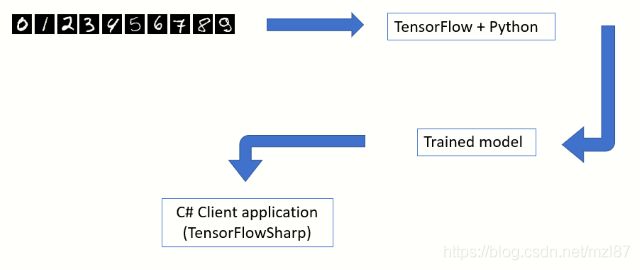
TensorFlow——使用TensorFlowSharp创建C#应用程序
目录
介绍
关于TensorFlow
TensorFlow本机库
Python和C#的TensorFlow绑定
背景
什么是MNIST?为何选择MNIST?
概述
示例图片
图片分布
深度学习
感知
单感知器
多层感知器
卷积神经网络
TensorflowSharp——使用来自C#应用程序的Tensorflow
使用Tensorflow和GPU
概述
GPU/NVDIA-什么为我工作?
使用TensorFlow和Python训练CNN模型
CNN架构
用于训练的图像文件
1-Python脚本(MnistImageLoader.py)
2-加载训练图像(TrainMnistFromFolder.py)
3-创建CNN模型(TrainMnistFromFolder.py)
4-训练模型(TrainMnistFromFolder.py)
5-保存模型(FreezeKerasToTF.py)
6-结果
C#控制台应用程序
概述
1-创建控制台应用程序
2-加载训练模型文件
3 Utils.ImageToTensorGrayScale
4- Utis.Quantized
5-结果
使用代码
Github存储库
解决方案结构
1-PythonTrainer
2-MNISTPng
3-ConsoleAppTester
兴趣点
- 从Github下载源代码
介绍
在模式识别领域,深度神经网络在过去的5年中获得了突出地位。这主要归功于更便宜的硬件,编程库和标签数据的可用性。如果训练得当,深度神经网络或卷积神经网络(CNN)可以产生惊人的效果。来自Google的TensorFlow是一个非常受欢迎的库,它们实现了一些复杂的算法。
在本文中,我将演示如何训练CNN模型以识别MNIST数据库中的手写数字。接下来是C#控制台应用程序,它将使用经过训练的模型来实际分类来自MNIST数据集的测试图像。本文的目的是演示如何充分利用Python来训练模型,以及如何使用.NET来构建一个假设的最终用户应用程序来使用经过训练的模型。
关于TensorFlow
TensorFlow本机库
///
///https://www.tensorflow.org/install/lang_c
///The windows native implementation is downloadable as a single ZIP and structured as follows
///
include
--------
|
|
|
--c_api.h
|
|
lib
--------
|
|
--tensorflow.dll
|
|
--tensorflow.libPython和C#的TensorFlow绑定
Tensorflow实现为C / C ++动态链接库。特定于平台的二进制文件在ZIP文件中可用。此库顶部提供了各种语言的绑定。这些是特定于语言的包装器,用于调用本机库。Python可能是构建在本机TensorFlow实现之上的最通用的编程层之一。TensorFlowSharp是TensorFlow上的.NET包装器。
TensorFlow(C/C++)
----------------
|
|
------------------------------------------------
| |
| |
| |
Python TensorFlowSharp(C#)
------ -------------------
(train model) (use model in client application)背景
- Python——我使用Python训练CNN模型,使用手写数字的MNIST数据集。Python的基本知识至关重要。我使用Visual Studio Code(1.36.1)作为Python脚本编辑器。您可以使用任何适合您的Python编辑器。
- 我已经将Visual Studio 2017用于简单的控制台应用程序,该应用程序使用经过训练的模型并对测试图像进行分类。
- 在本文中,我使用了Tensorflow的GPU版本来提高学习速度。您需要支持GPU的桌面。请读者注意,使用GPU进行编码需要安装额外的CUDA库和驱动程序。本文还假设读者熟悉深度卷积神经网络的基本原理。
什么是MNIST?为何选择MNIST?
