SpringBoot2.0的@Cacheable(Redis)缓存失效时间解决方案
1、注释介绍 @Cacheable、@CachePut、@CacheEvict
spring cache 主要使用3个注释标签,即 @Cacheable、@CachePut 和 @CacheEvict,我们总结一下其作用和配置方法。
表 1. @Cacheable 作用和配置方法
| @Cacheable 的作用 | 主要针对方法配置,能够根据方法的请求参数对其结果进行缓存 | |
|---|---|---|
| @Cacheable 主要的参数 | ||
| value | 缓存的名称,在 spring 配置文件中定义,必须指定至少一个 | 例如: @Cacheable(value=”mycache”) 或者 @Cacheable(value={”cache1”,”cache2”} |
| key | 缓存的 key,可以为空,如果指定要按照 SpEL 表达式编写,如果不指定,则缺省按照方法的所有参数进行组合 | 例如: @Cacheable(value=”testcache”,key=”#userName”) |
| condition | 缓存的条件,可以为空,使用 SpEL 编写,返回 true 或者 false,只有为 true 才进行缓存 | 例如: @Cacheable(value=”testcache”,condition=”#userName.length()>2”) |
表 2. @CachePut 作用和配置方法
| @CachePut 的作用 | 主要针对方法配置,能够根据方法的请求参数对其结果进行缓存,和 @Cacheable 不同的是,它每次都会触发真实方法的调用 | |
|---|---|---|
| @CachePut 主要的参数 | ||
| value | 缓存的名称,在 spring 配置文件中定义,必须指定至少一个 | 例如: @Cacheable(value=”mycache”) 或者 @Cacheable(value={”cache1”,”cache2”} |
| key | 缓存的 key,可以为空,如果指定要按照 SpEL 表达式编写,如果不指定,则缺省按照方法的所有参数进行组合 | 例如: @Cacheable(value=”testcache”,key=”#userName”) |
| condition | 缓存的条件,可以为空,使用 SpEL 编写,返回 true 或者 false,只有为 true 才进行缓存 | 例如: @Cacheable(value=”testcache”,condition=”#userName.length()>2”) |
表 3. @CacheEvict 作用和配置方法
| @CachEvict 的作用 | 主要针对方法配置,能够根据一定的条件对缓存进行清空 | |
|---|---|---|
| @CacheEvict 主要的参数 | ||
| value | 缓存的名称,在 spring 配置文件中定义,必须指定至少一个 | 例如: @CachEvict(value=”mycache”) 或者 @CachEvict(value={”cache1”,”cache2”} |
| key | 缓存的 key,可以为空,如果指定要按照 SpEL 表达式编写,如果不指定,则缺省按照方法的所有参数进行组合 | 例如: @CachEvict(value=”testcache”,key=”#userName”) |
| condition | 缓存的条件,可以为空,使用 SpEL 编写,返回 true 或者 false,只有为 true 才清空缓存 | 例如: @CachEvict(value=”testcache”, condition=”#userName.length()>2”) |
| allEntries | 是否清空所有缓存内容,缺省为 false,如果指定为 true,则方法调用后将立即清空所有缓存 | 例如: @CachEvict(value=”testcache”,allEntries=true) |
| beforeInvocation | 是否在方法执行前就清空,缺省为 false,如果指定为 true,则在方法还没有执行的时候就清空缓存,缺省情况下,如果方法执行抛出异常,则不会清空缓存 | 例如: @CachEvict(value=”testcache”,beforeInvocation=true)/2、 |
2、基本原理
和 spring 的事务管理类似,spring cache 的关键原理就是 spring AOP,通过 spring AOP,其实现了在方法调用前、调用后获取方法的入参和返回值,进而实现了缓存的逻辑。我们来看一下下面这个图:
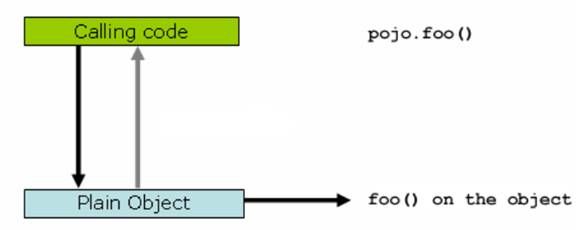
图 2. 原始方法调用图
上图显示,当客户端“Calling code”调用一个普通类 Plain Object 的 foo() 方法的时候,是直接作用在 pojo 类自身对象上的,客户端拥有的是被调用者的直接的引用。
而 Spring cache 利用了 Spring AOP 的动态代理技术,即当客户端尝试调用 pojo 的 foo()方法的时候,给他的不是 pojo 自身的引用,而是一个动态生成的代理类
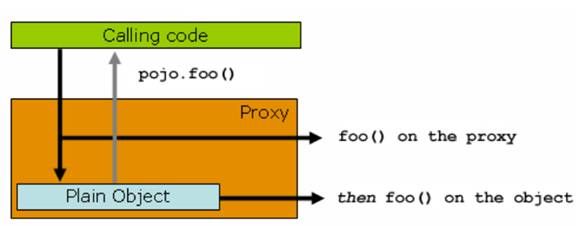
图 3. 动态代理调用图
如上图所示,这个时候,实际客户端拥有的是一个代理的引用,那么在调用 foo() 方法的时候,会首先调用 proxy 的 foo() 方法,这个时候 proxy 可以整体控制实际的 pojo.foo() 方法的入参和返回值,比如缓存结果,比如直接略过执行实际的 foo() 方法等,都是可以轻松做到的。
3、问题:@Cacheable注解不支持配置过期时间
@Cacheable注解不支持配置过期时间,所有需要通过配置CacheManneg来配置默认的过期时间和针对每个类或者是方法进行缓存失效时间配置。
4.1 解决
可以采用如下的配置信息来解决的设置失效时间问题修改配置类
