mysql必知必会读书笔记就——联结表、高级联结
vendor表:
products表:
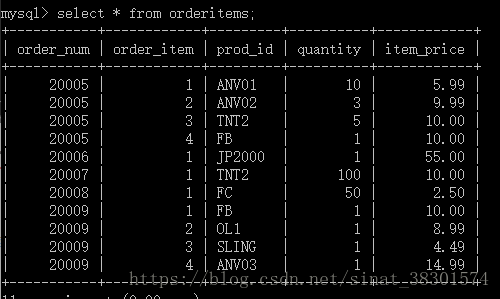
orderitems表:
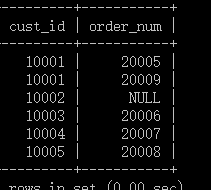
customers表:
orders表:
一.联结表:联结表是一种机制,用来在一条select语句中关联表,因此称为联结表。联结在运行的时候关联表中正确的行。
看个例子:
select vend_name,prod_name,prod_price
from vendors,products
where vendors.vend_id=products.vend_id
order by vend_name,prod_name;
其中where子句作为联结表的条件,当联结来两个表的时候,实际上是将第一个表的每一行与第二个表中的每一行配对,where作为过滤条件,它只包含哪些匹配给定条件(联结条件)的行。
假若没有where子句,则第一个表的每一行与第二个表中的每一行配对,而不管他们逻辑上是否可以匹配。即:在没有联结条件的时候返回的结果为笛卡儿积。检索出的行数是第一个表的行数乘以第二个表的行数。
如:
select vend_name,prod_name,prod_price
from vendors,products
order by vend_name,prod_name;
二.内部联结:
等值联结:基于两个表之间的相等测试,也称内部联结。联结的两个表之间的关系是from子句的组成部分,以inner join指定。联结的条件使用on指定,传给on的条件实际上与传递给where的相同。
如:select vend_name,prod_name,prod_price
from vendors inner join products
on vendors.vend_id=product.vend_id
order by vend_name,prod_name;
三.联结多个表
sql对一条select语句中可以联接的表的数目没有限制。创建联结表的基本规则也相同,首先列出所有的表,然后定义表之间的关系.如:
显示编号为2005的订单中的物品:
select prod_name,vend_name,prod_price,quantity
from orderitems,products,vendors
where products.vend_id=vendors.vend_id
and orderitems.prod_id=products.prod_id
and order_num=20005;
又如,在使用子查询检索订购产品TNT2的客户列表:
select cust_name,cust_contact from customers
where cust_id in(select cust_id from orders
where order_num in(select order_num from orderitems
where prod_id='TNT2'));
现在,我们可以使用联结表的方式来查询:
select cust_name,cust_contact from customers,orders,orderitems
where customers.cust_id=orders.cust_id
and orderitems.order_num=orders.order_num
and prod_id='TNT2';
四.高级联结
1.使用表的别名
作用:
1)缩短sql语句;
2)允许在单条select语句中多次使用相同的表。
别名除了用于列名和计算字段外,还可以给表起别名。
注意:表别名不仅仅可以用于where子句,还可以用于select的列表、order by子句以及语句的其他部分。但,表别名只在查询执行中使用,与列别名不一样,表别名不返回客户机。
如:
select cust_name,cust_contact
from customers as c,orders as o,orderitems as oi
where c.cust_id=o.cust_id
and oi.order_num=o.order_num
and prod_id='TNT2';
2.使用不同类型的联结
之前我们使用了内联结,现在再来看看自联结、自然联结和外部联结。
1)自联结(同一个表相联结),如:当我们发现物品(ID为DTNTR)存在问题,因此我们想知道生产该物品的供应商的其他物品是否也存在这些问题。步骤:首先找到生产ID为DTNTR的物品的供应商,然后找出这个供应商的其他物品。
第一种,可使用子查询:select prod_id,prod_name from products
where vend_id=(select vend_id from products where prod_id='DTNTR');
第二种,使用自联结:select p1.prod_id , p1.prod_name from products as p1, products as p2
where p1.vend_id=p2.vend_id
and p2.prod_id='DTNTR';
首先where通过匹配p1中的vend_id和p2中的vend_id来联结两个表,然后按第二个表中的prod_id过滤数据,返回所需的数据。
总结:用自联结而不用子查询。自联结通常作为外部语句用来替代从相同表中检索数据时使用的子查询语句。虽然,最终的结果是相同的,但有时候处理联结远比处理子查询要快得多。
2)标准的联结(前面所说的内部联结)返回所有数据,甚至相同的列多次出现。自然联结排除多次出现,使得每个列只返回一次。
自然联结:它是这样的一种联结,其中你只能选择那些唯一的列,一般通过对表使用通配符(select *),对所有其他表的列明确使用的子集来完成的。
如:
select c.*,o.order_num,o.order_date,oi.prod_id,oi.quantity,oi.item_price
from customers as c,orders as o,orderitems as oi
where c.cust_id=o.cust_id
and oi.order_num=o.order_num
and prod_id='FB';
通配符只对第一个表使用,所有其他列明确列出,所以没有重复的列被检索出来。
3)外部联结:联结包含了那些在相关表中没有关联行的行,这种类型的联结称为外部联结。
相反,只包含那些有关联行的行的联结称为内部联结。
如:一个简单的内部联结:检索所有客户及其订单。
select customers.cust_id,orders.order_num
from customers inner join orders
on customers.cust_id=orders.cust_id;
为了检索所有的客户,包括那些没有订单的客户,要使用外部联结:
select customers.cust_id,orders.order_num
from customers left outer join orders
on customers.cust_id=orders.cust_id;
关键字outer join指定联结的类型为外联结。在使用outer join语法时,必须使用right或left关键字指定其包括所有行的表(right指出的是outer join右边的表,而left则指出左边的表),即:在本例中使用left outer join从from子句的左边的表(customers表)中选择所有的行
3.使用带聚集函数的联结
如内联结:检索所有客户及其每个客户所下的订单数:
select customers.cust_name,customers.cust_id,count(orders.order_num) as num_ord
from customers inner join orders
on customers.cust_id=orders.cust_id
group by customers.cust_id;
左外联结:
select customers.cust_name,customers.cust_id, count(orders.order_num) as num_ord
from customers left outer join orders
on customers.cust_id=orders.cust_id
group by customers.cust_id;
使用左外联结来包含所有的客户,包括那些没有订单的客户。
4.使用带联结和联结条件
注意事项:
1)注意所使用的联结类型。一般使用内部联结,但使用外部联结也是有效的。
2)保证正确使用联结条件,否则将返回不正确的数据。
3)应该总是提供联结条件,否则会得出笛卡儿积;
4)在一个联结中可以包含多个表,甚至对于每个联结可以采用不同的联结类型。