专题5:不同种遍历结合恢复二叉树
不同种遍历结合恢复二叉树
1.先序与中序结合恢复二叉树(LeetCode105)
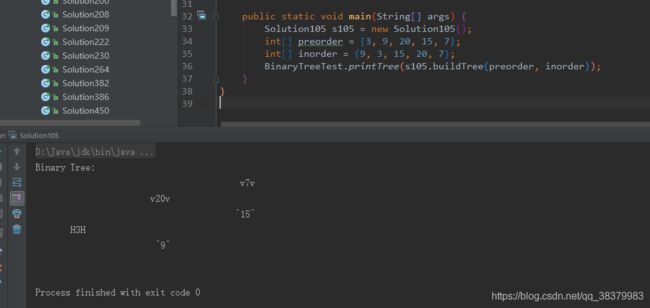
前序遍历 preorder = [3,9,20,15,7]
中序遍历 inorder = [9,3,15,20,7]
返回如下的二叉树:
3
/ \
9 20
/ \
15 7
代码思想:
前序遍历和中序遍历有以下特点:
前序遍历: 根节点 | 左子树 | 右子树 ; 例如:[1 | 2 4 5 | 3 6 7]
中序遍历: 左子树 | 根节点 | 右子树 ; 例如:[4 2 5 | 1 | 6 3 7]
对于每个左子树、右子树的前序遍历和中序遍历依然有此规律。
按前序遍历的顺序每次pop并建立节点root,在中序遍历中找到root的对应index,划分出哪些节点构成此节点的左子树inorder[:i],哪些构成右子树inorder[i+1:]。
返回值: 递归构建完当前节点root左右子树后,返回root,作为上轮递归父节点的left或right。
终止条件: 当inorder[i]中序遍历无剩余元素时,说明当前root已经越过叶子节点,直接返回null。
代码实现:
public TreeNode buildTree(int[] preorder, int[] inorder) {
if (preorder == null || preorder.length == 0 || inorder == null || inorder.length == 0) {
return null;
}
return build(preorder, 0, preorder.length - 1, inorder, 0, inorder.length - 1);
}
public TreeNode build(int[] pre, int preStart, int preEnd, int[] in, int inStart, int inEnd) {
if (preStart > preEnd || inStart > inEnd) {
return null;
}
TreeNode root = new TreeNode(pre[preStart]);
int index = 0;
while (in[index] != root.val) {
index++;
}
root.left = build(pre, preStart + 1, preStart + index, in, inStart, index-1);
root.right = build(pre, preStart + index + 1, preEnd, in, index + 1, inEnd);
return root;
}测试用例:
算法分析:
时间复杂度O(n),额外空间复杂度O(1)
2.先序和后序结合恢复二叉树(LeetCode889)
返回与给定的前序和后序遍历匹配的任何二叉树, pre 和 post 遍历中的值是不同的正整数。
示例:
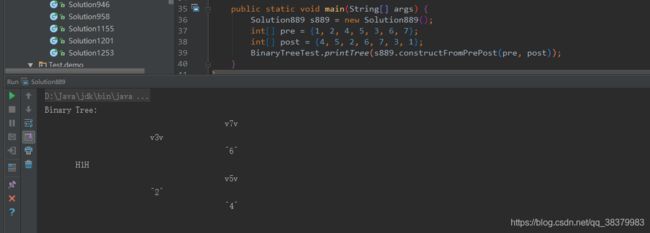
输入:pre = [1,2,4,5,3,6,7], post = [4,5,2,6,7,3,1]
输出:[1,2,3,4,5,6,7]
代码思想:
前序遍历和后序遍历有以下特点:
前序遍历: 根节点 | 左子树 | 右子树 ; 例如:[1 | 2 4 5 | 3 6 7]
后序遍历: 左子树 | 右子树 | 根节点 ; 例如:[4 2 5 | 6 7 3 |1 ]
对于每个左子树、右子树的前序遍历和后序遍历依然有此规律。
代码实现:
public TreeNode constructFromPrePost(int[] pre, int[] post) {
if (pre == null || pre.length == 0 || post == null || post.length == 0) {
return null;
}
return build(pre, 0, pre.length - 1, post, 0, post.length - 1);
}
public TreeNode build(int[] pre, int preStart, int preEnd, int[] post, int postStart, int postEnd) {
if (preStart > preEnd || postStart > postEnd) {
return null;
}
TreeNode root = new TreeNode(pre[preStart]);
if(preStart == preEnd){
return root;
}
int index = 0;
while (post[index] != pre[preStart+1]) {
index++;
}
root.left = build(pre, preStart + 1, preStart + 1 + index - postStart, post, postStart, index);
root.right = build(pre, preStart + 2 + index - postStart, preEnd, post, index + 1, postEnd - 1);
return root;
}测试用例:
算法分析:
时间复杂度O(n),额外空间复杂度O(1)
3.中序和后序结合恢复二叉树(LeetCode106)
中序遍历 inorder = [9,3,15,20,7]
后序遍历 postorder = [9,15,7,20,3]
返回如下的二叉树:
3
/ \
9 20
/ \
15 7
代码思想:
中序遍历和后序遍历有以下特点:
中序遍历: 左子树 | 根节点 | 右子树 ; 例如:[9 | 3 | 15 20 7 ]
后序遍历: 左子树 | 右子树 | 根节点 ; 例如:[9 | 15 7 20 | 3 ]
对于每个左子树、右子树的中序遍历和后序遍历依然有此规律。
代码实现:
public TreeNode buildTree(int[] inorder, int[] postorder) {
if (inorder == null || inorder.length == 0 || postorder == null || postorder.length == 0) {
return null;
}
return build(inorder, 0, inorder.length - 1, postorder, 0, postorder.length - 1);
}
public TreeNode build(int[] in, int inStart, int inEnd, int[] post, int postStart, int postEnd) {
if (inStart > inEnd || postStart > postEnd) {
return null;
}
TreeNode root = new TreeNode(post[postEnd]);
int index = inStart;
while (in[index] != root.val) {
index++;
}
root.left = build(in, inStart, index - 1, post, postStart, postStart + index - inStart - 1);
root.right = build(in, index + 1, inEnd, post, postStart + index - inStart, postEnd - 1);
return root;
}测试用例:
算法分析:
时间复杂度O(n),额外空间复杂度O(1)