操作系统概念(Operating System Concepts)学习笔记 chapter1 Introduction
操作系统概念(Operating System Concepts)chapter1
What Operating Systems Do
Computer-System Organization
Computer-System Architecture
Operating-System Structure
Operating-System Operations
Process Management
Memory Management
Storage Management
Protection and Security
Kernel Data Structures
Computing Environments
Open-Source Operating Systems
程序:指令集和 有序 完成某个任务
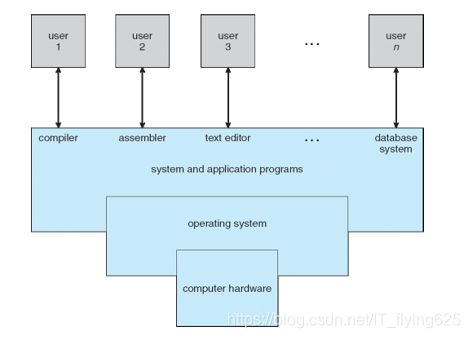
What is an Operating System?
A program that acts as an intermediary between a user of a computer and the computer hardware
Operating system goals:
Execute user programs and make solving user problems easier
Make the computer system convenient to use
Use the computer hardware in an efficient manner
Four Components of a Computer System
Depends on the point of view
Users want convenience, ease of use and good performance
Don’t care about resource utilization
But shared computer such as mainframe or minicomputer must keep all users happy
Users of dedicate systems such as workstations have dedicated resources but frequently use shared resources from servers
Handheld computers are resource poor, optimized for usability and battery life
Some computers have little or no user interface, such as embedded computers in devices and automobiles
友好性和效率:二者哪个更重要无法说明
对于如今的windows操作系统,为了实现友好性,CPU占用率相当低;但是在计算机刚刚兴起的时候,硬件的效率更“珍贵”,可能牺牲友好性来实现效率的提升。
OS is a resource allocator 资源分配
Manages all resources
Decides between conflicting requests for efficient and fair resource use
OS is a control program 控制程序
Controls execution of programs to prevent errors and improper use of the computer
操作系统是一直在CPU上运行的(系统)程序 区分操作系统和非操作系统
(在本书中,可以理解kernel(内核)和操作系统一致)
bootstrap program is loaded at power-up or reboot
Typically stored in ROM or EPROM, generally known as firmware
Initializes all aspects of system
Loads operating system kernel and starts execution
附加:操作系统的发展历程
图灵机的发明(纸带,读写头,控制部分(包含一些对应的规则))->阿塔纳索夫 贝利计算机(ABC)(没有指令的概念,和图灵机并不等价)->埃尼阿克计算机(第一台通用电子计算机)->存储程序计算机->第一台存储程序计算机 -> 加载用户程序至内存(放在ROM中,加载程序! 装入引导程序:操作系统 )-> 子程序 子程序库 自己编的程序
注:程序编译之后要链接,链接子程序库(运行时库)……
runtime 运行时系统 C语言函数库,Java虚拟机
中断(CPU)事件的发生通常通过硬件或者软件中断(interrupt)。硬件可随时通过系统总线向CPU发出信号,以触发中断。软件通过执行特别操作系统如系统调用(system call)(也称为监视器调用)也能触发中断。
. 1.内部中断 (CPU自身的中断)比如因为异常或者非法访问等
2.外部中断 外设的原因
计算机操作员:操作系统自己控制,替代了操作员的工作
监控程序:当时只需要监控
作业控制: 任务趋向于复杂 脱机输入输出:大型机计算之后放到小型机然后打印,打印速度相对于计算速度较慢
命令行(CLI)接口 命令解释器(shell) 系统调用:并行控制
计算机有内核态与用户态
ROM引导程序(较短 内存中 ) -> 磁盘引导程序(ROM将其装入)->识别哪一个分区是活动分区->分区引导程序装到内存
分层次的灵活性 ROM和磁盘引导程序不能放到一块,引导程序可能使用外部设备比如U盘引导。
ROM用来选择使用哪个设备进行启动,磁盘引导程序用来引导哪个操作系统
ROM装在CPU上 编址是一块的
引导程序位于系统安装包内??
