学习笔记----MySQL_增删改查(curd)基本使用
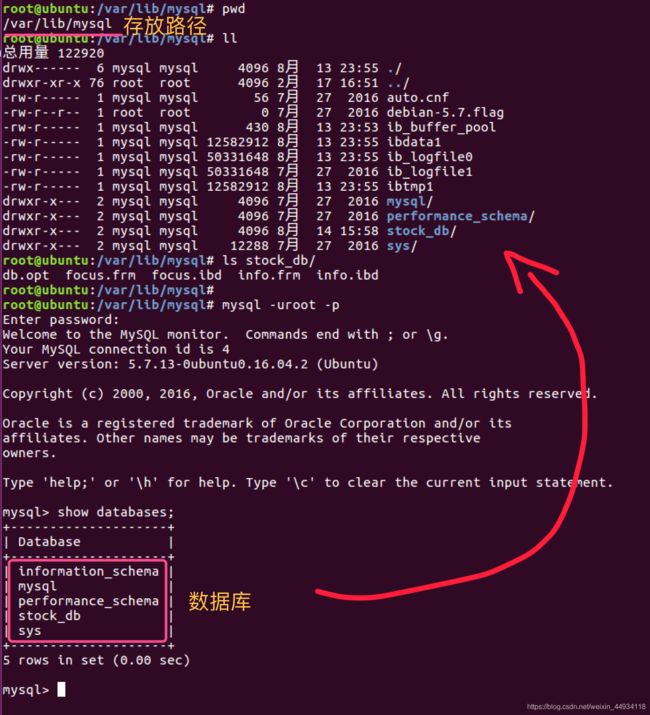
数据库
关系型数据库的核心元素
- 数据行(记录)
- 数据列(字段)
- 数据表(数据行的集合)
- 数据库(数据表的集合)
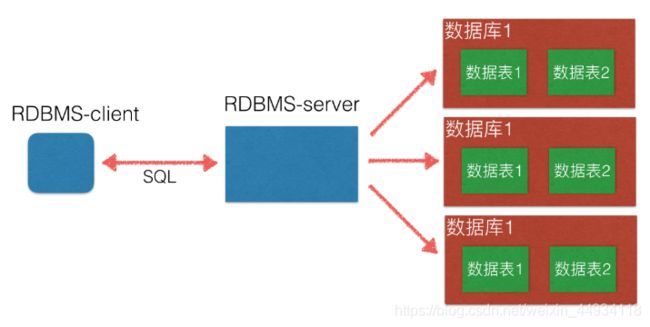
RDBMS
Relational Database Management System
通过表来表示关系型
- 当前主要使用两种类型的数据库:关系型数据库、非关系型数据库。
- 所谓的关系型数据库RDBMS,是简历在关系模型基础上的数据库,借助于集合代数等数学概念和方法来处理数据库中的数据
- 关系型数据库的主要产品:
- oracle:在以前的大型项目中使用,银行,电信等项目
- mysql:web时代使用最广泛的关系型数据库
- ms sql server:在微软的项目中使用
- sqlite:轻量级数据库,主要应用在移动平台
RDBMS和数据库的关系
SQL
Structured Query Language
SQL是结构化查询语言,是一种用来操作RDBMS的数据库语言,当前关系型数据库都支持使用SQL语言进行操作,也就是说可以通过 SQL 操作 oracle,sql server,mysql,sqlite 等等所有的关系型的数据库
- SQL语句主要分为:
- DQL:数据查询语言,用于对数据进行查询,如select
- DML:数据操作语言,对数据进行增加、修改、删除,如insert、udpate、delete
- TPL:事务处理语言,对事务进行处理,包括begin transaction、commit、rollback
- DCL:数据控制语言,进行授权与权限回收,如grant、revoke
- DDL:数据定义语言,进行数据库、表的管理等,如create、drop
- CCL:指针控制语言,通过控制指针完成表的操作,如declare cursor - 对于web程序员来讲,重点是数据的crud(增删改查),必须熟练编写DQL、DML,能够编写DDL完成数据库、表的操作,其他语言如TPL、DCL、CCL了解即可
- SQL是一门特殊的语言,专门用来操作关系数据库
- 不区分大小写
Mysql训练笔记
-- 基本使用
-- 修改表-添加字段
-- alter table 表名 add 列名 类型;
alter table students add birthday datetime;
-- 修改表-修改字段:不需命名版
-- alter table 表明 modify 列名 类型及约束;
alter table students modify birthday date;
-- 修改表-修改字段:重命名版
-- alter table 表名 change 原名 新名 类型及约束;
alter table students change birthday birth date default "2000-01-01";
-- 修改表-删除字段
-- alter table 表名 drop 列名;
alter table students drop high;
-- 删除表
-- drop table 表名;
-- drop datebase 数据库;
-- drop table 数据表;
-- 查看表的创建语句
-- show create table 表名字;
show create table students;
-- 增删改查(curd)
-- 增加
-- 全列插入
-- insert [into] 表名 values(...)
-- 主键字段 可以用 0 null default 来占位
-- 向classes表中插入 一个班级
insert into classes values(0,"菜鸟班");
+----------+----------------------------+------+-----+---------+----------------+
| Field | Type | Null | Key | Default | Extra |
+----------+----------------------------+------+-----+---------+----------------+
| id | int(10) unsigned | NO | PRI | NULL | auto_increment |
| name | varchar(30) | YES | | NULL | |
| age | tinyint(3) unsigned | YES | | NULL | |
| gender | enum('男','女','保密') | YES | | 保密 | |
| cls_id | int(10) unsigned | YES | | NULL | |
| birthday | date | YES | | NULL | |
+----------+----------------------------+------+-----+---------+----------------+
-- 向students表插入 一个学生信息
insert into students values(0,"小李飞刀",20,"女",1,"1990-01-01");
insert into students values(null, "小李飞刀", 20, "女", 1, "1990-01-01");
insert into students values(default, "小李飞刀", 20, "女", 1, "1990-01-01");
-- 失败
-- insert into students values(default, "小李飞刀", 20, "第4性别", 1, "1990-01-01");
-- 枚举中的下标从1开始 1---->"男" 2---->"女"...
insert into students values(default, "小李飞刀", 20, 1, 1, "1990-01-01");
-- 部分插入
-- insert into 表名 (列1,...) values(值1,...)
insert into students (name, gender)values (小乔", 2);
-- 多行插入
insert into students (name, gender)values ("小乔", 2),("貂蝉", 2);
insert into students values(default, "西施", 20, "女", 1, "1990-01-01"), (default, "王昭君", 20, "女", 1, "1990-01-01");
-- 修改
update 表名 set 列1=值1, 列2=值2... where 条件;
update students set age=22, gender=1 where id=3;
-- 查询_基本使用
-- 查询所有列
-- select * from 表名;
select * from students;
-- 指定条件查询
select * from students where name="小李飞刀"; -- 查询name为小李飞刀的所有信息
select * from students where id>3;
-- 查询指定列
-- select 列1,列2,... from 表名;
select name,gender from students;
-- 可以使用as为列或表指定别名
-- select 字段[as 别名], 字段[as 别名] from 数据表 where ...;
select name as 姓名,gender as 性别 from students;
-- 字段的顺序
select gender as 性别, name as 姓名 from students;
-- 删除
-- 物理删除
-- delete from 表名 where 条件
delete from students; -- 整个数据表中的所有数据全部删除
delete from students where name="小李飞刀";
-- 逻辑删除
-- 用一个字段来表示 这条信息是否已经不能在使用了
-- 给students表添加一个is_delete字段 bit类型
alter tables students add is_delete bit default 0;
update students set is_delete=1 where id=6;
针对查询语句训练
-- 数据的准备
-- 创建一个数据库
create database python_test charset=utf8;
-- 使用一个数据库
use python_test;
-- 显示使用的当前数据库是哪个?
select databese();
-- 创建一个数据表;
-- students表
create table students(
id int unsigned primary key auto_increment not null,
name varchar(20) default '',
age tinyint unsigned default 0,
height decimal(5,2),
gender enum('男','女','中性','保密') default '保密',
cls_id int unsigned default 0,
is_delete bit default 0
);
-- classes表
create table classes (
id int unsigned auto_increment primary key not null,
name varchar(30) not null
);
-- 查询
-- 查询所有字段
-- select * from 表名;
select * from students;
select * from classes;
select id, name from classes;
-- 查询指定字段
-- select 列1, 列2, ... from 表名;
select name, age from students;
-- 使用 as 给字段起别名
-- select 字段 as 名字... from 表名;
select name as 姓名, age as 年龄 from students;
-- select 表名.字段 ... from 表名;
select students.name, students.age from students;
-- 可以通过 as 给表起别名
-- select 别名.字段 ... from 表名 as 别名;
select students.name, students.age from students;
select s.name, s.age from students as s;
-- 失败的select students.name, students.age from students as s;
-- 消除重复行
-- distinct 字段
select distinct gender from students;
-- 条件查询
-- 比较运算符
-- select ... from 表名 where ...
