Android UI绘制流程之测量篇
经过前一片前奏的分析,我们知道从ViewRootImpl的performTraversals方法正式进入View的测量、布局、绘制流程。本文着重分析View的measure流程。直接上代码吧
frameworks/base/core/java/android/view/ViewRootImpl.java
private void performTraversals() {
...
if (!mStopped || mReportNextDraw) {
boolean focusChangedDueToTouchMode = ensureTouchModeLocally(
(relayoutResult&WindowManagerGlobal.RELAYOUT_RES_IN_TOUCH_MODE) != 0);
if (focusChangedDueToTouchMode || mWidth != host.getMeasuredWidth()
|| mHeight != host.getMeasuredHeight() || contentInsetsChanged ||
updatedConfiguration) {
// 注释2
int childWidthMeasureSpec = getRootMeasureSpec(mWidth, lp.width);
int childHeightMeasureSpec = getRootMeasureSpec(mHeight, lp.height);
if (DEBUG_LAYOUT) Log.v(mTag, "Ooops, something changed! mWidth="
+ mWidth + " measuredWidth=" + host.getMeasuredWidth()
+ " mHeight=" + mHeight
+ " measuredHeight=" + host.getMeasuredHeight()
+ " coveredInsetsChanged=" + contentInsetsChanged);
// 注释1
performMeasure(childWidthMeasureSpec, childHeightMeasureSpec);
...
}
...
}
...
}
在performTraversals方法中找到测量相关的逻辑代码注释1处的performMeasure方法,根据方法的参数定位到注释2处的代码,顾名思义,表示宽高的“测量规格“的意思。那测量规格具体指的是什么呢?带着疑问进入getRootMeasureSpec方法:
frameworks/base/core/java/android/view/ViewRootImpl.java
private static int getRootMeasureSpec(int windowSize, int rootDimension) {
int measureSpec;
switch (rootDimension) {
case ViewGroup.LayoutParams.MATCH_PARENT:
// Window can't resize. Force root view to be windowSize.
measureSpec = MeasureSpec.makeMeasureSpec(windowSize, MeasureSpec.EXACTLY);
break;
case ViewGroup.LayoutParams.WRAP_CONTENT:
// Window can resize. Set max size for root view.
measureSpec = MeasureSpec.makeMeasureSpec(windowSize, MeasureSpec.AT_MOST);
break;
default:
// Window wants to be an exact size. Force root view to be that size.
measureSpec = MeasureSpec.makeMeasureSpec(rootDimension, MeasureSpec.EXACTLY);
break;
}
return measureSpec;
}
这里我们看到了MeasureSpec对象,它的作用是在measure流程中,系统将View的LayoutParams根据父容器所施加的规则转换成对应的MeasureSpec(测量规格),然后在onMeasure中根据这个MeasureSpec来确定view的测量宽高。这是我们打开MeasureSpec源码,在这中间我们会看到下面这几个方法:
public static class MeasureSpec {
private static final int MODE_SHIFT = 30;
private static final int MODE_MASK = 0x3 << MODE_SHIFT;
/**
* UNSPECIFIED 模式:
* 父View不对子View有任何限制,子View需要多大就多大
*/
public static final int UNSPECIFIED = 0 << MODE_SHIFT;
/**
* EXACTYLY 模式:
* 父View已经测量出子Viwe所需要的精确大小,这时候View的最终大小
* 就是SpecSize所指定的值。对应于match_parent和精确数值这两种模式
*/
public static final int EXACTLY = 1 << MODE_SHIFT;
/**
* AT_MOST 模式:
* 子View的最终大小是父View指定的SpecSize值,并且子View的大小不能大于这个值,
* 即对应wrap_content这种模式
*/
public static final int AT_MOST = 2 << MODE_SHIFT;
//将size和mode打包成一个32位的int型数值
//高2位表示SpecMode,测量模式,低30位表示SpecSize,某种测量模式下的规格大小
public static int makeMeasureSpec(int size, int mode) {
if (sUseBrokenMakeMeasureSpec) {
return size + mode;
} else {
return (size & ~MODE_MASK) | (mode & MODE_MASK);
}
}
//将32位的MeasureSpec解包,返回SpecMode,测量模式
public static int getMode(int measureSpec) {
return (measureSpec & MODE_MASK);
}
//将32位的MeasureSpec解包,返回SpecSize,某种测量模式下的规格大小
public static int getSize(int measureSpec) {
return (measureSpec & ~MODE_MASK);
}
//...
