webpack环境变量与vue-cli3设置环境变量
1、在业务代码中使用环境变量(DefinePlugin)
DefinePlugin的正确用法
DefinePlugin中的每个键,是一个标识符或者通过.作为多个标识符。
- 如果value是一个字符串,它将会被当做code片段
- 如果value不是字符串,它将会被stringify(包括函数)
- 如果value是一个对象,则所有key的定义方式相同。
- 如果key有typeof前缀,它只是对typeof 调用定义的。
这些值将内联到代码中,压缩减少冗余。
new webpack.DefinePlugin({
PRODUCTION: JSON.stringify(true),
VERSION: JSON.stringify('5fa3b9'),
BROWSER_SUPPORTS_HTML5: true,
TWO: '1+1',
'typeof window': JSON.stringify('object'),
'process.env': {
NODE_ENV: JSON.stringify(process.env.NODE_ENV)
}
});
2、process.env.NODE_ENV的正确配置方式是什么?
'process.env.NODE_ENV': JSON.stringify('production')
好。因为仅仅对NODE_ENV值进行修改,不会破坏完整进程,也不会破坏兼容性。
3、vue-cli3中使用DefinePlugin
const apiConfig = require('./config/api');
module.exports = {
chainWebpack: config => {
config
.plugin('define')
.tap(args => {
args[0].API_CONFIG = JSON.stringify(apiConfig)
return args
})
}
}
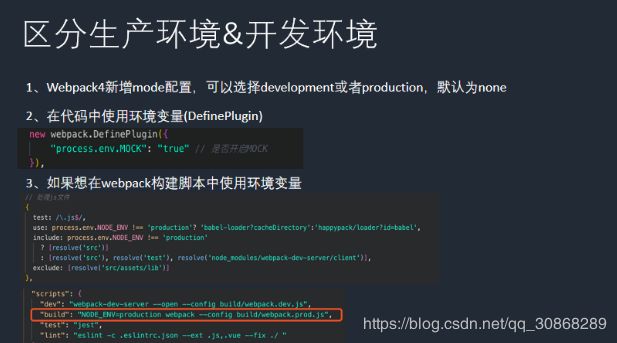
4、在webpack脚本中使用环境变量
当您使用NODE_ENV =production, 来设置环境变量时,大多数Windows命令提示将会阻塞(报错)。windows不支持NODE_ENV=development的设置方式。
cross-env能够提供一个设置环境变量的scripts,让你能够以unix方式设置环境变量,然后在windows上也能兼容运行
npm install --save-dev cross-env
{
"scripts": {
"build": "cross-env NODE_ENV=production webpack --config build/webpack.config.js"
}
}
5、vue-cli3环境变量与分环境打包的方法示例
我们可以根目录中的下列文件来指定环境变量:
.env # 在所有的环境中被载入
.env.local # 在所有的环境中被载入,但会被 git 忽略
.env.[mode] # 只在指定的模式中被载入
.env.[mode].local # 只在指定的模式中被载入,但会被 git 忽略
一个环境文件只包含环境变量的“键=值”对:
FOO=bar
VUE_APP_SECRET=secret
只有以 VUE_APP_ 开头的变量会被 webpack.DefinePlugin 静态嵌入到客户端侧的包中。你可以在应用的代码中这样访问它们:
console.log(process.env.VUE_APP_SECRET)
在构建过程中,process.env.VUE_APP_SECRET 将会被相应的值所取代。在 VUE_APP_SECRET=secret 的情况下,它会被替换为 “secret”。
除了 VUE_APP_* 变量之外,在你的应用代码中始终可用的还有两个特殊的变量:
NODE_ENV - 会是 “development”、“production” 或 “test” 中的一个。具体的值取决于应用运行的模式。
BASE_URL - 会和 vue.config.js 中的 publicPath 选项相符,即你的应用会部署到的基础路径。
详见环境变量和模式
6、关于progress
原始的process对象包含如下内容 ,包含了当前进程的很多信息。
process {
title: 'node',
version: 'v8.11.2',
moduleLoadList:
[ 'Binding contextify',],
versions:
{ http_parser: '2.8.0'},
arch: 'x64',
platform: 'darwin',
release:
{ name: 'node' },
argv: [ '/usr/local/bin/node' ],
execArgv: [],
env:
{ TERM: 'xterm-256color'},
pid: 14027,
features:
{ debug: false},
ppid: 14020,
execPath: '/usr/local/bin/node',
debugPort: 9229,
_startProfilerIdleNotifier: [Function: _startProfilerIdleNotifier],
_stopProfilerIdleNotifier: [Function: _stopProfilerIdleNotifier],
_getActiveRequests: [Function: _getActiveRequests],
_getActiveHandles: [Function: _getActiveHandles],
reallyExit: [Function: reallyExit],
abort: [Function: abort],
chdir: [Function: chdir],
cwd: [Function: cwd],
umask: [Function: umask],
getuid: [Function: getuid],
geteuid: [Function: geteuid],
setuid: [Function: setuid],
seteuid: [Function: seteuid],
setgid: [Function: setgid],
setegid: [Function: setegid],
getgid: [Function: getgid],
getegid: [Function: getegid],
getgroups: [Function: getgroups],
setgroups: [Function: setgroups],
initgroups: [Function: initgroups],
_kill: [Function: _kill],
_debugProcess: [Function: _debugProcess],
_debugPause: [Function: _debugPause],
_debugEnd: [Function: _debugEnd],
hrtime: [Function: hrtime],
cpuUsage: [Function: cpuUsage],
dlopen: [Function: dlopen],
uptime: [Function: uptime],
memoryUsage: [Function: memoryUsage],
binding: [Function: binding],
_linkedBinding: [Function: _linkedBinding],
_events:
{ newListener: [Function],
removeListener: [Function],
warning: [Function],
SIGWINCH: [ [Function], [Function] ] },
_rawDebug: [Function],
_eventsCount: 4,
domain: [Getter/Setter],
_maxListeners: undefined,
_fatalException: [Function],
_exiting: false,
assert: [Function],
config: {},
emitWarning: [Function],
nextTick: [Function: nextTick],
_tickCallback: [Function: _tickDomainCallback],
_tickDomainCallback: [Function: _tickDomainCallback],
stdout: [Getter],
stderr: [Getter],
stdin: [Getter],
openStdin: [Function],
exit: [Function],
kill: [Function],
_immediateCallback: [Function: processImmediate],
argv0: 'node' }
7、“NODE_ENV”总结
node中有全局变量process表示当前node进程,process.env包含着关于系统环境的信息。但是process.env中并不存在NODE_ENV这个东西。其实NODE_ENV只是一个用户自定义的变量,但是这个NODE_ENV变量语义非常恰当,并且在前端工程化配置中作为判断生产环境/开发环境的依据是非常自然而方便的事情,因而在前端工程化中逐渐成为一个事实规范。当我们在服务启动时配置NODE_ENV,或在代码中给process.env.NODE_ENV赋值,便能通过process.env.NODE_ENV获取信息。
参考链接
实用webpack插件之DefinePlugin