-- >
-- 查询大于18岁的信息
select * from students where age>18;
select id, name, gender from students where age>18;
-- <
-- 查询小于18岁的信息
select * from students where age<18;
-- >=
-- <=
-- 查询小于或等于18岁的信息
select * from students where age<=18;
-- =
-- 查询年龄为18岁的所有学生的名字
select * from students where age=18;
-- !=或者<> 不等于
-- 逻辑运算符
-- and
-- 18到28之间的所有学生信息
select * from students where age>18 and age<28;
-- 失败select * from students where age>18 and <28;
-- 18岁以上的女性
select * from students where age>18 and gender="女";
select * from students where age>18 and gender=2;
-- or
-- 不在18岁以上的女性这个范围内的信息
-- select * from students where not age>18 and not gender=2;
select * from students where not (age>18 and gender=2);
-- 年龄不是小于或等于18 并且是女性
select * from students where (not age<=18) and gender=2;
-- 模糊查询
-- like
-- % 替换1个或者多个
-- _替换1个
-- 查询姓名中 以“小”开始的名字
select name from students where name like "小%";
-- 查询姓名中 有“小”所有的名字
select name from students where name like "%小%";
-- 查询有2个字的名字
select name from students where name like "__";
-- 查询有3个字的名字
select name from students where name like "___";
-- 查询至少有2个字的名字
select name from students where name like "__%";
-- rlike 正则
-- 查询以 周开始的名字
select name from students where name rlike “^周.*";
-- 查询以 周开头,伦结尾的姓名
select name from students where name rlike "^周.*伦";
-- 范围查询
-- in(1, 3, 8)表示在一个非连续的范围内
-- 查询 年为18、34的姓名
select name,age from students where age=18 or age=34;
select name,age from students where age in(12, 18, 34);
-- not in 不非连续的范围之内
-- 年龄不是18、34年之间的信息
select name,age from students where age not between 18 and 34;
select name,age from students where not age between 18 and 34;
-- 失败select name,age from students where age not (between 18 and 34);
-- 空判断
-- 判空is null
-- 查询身高为空的信息
select * from students where height is null;
-- 判非空is not null
select * from students where height is not null;
-- 排序
-- order by 字段
-- asc 从小到大排序,即升序
-- desc 从大到小排序,即降序
-- 查询年龄在18到34岁之间的男性,按照年龄从小到大排序
select * from students where (age between 18 and 34) and gender=1;
select * from students where (age between 18 and 34) and gender=1 order by age;
select * from students where (age between 18 and 34) and gender=1 order by age asc;
-- 查询年龄在18到34岁之间的女性,身高从高到矮排序
select * from students where (age between 18 and 34) and gender=2 order by height desc;
-- order by 多个字段
-- 查询年龄在18到34岁之间的女性,身高从高到矮排序,如果身高相同的情况下按照年龄从小到大排序
select * from students where (age between 18 and 34) and gender=2 order by height desc,age asc;
-- 查询年龄在18到34岁之间的女性,身高从高到矮排序,如果身高相同的情况下按照年龄从小到大排序,如果年龄也相同那么按照id从大到小排序
select * from students where (age between 18 and 34) and gender=2 order by height desc,age asc,id desc;
-- 按照年龄从小到大,身高从高到矮的排序
select * from students order by age asc,height desc;
-- 聚合函数
-- 总数
-- count
-- 查询男性有多少人,女性有多少人
select * from students where gender=1;
select count(*) as 男性人数 from students where gender=1;
select count(*) as 女性人数 from students where gender=2;
-- 最大值
-- max
-- 查询最大的年龄
select max(age) from students;
-- 查询女性的最高身高
select max(height) from students where gender=2;
-- 最小值
-- min
-- 求和
-- sum
-- 计算所有人年龄总和
select sum(age) from students;
-- 计算平均年龄 sum(age)/count(*)
select avg(age) from students;
select sum(age)/count(*) from students;
-- 四舍五入 round(123.23 , 1) 保留1位小数
-- 计算所有人的平均年龄,保留2位小数
select round(avg(age) , 2) from students;
-- 计算男性的平均身高 保留2位小数
select round(avg(height) , 2) from students where gender=1;
-- 分组 (与聚合一起用才能显示分组的意义)
-- group by
-- 按照性别分组,查询所有的性别
select gender from students group by gender;
-- 计算每种性别中的人数
select gender, count(*) from students group by gender;
-- 计算男性的人数
select gender, count(*) from students where gender=1 group by gender;
-- group_concat(...)
-- 查询同种性别中的姓名
select gender, group_concat(name) from students where gender=1 group by gender;
select gender, group_concat(name,age, id) from students where gender=1 group by gender;
select gender, group_concat(name, "_", age, "_", id) from students where gender=1 group by gender;
-- having
-- 查询平均年龄超过30岁的性别,以及姓名 having avg(age) > 30
select gender, group_concat(name), avg(age) from students group by gender having avg(age)>30;
-- 查询每种性别中的人数多于2个的信息
select gender,group_concat(name) from students group by gender having count(*)>2;
-- 分页
-- limit start, count
-- 限制查询出来的数据个数
select * from students where gender=1 limit 2;
-- 查询前5个数据
select * from students limit 0, 5;
-- 查询id6-10(包含)的书序
select * from students limit 5, 5;
-- 每页显示2个,第1个页面
select * from students limit 0, 2;
-- 每页显示2个,第2个页面
select * from students limit 2, 2;
-- 每页显示2个,第3个页面
select * from students limit 4, 2;
-- 每页显示2个,第4个页面
select * from students limit 6, 2; -----> limit (第N页-1)*每页的个数, 每页的个数;
-- 每页显示2个,显示第6页的信息,按照年龄从小到大排序
-- 失败select * from students limit 2*(6-1), 2;
-- 失败select * from students limit 10,2 order by age asc;
select * from students order by age asc limit 10, 2;
-- 查询所有女性信息并且按照身高从高到矮排序,只显示2个
select * from students where gender=2 order by height desc limit 2;
-- 连接查询
-- inner join ... on
-- select ... from 表A inner join 表B;
select * from students inner join classes;
-- 查询 有能够对应班级的学生以及班级信息
select * from students inner join classes on students.cls_id=classes.id;
-- 按照要求显示姓名、班级
select students.*,classes.name from students inner join classes on students.cls_id=classes.id;
select students.name,classes.name from students inner join classes on students.cls_id=classes.id;
-- 给数据表起名字
select s.name,c.name from students as s inner join classes as c on s.cls_id=c.id;
-- 查询 有能够对应班级的学生以及班级信息,显示学生的所有信息,只显示班级名称
select s.*,c.name from students as s inner join classes as c on s.cls_id=c.id;
-- 在以上的查询中,将班级姓名显示在第1列
select c.name, s.*from students as s inner join classes as c on s.cls_id=c.id;
-- 查询 有能够对应班级的学生以及班级信息,按照班级进行排序
select c.name, s.*from students as s inner join classes as c on s.cls_id=c.id order by c.name asc;
-- 当时同一个班级的时候,按照学生的id进行从小到大排序
select c.name, s.*from students as s inner join classes as c on s.cls_id=c.id order by c.name asc,s.id asc;
-- left join
-- 查询每位学生对应的班级信息
select * from students as s left join classes as c on s.cls_id=c.id;
-- 查询没有对应班级信息的学生
-- 表中查询条件用where 集间查询条件用having
select * from students as s left join classes as c on s.cls_id=c.id having c.id is null;
select * from students as s left join classes as c on s.cls_id=c.id where c.id is null;
-- right join on
-- 将数据名字互换位置,用left join完成
-- 自关联
-- 查询出山东省有哪些城市
select * from province_city_county as province inner join province_city_county as city on city.pid=province.id having name="山东省";
select province.name, city.name from province_city_county as province inner join province_city_county as city opid=province.id having province.name="山东省";
-- 查询出青岛市有哪些县城
select city.name, county.name from province_city_county as city inner join province_city_county as county on county.pid=city.id having city.name="青岛市";
-- 子查询
-- 标量子查询
-- 查询出高于平均身高的信息
select * from students where height > (select avg(height) from students);
-- 查询最高的男生信息
