目录
- WebServer
- 1. 实验目的
- 2. 实验内容
- 3. 程序代码
- 4. 实验过程
- 5. 实验结果
- 6. 实验小结
- UDP Pinger
- 1. 实验目的
- 2. 实验内容
- 3. 程序代码
- 4. 实验过程
- 5. 实验结果
- 6. 实验小结
- STMP
- 1. 实验目的
- 2. 实验内容
- 3. 程序代码
- 4. 实验过程
- 5. 实验结果
- 6. 实验小结
- ProxyServer
- 1. 实验目的
- 2. 实验内容
- 3. 程序代码
- 4. 实验步骤
- 5. 实验结果
WebServer
1. 实验目的
- 了解Python中的TCP套接字编程基础,包括创建套接字,将套接字保定到指定的地址与接口,以及收发包
- 了解一些 HTTP 首部行格式
2. 实验内容
- 开发一个网页服务器,单线程地处理HTTP请求
- 此服务器应该能完成以下工作
- 接收并分析 HTTP 请求
- 从本地文件系统中查找被请求地文件
- 创建包含首部行和请求文件内容的响应报文
- 将响应报文发送给客户端
- 当文件不存在时,应发送给客户端“404 Not Found”
3. 程序代码
#import socket module
from socket import *
import sys # In order to terminate the program
# 1. Create a socket for TCP connection
serverSocket = socket(AF_INET, SOCK_STREAM) # the parameters indicate this is a socket based on Ipv4 and TCP
# Prepare a server socket
serverPort = 6789
serverSocket.bind(('', serverPort))
serverSocket.listen(1) #the parameter specifies the number of unaccepted connections that the system will allow before refusing new connections
while True:
#2. Establish the connection
print('Ready to serve...')
connectionSocket, addr = serverSocket.accept()
try:
# 3. recieve a HTTP query
message = connectionSocket.recv(2048).decode()
print(message)
# 4. search the file in local system
filename = message.split()[1]
f = open(filename[1:])
outputdata = f.read()
# 5. create and send the response message
# Send one HTTP header line into socket
header = 'HTTP/1.1 200 OK\n'
header += 'Connection: close\n'
header += 'Content-Type: text/html\n'
header += 'Content-Length: %d\n\n' % (len(outputdata))
connectionSocket.send(header.encode())
# Send the content of the requested file to the client
for i in range(0, len(outputdata)):
connectionSocket.send(outputdata[i].encode())
#send the end message
connectionSocket.send("\r\n".encode())
except IOError:
#6. Send response message for file not found
connectionSocket.send('HTTP/1.1 404 Not Found'.encode())
connectionSocket.send("\r\n".encode())
connectionSocket.close()
serverSocket.close()
sys.exit()#Terminate the program after sending the corresponding data
4. 实验过程
- 在主机上运行网页服务器代码
WebServer.py - 通过浏览器访问服务器中的文件
http://localhost:6789/HelloWorld.htmlhttp://localhost:6789/NotExisted.html
5. 实验结果
-
使用
http://localhost:6789/HelloWorld.html成功地请求并加载了本地的页面 -
使用
http://localhost:6789/HelloWorld.html得到404的提示 -
网页服务器接收的请求报文部分内容如下
-
GET /HelloWorld.html HTTP/1.1 Host: localhost:6789 Connection: keep-alive Cache-Control: max-age=0 Upgrade-Insecure-Requests: 1 User-Agent: Mozilla/5.0 (Windows NT 10.0; Win64; x64) AppleWebKit/537.36 (KHTML, like Gecko) Chrome/83.0.4103.116 Safari/537.36 Accept: text/html,application/xhtml+xml,application/xml;q=0.9,image/webp,image/apng,*/*;q=0.8,application/signed-exchange;v=b3;q=0.9 Accept-Encoding: gzip, deflate, br Accept-Language: zh-CN,zh;q=0.9,en;q=0.8 Cookie: _ga=GA1.1.873531135.1587267004; _gid=GA1.1.970751890.1594543167
-
6. 实验小结
-
掌握了如何使用Python创建基于TCP连接的服务器端套接字
- 对象
socket - 方法
.bind().listen().accept().send().recv()
- 对象
-
实际查看了 HTTP 的请求报文中的首行部信息,并在响应报文中编辑了相应的首部行
-
header = 'HTTP/1.1 200 OK\n' header += 'Connection: close\n' header += 'Content-Type: text/html\n' header += 'Content-Length: %d\n\n' % (len(outputdata))
-
UDP Pinger
1. 实验目的