import com.fasterxml.jackson.annotation.JsonAutoDetect;
import com.fasterxml.jackson.annotation.PropertyAccessor;
import com.fasterxml.jackson.databind.ObjectMapper;
import org.springframework.cache.CacheManager;
import org.springframework.cache.annotation.EnableCaching;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
import org.springframework.data.redis.cache.RedisCacheConfiguration;
import org.springframework.data.redis.cache.RedisCacheManager;
import org.springframework.data.redis.cache.RedisCacheWriter;
import org.springframework.data.redis.connection.RedisConnectionFactory;
import org.springframework.data.redis.core.RedisTemplate;
import org.springframework.data.redis.serializer.Jackson2JsonRedisSerializer;
import org.springframework.data.redis.serializer.RedisSerializationContext;
import java.io.Serializable;
import java.time.Duration;
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.Map;
/**
*/
@Configuration
@EnableCaching
public class RedisConfig implements Serializable {
/**
* 申明缓存管理器,会创建一个切面(aspect)并触发Spring缓存注解的切点(pointcut)
* 根据类或者方法所使用的注解以及缓存的状态,这个切面会从缓存中获取数据,将数据添加到缓存之中或者从缓存中移除某个值
*/
/* @Bean
public RedisCacheManager cacheManager(RedisConnectionFactory redisConnectionFactory) {
return RedisCacheManager.create(redisConnectionFactory);
}
@Bean
public RedisTemplate redisTemplate(RedisConnectionFactory factory) {
// 创建一个模板类
RedisTemplate template = new RedisTemplate();
// 将刚才的redis连接工厂设置到模板类中
template.setConnectionFactory(factory);
// 设置key的序列化器
template.setKeySerializer(new StringRedisSerializer());
// 设置value的序列化器
//使用Jackson 2,将对象序列化为JSON
Jackson2JsonRedisSerializer jackson2JsonRedisSerializer = new Jackson2JsonRedisSerializer(Object.class);
//json转对象类,不设置默认的会将json转成hashmap
ObjectMapper om = new ObjectMapper();
om.setVisibility(PropertyAccessor.ALL, JsonAutoDetect.Visibility.ANY);
om.enableDefaultTyping(ObjectMapper.DefaultTyping.NON_FINAL);
jackson2JsonRedisSerializer.setObjectMapper(om);
template.setValueSerializer(jackson2JsonRedisSerializer);
return template;
}*/
/**
* 最新版,设置redis缓存过期时间
*/
@Bean
public RedisCacheManager cacheManager(RedisConnectionFactory redisConnectionFactory) {
return new RedisCacheManager(
RedisCacheWriter.nonLockingRedisCacheWriter(redisConnectionFactory),
this.getRedisCacheConfigurationWithTtl( 60), // 默认策略,未配置的 key 会使用这个
this.getRedisCacheConfigurationMap() // 指定 key 策略
);
}
private Map getRedisCacheConfigurationMap() {
Map redisCacheConfigurationMap = new HashMap<>();
//SsoCache和BasicDataCache进行过期时间配置
redisCacheConfigurationMap.put("messagCache", this.getRedisCacheConfigurationWithTtl(30 * 60));
//自定义设置缓存时间
redisCacheConfigurationMap.put("userCache", this.getRedisCacheConfigurationWithTtl(60));