}
MeasureSpec代表一个32位的int值,高2位代表SpecMode,表示测量模式,低30位代表SpecSize,表示在某种测量模式下的规格大小。MeasureSpec将SpecMode和SpecSize打包成一个int值来避免过多的对象内存分配,为了方便操作,其提供了打包的方法makeMeasureSpec,SpecMode和SpecSize也是一个int值,MeasureSpec也可以通过解包的方法getMode和getSize得到原始的SpecMode和SpecSize。具体的运算就是借助MODE_MASK这个常量来辅助实现的。
ModeMask
第一个常量ModeMask是3向左位移了30位,因为int型以四个字节存储,所以3的二进制在内存中存储:
00000000 00000000 00000000 00000011
左位移30位之后:
11000000 00000000 00000000 00000000
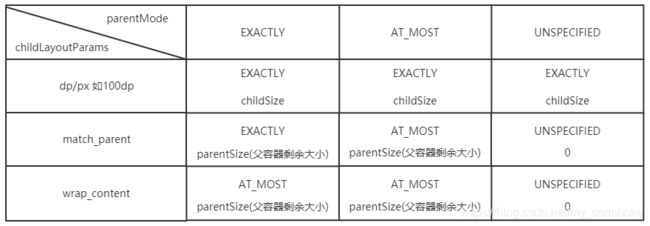
SpecMode有三类,每一类都表示特殊的含义,如下所示。
UNSPECIFIED
父容器不对View有任何限制,要多大给多大,这种情况一般用于系统内部,表示一
种测量的状态。
EXACTLY : 精确模式
父容器已经检测出View所需要的精确大小,这个时候View的最终大小就是SpecSize所
指定的值。它对应于LayoutParams中的match_parent和具体的数值这两种模式。
EXACTLY常量1在内存中存储:
00000000 00000000 00000000 00000001
左位移30位之后:
01000000 00000000 00000000 00000000
AT_MOST :最大模式
父容器指定了一个可用大小即SpecSize,View的大小不能大于这个值,具体是什么值
要看不同View的具体实现。它对应于LayoutParams中的wrap_content。
AT_MOST常量2在内存存储:
00000000 00000000 00000000 00000010
左位移30位之后:
10000000 00000000 00000000 00000000
相关的计算原理分析:
| 符号 | 描述 | 运算规则 |
|---|---|---|
| & | 与 | 两个位都为1时,结果才为1 |
| | | 或 | 两个位都为0时,结果才为0 |
| ^ | 异或 | 两个位相同,结果为0,相异为1 |
| ~ | 取反 | 0变为1, 1变为0 |
| << | 左移 | 二进位全部左移若干位,高位丢弃,低位补0 |
| >> | 右移 | 二进位全部右移若干位,对无符号数,高位补0,有符号数,各编译器处理方法不一样,有的补符号位(算术右移),有的补0(逻辑右移) |
比如makeMeasureSpec(8, MeasureSpec.EXACTLY),
即size=8, 二进制表示为:00000000 00000000 00000000 00001000
MeasureSpec.EXACTLY= 1 << 30
二进制表示为:01000000 00000000 00000000 00000000
方法返回表达式 (size & ~MODE_MASK) | (mode & MODE_MASK)的值
MODE_MASK :11000000 00000000 00000000 00000000
~MODE_MASK:00111111 11111111 11111111 11111111
size & ~MODE_MASK:
00000000 00000000 00000000 00001000
&
00111111 11111111 11111111 11111111
=
00000000 00000000 00000000 00001000
mode = MeasureSpec.EXACTLY= 1 << 30 : 01000000 00000000 00000000 00000000
mode & MODE_MASK
01000000 00000000 00000000 00000000
&
11000000 00000000 00000000 00000000
=
01000000 00000000 00000000 00000000
(size & ~MODE_MASK) | (mode & MODE_MASK)
00000000 00000000 00000000 00001000
|
01000000 00000000 00000000 00000000
=
01000000 00000000 00000000 00001000
measureSpec的值,二进制表示为:01000000 00000000 00000000 00001000
再看getSize()方法:measureSpec & ~MODE_MASK
01000000 00000000 00000000 00001000
&
00111111 11111111 11111111 11111111
=
00000000 00000000 00000000 00001000
返回值二进制表示为8
对MeasureSpec有了初步的认识后,我们再回到performTraversals方法的注释2处的getRootMeasureSpec方法,点击进入,我们发现参数mWindow对应参数windowSize表示窗口的宽度,lp.width对应rootDimension表示就是顶层View即DecorView布局属性设置的宽度。结合方法内部的switch语句,不难得出结论,对于DecorView而言,其MeasureSpec由窗口的尺寸和自身的LayoutParams来共同决定的。
再次回到源码分析流程,进入performMeasure方法:
frameworks/base/core/java/android/view/ViewRootImpl.java
private void performMeasure(int childWidthMeasureSpec, int childHeightMeasureSpec) {
if (mView == null) {
return;
}
Trace.traceBegin(Trace.TRACE_TAG_VIEW, "measure");
try {
// 注释1
// mView表示DecorView,可进入setView查看
mView.measure(childWidthMeasureSpec, childHeightMeasureSpec);
} finally {
Trace.traceEnd(Trace.TRACE_TAG_VIEW);
}
}
进入measure方法,来到了View的measure方法,我们发现它内部调用了onMeasure方法:
frameworks/base/core/java/android/view/View.java
public final void measure(int widthMeasureSpec, int heightMeasureSpec) {
...
