信息检索(IR)笔记1: 倒排索引(Inverted Index)
建立索引是 information retrieval 的一个核心问题,这一节简单记录关于index的相关笔记.
所有内容均来自 stanford cs276 information retrieval & web search
文章目录
- text preprocessing
- inverted index
- simple construction
- posional index
- index construction
- Block sort-based index(BSBI)
- complexity
- single pass in memory indexing
- index compression
- code 简单实现
- ref
text preprocessing
一些术语
- tokenization
- 将文本编程token流,通常处理 "I’m "…
- normalization
- text 和query term 映射统一(e.g. U.S.A USA)
- stemming
- 形式(中文通常没这个问题,e.g. authorize, authorization)
- Stop words
- omit 掉一些无用的,e.g a,an …
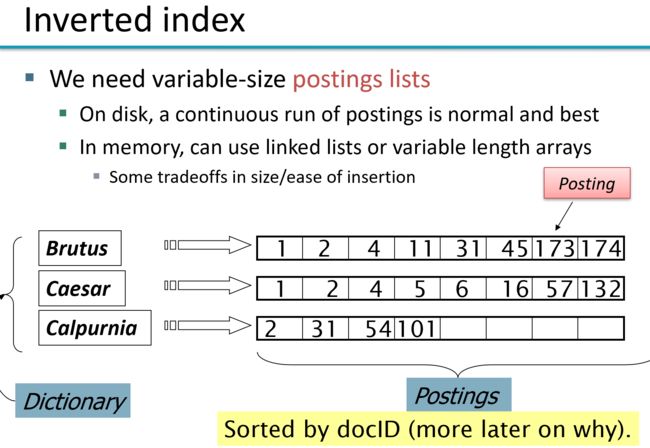
inverted index
term -> (frq,posting_list(docId))frq = len(posting_list)
simple construction
text -> tokenstream -> list ( term, docId) -> sort->unique -> merge
IR 系统两个核心的问题是 index高效和storage 高效,
比如这种索引可以应对简单 boolean query,
也就是说 term1 & term2 的问题,仅需对两个term的posting list merge就行了,并且效率在 O ( f r q 1 + f r q 2 ) O(frq_1+frq_2) O(frq1+frq2)
注意可以证明 任意的boolean 查询都能保证在 O ( ∑ f r q i ) O(\sum frq_i) O(∑frqi) 也就是说linear on sum of size of posting_list
但是这种索引如果用来处理 短语查询(phase query) 是有问题的
一种简单的解决方案是建立positional index,着种索引类似 inverted index,不过还存储了位置信息,因此storage用的会更多
posional index
(term , frq[Int], List[(docId, List[post[Int]]])
trem : frq
- docId1 : list(pos in docId2)
- docId2 : list(pos in docId2)
查询也是高效的(POSITIONALINTERSECT(p1, p2, k), ref1 P42, 本质上还是基于有序list的merge)
index construction
由于index 通常非常大,不可能简单地把它全部存在memory中,肯定是要存到disk上的,(这里的计算机模型还是简单的PC机,没考虑集群),因此除了简单考虑memory中的算法效率外,还得尽量让算法具备disk-友好性(note 就是能够利用disk访问的时候询盘耗时的特点,多访问block少访问多的小数据)
简单总结几种index
Block sort-based index(BSBI)
回忆前面提到的 simple construction 方法,会存在一个问题,要将所有的文本集合产生的 term dict 放在memory中,当集合很大的时候就会导致memory不够用,因此必须要用second storage(简单起见,后面就称为disk)
BSBI 构造非常简单
algo
将text集合分成 n n n 个块(block), 每个块在memory中构造好inverted-index,然后写到disk
对每个block中的inverted-index做multi-way merge
block process
这个算法比较蠢的地方就在于每个block的处理,它采用的是上面提到的(simple construction 的做法) 先简单的 生成 List[(termID,docId)] 然后再排序,注意这是很慢的,有一个sort的过程,后面的SPIMI就是在这个上做了一些改进
multi-way merge
multi-way merge 的过程很简单,就是在memory中维护一个 buffer,存贮当前的term的posting_list,同时用一个priority-queue维护每个block的最小的 termId,每次却出queue中最小的termId,从磁盘中读取posting_list,合并到buffer中,当当前的term的posting_list处理完毕,或者,buffur到达给定的size,写到disk中
(note 注意这是一个非常典型的有限缓冲区读写问题)
简单实现
import heapq
class BSBIIndex(BSBIIndex):
def merge(self, indices, merged_index,buffur_size=1024*1024):
"""Merges multiple inverted indices into a single index
Parameters
----------
indices: List[InvertedIndexIterator]
A list of InvertedIndexIterator objects, each representing an
iterable inverted index for a block
merged_index: InvertedIndexWriter
An instance of InvertedIndexWriter object into which each merged
postings list is written out one at a time
"""
### Begin your code
cur_term=None
buffer= []
for merged_item in heapq.merge(*indices,key=lambda x : x[0]):
if cur_term is None or cur_term == merged_item[0]:
cur_term = merged_item[0]
buffer.extend(merged_item[1])
else :
merged_index.append(cur_term,buffer)
cur_term = merged_item[0]
buffer=[]
buffer.extend(merged_item[1])
if len(buffer) > buffur_size:
merged_index.append(cur_term,buffer)
buffer = []
complexity
假设总的term 为 T T T, 分为 n n n 块
O ( n ∗ T / n l o g ( T / n ) + l o g ( n ) T ) O(n*T/nlog(T/n) + log(n)T) O(n∗T/nlog(T/n)+log(n)T)
同时 BSBI还用了一个map term-> termID,这个也是耗费存储的
single pass in memory indexing
其实我感觉这算法就是正常人的写法, ?
因为这个posting_list本来就是递增的所以在处理每个block的时候仅仅需要维护一个dict然后每次append到posting_list的末尾就行了,满了之后放到磁盘中
不太清楚 single-pass的意义,因为每个block仍旧需要merge的过程
可以加色blockmerge的过程近似线性,block很少啊
complexity Θ ( T ) \Theta(T) Θ(T)
index compression
这东西大概是研究index的编解码,不太感兴趣…
补充一个作业中用到的吧
variable-byte-code
很简单就是将一个数字按照7bit一个byte表示, 仅仅表示有效的byte(全0的byte就不要了),最后一个byte(最高位)做高bit为1,其他byte最高bit为0,这样就能分辨一个数字结尾了
e.g
11111000011111 -> 1111100 0011111 -> 00011111 11111100
code
补充
这个算法对于assigment中的例子来说 57M-> 31M
code 简单实现
code
ref
- Introduction to Information Retrieval, by C. Manning, P. Raghavan, and H. Schütze (Cambridge University Press, 2008).
版权声明
本作品为作者原创文章,采用知识共享署名-非商业性使用-相同方式共享 4.0 国际许可协议
作者: taotao
仅允许非商业转载,转载请保留此版权声明,并注明出处