【机器学习】【逻辑回归】Python实现逻辑回归
1.逻辑回归python实现
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*-
"""
@author: 蔚蓝的天空Tom
"""
import numpy as np
import os
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from sklearn.datasets import make_blobs
#global variable
path = r'D:\tom\data'
train_set = 'train_lr.txt'
test_set = 'test_lr.txt'
#load data set from txt file
def load_data_set(path, file_name):
data_list = []
label_list = []
f = open(os.path.join(path, file_name))
for line in f.readlines():
#feature1 feature2 label
text = line.strip().split()
#data_m追加[feature0=1, feature1, feature2]
#样本的实际特征值有2个,附加一个恒值为1的特征值feature0,以便运算
#记作features_cnt = 1 + n_features
data_list.append([1.0, float(text[0]), float(text[1])])
#label_m追加label value
label_list.append(int(text[2]))
return data_list, label_list
#sigmoid function
def sigmoid(z):
return 1/(1+np.exp(-1*z))
def sigmoid_for_m(Z):
fin = 1
fout = 1
sigmoid_func = np.frompyfunc(sigmoid, fin, fout)
return sigmoid_func(Z)
def trainLogisticRegression(data_list, label_list):
#samples feature matrix, samples_cnt * features_cnt
#其中samples_cnt = n_samples
#其中features_cnt = 1 + n_features
data_m = np.mat(data_list).astype(np.float64)
#samples label matrix, samples_cnt * 1
#其中samples_cnt = n_samples
label_m = np.mat(label_list).T.astype(np.float64)
#get samples features shape
#其中m = samples_cnt = n_samples
#其中n = features_cnt = 1 + n_samples
m,n = np.shape(data_m)
#初始化权重系数w,features_cnt * 1
#其中features_cnt = 1 + n_features
w = np.ones((n,1))
#初始化学习效率learning rate, alpha
alpha = 0.001
#设置循环迭代计算的执行最大次数,loop_limit
loop_limit = 1000
#误差初始化
error = 10000
#开始迭代计算
for i in range(loop_limit):
predict = sigmoid_for_m(data_m * w)
error = predict - label_m
w = w - alpha * data_m.T * error
return w
#train the test set
def train_test_set(weights, data):
w = weights
return w[0]/w[2] - w[1]/w[2]*data
#显示拟合图形
def plot_fit_line(weights, data, label):
if type(weights).__name__ == 'ndarray':
w = weights
else:
w = weights.getA()
#test set
test_data_list,test_label_list = make_blobs(n_samples=200, n_features=2, centers=2)
#
plt.figure(1)
test_data_set = np.arange(-3, 3, 0.1)
lr_test_label = -1 * w[0]/w[2] - w[1]/w[2]*test_data_set
#lr_test_label = train_test_set(w, test_data_set)
plt.plot(test_data_set, lr_test_label)
negative = [] #否定的
positive = [] #肯定的
for i in range(len(label)):
if 1 == label[i]:
positive.append(data[i][1:3])
else:
negative.append(data[i][1:3])
positive = np.array(positive)
negative = np.array(negative)
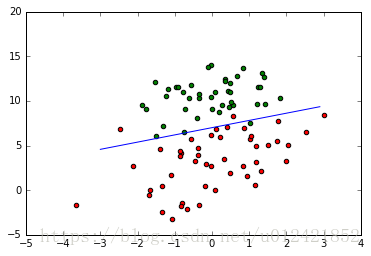
plt.scatter(positive[:,0], positive[:,1], c='red')
plt.scatter(negative[:,0], negative[:,1], c='green')
plt.show()
if __name__ == "__main__":
data,label = load_data_set(path, train_set)
data = np.array(data).astype(np.float64)
label = [int(item) for item in label]
weights = trainLogisticRegression(data,label)
plot_fit_line(weights,data,label)
2.拟合结果
3.帮助文档
python实现逻辑回归的方法示例:http://www.jb51.net/article/112719.htm
scikit-learn文档:http://scikit-learn.org/stable/modules/linear_model.html#logistic-regression
逻辑回归在线交互服务器:http://www.vassarstats.net/logreg1.html#down
python编写Logistic逻辑回归:http://www.jb51.net/article/131182.htm
python实现逻辑回归的方法示例:http://www.jb51.net/article/112719.htm
(end)