return redisCacheConfigurationMap;
}
private RedisCacheConfiguration getRedisCacheConfigurationWithTtl(Integer seconds) {
Jackson2JsonRedisSerializer 4.2 测试
- 设置缓存名称及缓存时间(如下为60秒)
redisCacheConfigurationMap.put("userCache",this.getRedisCacheConfigurationWithTtl(60));
复制代码- 使用 加上注解即可
@Cacheable("userCache") - 注:名称为配置类里面设置的名称userCache,可设置多个缓存名称及时间
- 注意:使用@CacheEvict注解的方法必须是controller层直接调用,service里间接调用不生效。@CacheEvict的方法和@Cache的方法放到一个java文件中写,他俩在两个java文件的话,会导致@CacheEvict失效。https://docs.spring.io/spring/docs/current/spring-framework-reference/integration.html#cache-annotations-evict
Controller测试类
import com.ml.demo.dao.UserDao;
import com.ml.demo.entity.User;
import org.springframework.cache.annotation.CacheEvict;
import org.springframework.cache.annotation.CachePut;
import org.springframework.cache.annotation.Cacheable;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestParam;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RestController;
import javax.annotation.Resource;
import java.io.Serializable;
/**
*/
@RestController
public class testController implements Serializable {
@Resource
private UserDao userDao;
/**
* 查询出一条数据并且添加到缓存
*
* @param userId
* @return
*/
@RequestMapping("/getUser")
@Cacheable("userCache")
public User getUser(@RequestParam(required = true) String userId) {
System.out.println("如果没有缓存,就会调用下面方法,如果有缓存,则直接输出,不会输出此段话");
return userDao.getUser(Integer.parseInt(userId));
}
/**
* 删除一个缓存
*
* @param userId
* @return
*/
@RequestMapping(value = "/deleteUser")
@CacheEvict("userCache")
public String deleteUser(@RequestParam(required = true) String userId) {
return "删除成功";
}
/**
* 添加一条保存的数据到缓存,缓存的key是当前user的id
*
* @param user
* @return
*/
@RequestMapping("/saveUser")
@CachePut(value = "userCache", key = "#result.userId +''")
public User saveUser(User user) {
return user;
}
/**
* 返回结果userPassword中含有nocache字符串就不缓存
*
* @param userId
* @return
*/
@RequestMapping("/getUser2")
@CachePut(value = "userCache", unless = "#result.userPassword.contains('nocache')")
public User getUser2(@RequestParam(required = true) String userId) {
System.out.println("如果走到这里说明,说明缓存没有生效!");
User user = new User(Integer.parseInt(userId), "name_nocache" + userId, "nocache");
return user;
}
@RequestMapping("/getUser3")
@Cacheable(value = "userCache", key = "#root.targetClass.getName() + #root.methodName + #userId")
public User getUser3(@RequestParam(required = true) String userId) {
System.out.println("如果第二次没有走到这里说明缓存被添加了");
return userDao.getUser(Integer.parseInt(userId));
}
}
参考:
https://www.ibm.com/developerworks/cn/opensource/os-cn-spring-cache/
https://juejin.im/post/5ca07a98f265da30933fc4c4