parentVnode.data
/* istanbul ignore else */
// 忽略
if (process.env.NODE_ENV !== 'production') {
defineReactive(vm, '$attrs', parentData && parentData.attrs || emptyObject, () => {
!isUpdatingChildComponent && warn(`$attrs is readonly.`, vm)
}, true)
defineReactive(vm, '$listeners', options._parentListeners || emptyObject, () => {
!isUpdatingChildComponent && warn(`$listeners is readonly.`, vm)
}, true)
} else {
// 响应化:通过defineProperty的set去notify()通知subscribers有值被修改,并执行watchers的update函数
defineReactive(vm, '$attrs', parentData && parentData.attrs || emptyObject, null, true)
defineReactive(vm, '$listeners', options._parentListeners || emptyObject, null, true)
}
}
callHook(vm, ‘beforeCreate’)
触发beforeCreate生命周期钩子函数
callHook(vm, 'beforeCreate')
initInjections
initInjections 在初始化data/props之前resolve injections
内部调用resolveInject,resolveInject递归遍历父组件,把父组件的provide值抽出来(default也有),并return给iniInjections。
initInjections将返回的父组件的provide值通过defineReactive加入观察者中,如果有修改到provide父组件的值则发出警告(这里可以证明后代注入进来的组件也是响应式的)
// provide 和 inject 绑定并不是可响应的。这是刻意为之的。然而,如果你传入了一个可监听
// 解析inject 注入
// inject 选项应该是一个字符串数组或一个对象,该对象的 key 代表了本地绑定的名称,valu
export function initInjections (vm: Component) {
// 解析inject,结果为result
const result = resolveInject(vm.$options.inject, vm)
// 如果结果存在 对传入的数据做响应化处理
if (result) {
// 不可以添加到观察者模式
toggleObserving(false)
// 遍历
Object.keys(result).forEach(key => {
/* istanbul ignore else */
// 忽略
if (process.env.NODE_ENV !== 'production') {
defineReactive(vm, key, result[key], () => {
warn(
`Avoid mutating an injected value directly since the changes will be ` +
`overwritten whenever the provided component re-renders. ` +
`injection being mutated: "${key}"`,
vm
)
})
} else {
// 给每个加上响应式 这里可以证明后代注入进来的组件也是响应式的
defineReactive(vm, key, result[key])
}
})
// 可以添加到观察者模式
toggleObserving(true)
}
}
initState
initState 初始化组件各种状态,从props methods data computed watch按顺序初始化
// 初始化一些data props methods那些
export function initState (vm: Component) {
// 初始化watchers数组 观察者队列
vm._watchers = []
// 获取选项
const opts = vm.$options
// 初始化props
if (opts.props) initProps(vm, opts.props)
// 初始化methods
if (opts.methods) initMethods(vm, opts.methods)
// 初始化data
if (opts.data) {
// 如果存在,直接InitData
initData(vm)
} else {
// 如果不存在data,直接进行observe,true作为根的data observe:todo
observe(vm._data = {}, true /* asRootData */)
}
// 初始化computed
if (opts.computed) initComputed(vm, opts.computed)
// 初始化watch
if (opts.watch && opts.watch !== nativeWatch) {
initWatch(vm, opts.watch)
}
}
initProps
initProps 初始化props
遍历props的key,调用validateProp验证props属性是否规范,例如是否有类型或默认值,如果有默认值,将默认值添加到观察者中。
通过defineReactive将props的key都添加到观察者中。
之后再调用proxy(vm, `_props`, key)进行代理,将vm.props.key代理成vm.key
// 初始化props
function initProps (vm: Component, propsOptions: O
// 获取props数据
const propsData = vm.$options.propsData || {}
const props = vm._props = {}
// cache prop keys so that future props updates
// 缓存prop keys以便以后props更新可以使用数组迭
// instead of dynamic object key enumeration.