- 了解Python中的UDP套接字编程,包括收发数据包、设置套接字超时
- 熟悉Ping的相关应用,如计算丢包率
2. 实验内容
- 学习一个简单的互联网Ping服务器的Python代码,然后完成对应的客户端代码
- 使用了简单的 UDP,而不是 ICMP(Internet Control Message Protocol)
3. 程序代码
# UDPPingerServer.py
# We will need the following module to generate randomized lost packets
import random
from socket import *
# Create a UDP socket
# Notice the use of SOCK_DGRAM for UDP packets
serverSocket = socket(AF_INET, SOCK_DGRAM)
# Assign IP address and port number to socket
serverSocket.bind(('', 12000))
while True:
# Generate random number in the range of 0 to 10
rand = random.randint(0, 10)
# Receive the client packet along with the address it is coming from
message, address = serverSocket.recvfrom(1024)
# Capitalize the message from the client
message = message.upper()
# If rand is less is than 4, we consider the packet lost and do not respond
if rand < 4:
continue
# Otherwise, the server responds
serverSocket.sendto(message, address)
# UDPPingerClient.py
# We will need the following module to calculate the round-trip time
import time
from socket import *
# 1. Create a UDP socket
clientSocket = socket(AF_INET, SOCK_DGRAM) # IPv4 + UDP
# set timeout as 1s
clientSocket.settimeout(1)
# 2. set the address and port of server
# serverName = '***.***.***.***' #server IP
serverName = '127.0.0.1' #localhost, for test
serverPort = 12000
# 3. Ping: send ping package and wait to recieve. The RTT is stored in the array RTTs.
RTTs = []
for i in range(10):
sendTime = time.time()
sentence = 'Ping %d %s' % ((i+1),(sendTime))
try:
clientSocket.sendto(sentence.encode(), (serverName, serverPort))
modifiedMessage, hostAddress = clientSocket.recvfrom(2048)
RTT = time.time() - sendTime
RTTs.append(RTT)
print('Sequence %d: Reply from %s, RTT = %.3fs.' % ((i+1), hostAddress, RTT))
print(modifiedMessage.decode())
except Exception as e:
print('Sequence %d: Request time out.' % (i+1))
# 4. Post processing: calculate some statistical information, then display them
maxRTT = max(RTTs)
minRTT = min(RTTs)
meanRTT = sum(RTTs)/len(RTTs)
print('**********************************************************************')
print(('The max RTT is: %.3fs. \nThe min RTT is: %.3fs.\nThe average RTT is : %.3fs')
% (maxRTT, minRTT, meanRTT))
4. 实验过程
- 分别在两台主机上运行
UDPPingerServer.py和UDPPingerClient.py,或者在同一台主机上运行两个程序,注意此时IP地址要使用localhost - 观察客户端的输出
5. 实验结果
Sequence 1: Reply from ('127.0.0.1', 12000), RTT = 0.001s.
PING 1 1594798645.6439474
Sequence 2: Reply from ('127.0.0.1', 12000), RTT = 0.001s.
PING 2 1594798645.6459286
Sequence 3: Reply from ('127.0.0.1', 12000), RTT = 0.000s.
PING 3 1594798645.6493983
Sequence 4: Reply from ('127.0.0.1', 12000), RTT = 0.001s.
PING 4 1594798645.6518812
Sequence 5: Reply from ('127.0.0.1', 12000), RTT = 0.000s.
PING 5 1594798645.6535127
Sequence 6: Request time out.
Sequence 7: Reply from ('127.0.0.1', 12000), RTT = 0.000s.
PING 7 1594798646.6565206
Sequence 8: Reply from ('127.0.0.1', 12000), RTT = 0.000s.
PING 8 1594798646.6580553
Sequence 9: Request time out.
Sequence 10: Reply from ('127.0.0.1', 12000), RTT = 0.000s.
PING 10 1594798647.6608508
**********************************************************************
The max RTT is: 0.001s.
The min RTT is: 0.000s.
