内功之---栈
一.栈的介绍
- 是一个先进后出的有序列表。
- 限制元素的插入和删除只能在线性表的同一端进行。插入和删除元素的一端称为栈顶,不变化的一段称为栈底。
- 最先放入的元素在栈底,最后放入的元素在栈顶。
二.栈的使用场景
三.栈的基本操作
原理图:
代码实现:
/**
* Project Name:leetcode
* File Name:StackDemo.java
* Package Name:stack
* Date:2020年2月11日下午4:45:24
* Copyright (c) 2020, [email protected] All Rights Reserved.
*
*/
package stack;
import java.util.Scanner;
/**
* ClassName:StackDemo
* Function: TODO ADD FUNCTION.
* Reason: TODO ADD REASON.
* Date: 2020年2月11日 下午4:45:24
*
* @author yrz
* @version
* @see
*/
public class StackDemo {
public static void main(String[] agrs) {
// 测试一下ArrayStack 是否正确
// 先创建一个ArrayStack对象->表示栈
Stack stack = new Stack(4);
String key = "";
boolean loop = true; // 控制是否退出菜单
Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in);
while (loop) {
System.out.println("show: 表示显示栈");
System.out.println("exit: 退出程序");
System.out.println("push: 表示添加数据到栈(入栈)");
System.out.println("pop: 表示从栈取出数据(出栈)");
System.out.println("请输入你的选择");
key = scanner.next();
switch (key) {
case "show":
stack.list();
break;
case "push":
System.out.println("请输入一个数");
int value = scanner.nextInt();
stack.push(value);
break;
case "pop":
try {
int res = stack.pop();
System.out.printf("出栈的数据是 %d\n", res);
} catch (Exception e) {
// TODO: handle exception
System.out.println(e.getMessage());
}
break;
case "exit":
scanner.close();
loop = false;
break;
default:
break;
}
}
System.out.println("程序退出~~~");
}
}
//创建栈
class Stack {
int top = -1;
int maxsize;
int arr[];
public Stack(int maxsize) {
this.maxsize = maxsize;
arr = new int[maxsize];// 初始化数组
}
// 判断栈空
public boolean isEmpty() {
return top == -1;
}
// 判断栈满
public boolean isFull() {
return top == maxsize - 1;
}
// 入栈
public void push(int data) {
if (isFull()) {
System.out.println("栈满");
return;
}
top++;
arr[top] = data;
}
// 出栈
public int pop() {
if (isEmpty()) {
System.out.println("栈空,无元素");
return -1;
}
int value = arr[top];
top--;
return value;
}
// 遍历栈
public void list() {
if (isEmpty()) {
System.out.println("栈空,无元素");
return;
}
for (int i = top; i >= 0; i--) {
System.out.printf("出栈元素为arr[%d]=%d\n", i, arr[i]);
}
}
}四.栈实现计算器(中缀表示)
思路分析:
代码实现:
/**
* Project Name:leetcode
* File Name:Calculator.java
* Package Name:stack
* Date:2020年2月11日下午5:20:09
* Copyright (c) 2020, [email protected] All Rights Reserved.
*
*/
package stack;
/**
* ClassName:Calculator
* Function: TODO ADD FUNCTION.
* Reason: TODO ADD REASON.
* Date: 2020年2月11日 下午5:20:09
*
* @author yrz
* @version
* @see
*/
public class Calculator {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Stack2 numStack2 = new Stack2(10);//数字栈
Stack2 operStack2 = new Stack2(10);//字符栈
String expression = "34+4*8-9";
int index = 0;// 用来遍历表达式
int num1 = 0;
int num2 = 0;
char ch = 0;// 记录当前扫描到的字符
String keepNum = "";// 拼接数字字符
int res = 0;
char temp;
// 判断扫描到的字符是数字还是字符
while (true) {
ch = expression.substring(index, index + 1).charAt(0);
if (operStack2.isOper(ch)) {
// 判断当前符号栈是否为空,为空直接进符号栈
if (operStack2.isEmpty()) {
operStack2.push(ch);
} else {
// 判断优先级
// 优先级高入符号栈,否则数栈弹出两个数,
// 符号栈弹出当前符号,计算后结果入数栈,当前扫描到的字符入符号栈