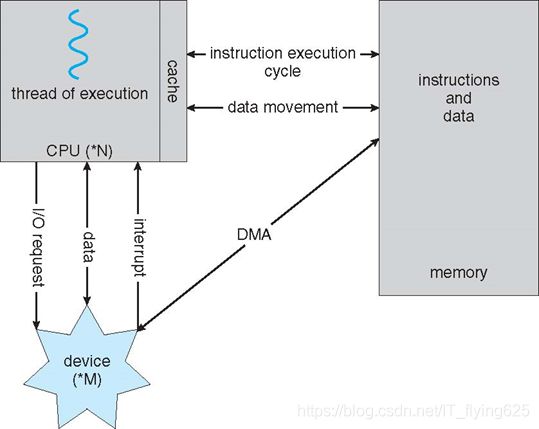
Computer System Organization
计算机组成:并发包括并行 任何一个并行的进程都可以用并发执行来模拟
外部设备 ——控制器—— CPU
都连接到总线上
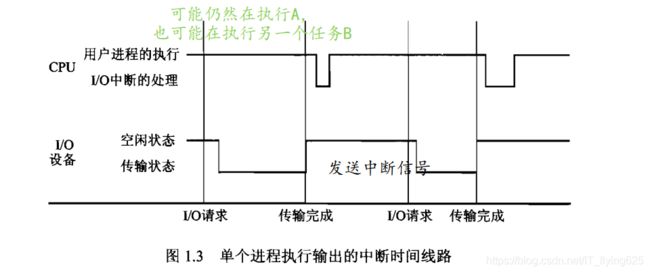
Computer-System Operation
I/O devices and the CPU can execute concurrently 并发工作
Each device controller is in charge of a particular device type
Each device controller has a local buffer
CPU moves data from/to main memory to/from local buffers 局部缓冲区 过程的并发执行
I/O is from the device to local buffer of controller 从外设到缓冲区
Device controller informs CPU that it has finished its operation by causing an interrupt 外部设备发给CPU中断信号
外部设备完成了任务或者出现了问题
Common Functions of Interrupts
Interrupt transfers control to the interrupt service routine generally, through the interrupt vector, which contains the addresses of all the service routines 中断向量
Interrupt architecture must save the address of the interrupted instruction
A trap or exception is a software-generated interrupt caused either by an error or a user request
An operating system is interrupt driven
Storage Structure
Main memory – only large storage media that the CPU can access directly
Random access
Typically volatile 不稳定,易失性
Secondary storage – extension of main memory that provides large nonvolatile storage capacity
Hard disks – rigid metal or glass platters covered with magnetic recording material 硬盘
Disk surface is logically divided into tracks, which are subdivided into sectors
The disk controller determines the logical interaction between the device and the computer
Solid-state disks – faster than hard disks, nonvolatile SSD固态硬盘
Various technologies
Becoming more popular
Storage Hierarchy
Storage systems organized in hierarchy
Speed Cost Volatility
Caching – copying information into faster storage system; main memory can be viewed as a cache for secondary storage
Device Driver for each device controller to manage I/O 驱动程序属于操作系统。
Provides uniform interface between controller and kernel
cache:高速缓存 CPU中,内存中均有
buffer 缓冲区
RAM 内存 随机访问内存 DRAM 动态随机访问内存
驱动程序
Direct Memory Access Structure DMA 直接内存访问 不通过CPU直接从外部设备输出到内存
Used for high-speed I/O devices able to transmit information at close to memory speeds
Device controller transfers blocks of data from buffer storage directly to main memory without CPU intervention
Only one interrupt is generated per block, rather than the one interrupt per byte
How a Modern Computer Works
1.3Computer-System Architecture
Most systems use a single general-purpose processor
Most systems have special-purpose processors as well
Multiprocessors systems growing in use and importance
Also known as parallel systems, tightly-coupled systems
Advantages include:
1.Increased throughput
2.Economy of scale
3.Increased reliability – graceful degradation or fault tolerance
Two types:
1.Asymmetric Multiprocessing – each processor is assigned a specie task.
2.Symmetric Multiprocessing
1.4 Operating System Structure
Multiprogramming (Batch system) needed for efficiency
Single user cannot keep CPU and I/O devices busy at all times
Multiprogramming organizes jobs (code and data) so CPU always has one to executelA subset of total jobs in system is kept in memory
One job selected and run via job scheduling
When it has to wait (for I/O for example), OS switches to another job
Timesharing (multitasking) is logical extension in which CPU switches jobs so frequently that users can interact with each job while it is running, creating interactive computing 分时系统
Response time should be < 1 second 响应时间小于1s
Each user has at least one program executing in memory process 程序的运行过程
If several jobs ready to run at the same time CPU scheduling CPU调度
If processes don’t fit in memory, swapping moves them in and out to run CPU切换
Virtual memory allows execution of processes not completely in memory 虚拟内存
虚拟内存:虚拟内存允许将一个执行的作业不完全放入内存中,主要优点是程序可以比物理内存大。再者,它将内存抽象成一个庞大且同意的存储数组,将用户所理解的逻辑内存与真正的物理内存区分开来
– each processor performs all tasks
1.5 操作系统操作
中断激活 系统调用,时钟,都会激活操作系统
Interrupt driven (hardware and software)
Hardware interrupt by one of the devices
Software interrupt (exception or trap):
Software error (e.g., division by zero)
Request for operating system service
Other process problems include infinite loop, processes modifying each other or the operating system
双重模式操作: