Android4.4-Launcher源码分析系列之CellLayout
一.CellLayout是什么
在前面的 Android4.4-Launcher源码分析系列之Launcher介绍分析了Launcher的布局,CellLayout继承自ViewGroup,
一个Workspace由多个CellLayout组成,每一个CellLayout负责里面图标(favorite)和widget的显示.说白了,我们滑动屏幕的每一页就是一个CellLayout.
二、CellLayout的布局
CellLayout的布局为workspace_screen.xml.
hapticFeedbackEnabled是触力反馈的意思,比如说按一下震动就是触力反馈.
maxGap是CellLayout中元素(图标,widget)之间的最大距离
除了这两个属性其他的属性都是在代码中定义的.
WorkSpace是在insertNewWorkspaceScreen方法中加载CellLayout的布局的.
/**
* @param screenId 屏幕Id
* @param insertIndex 插入的序号
* 插入新的屏幕
*/
public long insertNewWorkspaceScreen(long screenId, int insertIndex) {
System.out.println(".............WorkSpace.......增加一页");
if (mWorkspaceScreens.containsKey(screenId)) {
throw new RuntimeException("Screen id " + screenId + " already exists!");
}
//加载CellLayout的布局
CellLayout newScreen = (CellLayout)mLauncher.getLayoutInflater().inflate(R.layout.workspace_screen, null);
newScreen.setOnLongClickListener(mLongClickListener);
newScreen.setOnClickListener(mLauncher);
newScreen.setSoundEffectsEnabled(false);
mWorkspaceScreens.put(screenId, newScreen);
mScreenOrder.add(insertIndex, screenId);
addView(newScreen, insertIndex);
return screenId;
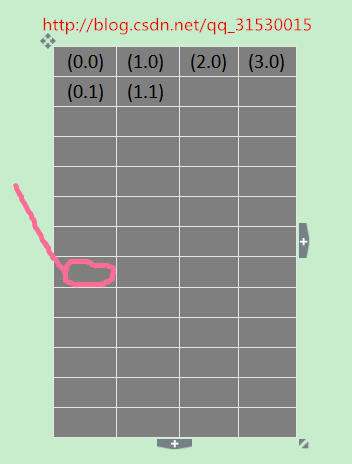
}CellLayout上有很多Cell,都有对应的坐标
红色圆圈就是一个Cell.一个item可以占多个Cell. 那么怎么知道一个item的起始坐标,占据多少格呢,CellLayout类里有一个静态内部类CellInfo用来纪录这些信息.
static final class CellInfo {
View cell; //当前这个item对应的View
int cellX = -1; //该item水平方向上的起始单元格
int cellY = -1; //该item垂直方向上的起始单元格
int spanX; //该item水平方向上占据的单元格数目
int spanY; //该item垂直方向上占据的单元格数目
long screenId; //屏幕所在的Id
long container;
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Cell[view=" + (cell == null ? "null" : cell.getClass())
+ ", x=" + cellX + ", y=" + cellY + "]";
}
}之前说过CellLayout的主要属性都在代码里定义的,那我们就看下它的一些重要的属性.
//item之间的宽度
mWidthGap = mOriginalWidthGap =0;
//item之间的高度
mHeightGap = mOriginalHeightGap = 0;现在我把item之间的宽度调到50像素,看下对比
//一行有多少个Cell
mCountX = (int) grid.numColumns;
//一列有多少个Cell
mCountY = (int) grid.numRows;DeviceProfile grid = app.getDynamicGrid().getDeviceProfile();DeviceProfile类里定义了整个Launcher的很多属性
class DeviceProfile {
String name;
float minWidthDps;
float minHeightDps;
float numRows;
float numColumns;
float iconSize;
float iconTextSize;
float numHotseatIcons;
float hotseatIconSize;
boolean isLandscape;
boolean isTablet;
boolean isLargeTablet;
boolean transposeLayoutWithOrientation;
int desiredWorkspaceLeftRightMarginPx;
int edgeMarginPx;
Rect defaultWidgetPadding;
int widthPx;
int heightPx;
int availableWidthPx;
int availableHeightPx;
int iconSizePx;
int iconTextSizePx;
int cellWidthPx;
int cellHeightPx;
int folderBackgroundOffset;
int folderIconSizePx;
int folderCellWidthPx;
int folderCellHeightPx;
int hotseatCellWidthPx;
int hotseatCellHeightPx;
int hotseatIconSizePx;
int hotseatBarHeightPx;
int hotseatAllAppsRank;
int allAppsNumRows;
int allAppsNumCols;
int searchBarSpaceWidthPx;
int searchBarSpaceMaxWidthPx;
int searchBarSpaceHeightPx;
int searchBarHeightPx;
int pageIndicatorHeightPx;继续介绍CellLayout的属性.