// 而不是动态 object.key枚举
const keys = vm.$options._propKeys = []
// 是否是根 如果不存在父节点 就是根
const isRoot = !vm.$parent
// root instance props should be converted
// 根实例的props需要被响应式
// 如果不是根
if (!isRoot) {
// 则不会添加监听观察者
toggleObserving(false)
}
// propsOptions是传入的options.props,也就是选项
// 遍历props属性的key
for (const key in propsOptions) {
// 将key放进数组,容易迭代
keys.push(key)
// 判断prop.type是否是Boolean或String,如果不
// 获取默认值,并给value添加value._ob_属性,添
const value = validateProp(key, propsOptions,
/* istanbul ignore else */
// 忽略
if (process.env.NODE_ENV !== 'production') {
// 驼峰转换 vOn v-on
const hyphenatedKey = hyphenate(key)
if (isReservedAttribute(hyphenatedKey) ||
config.isReservedAttr(hyphenatedKey)) {
warn(
`"${hyphenatedKey}" is a reserved attrib
vm
)
}
defineReactive(props, key, value, () => {
if (!isRoot && !isUpdatingChildComponent)
warn(
`Avoid mutating a prop directly since
`overwritten whenever the parent compo
`Instead, use a data or computed prope
`value. Prop being mutated: "${key}"`,
vm
)
}
})
} else {
// 通过defineProperty的set方法去notify()通知
defineReactive(props, key, value)
}
// static props are already proxied on the com
// during Vue.extend(). We only need to proxy
// instantiation here.
// 静态props已经在组件的原型上代理了
// 在Vue.extend()期间. 我们只需要代理
// 在这里实例化定义的key。
if (!(key in vm)) {
proxy(vm, `_props`, key)
}
}
// 可加入观察者模式
toggleObserving(true)
}
initMethods
initMethods 初始化methods
遍历methods的key
如果key不是函数,发出警告,赋值noop,一个空函数
如果key和props中的key同名,发出警告
如果key是以$或_开头,发出警告
给最外层一个相同key属性,使vm.methods.sum() 可以变成this.sum()
如果key是函数,进行bind绑定
// 初始化Methods 代理
function initMethods (vm: Component, methods: Object) {
// 获取props
const props = vm.$options.props
// 遍历methods的属性key
for (const key in methods) {
if (process.env.NODE_ENV !== 'production') {
// 如果不是函数
if (typeof methods[key] !== 'function') {
warn(
`Method "${key}" has type "${typeof methods[key]}" in the component definition.
`Did you reference the function correctly?`,
vm
)
}
//判断key是否是改对象实例化的
//如果属性中定义了key,则在methods中不能定义同样的key
if (props && hasOwn(props, key)) {
warn(
`Method "${key}" has already been defined as a prop.`,
vm
)
}
// $ 或_
if ((key in vm) && isReserved(key)) {
warn(
`Method "${key}" conflicts with an existing Vue instance method. ` +
`Avoid defining component methods that start with _ or $.`
)
}
}
// 把事件放在最外层对象中,如果是函数为空则给一个空函数,如果是有函数则执行改函数
// 给最外层一个相同key属性,data.methods.sum() 变成data.sum(),代理
// 如果methods.sum不是函数 给空函数noop
// 如果是函数,执行该函数
vm[key] = typeof methods[key] !== 'function' ? noop : bind(methods[key], vm)
}
}
initData
initData 初始化data
如果data是函数,调用getData,执行data()返回数据
如果data不是函数,就直接使用这个data
遍历data的key,如果与props或methods中的key同名,发出警告
如果key不是$或_开头的,调用proxy(vm, `_data`, key)进行代理,将vm.data.key代理成vm.key
最后把data数据添加到观察者中,对data调用observe方法
参数value必须是对象 ,如果不是对象,return
实例化 dep对象,获取dep对象 为 value添加__ob__ 属性,返回 new Observer 实例化的对象