if (operStack2.prioprity(ch) > operStack2.prioprity(operStack2.peek())) {
operStack2.push(ch);
} else {
num1 = numStack2.pop();
num2 = numStack2.pop();
temp = (char) operStack2.pop();
res = operStack2.calculator(num1, num2, temp);
numStack2.push(res);
operStack2.push(ch);
}
}
} else {
keepNum += ch;
// 已经是最后一个,直接入栈
if (index == expression.length() - 1) {
numStack2.push(Integer.parseInt(keepNum));
break;
}
// 如果当前字符的后一位是运算符,字符前面的数字字符串入栈
if (operStack2.isOper(expression.substring(index + 1, index + 2).charAt(0))) {
numStack2.push(Integer.parseInt(keepNum));
// 清空keepNum
keepNum = "";
}
}
index++;
// 退出循环
if (index > expression.length() - 1) {
break;
}
}
// 按顺序计算数栈和字符栈中的结果
while (true) {
// 符号栈为空,跳出循环
if (operStack2.isEmpty()) {
break;
}
num1 = numStack2.pop();
num2 = numStack2.pop();
temp = (char) operStack2.pop();
res = operStack2.calculator(num1, num2, temp);
numStack2.push(res);
}
// 弹出计算结果
int value = numStack2.pop();
System.out.println("表达式最终结果=" + value);
}
}
//创建栈
class Stack2 {
int top = -1;
int maxsize;
int arr[];
public Stack2(int maxsize) {
this.maxsize = maxsize;
arr = new int[maxsize];// 初始化数组
}
// 判断栈空
public boolean isEmpty() {
return top == -1;
}
// 判断栈满
public boolean isFull() {
return top == maxsize - 1;
}
// 入栈
public void push(int data) {
if (isFull()) {
System.out.println("栈满");
return;
}
top++;
arr[top] = data;
}
// 出栈
public int pop() {
if (isEmpty()) {
System.out.println("栈空,无元素");
return -1;
}
int value = arr[top];
top--;
return value;
}
// 遍历栈
public void list() {
if (isEmpty()) {
System.out.println("栈空,无元素");
return;
}
for (int i = top; i >= 0; i--) {
System.out.printf("出栈元素为arr[%d]=%d\n", i, arr[i]);
}
}
// 判断当前字符是否是符号
public boolean isOper(char ch) {
return ch == '*' || ch == '/' || ch == '+' || ch == '-';
}
// 判断运算符的优先级
public int prioprity(char ch) {
if (ch == '*' || ch == '/') {
return 1;
} else if (ch == '+' || ch == '-') {
return 0;
} else {
return -1;
}
}
// 计算方法
public int calculator(int num1, int num2, char oper) {
int res = 0;
switch (oper) {
case '*':
res = num1 * num2;
break;
case '/':
res = num2 / num1;
break;
case '+':
res = num1 + num2;
break;
case '-':
res = num2 - num1;
break;
default:
break;
}
return res;
}
// 弹出栈顶元素
public char peek() {
return (char) arr[top];
}
}
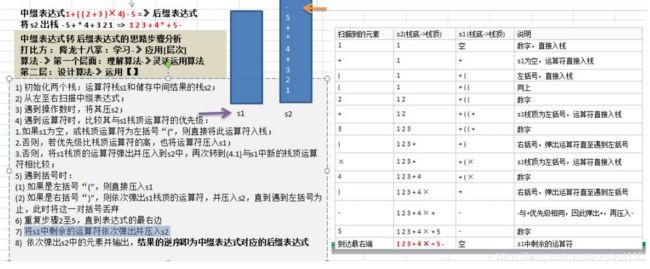
五.实现逆波兰计数器
中缀表达式转换对应的后缀表
1) 初始化两个栈:运算符栈 s1 和储存中间结果的栈 s2;
2) 从左至右扫描中缀表达式;
3) 遇到操作数时,将其压 s2;
4) 遇到运算符时,比较其与 s1 栈顶运算符的优先级:1.如果 s1 为空,或栈顶运算符为左括号“(”,则直接将此运算符入栈;2.否则,若优先级比栈顶运算符的高,也将运算符压入 s1;3.否则,将 s1 栈顶的运算符弹出并压入到 s2 中,再次转到(4-1)与 s1 中新的栈顶运5) 遇到括号时:(1) 如果是左括号“(”,则直接压入 s1(2) 如果是右括号“)”,则依次弹出 s1 栈顶的运算符,并压入 s2,直到遇到左括
6) 重复步骤 2 至 5,直到表达式的最右边
7) 将 s1 中剩余的运算符依次弹出并压入 s2依次弹出 中的元素并输出,结果的逆序即为中缀表达式对应的后缀表
代码实现
/**
* Project Name:leetcode
* File Name:PoLandNotation.java
* Package Name:stack
* Date:2020年2月13日上午11:40:58
* Copyright (c) 2020, [email protected] All Rights Reserved.
*
*/
package stack;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.Stack;
/**
* ClassName:PoLandNotation
* Function: TODO ADD FUNCTION.
* Reason: TODO ADD REASON.