这是CellLayout缩略图背景,就是当你长按屏幕空白处时CellLayout缩小时的背景图.
mNormalBackground = res.getDrawable(R.drawable.screenpanel);下面两个分别是滑动屏幕到左右边缘,继续拖动而不能滑动过去时显示的背景.
mOverScrollLeft = res.getDrawable(R.drawable.overscroll_glow_left)
mOverScrollRight = res.getDrawable(R.drawable.overscroll_glow_right);CellLayout只有一个onInterceptTouchEvent方法
@Override
public boolean onInterceptTouchEvent(MotionEvent ev) {
final int action = ev.getAction();
if (action == MotionEvent.ACTION_DOWN) {
System.out.println(".................776"+"ACTION_DOWN1");
//清除cellInfo信息
clearTagCellInfo();
}
if (mInterceptTouchListener != null && mInterceptTouchListener.onTouch(this, ev)) {
return true;
}
if (action == MotionEvent.ACTION_DOWN) {
System.out.println(".................787"+"ACTION_DOWN2");
setTagToCellInfoForPoint((int) ev.getX(), (int) ev.getY());
}
return false;
}默认是返回false的,如果mInterceptTouchListener不为空并且执行了onTouch方法那么返回true.mInterceptTouchListener
是在setOnInterceptTouchListener方法里初始化的.
public void setOnInterceptTouchListener(View.OnTouchListener listener) {
mInterceptTouchListener = listener;
}
CellLayout cl = ((CellLayout) child);
cl.setOnInterceptTouchListener(this);clearTagCellInfo方法是是清除cellInfo的信息,然后设置一个Tag
private void clearTagCellInfo() {
final CellInfo cellInfo = mCellInfo;
cellInfo.cell = null;
cellInfo.cellX = -1;
cellInfo.cellY = -1;
cellInfo.spanX = 0;
cellInfo.spanY = 0;
setTag(cellInfo);
}
public void setTagToCellInfoForPoint(int touchX, int touchY) {
final CellInfo cellInfo = mCellInfo;
Rect frame = mRect;
final int x = touchX + getScrollX();
final int y = touchY + getScrollY();
final int count = mShortcutsAndWidgets.getChildCount();
boolean found = false;
for (int i = count - 1; i >= 0; i--) {
final View child = mShortcutsAndWidgets.getChildAt(i);
final LayoutParams lp = (LayoutParams) child.getLayoutParams();
//如果item可见并且item有动画
if ((child.getVisibility() == VISIBLE || child.getAnimation() != null) &&
lp.isLockedToGrid) {
//获取item的尺寸信息,相对于CellLayout
child.getHitRect(frame);
float scale = child.getScaleX();
frame = new Rect(child.getLeft(), child.getTop(), child.getRight(),
child.getBottom());
frame.offset(getPaddingLeft(), getPaddingTop());
frame.inset((int) (frame.width() * (1f - scale) / 2),
(int) (frame.height() * (1f - scale) / 2));
//如果当前事件正好落在该child上
if (frame.contains(x, y)) {
cellInfo.cell = child;
cellInfo.cellX = lp.cellX;
cellInfo.cellY = lp.cellY;
cellInfo.spanX = lp.cellHSpan;
cellInfo.spanY = lp.cellVSpan;
found = true;
break;
}
}
}
mLastDownOnOccupiedCell = found;
//如果点击的是空白区域
if (!found) {
final int cellXY[] = mTmpXY;
//得到当前事件所在的单元格
pointToCellExact(x, y, cellXY);
//然后保存当前位置信息
cellInfo.cell = null;
cellInfo.cellX = cellXY[0];
cellInfo.cellY = cellXY[1];
cellInfo.spanX = 1;
cellInfo.spanY = 1;
}
//将位置信息保存在CellLayout的tag中
setTag(cellInfo);
}