// initData 初始化data 接收组件实例
// 做了两件事:1、代理,将data的所有key代理到vm实例上
// 2、observe(data, true /* asRootData */)
function initData (vm: Component) {
// 获取到选项中的data data可能是对象可能是函数 取决于根
let data = vm.$options.data
// 如果data是一个函数 执行getData,如果是对象就是根data
data = vm._data = typeof data === 'function'
? getData(data, vm)
: data || {}
// 如果不是纯对象 报错
if (!isPlainObject(data)) {
data = {}
process.env.NODE_ENV !== 'production' && warn(
'data functions should return an object:\n' +
'https://vuejs.org/v2/guide/components.html#data-Must-Be-a-Function',
vm
)
}
// proxy data on instance
// 获取data所有属性 准备进行代理
const keys = Object.keys(data)
// 获取props,因为props在data之前先初始化
const props = vm.$options.props
// 获取methods,因为methods在data之前先初始化
const methods = vm.$options.methods
// 所有属性的长度
let i = keys.length
//
while (i--) {
// 从最后开始
const key = keys[i]
if (process.env.NODE_ENV !== 'production') {
if (methods && hasOwn(methods, key)) {
warn(
`Method "${key}" has already been defined as a data property.`,
vm
)
}
}
if (props && hasOwn(props, key)) {
process.env.NODE_ENV !== 'production' && warn(
`The data property "${key}" is already declared as a prop. ` +
`Use prop default value instead.`,
vm
)
// 如果不是$和_开头,代理
} else if (!isReserved(key)) {
// 执行代理函数,将data的所有key全部挂到vm上,可以直接vm.获取
// data:{foo: 'foo'} vm.data.foo vm.foo
proxy(vm, `_data`, key)
}
}
// observe data
// 将data作为根data进行observe
observe(data, true /* asRootData */)
}
initComputed
initComputed 初始化computed
在vm中创建_computedWatchers:监听对象
遍历computed的key,进行了对get默认的判断
const getter = typeof computed[key] === 'function' ? computed[key] : computed[key].get
如果不是ssr渲染,把computed的key都添加到Watcher中
如果key不在vm中(如果在data或props有key同名,警告),调用defineComputed,其通过判断shouldCache是否是浏览器调用:
如果不是浏览器调用,createComputedGetter,createComputedGetter为_computedWatchers 收集观察者,为watcher添加dep
如果是浏览器调用,createGetterInvoker,返回computedGetter
// 初始化计算属性
function initComputed (vm: Component, computed: Object) {
// $flow-disable-line
// 创建新的监听空对象
const watchers = vm._computedWatchers = Object.create(null)
// computed properties are just getters during SSR
// computed属性只是SSR期间的getter
const isSSR = isServerRendering()
// 遍历computed的key属性
for (const key in computed) {
// 每个值
const userDef = computed[key]
// 如果是函数 就默认,不是就获取get computed的get默认写
const getter = typeof userDef === 'function' ? userDef : userDef.get
if (process.env.NODE_ENV !== 'production' && getter == null) {
warn(
`Getter is missing for computed property "${key}".`,
vm
)
}
// 如果不是ssr渲染
if (!isSSR) {
// create internal watcher for the computed property.
// 为计算属性创建wathcer。
watchers[key] = new Watcher(
vm,
getter || noop,
noop,
computedWatcherOptions
)
}
// component-defined computed properties are already defined on the
// component prototype. We only need to define computed properties defined
// at instantiation here.