The average RTT is : 0.001s
6. 实验小结
- 学习了Python中UDP套接字相关的方法
.recv()的返回是一个元组,由两个元素组成,分别是报文和发送方的地址.sendto(message, address).settimeout()
- Python可以方便的进行字符串格式化输出
sentence = 'Ping %d %s' % ((i+1),(sendTime))
STMP
1. 实验目的
- 通过实践进一步了解 STMP
2. 实验内容
- 通过 STMP 连接邮件服务器,与之对话(dialogue),并最终发送邮件报文
3. 程序代码
from socket import *
import base64
# message content
msg = "\r\n I love computer networks!"
subject = 'Computer networks'
contentType = 'text/plain'
endMsg = "\r\n.\r\n"
# Choose a mail server (e.g. Google mail server) and call it mailServer
mailServer = 'pop.qq.com'
# Create socket called clientSocket and establish a TCP connection with mailServer
# Sender and reciever
fromAddress = "********@qq.com" #your email eddress
toAddress = "*******@qq.com" #reciever address, can be the same to fromaddress
# Auth information (Encode with base64, which is suitable for mail to transmit data safely.)
username = base64.b64encode(fromAddress.encode()).decode()
password = base64.b64encode("************".encode()).decode() #not your password, but Authorization code!!! see https://service.mail.qq.com/cgi-bin/help?subtype=1&&no=1001256&&id=28
# Create clientSocket
print('connect to mailServer:')
clientSocket = socket(AF_INET, SOCK_STREAM)
clientSocket.connect((mailServer, 25))
recv = clientSocket.recv(1024).decode()
print(recv)
if recv[:3] != '220':
print('220 reply not received from server.')
# Send HELO command and print server response.
print('send HELO command:')
heloCommand = 'HELO Alice\r\n'
clientSocket.send(heloCommand.encode())
recv1 = clientSocket.recv(1024).decode()
print(recv1)
if recv1[:3] != '250':
print('250 reply not received from server.')
#Authorization
print('send AUTH LOGIN:')
clientSocket.sendall('AUTH LOGIN\r\n'.encode())
recv = clientSocket.recv(1024).decode()
print(recv)
if (recv[:3] != '334'):
print('334 reply not received from server')
print('Send username:')
clientSocket.sendall((username + '\r\n').encode())
recv = clientSocket.recv(1024).decode()
print(recv)
if (recv[:3] != '334'):
print('334 reply not received from server')
print('Send password:')
clientSocket.sendall((password + '\r\n').encode())
recv = clientSocket.recv(1024).decode()
print(recv)
if (recv[:3] != '235'):
print('235 reply not received from server')
# Send MAIL FROM command and print server response.
print('Send FROM command:')
fromCommand = 'MAIL FROM: <' + fromAddress + '>\r\n' #must be the same of fromAddress
clientSocket.send(fromCommand.encode())
recv = clientSocket.recv(1024).decode()
print(recv)
if (recv[:3] != '250'):
print('250 reply not received from server')
# Send RCPT TO command and print server response.
print('Send RCPT command:')
rcptCommand = 'RCPT TO: <' + toAddress + '>\r\n'
clientSocket.send(rcptCommand.encode())
recv = clientSocket.recv(1024).decode()
print(recv)
if (recv[:3] != '250'):
print('250 reply not received from server')
# Send DATA command and print server response.
print('Send DATA command:')
clientSocket.send('DATA\r\n'.encode())
recv = clientSocket.recv(1024).decode()
print(recv)
if (recv[:3] != '354'):
print('354 reply not received from server')
# Send message data.
message = 'from:' + fromAddress + '\r\n'
message += 'to:' + toAddress + '\r\n'
message += 'subject:' + subject + '\r\n'
message += 'Content-Type:' + contentType + '\t\n'
message += '\r\n' + msg
clientSocket.sendall(message.encode())
# Message ends with a single period.
print('Send endMsg:')
clientSocket.send(endMsg.encode())
recv = clientSocket.recv(1024).decode()
print(recv)
if (recv[:3] != '250'):
print('250 reply not received from server')