概述
MNIST数据库是手写数字(0-9)的集合。这包括60,000个训练和10,000个测试图像。每个图像宽28像素,高28像素,所有图像均为灰度。在机器学习和计算机视觉领域,MNIST已经成为测试任何新范例的事实上的标准。(参考http://yann.lecun.com/exdb/mnist/)
示例图片
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
图片分布
| 0 |
1 |
2 |
3 |
4 |
5 |
6 |
7 |
8 |
9 |
|
| 训练 |
5923 |
6742 |
5985 |
6131 |
5842 |
5421 |
5918 |
6265 |
5851 |
5949 |
| 测试 |
980 |
1135 |
1032 |
1010 |
982 |
892 |
958 |
1028 |
974 |
1009 |
深度学习
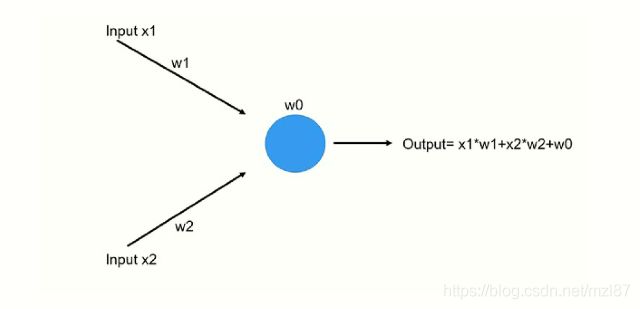
感知
在20世纪40年代和50年代,一个非常基础的数学神经元的想法开始形成。研究人员(McCulloch,Pitts和Rosenblatt)从生物神经元的工作中汲取灵感。神经元是神经系统的基石。平均人类大脑有数十亿个神经元通过突触间接相互连接。他们设想一个单独的神经元表现得像一个直线分类器。流过树突的电信号表示实际信号(矢量),输出信号表示二进制(开/关)分类状态。Frank Rosenblatt(1962)通过在他的“神经动力学原理”(1962年出版,“完全线性感知器”一节)中提出线性感知器的设计,将McCulloch和Pitts神经元的设计向前推进了一步。
单感知器
蓝色圆圈表示a.x + b.y + c = 0形式的直线方程。
给定两类点X和O,它们是线性可分的,你可以找到一条直线来划分这两个类。如果你将类X中的点的坐标输入方程a.x + b.y + c然后对类O中的所有点进行相同的操作,那么你将看到类X中的所有点都产生了正值,而O类中的所有点都产生负值(反之亦然)。符号的变化可能是相反的,取决于常数a,b和c。然而,这是使感知器表现为线性分类器的首要原则。
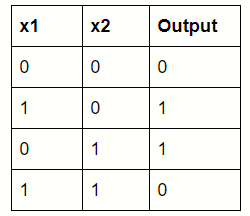
多层感知器
如果我们找不到分隔X和O类的单行,就像著名的XOR问题一样,那么我们就可以级联多个线性分类器。
卷积神经网络
通过结合特征提取和超平面发现,深度学习使多层感知器向前迈进了一步。功能由过滤器层提取。有关此主题的详尽论述,请读者阅读Andrew Ng的教程。
TensorflowSharp——使用来自C#应用程序的Tensorflow
TensorFlowSharp是TensorFlow的非托管本机库的.NET包装器。这是Miguel de lcaza开创性工作的结果。TensorFlowSharp可以使用Python训练的CNN模型,这开辟了创建令人兴奋的最终用户应用程序的可能性。
nuget install TensorFlowSharp///
///Skeletal code using TensorFlowSharp
///
byte[] buffer = System.IO.File.ReadAllBytes(modelfile);
using (var graph = new TensorFlow.TFGraph())
{
graph.Import(buffer);
using (var session = new TensorFlow.TFSession(graph))
{
/*
1)pick a test image
2)Created tensor object using this image
*/
var runner = session.GetRunner();
runner.AddInput(...,tensor,)
runner.Fetch(...)
var output = runner.Run();
}
}使用Tensorflow和GPU
概述
Python script
--------------
|
|
|
TensorFlow GPU package
----------------------
|
|
|
cuDNN
-----
|
|
|
CUDA Toolkit
--------------
|
|
|
Drivers
-------
|
|
|
GPU
---GPU/NVDIA-什么为我工作?