select * from students where height = (select max(height) from students);
-- 列级子查询
-- 查询学生的班级号能够对应的学生信息
select * from students where cls_id in (select id from classes);
MySQL与Python交互
引入模块
- 在py文件中引入pymysql模块
from pymysql import *
Connection 对象
- 用于建立与数据库的连接
- 创建对象:调用connect()方法
conn=connect(参数列表)
- 参数host:连接的mysql主机,如果本机是’localhost’
- 参数port:连接的mysql主机的端口,默认是3306
- 参数database:数据库的名称
- 参数user:连接的用户名
- 参数password:连接的密码
- 参数charset:通信采用的编码方式,推荐使用utf8
对象的方法
- close()关闭连接
- commit()提交
- cursor()返回Cursor对象,用于执行sql语句并获得结果
Cursor对象
- 用于执行sql语句,使用频度最高的语句为select、insert、update、delete
- 获取Cursor对象:调用Connection对象的cursor()方法
cs1=conn.cursor()
对象的方法
- close()关闭
- execute(operation [, parameters ])执行语句,返回受影响的行数,主要用于执行insert、update、delete语句,也可以执行create、alter、drop等语句
- fetchone()执行查询语句时,获取查询结果集的第一个行数据,返回一个元组
- fetchall()执行查询时,获取结果集的所有行,一行构成一个元组,再将这些元组装入一个元组返回
对象的属性
- rowcount只读属性,表示最近一次execute()执行后受影响的行数
- connection获得当前连接对象
Demo演示
增删改
from pymysql import *
def main():
# 创建Connection连接
conn = connect(host='localhost',port=3306,database='jing_dong',user='root',password='mysql',charset='utf8')
# 获得Cursor对象
cs1 = conn.cursor()
# 执行insert语句,并返回受影响的行数:添加一条数据
# 增加
count = cs1.execute('insert into goods_cates(name) values("硬盘")')
#打印受影响的行数
print(count)
count = cs1.execute('insert into goods_cates(name) values("光盘")')
print(count)
# # 更新
# count = cs1.execute('update goods_cates set name="机械硬盘" where name="硬盘"')
# # 删除
# count = cs1.execute('delete from goods_cates where id=6')
# 提交之前的操作,如果之前已经之执行过多次的execute,那么就都进行提交
conn.commit()
# 关闭Cursor对象
cs1.close()
# 关闭Connection对象
conn.close()
if __name__ == '__main__':
main()
注:
1.MySQL与Python交互主要步骤:
(1)创建Connection连接;
(2)获得Cursor对象;
(3)在cursor的方法:execute中添加sql语句;
(4)关闭cursor对象
(5)关闭Connection对象
2.对于增删改时,确认提交:conn.commit() 此时数据库才真正修改; 回滚:conn,rollback() 逻辑上撤销增删改上内容;
查询一行/多行数据
from pymysql import *
def main():
# 创建Connection连接
conn = connect(host='localhost',port=3306,user='root',password='mysql',database='jing_dong',charset='utf8')
# 获得Cursor对象
cs1 = conn.cursor()
# 执行select语句,并返回受影响的行数:查询一条数据
count = cs1.execute('select id,name from goods where id>=4')
# 打印受影响的行数
print("查询到%d条数据:" % count)
# for i in range(count):
# # 获取查询的结果
# result = cs1.fetchone()
# # 打印查询的结果
# print(result)
# # 获取查询的结果
result = cs1.fetchall()
print(result)
# 关闭Cursor对象
cs1.close()
conn.close()
if __name__ == '__main__':
main()
参数化
- sql语句的参数化,可以有效防止sql注入
- 注意:此处不同于python的字符串格式化,全部使用%s占位
from pymysql import *
def main():
find_name = input("请输入物品名称:")
# 创建Connection连接
conn = connect(host='localhost',port=3306,user='root',password='mysql',database='jing_dong',charset='utf8')
# 获得Cursor对象
cs1 = conn.cursor()
# # 非安全的方式
# # 输入 " or 1=1 or " (双引号也要输入)
# sql = 'select * from goods where name="%s"' % find_name
# print("""sql===>%s<====""" % sql)
# # 执行select语句,并返回受影响的行数:查询所有数据
# count = cs1.execute(sql)
# 安全的方式
# 构造参数列表
params = [find_name]
# 执行select语句,并返回受影响的行数:查询所有数据
count = cs1.execute('select * from goods where name=%s', params)
# 注意:
# 如果要是有多个参数,需要进行参数化
# 那么params = [数值1, 数值2....],此时sql语句中有多个%s即可
# 打印受影响的行数
print(count)
# 获取查询的结果
# result = cs1.fetchone()
result = cs1.fetchall()
# 打印查询的结果
print(result)
# 关闭Cursor对象
cs1.close()
# 关闭Connection对象
conn.close()
if __name__ == '__main__':
main()