# Send QUIT command and get server response.
print('Send QIUT command')
clientSocket.send('QUIT\r\n'.encode())
recv = clientSocket.recv(1024).decode()
print(recv)
if (recv[:3] != '221'):
print('reply not received from server')
# Close connection
clientSocket.close()
4. 实验过程
- 运行代码,观察输出,并在邮箱中查看邮件。
5. 实验结果
-
#output: # connect to mailServer: # 220 newxmesmtplogicsvrszb5.qq.com XMail Esmtp QQ Mail Server. # send HELO command: # 250-newxmesmtplogicsvrszb5.qq.com-100.66.14.230-51224702 # 250-SIZE 73400320 # 250 OK # send AUTH LOGIN: # 334 VXNlcm5hbWU6 # Send username: # 334 UGFzc3dvcmQ6 # Send password: # 235 Authentication successful # Send FROM command: # 250 OK. # Send RCPT command: # 250 OK # Send DATA command: # 354 End data with. . # Send endMsg: # 250 OK: queued as. # Send QIUT command # 221 Bye. -
在收件箱中成功查看邮件
6. 实验小结
- 从代码中可以看出,STMP依靠TCP实现可靠数据传输,而非UDP
- STMP使用端口 25
- 使用
base64来进行邮件报文编码 - 与邮件服务器的对话包含一下几个基本环节
- HELO
- AUTH LOGIN
- FROM
- RCPT
- DATA + message + endMsg
- QUIT
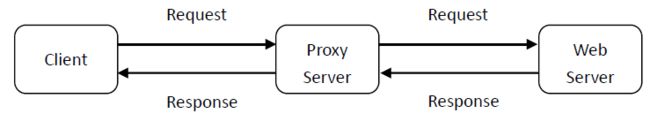
ProxyServer
1. 实验目的
- 实际观察代理服务器的工作过程与缓存功能
2. 实验内容
3. 程序代码
# ProxyServer.py
from socket import *
# 1. Create a server socket, bind it to a port and start listening
port = 8888
tcpSerSock = socket(AF_INET, SOCK_STREAM)
tcpSerSock.bind(('', port))
tcpSerSock.listen(1)
while True:
# 2. Strat receiving data from the client
print('Ready to serve...')
tcpCliSock, addr = tcpSerSock.accept()
print('Received a connection from:', addr)
message = tcpCliSock.recv(2048).decode()
print(message)
# 3. Extract the filename from the given message
print(message.split()[1])
filename = message.split()[1].partition("/")[2]
print(filename)
fileExist = "false"
fileToUse = "/" + filename
print(fileToUse)
try:
# 4. Check wether the file exist in the cache
f = open(fileToUse[1:], "r")
outputdata = f.readlines()
fileExist = "true"
# 5. ProxyServer finds a cache hit and generates a response message
tcpCliSock.send("HTTP/1.0 200 OK\r\n")
tcpCliSock.send("Content-Type:text/html\r\n")
tcpCliSock.send("Content-Length:" + len(outputdata) + "\r\n")
for i in range(0, len(outputdata)):
tcpCliSock.send(outputdata[i].encode())
print('Read from cache')
# 5. Error handling for file not found in cache
except IOError:
if fileExist == "false":
# Create a socket on the proxyserver
c = socket(AF_INET, SOCK_STREAM)
hostn = filename.replace("www.","",1)
print("Host name:" + hostn)
try:
# Connect to the socket to port 80
c.connect((hostn, 80))
print('Socket connected to port 80 of the host')
newMessage = message.replace('localhost:' + port, hostn)
print('newMessage:')
print(newMessage)
c.sendall(newMessage.encode())
# 6. Create a new file in the cache for the requested file.
# Also send the response in the buffer to client socket
# and the corresponding file in the cache
# Read the response into buffer
buff = c.recv(4096)
tmpFile = open("./" + filename,"w")
tmpFile.writelines(buff.decode().replace('\r\n','\n'))
tcpCliSock.sendall(buff)
tmpFile.close()
except Exception as e:
print(e)
print("Illegal request")
else:
# HTTP response message for file not found
print('File Not Found')
# 7. Close the client and the server sockets
tcpCliSock.close()
tcpSerSock.close()
4. 实验步骤
- 在主机上运行代码
ProxyServer.py - 首次通过浏览器访问
http://localhost:8888/www.baidu.com - 再次通过浏览器访问
http://localhost:8888/www.baidu.com
5. 实验结果
- 首次运行代码后,在代码的根目录下,创建了一个新的文件
www.baidu.com