使用TensorFlow进行训练时,您可以选择使用CPU包或GPU包。GPU是首选,因为训练速度明显更快。您将需要正确版本的NVIDIA驱动程序和CUDA库。根据经验,NVIDIA驱动程序的版本应与当前版本的TensorFlow相匹配。在撰写本文时,我使用了python包TensorFlow-GPU 1.14.0。我要提醒读者,我安装驱动程序和让TensorFlow GPU工作的经验并不顺利。
- 更新NVIDIA驱动程序的版本。我没有通过NVIDIA网站安装。我通过Windows设备管理器用户界面更新了显示适配器。版本24.21.14.1131适合我。

- 安装CUDA Toolkit 10.0版本
- 安装cuDNN SDK版本7.6.2。我选择了Windows 10版。我将cudnn64_7.dll复制到%ProgramFiles%\NVIDIA GPU Computing Toolkit\CUDA\v10.0\bin
- Python包Tensorflow 1.14
- Python包Keras 2.2.4
- Python包Numpy 1.16.1
使用TensorFlow和Python训练CNN模型
CNN架构
Input layer (28X28,1 channel)
-----------------------------
|
|
|
Convolution layer (5X5,20,RELU)
--------------------------------
|
|
|
Max Pool layer (2X2,stride=2)
------------------------------
|
|
|
Convolution layer (5X5,50,RELU)
--------------------------------
|
|
|
Max Pool layer (2X2,stride=2)
-----------------------------
|
|
|
Flatten
---------
|
|
|
Dense layer (500 nodes,RELU)
----------------------------
|
|
|
Dense layer (10 nodes,RELU)
----------------------------
|
|
|
Output layer(Softmax)
----------------------用于训练的图像文件
可以从scikit-learn包中轻松访问MNIST数据集。但是,在本教程中,我演示了如何从磁盘加载图像。各个PNG文件在随附的项目MNISpng.csproj中提供。将在目录结构上枚举python脚本MnistImageLoader.py并构建训练/测试图像列表。每个PNG文件的父文件夹将提供训练标签(0-9)。
MNIST
-----
|
|
training.zip
-----------
| |
| |
| |--(folders 0 to 9)
| |
| |
| |_0
| |
| |
| |_1
| |
| |
| |_2
| .
| .