onMeasure()
...
}
进入View的onMea方法:
protected void onMeasure(int widthMeasureSpec, int heightMeasureSpec) {
setMeasuredDimension(getDefaultSize(getSuggestedMinimumWidth(), widthMeasureSpec),
getDefaultSize(getSuggestedMinimumHeight(), heightMeasureSpec));
}
总体来说,performMeasure在最终调用到具体View的onMeasure方法,而我们的控件会更具自身的业务需求来重写onMeasure方法,无论是系统的FrameLayout、LinearLayout等控件,还是我们自定义控件的时候,onMeasure的逻辑都不尽相同。这也是为什么ViewGroup没有onMeasure方法,即没有定义测量的具体过程,ViewGroup是一个抽象类,测量过程的onMeasure方法需要各个子类去具体实现,不同的ViewGroup子类有不同的布局特性,这导致它们的测量细节各不相同,因此ViewGroup无法统一实现(onMeasure方法)。
由于前面的mView表示DecorView,而DecorView继承FrameLayout,所以这里以FrameLayout为例分析ViewGroup的测量过程。进入FrameLayout的onMeasure方法:
frameworks/base/core/java/android/widget/FrameLayout.java
protected void onMeasure(int widthMeasureSpec, int heightMeasureSpec) {
//获取当前布局内的子View数量
int count = getChildCount();
//判断当前布局的宽高是否是match_parent模式或者指定一个精确的大小,如果宽高中只要有一个为
//wrap_content,那么measureMatchParentChildren为true,否则为false
final boolean measureMatchParentChildren =
MeasureSpec.getMode(widthMeasureSpec) != MeasureSpec.EXACTLY ||
MeasureSpec.getMode(heightMeasureSpec) != MeasureSpec.EXACTLY;
...
// 遍历所有可见类型不为GONE的子View
for (int i = 0; i < count; i++) {
final View child = getChildAt(i);
if (mMeasureAllChildren || child.getVisibility() != GONE) {
// 对每一个子View进行测量
measureChildWithMargins(child, widthMeasureSpec, 0, heightMeasureSpec, 0);
final LayoutParams lp = (LayoutParams) child.getLayoutParams();
// 寻找子View中宽高的最大者,因为如果FrameLayout是wrap_content属性
// 那么它的大小取决于子View加上margin的大小
maxWidth = Math.max(maxWidth,
child.getMeasuredWidth() + lp.leftMargin + lp.rightMargin);
maxHeight = Math.max(maxHeight,
child.getMeasuredHeight() + lp.topMargin + lp.bottomMargin);
childState = combineMeasuredStates(childState, child.getMeasuredState());
// 表示FrameLayout宽高中至少有一个为wrap_content
// 当FrameLayout为wrap_content的时候,子View的测量大小会影响FrameLayout的测量大小
if (measureMatchParentChildren) {
if (lp.width == LayoutParams.MATCH_PARENT ||
lp.height == LayoutParams.MATCH_PARENT) {
// 满足FrameLayout宽或高有一个为wrap_content, 子View的宽或高有一个
// match_parent时,将子View添加到集合
mMatchParentChildren.add(child);
}
}
}
}
// Account for padding too
maxWidth += getPaddingLeftWithForeground() + getPaddingRightWithForeground();
maxHeight += getPaddingTopWithForeground() + getPaddingBottomWithForeground();
// Check against our minimum height and width
maxHeight = Math.max(maxHeight, getSuggestedMinimumHeight());
maxWidth = Math.max(maxWidth, getSuggestedMinimumWidth());
// Check against our foreground's minimum height and width
final Drawable drawable = getForeground();
if (drawable != null) {