// 组件定义的计算属性已在组件原型上定义
// 我们只需要定义已在这里定义实例化的计算属性
// 如果computed 属性key 不在虚拟dom中
if (!(key in vm)) {
// 定义computed 并将key加入到对象监听中
defineComputed(vm, key, userDef)
} else if (process.env.NODE_ENV !== 'production') {
if (key in vm.$data) {
// 如果key在data中,警告
warn(`The computed property "${key}" is already defined in data.`, vm)
} else if (vm.$options.props && key in vm.$options.props) {
// 如果key在props中,警告
warn(`The computed property "${key}" is already defined as a prop.`, vm)
}
}
}
}
initWatch
initWatch 初始化watch
循环遍历options中的watch调用createWatcher
createWatcher 转义handler并且为数据创建Watcher观察者
调用Vue.prototype.$watch实例化Watcher
如果是对象,进行递归creteWatcher创建观察者,直到不是对象,跳出递归
如果不是对象了(递归结束后),添加到Watcher
// 初始化watch
function initWatch (vm: Component, watch: Object) {
// 循环遍历watch属性key
for (const key in watch) {
// 获取值
const handler = watch[key]
// 如果值是数组
if (Array.isArray(handler)) {
// 循环这个数组 创建监听
for (let i = 0; i < handler.length; i++) {
createWatcher(vm, key, handler[i])
}
} else {
// 不是数组,就直接创建监听
createWatcher(vm, key, handler)
}
}
}
initProvide
initProvide 在初始化data/props之后resolve provide
如果vm.$options.provide是函数,返回函数执行结果
如果vm.$options.provide不是函数,原样返回
// 解析provide
// provide 选项应该是一个对象或返回一个对象的函数。该对象包含可注入其子孙的属性,用于组件通信。
export function initProvide (vm: Component) {
// 获取provide
const provide = vm.$options.provide
// 如果存在
if (provide) {
// 如果是函数,立马执行,不是就还是provide
vm._provided = typeof provide === 'function'
? provide.call(vm)
: provide
}
}
callHook(vm, ‘created’)
触发create生命周期钩子函数
callHook(vm, 'created')
如果vm.$options.el存在,执行$mount
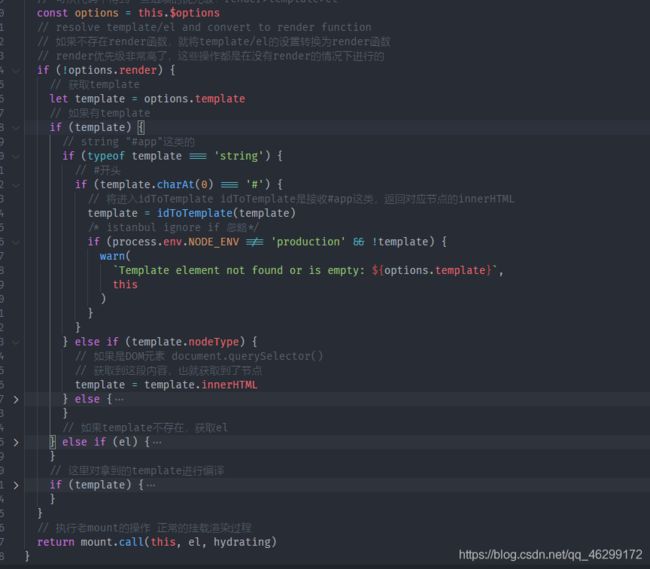
如果render函数存在,return mount.call(this, el, hydrating),直接执行老的mount函数

如果render函数不存在并且template不存在,调用template = getOuterHTML(el),获取包括标签的内容
例如
如果render函数不存在tmeplate存在且为字符串类型并且以"#"开头,调用template = idToTemplate(template),返回对应节点的innerHTML
例如"#app"
如果render函数不存在tmeplate存在且template.nodeType存在, template = template.innerHTML 获取到这段内容,也就获取到了节点
例如document.querySelector()
最后将之前得到的template进行compileToFunctions,进行一系列过程后,返回render函数,然后通过diff和patch最终生成真实dom。
// 这里对拿到的template进行编译
if (template) {
/* istanbul ignore if */
if (process.env.NODE_ENV !== 'production' && config.performance && mark) {
mark('compile')
}
// 如果是模板字符串,需要编译器去编译 也就是进入compileToFunctions这个函数
// 可以通过这个函数查看编译器的工作机制,也就是把template转换为render:todo
const { render, staticRenderFns } = compileToFunctions(template, {
outputSourceRange: process.env.NODE_ENV !== 'production',
shouldDecodeNewlines,
shouldDecodeNewlinesForHref,
delimiters: options.delimiters,
comments: options.comments
}, this)
// 赋值给当前选项的render
options.render = render
options.staticRenderFns = staticRenderFns
/* istanbul ignore if */
if (process.env.NODE_ENV !== 'production' && config.performance && mark) {
mark('compile end')
measure(`vue ${this._name} compile`, 'compile', 'compile end')
}
}
至此,一次执行完成!
总结
思维导图
我将这一条代码发生的流程总结成了脑图,执行顺序从脑图由上而下依次执行
图片可能太模糊,可以在我的github上拿,顺便给俺来个star吧!爱你们