| ._9
|
|
testing.zip
-----------
|
|
|--(folders 0 to 9)1-Python脚本(MnistImageLoader.py)
#
#Load images and labels. Returns a tuple of image data,label
#
def load_images(path_in):
filenames = glob.glob(path_in)
images=[]
labels=[] #labels for each training file
filenames = glob.glob(path_in)
for filename in filenames:
#get the parent folder from the full path of the
#file /mnist/blah/training/3/34348.png
fulldir=os.path.dirname(filename)
parentfolder=os.path.basename(fulldir)
imagelabel=int(parentfolder)
labels.append(imagelabel)
img = get_im(filename)
images.append(img)
return images,labels
#
#The output from load_images() is further refined
#
def ReShapeData(data,target,numclasses):
data_out = np.array(data, dtype=np.uint8)
target_out = np.array(target, dtype=np.uint8)
data_out = data_out.reshape(data_out.shape[0], 28,28)
data_out = data_out[:, :, :, np.newaxis]
data_out = data_out.astype('float32')
data_out /= 255
target_out = np_utils.to_categorical(target_out, numclasses)
return data_out,target_out2-加载训练图像(TrainMnistFromFolder.py)
主python脚本TrainMnistFromFolder.py将调用函数load_images和ReShapeData。
#
#Load training images
#
from MnistImageLoader import load_images,ReShapeData
print("Loading training images")
(train_data, train_target)=load_images(mnist_train_path_full)
(train_data1,train_target1)=ReShapeData(train_data,train_target,nb_classes)
print('Shape:', train_data1.shape)
print(train_data1.shape[0], ' train images were loaded')3-创建CNN模型(TrainMnistFromFolder.py)
#
# Create a sequential model
#
model = Sequential()
# Add the first convolution layer
model.add(Convolution2D(
name="conv1",
filters = 20,
kernel_size = (5, 5),
padding = "same",
input_shape = (28, 28, 1)))
# Add a ReLU activation function
model.add(Activation(
activation = "relu"))
# Add a pooling layer
model.add(MaxPooling2D(
name="maxpool1",
pool_size = (2, 2),
strides = (2, 2)))
# Add the second convolution layer
model.add(Convolution2D(
name="conv2",
filters = 50,
kernel_size = (5, 5),
padding = "same"))
# Add a ReLU activation function
model.add(Activation(
activation = "relu"))
# Add a second pooling layer
model.add(MaxPooling2D(
name="maxpool2",
pool_size = (2, 2),
strides = (2, 2)))
# Flatten the network
model.add(Flatten())
# Add a fully-connected hidden layer
model.add(Dense(500))
# Add a ReLU activation function
model.add(Activation(activation = "relu"))
# Add a fully-connected output layer - the output layer nodes
# should match the count of image classes
model.add(Dense(nb_classes,name="outputlayer"))
# Add a softmax activation function
model.add(Activation("softmax"))
#
#Display Summary
#
model.summary()
# Compile the network
model.compile(
loss = "categorical_crossentropy",
optimizer = SGD(lr = 0.01),
metrics = ["accuracy"])
print("Compilation complete");4-训练模型(TrainMnistFromFolder.py)
#
# Train the model
#
total_epochs=20
start = time.time()
model.fit(
train_data1,
train_target1,
batch_size = 128,
epochs = total_epochs,
verbose = 1)
print("Train complete");
#
#Test the model
#
print("Testing on test data")
(loss, accuracy) = model.evaluate(
test_data1,
test_target1,
batch_size = 128,
verbose = 1)
# Print the model's accuracy
print("Accuracy="+ str(accuracy))5-保存模型(FreezeKerasToTF.py)
训练完成后,模型必须以原始TensorFlow格式(.pb)保存。在FreezeKerasToTF.py文件中的freeze_session函数为我们做了这个。保存的模型包含网络布局和权重。