maxHeight = Math.max(maxHeight, drawable.getMinimumHeight());
maxWidth = Math.max(maxWidth, drawable.getMinimumWidth());
}
setMeasuredDimension(resolveSizeAndState(maxWidth, widthMeasureSpec, childState),
resolveSizeAndState(maxHeight, heightMeasureSpec,
childState << MEASURED_HEIGHT_STATE_SHIFT));
// 有match_parent的子View个数
count = mMatchParentChildren.size();
if (count > 1) {
for (int i = 0; i < count; i++) {
final View child = mMatchParentChildren.get(i);
final MarginLayoutParams lp = (MarginLayoutParams) child.getLayoutParams();
// 对FrameLayout的宽度规格设置,因为这会影响子View的测量
final int childWidthMeasureSpec;
/**
* 如果子View的宽度是match_parent属性,那么对当前FrameLayout的MeasureSpec修改:
* 把widthMeasureSpec的宽度规格修改为:总宽度 - padding - margin,这样做的意思是:
* 对于子Viw来说,如果要match_parent,那么它可以覆盖的范围是FrameLayout的测量宽度
* 减去padding和margin后剩下的空间。
*
* 以下两点的结论,可以查看getChildMeasureSpec()方法:
*
* 如果子View的宽度是一个确定的值,比如50dp,那么FrameLayout的widthMeasureSpec
* 的宽度 规格修改为:
* SpecSize为子View的宽度,即50dp,SpecMode为EXACTLY模式
*
* 如果子View的宽度是wrap_content属性,那么FrameLayout的widthMeasureSpec
* 的宽度规格修改为:
* SpecSize为子View的宽度减去padding减去margin,SpecMode为AT_MOST模式
*/
if (lp.width == LayoutParams.MATCH_PARENT) {
final int width = Math.max(0, getMeasuredWidth()
- getPaddingLeftWithForeground()
- getPaddingRightWithForeground()
- lp.leftMargin - lp.rightMargin);
childWidthMeasureSpec = MeasureSpec.makeMeasureSpec(
width, MeasureSpec.EXACTLY);
} else {
childWidthMeasureSpec = getChildMeasureSpec(widthMeasureSpec,
getPaddingLeftWithForeground() + getPaddingRightWithForeground()
+lp.leftMargin + lp.rightMargin,lp.width);
}
// 对高度进行同样的处理,省略...
...
//对于这部分的子View需要重新进行measure过程
child.measure(childWidthMeasureSpec, childHeightMeasureSpec);
}
}
}
对于FrameLayout的测量流程详细分析,可对照注释进行查阅,再次总结一下,FrameLayout根据它的MeasureSpec来对每一个子View进行测量,即调用measureChildWithMargin方法,这个方法下面会详细说明;对于每一个测量完成的子View,会寻找其中最大的宽高,那么FrameLayout的测量宽高会受到这个子View的最大宽高的影响(wrap_content模式),接着调用setMeasureDimension方法,把FrameLayout的测量宽高保存。最后则是特殊情况的处理,即当FrameLayout为wrap_content属性时,如果其子View是match_parent属性的话,则要重新设置FrameLayout的测量规格,然后重新对该部分View测量。
在上面提到setMeasureDimension方法,该方法用于保存测量结果,在上面的源码里面,该方法的参数接收的是resolveSizeAndState方法的返回值那么我们直接看View#resolveSizeAndState方法:
frameworks/base/core/java/android/view/View.java
public static int resolveSizeAndState(int size, int measureSpec, int childMeasuredState){
final int specMode = MeasureSpec.getMode(measureSpec);
final int specSize = MeasureSpec.getSize(measureSpec);
final int result;
switch (specMode) {
case MeasureSpec.AT_MOST:
if (specSize < size) {
result = specSize | MEASURED_STATE_TOO_SMALL;
} else {
result = size;
}
break;
case MeasureSpec.EXACTLY:
result = specSize;
break;