* Date: 2020年2月13日 上午11:40:58
*
* @author yrz
* @version
* @see
*/
public class PoLandNotation {
public static void main(String[] args) {
/*
* String str="3 4 + 5 * 6 -"; List res =
* PoLandNotation.getPoLandList(str); System.out.println(res);
*
* System.out.println(); int result = PoLandNotation.Calculator(res);
* System.out.println("逆波兰表达式计算结果="+result);
*/
// 完成将一个中缀表达式转成后缀表达式的功能
// 说明
// 1. 1+((2+3)×4)-5 => 转成 1 2 3 + 4 × + 5 –
// 2. 因为直接对 str 进行操作,不方便,因此 先将 "1+((2+3)×4)-5" =>
// 中缀的表达式对应的列表即“1(23)×4)-5”=>Array List[1,(2,3,),*4,),-5]
// 3。将得到的中缀表达式对应的列表=>后缀表达式对应的列表/即Array List[1,(,(,2,3,),*,4,),-5]
String expression = "1+((2+3)*4)-5";// 注意表达式
List res = PoLandNotation.getInfixList(expression);
System.out.println("中缀list="+res);
System.out.println();
List resSuf = PoLandNotation.toSuffixList(res);
System.out.println("后缀list="+resSuf);
System.out.println();
int result = PoLandNotation.Calculator(resSuf);
System.out.println("逆波兰表达式计算结果="+result);
}
// 中缀表达式存放在ArrayList中
public static List getInfixList(String s) {
List infixList = new ArrayList();
int index = 0;
char ch = 0;
String temp = null;// 拼接多个数字
while (true) {
ch = s.substring(index, index + 1).charAt(0);
if (ch < 48 || ch > 57) {
infixList.add("" + ch);
} else {
temp = "";
if (ch >= 48 || ch <= 57) {
temp += ch;
}
infixList.add(temp);
}
index++;
if (index > s.length() - 1) {
break;
}
}
return infixList;
}
// 中缀list转化为后缀list
public static List toSuffixList(List infixList) {
// 运算符栈
Stack opertorStack = new Stack();
// 中间结果栈
Stack intermediateResultStack = new Stack();
for (String res : infixList) {
if (res.matches("\\d+")) {
intermediateResultStack.push(res);
} else {
if (opertorStack.isEmpty() ||res.equals("(")|| opertorStack.peek().equals("(")) {
opertorStack.push(res);
} else if (res.equals(")")) {
// 如果是右括号“)”,则依次弹出 opertorStack 栈顶的运算符,并压入 intermediateResultStack,直到遇到左括号为止,此时将这 一对括号丢弃
while (!opertorStack.peek().equals("(")) {
intermediateResultStack.push(opertorStack.pop());
}
opertorStack.pop();// 消除“(”
} else {
// 当 item 的优先级小于等于 opertorStack 栈顶运算符,
// 将 opertorStack 栈顶的运算符弹出并加入到 intermediateResultStack 中,再次转到(4.1) 与 opertorStack 中新的栈顶运算符相比较
while (opertorStack.size() != 0 && PoLandNotation.prioprity(res.charAt(0)) <= PoLandNotation
.prioprity(((String)opertorStack.peek()).charAt(0))) {
intermediateResultStack.push(opertorStack.pop());
}
opertorStack.push(res);
}
}
}
while (opertorStack.size() != 0) {
intermediateResultStack.push(opertorStack.pop());
}
return intermediateResultStack;
}
// 将后缀表达式存放到List中
public static List getPoLandList(String s) {
List poLandList = new ArrayList();
String[] spilt = s.split(" ");
for (String str : spilt) {
poLandList.add(str);
}
return poLandList;
}
// 计算后缀表达式
/*
* 1.从左至右扫描,将 3 和 4 压入堆栈; 2.遇到+运算符,因此弹出 4 和 3(4 为栈顶元素,3 为次顶元素),计算出 3+4 的值,得 7,再将
* 7 入栈; 3.将 5 入栈; 4.接下来是×运算符,因此弹出 5 和 7,计算出 7×5=35,将 35 入栈; 5.将 6 入栈;
* 6.最后是-运算符,计算出 35-6 的值,即 29,由此得出最终结果
*/
public static int Calculator(List poLandList) {
Stack stack = new Stack();
for (String str : poLandList) {
if (str.matches("\\d+")) {
// 数字直接入栈
stack.push(str);
} else {
int num1 = Integer.parseInt(stack.pop());
int num2 = Integer.parseInt(stack.pop());
int res = CalculatorInStack(num1, num2, str);
stack.push(res + "");
}
}
// 最后出战返回结果
int res = Integer.parseInt(stack.pop());
return res;
}
// 栈内元素进行计算
public static int CalculatorInStack(int num1, int num2, String str) {
int res = 0;
if (str.equals("+")) {
res = num1 + num2;
}
if (str.equals("*")) {
res = num1 * num2;
}
if (str.equals("-")) {
res = num2 - num1;
}
if (str.equals("/")) {
res = num2 / num1;
}
return res;
}
// 判断运算符的优先级
public static int prioprity(char ch) {
if (ch == '*' || ch == '/') {
return 1;
} else if (ch == '+' || ch == '-') {
return 0;
} else {
return -1;
}
}
}