#
#Saving using Freeze approach
#https://stackoverflow.com/questions/45466020/how-to-export-keras-h5-to-tensorflow-pb
#
frozen_graph = freeze_session(K.get_session(),
output_names=[out.op.name for out in model.outputs])
tf.train.write_graph(frozen_graph, "Out", "Mnist_model.pb", as_text=False)6-结果
C#控制台应用程序
概述
-----------------------
1)Load trained model file
-----------------------
|
|
-----------------
2)Load test images
-----------------
|
|
-----------------------------------
3)Evaluate the test image using CNN
-----------------------------------1-创建控制台应用程序
- 使用.NET Framework(64位,4.6.1或更高版本)创建新的控制台应用程序
- 将NUGET包引用添加到TensorflowSharp
2-加载训练模型文件
///
///Skeletal code using TensorFlowSharp
///
var modelfile=@"c:\\MyTensorFlowModel.pb";//Produced by training
byte[] buffer = System.IO.File.ReadAllBytes(modelfile);
using (var graph = new TensorFlow.TFGraph())
{
graph.Import(buffer);
using (var session = new TensorFlow.TFSession(graph))
{
var file="test.png";
var runner = session.GetRunner();
var tensor = Utils.ImageToTensorGrayScale(file);
runner.AddInput(graph["conv1_input"][0], tensor);
runner.Fetch(graph["activation_4/Softmax"][0]);
var output = runner.Run();
var vecResults = output[0].GetValue();
float[,] results = (float[,])vecResults;
///
/// Evaluate the results
///
int[] quantized = Utils.Quantized(results);
}
}3 Utils.ImageToTensorGrayScale
此函数将加载MNIST图片文件并创建一个TFTensor:
public static TensorFlow.TFTensor ImageToTensorGrayScale(string file)
{
using (System.Drawing.Bitmap image = (System.Drawing.Bitmap)System.Drawing.Image.FromFile(file))
{
var matrix = new float[1, image.Size.Height, image.Size.Width, 1];
for (var iy = 0; iy < image.Size.Height; iy++)
{
for (int ix = 0, index = iy * image.Size.Width; ix < image.Size.Width; ix++, index++)
{
System.Drawing.Color pixel = image.GetPixel(ix, iy);
matrix[0, iy, ix, 0] = pixel.B / 255.0f;
}
}
TensorFlow.TFTensor tensor = matrix;
return tensor;
}
}4- Utis.Quantized
此函数将TF结果转换为包含10个元素的数组。第0个元素表示数字0的概率,第9个元素表示数字9的概率。
//Silly repetitions here! I was running out of time.
internal static int[] Quantized(float[,] results)
{
int[] q = new int[]
{
results[0,0]>0.5?1:0,
results[0,1]>0.5?1:0,
results[0,2]>0.5?1:0,
results[0,3]>0.5?1:0,
results[0,4]>0.5?1:0,
results[0,5]>0.5?1:0,
results[0,6]>0.5?1:0,
results[0,7]>0.5?1:0,
results[0,8]>0.5?1:0,
results[0,9]>0.5?1:0,
};
return q;
}5-结果
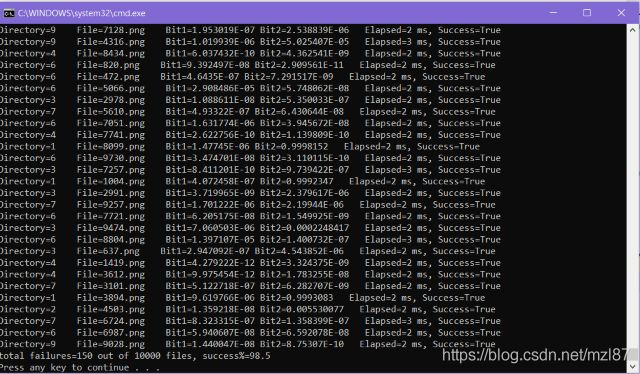
在遍历所有10,000个测试图像并通过MNIST对它们进行分类之后,我们得到98.5%的预测成功率。150张图片被错误分类。根据MNIST主页,最先进的基准测试成功率超过99.5%。
使用代码
Github存储库
- https://github.com/sdg002/MNISTpng
解决方案结构
Solution
--------
|
|
MNISTPng (ZIP of individual PNG train and test files)
------------------------------------------------------
|
|
PythonTrainer (Python script to train using TensorFlow)
-------------------------------------------------------
|
|
ConsoleAppTester (C# console app using TensorFlowSharp)
-------------------------------------------------------1-PythonTrainer
用于训练CNN模型的Python脚本:
- TrainMnistFromFolder.py——加载和训练图像的最外层Python脚本
- MnistImageLoader.py——用于将PNG转换为Tensor
- FreezeKerasToTF.py——用于将训练过的模型保存为.PB文件
2-MNISTPng
ZIP训练和测试图像:
- testing.zip——10,000个单独的测试文件,组织成10个目录
- training.zip——将50,000个单独的训练文件组织到10个目录中
3-ConsoleAppTester
C#EXE将使用TensorFlowSharp加载训练模型
兴趣点
- Andrew Ng教程
- MNIST主页