case MeasureSpec.UNSPECIFIED:
default:
result = size;
}
return result | (childMeasuredState & MEASURED_STATE_MASK);
}
可以看到该方法的思路是相当清晰的,当specMode是EXACTLY时,那么直接返回MeasureSpec里面的宽高规格,作为最终的测量宽高;当specMode时AT_MOST时,那么取MeasureSpec的宽高规格和size的最小值,前面也提到过,当SpecMode为AT_MOST时,父容器指定了一个可用大小即SpecSize,View的大小不能大于这个值。
上面有提到在FrameLayout测量过程中会遍历测量子View,调用的是measureChildWithMargins方法:
frameworks/base/core/java/android/view/ViewGroup.java
protected void measureChildWithMargins(View child,
int parentWidthMeasureSpec, int widthUsed,
int parentHeightMeasureSpec, int heightUsed) {
final MarginLayoutParams lp = (MarginLayoutParams) child.getLayoutParams();
final int childWidthMeasureSpec = getChildMeasureSpec(parentWidthMeasureSpec,
mPaddingLeft + mPaddingRight + lp.leftMargin + lp.rightMargin
+ widthUsed, lp.width);
final int childHeightMeasureSpec = getChildMeasureSpec(parentHeightMeasureSpec,
mPaddingTop + mPaddingBottom + lp.topMargin + lp.bottomMargin
+ heightUsed, lp.height);
child.measure(childWidthMeasureSpec, childHeightMeasureSpec);
}
内部调用了getChildMeasureSpec方法,看方法的参数就明白了,把父容器的MeasureSpec以及自身的layoutParams属性传递进去来获取子View的MeasureSpe,可见普通View的MeasureSpec由父容器的MeasureSpec和自身的LayoutParams来共同决定的。在这里我们可以看到直接又调用了子类的measure测量方法遍历测量子View。ViewGroup那么现在我们能得到整体的测量流程:在performTraversals开始获得DecorView种的系统布局的尺寸,然后在performMeasure方法中开始测量流程,对于不同的layout布局有着不同的实现方式,但大体上是在onMeasure方法中,对每一个子View进行遍历,根据ViewGroup的MeasureSpec及子View的layoutParams来确定自身的测量宽高,然后最后根据所有子View的测量宽高信息再确定爸爸的宽高
不断的遍历子View的measure方法,根据ViewGroup的MeasureSpec及子View的LayoutParams来决定子View的MeasureSpec,进一步获取子View的测量宽高,然后逐层返回,不断保存ViewGroup的测量宽高
总结
-
对于DecorView,其MeasureSpec由窗口的尺寸和其自身的LayoutParams共同决定的
-
MeasureSpec代表一个32位的int值,高2位代表SpecMode,表示测量模式,低30位代表SpecSize,表示在某种测量模式下的规格大小。MeasureSpec将SpecMode和SpecSize打包成一个int值来避免过多的对象内存分配,为了方便操作,其提供了打包的方法makeMeasureSpec,SpecMode和SpecSize也是一个int值,MeasureSpec也可以通过解包的方法getMode和getSize得到原始的SpecMode和SpecSize
-
SpecMode有三类
-
UNSPECIFIED :父容器不对View有任何限制,要多大给多大,这种情况一般用于系统内部,表示一 种测量的状态。
-
EXACTLY:父容器已经检测出View所需要的精确大小,这个时候View的最终大小就是SpecSize所 指定的值。它对应于LayoutParams中的match_parent和具体的数值这两种模式。
-
AT_MOST:父容器指定了一个可用大小即SpecSize,View的大小不能大于这个值,具体是什么值要看不同View的具体实现。它对应于LayoutParams中的wrap_content。
-
-
performMeasure中会调用measure方法,在measure方法中又会调用onMeasure方法,在onMeasure方法中则会对所有的子元素进行measure过程,这个时候measure流程就从父容器传递到子元素了,接着子元素就会重复父容器的measure过程,如此反复就完成了整个View数的遍历。
-
ViewGroup是一个抽象类,没有具体的测量方法,其测量过程由具体的子类去实现,因为ViewGroup的不同子类有不同的布局特性,导致测量细节各不相同,比如FrameLayout,LinearLayout, RelativeLayout布局特性就不同,因此它无法做统一实现。但是也有相同的部分就是,要遍历测量子元素。ViewGroup提供了不同measureChild,measureChildWithMargins等方法供它们调用,在内部都包含了获取子元素的MeasureSpec,执行child.measure, 遍历测量子元素